宫颈锥切术后行子宫全切术的间隔时间对手术效果的影响分析
2019-08-14赵福英张洪炜贾佳郭玉娥高智达
赵福英 张洪炜 贾佳 郭玉娥 高智达
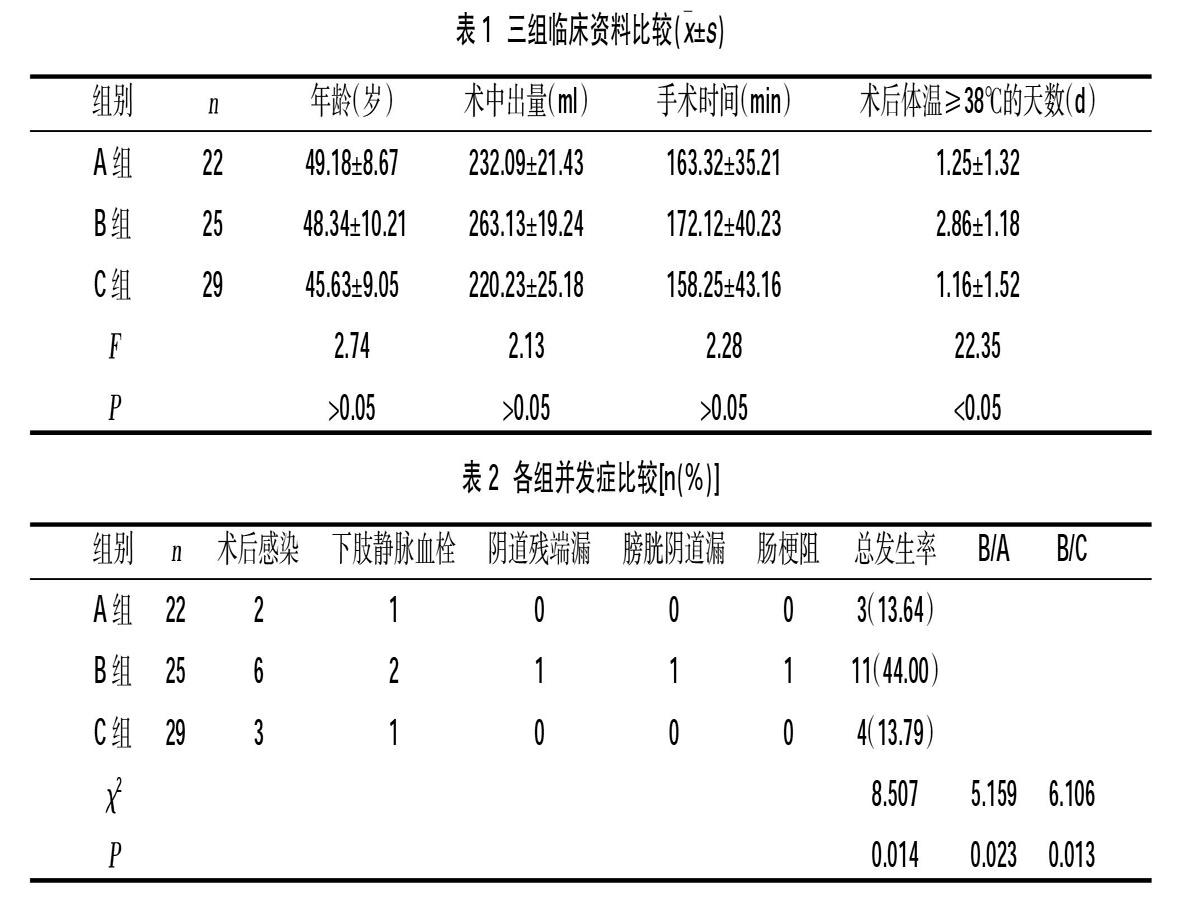
摘要:目的 探討宫颈锥切术后再行子宫全切术的手术间隔时间对手术并发症的影响。方法 回顾性分析2012年1月~2018年10月银川市妇幼保健院宫颈锥切术后行子宫全切术76例患者临床资料,按照手术间隔时间不同分为三组,宫颈锥切术后72 h内行子宫全切术的22例患者设为A组;宫颈锥切术后72 h~4周行子宫全切术的患者25例设为B组;宫颈锥切术后4周以上行子宫全切术的29例患者设为C组,比较三组之间术中出血、手术时间、术后体温、手术并发症。结果 三组之间术中出血、手术时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而三组之间术后体温≥38℃的天数比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),且B组术后体温≥38℃的天数多于A组与C组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。B组并发症发生率为44.00%,分别高于A组的13.64%和C组的13.79%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 宫颈锥切术后72 h~4周行子宫全切术,术后并发症发生率高,术后感染率高,应避免在此时间段手术。
关键词:宫颈锥切术后;子宫全切术;间隔时间;并发症
中图分类号:R737.33 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2019.13.028
文章编号:1006-1959(2019)13-0100-02
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of surgical interval of total hysterectomy after cervical conization on surgical complications. Methods The clinical data of 76 patients undergoing total hysterectomy after cervical conization in Yinchuan Maternal and Child Health Hospital from January 2012 to October 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. The patients were divided into three groups according to the time interval of surgery.22 patients undergoing hysterectomy within 72 h after cervical conization were set to group A; 25 patients who underwent total hysterectomy between 72 h-4 weeks after cervical conization were set to group B; cervical cone Twenty-nine patients who underwent total hysterectomy more than 4 weeks after operation were enrolled in the C group. The intraoperative hemorrhage, operation time, postoperative temperature and surgical complications were compared between the three groups. Results There was no significant difference in the intraoperative bleeding and operation time between the three groups (P>0.05), and the difference in the postoperative temperature between the three groups was ≥38°C,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05), and the number of days after ≥38°C in group B was higher than that in group A and C, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The complication rate of group B was 44.00%, which was higher than 13.64% in group A and 13.79% in group C, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Total hysterectomy is performed between 72 h -4 weeks after cervical conization. The postoperative complication rate is high and the postoperative infection rate is high. Surgery should be avoided during this period.
Key words:Cervical conization;Total hysterectomy;Interval;Complications
近年来,随着宫颈癌筛查方法的不断完善,宫颈癌前病变的发现越来越多,宫颈锥切术是治疗宫颈癌前病变的标准方法[1],当患者无生育要求,宫颈锥切切缘阳性时或患者过分恐惧时,患者常选择进一步行子宫全切术。但宫颈锥切术后间隔多长时间适合行子宫全切术,目前尚不明确。本研究回顾性分析了我院76例宫颈锥切术后行子宫全切术的间隔时间对于手术并发症的影响,现报道如下。
1资料与方法
1.1一般资料 选择2012年1月~2018年10月银川市妇幼保健院收治的因宫颈病变行子宫全切术患者宫76例,其中宫颈高级别鳞状上皮内病变71例,宫颈浸润癌Ⅰa1期5例,患者均先行宫颈锥切术,术后因切缘阳性或过分恐惧等原因要求子宫全切术,术后均行子宫全切术,其中32例行经腹子宫全切术,44例行腹腔镜子宫全切术。
1.2方法 通过电子病案系统,收集患者的临床资料,根据宫颈锥切术后再行子宫全切术的间隔时间不同分为三组,宫颈锥切术后72 h内行子宫全切术的22例患者设为A组;宫颈锥切术后72 h~4周行子宫全切术的患者25例设为B组;宫颈锥切术后4周以上行子宫全切术的29例患者设为C组。比较三组手术时间、术中出血量、术后体温≥38℃的天数及术后并发症发生率。手术时间及术中出血量为术者在手术记录中所记录,术后体温是根据患者术后体温单上所记录的≥38℃的天数,术后并发症包括术后感染(盆腔感染、尿路感染、伤口感染、呼吸道感染)、阴道残端愈合不良、肠梗阻、下肢血栓等。
1.3统计学方法 采用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行分析,计量资料以(x±s)表示,组间比较用方差分析,组间两两比较采用SNK法;计数资料使用(n)表示,采用?字2检验。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1 三组临床资料比较 三组经腹和经腹腔镜子宫全切手术例数、年龄、术中出血量及手术时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而三组之间术后体温≥38℃的天数的比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 B组术后体温≥38℃的天数多于A组及C组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),而A组与C组之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.2三组之间并发症的比较 三组之间并发症比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),A组与C组的并发症明显低于B组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表2。
3讨论
宫颈锥切术是诊断和治疗宫颈癌前病变及微小浸润癌的重要方法[2],当宫颈锥切术后切缘阳性时,往往需要进一步治疗,Dou Y[3]等研究表明,切缘阳性是宫颈上皮内病变复发的独立危险因素。当患者无生育要求,而宫颈锥切术后病理回报切缘阳性,或患者精神高度紧张,进一步行子宫全切术是必要的[4],但锥切术后选择什么时机进一步行子宫全切术,目前尚不明确。研究表明[5],合适的手术间隔时间对手术的顺利实施及术后的恢复具有一定的意义。
Lin J[6]等研究认为,宫颈锥切术后再次行子宫切除术的时间间隔对术后病率及术后并发症存在影响。殷新明等[7]对宫颈锥切术后的宫颈组织进行研究发现,术后1周至术后4周组织中的炎性因子明显高于术后48 h和术后4周以后,在48 h内炎性细胞及炎性反应轻微,而在1~2周时最为严重,术后4周炎症基本消退。陈映芬[8]的研究发现锥切术后72 h至术后1周进行子宫全切术,患者的并发症明显高于其他时间段。
我院因宫颈锥切术后病理要在48 h以后才能回报,故本研究中选择锥切术后72 h以内、72 h至4周以及4周以上进行子宫全切术的三组病例。本研究发现术后72 h~4周的患者术后发热、术后并发症高于术后72 h内及4周以上进行子宫全切术的患者,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),而在三个不同的时间进行手术,术中出血及手术时间无明显差异。
锥切术后盆腔及宫颈创面周围会有充血、反应性炎症,在充血及炎症高峰期进一步行子宫全切术可能会增加术中及术后并发症,而合适的手术间隔时间可以减少手术的并发症的发生。故应避免选择在锥切术后72 h~4周进行子宫全切术。
参考文献:
[1]沈铿,郎景和,黄惠芳,等.子宫颈锥切术在子宫颈上皮内瘤变诊断和治疗中的价值[J].中华妇产科杂志,2001,36(5):264-266.
[2]Baser E,Ozgu E,Eekilinc S,et al.Clinical outcomes of cases with cervical dysplasia absent in cold knife conization specimens[J].Asian Pac J cancer Prev,2014,14(11):6693-6696.
[3]Dou Y,Zhang X,Li Y,et al.Triage for management of cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion patients with positive margin by conization:a retrospective analysis[J].Front Med,2017,11(2):223-228.
[4]劉淼,齐跃,刘娟娟,等.宫颈上皮内瘤变宫颈锥切术后二次手术术式探讨及临床疗效分析[J].中国实用妇科与产科杂志,2018,34(3):298-303.
[5]程英.85 例宫颈原位鳞状细胞癌的临床病理学分析[J].江西医药,2013,48(7):644-646.
[6]Lin J,Wu D,Li Z,et al.Residual lesions in uterine specimens after loop electrosurgical excision procedure in patients with CIN[J].Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics,2018,298(4):805-812.
[7]殷新明,朱小兰,温坚,等.宫颈锥形切除术后宫颈组织中TNF-α、IL-6、HMGB1的表达及其意义研究[J]. 重庆医学,2017,46(11):1472-1475.
[8]陈映芬.宫颈锥切术后行子宫切除术的时机选择研究[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2016,26(12):105-106.
收稿日期:2019-2-18;修回日期:2019-3-12
编辑/宋伟
