Green tea and its active compounds in cancer prevention andtreatment
2019-05-17YiLuLuXuHaiTaoChenQingHuaYao
Yi Lu, Lu Xu, Hai-Tao Chen, Qing-Hua Yao,4,5*
Abstract Green tea is now widely considered as anticancer substance or food in global. Catechin, the main anticancer component in green tea, exhites the strong biological activity which not only eliminate free radicals showing antioxygenic function, but also suppress cell proliferation as well as induce cancer cell apoptosis via blocking corresponding signaling pathway. Furthermore, several studies have demonstrated it could regulate the gut microbiota. It also could regulate gut microbiota. Through these functions, it plays important roles in the occurrence and development of cancer.Here, the anticancer compounds in green tea, the theoretical basis of TCM, the clinic applications, as well as the anticancer mechanism are reviewed.
Key words: Green tea, Anti-cancer compositions, TCM theory,Clinic application, Anticancer mechanism
Introduction
C ancer, as one of the most serious public health problems in the world, is a serious threat to human health. There will be 14 million new cancer patients and 8.2 million deaths worldwide in 2019 [1]. At present,surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are still the main treatments for cancer, but the serious side effects in the process of treatment can not be underestimated. It is of great clinical significance to seek anti-tumor drugs with strong curative effect and few side effects. In recent years, a variety of pharmacologically active polyphenols extracted from tea have been proved to play a role in the prevention and treatment of tumors. Epidemiological studies had found an inverse association in green tea consumption and the prevalence of colon cancer [2],bladder cancer [3], stomach cancer[4], pancreatic cancer [5], esophageal cancer [6], prostate cancer [7],and lung cancer [8]. In this study, the anticancer components in green tea,the theoretical basis in TCM, clinic applications, as well as the anticancer mechanism of tea are reviewed.
1 Ingredient
Tea is made from Camellia sinensis leaves and buds. Green tea is a type of tea that has not undergone withering and oxidation process. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that [9],the unfermented tea, green tea has the role of cancer prevention. Components in green tea is very complex, including tea polyphenols, alkaloids, sugars, proteins, organic acids, fats, pigments, aromatic substances, vitamins, minerals,etc. [10] The anti-cancer active ingredients in tea mainly include tea pigments,caffeine, tea polysaccharides, and tea polyphenols.
Phenols account for 30% of the dry weight of green tea, including flavonols(catechins), flavanols, phenolic acids and anthocyanins. The catechins generally have a content of 12% to 24%,mainly including catechin (C), epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin (EGC),epicatechin gallate (ECG), epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and gallnuts. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) was the most catechin [11], accounting for about 50% of catechins. Another component of green tea, theanine, which accounts for 1% to 3% of the dry weight of tea,also has anti-tumor effects. It has been found that green tea and its components have significant effects in reducing the risk of cancer [12 - 14].
2 Chinese medicine theory of tea
Tea, sweet and bitter to taste, cold and coldness in property, is in hand and foot-Shaoyin, Taiyin and Jueyin meridian. Tea has the functions of clearing away lungheart, promoting digestion and removing food retention.Furthermore, tea also has the effects of cooling the brain,hypnosis, anti-inflammation, improving vision, detoxification, anti-diarrhea, thirst-quenching, refreshing, and promoting digestion. Phlegm - dampness syndrome and toxic heat syndrome are two common types of syndromes in cancer. Thousands prescriptions record that patients who has severe headaches can drink boiled tea until spit out,then the disease is cured when the patient feels thirsty. It means tea can alleviate headache caused by phlegm. Cancer patients often show phlegm - dampness syndrome such as dizziness, nausea, confusion, spitting clear water, shortness of breath, thready and slippery pulse. However, tea can alleviate these related symptoms. Li Shizhen in Ming Dynasty believed tea is the best to reduce fire because of its bitter and cold effects. The book of Ben Cao Qiu Zhen in Qing Dynasty recorded tea can promote digestion and remove food retention. It means tea has the function of heat-clearing, detoxifying, softening and resolving hard masses. The book of Ben Cao Bei Yao mentioned that ginger tea can treat diarrhea. In a word, tea can affect the body's major systems, especially the digestive system. Tea not only treats syncope due to phlegm, reduces fire, and resolves the hard mass, but also is closely associated with“Jia Shan”, which is a lump caused by the accumulation of the liver and kidney. The lump formed in the man is called“Shan”, and the lump formed in the woman is called “Jia”.
3 Clinical studies on tea
The results of existing small-scale randomized clinical trials (RCT) with green tea extracts are inconsistent. An earlier study in China [15] found that 3g tea extract was taken orally every day by patients with oral leukoplakia could significantly inhibit the proliferation of precancerous cells in six months compared with the control group.However, in a US study, green tea extracts (500, 750 or 1000 mg/m2twice a day) did not show significant cancer prevention effects in patients with oral precancerous lesions (n=28) [16]. In the clinical trial NCT00685516(a multicenter, randomized, phase II trial), researchers randomized 113 prostate cancer patients into six groups.Before radical prostatectomy, patients were given 6 cups of green tea, black tea or water a day (control group). The effects of green tea and black tea on inducing cancer cell apoptosis, inhibiting cell proliferation, anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation in radical prostate cancer were proved.Current studies have shown that green tea can alter the state of NF-κB and oxidation in radical prostate cancer tissues. It contains components that prevent or slow down the growth of prostate cancer. However, whether green tea is more effective than black tea or water in the treatment of prostate cancer is not sure in the latest data published in August 2018. It is necessary to further explore the role of green tea in the prevention and treatment of prostate cancer.
4 Anti-cancer mechanism
Recent researches [17, 18] have shown that the green tea possess cancer chemopreventive effects in some kinds of cancer, such as gastrointestinal cancer, lung cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, and breast cancer, especially the polyphenolic antioxidants, catechins or EGCG. This following will discuss the cancer chemopreventive effects associated with green tea and the molecular mechanisms that underlie the broad anticarcinogenic effects.
4.1 Antioxidant effect
The chemical structure of catechin has multiple ortho-phenolic hydroxyl groups, which are frangibility to oxidation and provide H+, resulting in scavenging excess free radicals [19]. As shown in Figure 2, the catechin has a strong antioxidant effect. The antioxidant effects were attained through inhibting the production of oxidase or capturing free radicals to protect antioxidant enzymes [20].An imbalance between antioxidants and reactive oxygen species can cause oxidative stress, leading to cell damage.Catechin prevents caner by synergizing antioxidant vitamins and antioxidant enzymes, which further increases the anti-oxidation capability and relieves the damage of free radicals [21]. The in vivo studies [22] have shown that green tea catechins can increase total plasma antioxidant activity. Ingestion of green tea extract also increases the activity of superoxide dismutase in the serum and the expression of catalase in the aorta; these enzymes are involved in the cytoprotection of reactive oxygen species[23]. Catechin can be used as an antioxidant in vitro, but the intake of green tea catechins does not alter the plasma status of vitamins E and C in the body. In a study report[24], catechins can increase the concentration of vitamin E in low-density lipoproteins, which protects LDL from peroxidation.
4.2 Promotion of carcinogen metabolism
Cytochrome P450 metabolic enzymes play a critical role in the oxidative metabolism of a variety of environmental procarcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons(PAHs) and heterocyclic amine carcinogens, depending on which these procarcinogens, induce carcinogenic effects.While catechin can inhibit the activity of cytochrome P450 metabolic enzymes [25] and enhance the activity of glucuronosyltransferase, promote the metabolism of precarcinogens into inactive products. An in vitro study found[26] that when the concentration of EGCG in drinking water reached 0.02% - 0.32%, it could inhibit the intestinal tumor of ApcMin/+ mice effectively, and the inhibitory effect was related to the increase of cadherin concentration on plasma membrane as well as the decrease of β-catenin,c-myc, AKT, and ERK1/2. At the same time, EGCG can inhibit the phosphorylation and activation of ERK1/2 and AKT in EBV positive cells, meanwhile effectively block the lytic infection of EVB at the gene transcription and translation level [27], suggesting the clinical signif icance of EGCG in the prevention and treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and lymphoma.
4.3 Induction of apoptosis in tumor cells
Effective substances in green tea can induce apoptosis of cancer cells. The components in green tea induce cell apoptosis mainly through the following ways: ①Induction of cell cycle arrest. EGCG can block gastric cancer cells into S phase by demethylation regulation of tumor suppressor genes [28], meanwhile, arrest human breast cancer cell line T47D at G2/ M phase, possibly by phosphorylation of JNK / SAPK and p38. It inhibits the phosphorylation of cyclin 2 and regulates other cyclin, resulting in G2stagnation [29], while prostate cancer LNCaP cells are controlled by catechin to stagnate in G0/ G1phase [30]. ②Inducing apoptosis through P53/ caspase. Catechin hydrate inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells by promoting the expression of caspase-3, caspase-8,caspase-9 and TP53 [31]. ③Promoting the apoptosis through inhibiting Bcl-2 family. The apoptosis induced by tea polyphenols is associated with inactivating the Bcl-2 and Bcl-X proteins [32], and increasing the expression of pro-apoptosis factor Bax protein, which is correlated with NF-κB, JAK-stat and PI3K pathways [33]. ④Inducing cancer cell apoptosis through Ca2+. EGCG induces endoplasmic reticulum calcium increase and intracellular Ca2+decrease by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum Bcl-2-mediated Ca2+leakage in MCF-7 cells [34]. EGCG could suppress cell proliferation and induce apoptosis through signaling pathways associated with cell membrane and endoplasmic reticulum stress [35].
4.4 Blocking signaling pathway
As shown in Figure 1, Catechin inhibits tumor growth by selectively blocking signaling pathways. EGCG can inhibit epidermal growth factor (EGF) - induced autophosphorylation of EGFR and prevent EGF from binding to its receptor, by which prevent mitotic signaling and inhibit tumor cell proliferation. The activation of AP1 promotes the abnormal initiation of the cell cycle and is closely related to the proliferation of tumor cells; NF - κB transcription factors are involved in various biological functions such as cell proliferation and differentiation. NF - κB and AP1 are also known as oxidative stress transcription factors. By affecting intracellular redox status, catechins can interfere the signal transduction pathways involved in NF -κB and AP1, then inhibit cancer cell proliferation [36]. In addition,catechin signif icantly inhibits extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) and c-Jun amino-terminal kinase(JNK), and inhibits tumor cell proliferation by interfering with the MAPK signal transduction pathway [37]. Wnt proteins are a group of highly conserved molecules that play a key role in embryonic development and adult tissue regeneration. Many cancers are caused by abnormal conduction of the Wnt signaling pathway. EGCG induces HBP1 transcriptional repressor, which leads to the blockade of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, thereby inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and invasion [38].
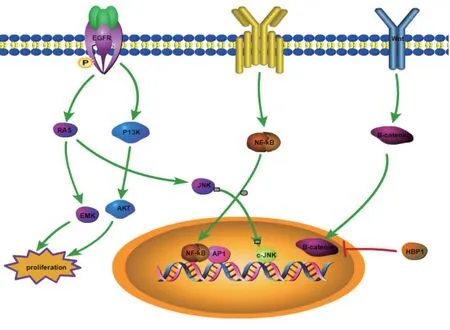
Figure1: Catechin inhibits tumor growth by blocking signaling pathways like EGFR pathyway, NF-κB pathyway,Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
4.5 Regulation of gut microbiota
As a new research hotspot, the diversity and complexity of intestinal flora give it an important role in maintaining intestinal homeostasis and human health. It has been reported that 90% to 95% of the polyphenols are absorbed in the large intestine [39]. As shown in Figure 2, the polyphenols in tea need to be metabolized into small molecular substances with higher bioactivity after being processed by gut microbiota [40], the interactions between effective tea compounds in tea and gut microbiota may help to improve host immunity and prevent various diseases. The change of intestinal environment is the key to the formation of adenoma, which will progress to colon cancer. The intestinal gut microflora in patients with colon cancer is significantly changed and pH is significantly increased. The results of in vitro [41] experiments showed that tea catechin samples had significant proliferation effects on probiotics (Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus), and inhibited Bacteroides and Clostridium through decreasing the PH. At the same time,methylated catechin can regulate intestinal microecology effectively. It is widely believed in TCM that tea can relieve heat and treat dysentery, by which significantly improve intestinal discomfort. Catechin can prevent and treat colorectal cancer by improving intestinal flora. The specific signaling pathways involved in the alteration of intestinal bacteria need to be further studied.

Figure 2: ①Catechin can prevent and treat cancer by improving intestinal flora. ② Catechin can provide H+ to protect antioxidant enzymes, which are closely related to cancer apoptosis and blocking signal pathway.
5 Conclusion and outlook
The direct anticancer function of tea is moderate, but the in vitro and in vivo experiments have shown that tea extract and methylated catechin have a better inhibitory effect on tumor cell growth. Proper application of catechin could increase the sensitivity of chemotherapy drugs and reduce resistance and educe adverse side effects. It has also been reported that catechin combined with cetuximab(EGFR antibody) has strong antitumor activity against in situ metastasis of triple negative breast cancer, without toxic side effect [42]. In addition, the influence of tea on intestinal micro-ecology worth further investigation. The correlation between colorectal cancer and intestinal flora is obvious, and experiments in vitro and in vivo have confirmed the effects of catechin on intestinal flora, but the mechanisms are not clear. Although useful in cancer treatment and prevention, the potential of hepatotoxicity of high doses of EGCG has been reported. Before clinical applications, potential safety hazards must be considered and more in-depth researches should be conducted.
Overall, tea drinking is of great benefit to human health.By preventing the onset of metabolic syndrome, tea drinking may help to reduce the risk of cancer as well as prevent the occurrence of cancer.
杂志排行
Food and Health的其它文章
- Intestinal microflora in patients with liver disease
- Effects of medicinal diets on patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing chemotherapy
- Reporting and methodological quality of systematic reviews or meta-analyses in nasogastric and nasojejunal enteral nutrition for severe acute pancreatitis
- Progress of Bai He Di Huang decoction on intestinal flora of mouse with depression
