Role and mechanism of circ-PRKCI in hepatocellular carcinoma
2019-05-08SuXiaQiHuiSunHuiLiuJingYuZhiYongJiangPingYan
Su-Xia Qi,Hui Sun,Hui Liu,Jing Yu,Zhi-Yong Jiang,Ping Yan
Abstract
Key words: Circ-PRKCI;Hepatocellular carcinoma;Cell invasion;Protein kinase B signaling pathway;Progression
INTRODUCTION
Digestive system tumors have high morbidity and mortality and account for a large proportion of all tumors[1,2].It has been confirmed that some non-coding RNAs(ncRNAs) are engaged in the pathogenesis of digestive system tumors,and elucidating the role of these ncRNAs can help to understand the potential pathogenesis of digestive system tumors.For example,the long ncRNA (lncRNA)DANCR has been identified to be involved in the carcinogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[3].The expression level of plasma miR-718 was found to be significantly lower in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) than in healthy controls[4].Additionally,silencing MALAT1 inhibits chemotherapy-induced autophagy,while MALAT1 promotes autophagy of gastric cancer (GC) cells,making GC cells sensitive to chemotherapeutic agents[5].And miR-224-5p is up-regulated in digestive system cancers and shows moderate diagnostic ability,which may become a biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of digestive system cancers[6].
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have recently been recognized as a naturally occurring and diverse family of endogenous ncRNAs,regulating gene expression in mammals.It has been confirmed that circRNAs are important in the occurrence and development of some digestive system tumors,for example GC,liver cancer,and colon cancer[7].There are 125 down-regulated circRNAs and 76 up-regulated circRNAs in human colorectal cancer tissues compared with normal tissues[8].Circ-0000190 is down-regulated in GC tissues and plasma samples from patients with GC[9].Circ-PRKCI is produced from thePRKCIgene at 3q26.2 amplicon.It has been verified that down-regulation of circ-PRKCI can inhibit the expression of PLCB1,a target of miR-1324,to inhibit the cell migration and proliferation in congenital Hirschsprung's disease[10].In lung adenocarcinoma,circ-PRKCI acts as a sponge of miRNA-545 and miRNA-589,and eliminates their inhibitory effects on protooncogene transcription factor E2F transcription factor 7 (E2F7)[11].In ESCC,circ-PRKCI can sponge miR-3680-3p to regulate AKT3 expression[12].In this study,we explored the role and mechanism of circ-PRKCI in HCC.The findings may provide us with a new insight into the diagnosis of digestive system tumors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Clinical samples
All tumor tissues and adjacent non-tumor tissues were taken from patients undergoing thoracic surgery at the Qingdao Municipal Hospital (Group),and were confirmed by experienced pathologists.Informed consent was obtained from all patients.Human tissue samples were collected according to the International Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical Research involving Human and Subjects.This study was approved by Qingdao Municipal Hospital (Group) Ethics Committee,and carried out in accordance with the regulations of the Ethics Committee.
Cell culture
All cell lines (HaCAT,LO2,CaES-17,EC109,MKN45,SNU-5,SW60,HepG2,and Hep3B) were purchased from ATCC cell bank.LO2 cells were cultured in Minimum Essential Medium (MEM) Eagles with Earle's Balanced Salts (MEM-EBSS).Other cells were cultured in DMEM medium (Gibco).Penicillin (100 U/mL),streptomycin (100 mg/mL),and 10% fetal bovine serum were added to the media.All cell lines grew in a humidified air containing 5% CO2at 37 °C.Passage 10 cells were used in the experiments.
RNA extraction,siRNA construction,and quantitative PCR analysis
According to the kit instructions (Invitrogen),total RNA was isolated from tissues,blood cells,and cultured cells with Trizol.The extracted RNA was then purified with phenol/chloroform and precipitated in three volumes of ethanol.The quantity and purity of RNA were detected with a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer(ThermoScience).The expression of circ-PRKCI was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) after treatment of RNA with RNase R.GAPDH,beta-actin,and SNRNA U6 were used as controls.Primer sequences were synthesized by Takara.SiRNA was synthesized by the corresponding primer sequence by Suzhou Bainin.All primer sequences are listed in Table 1.qRT-PCR (QIAGEN 208152) is a method to measure the total amount of products after each cycle of PCR with fluorescent chemicals in DNA amplification reaction.We used qPCR to detect circ-PRKCI levels in liver cancer tissues,adjacent tissues,and blood.
Western blot analysis
RIPA buffer was mixed with a protease inhibitor to extract protein from cultured cells.Then,the protein concentration was quantified by using BCA assay (BEOOTIME).And proteins with the same amount loaded on the 10% SDS-PAGE gel were transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore).After incubation at room temperature for 1 hour in a closed buffer,the blots were incubated with primary antibodies (Abcam),and ECL PLUS/KIT (GE Healthor) was used for chemiluminescence detection.
Plasmid construction and cell transfection
The full-length human circ-PRKCI gene was synthesized by InEnthigon (Shanghai,China) and cloned into the expression vector PCDNa3.1 (C clone Teal Inc.,Inc.).The final structure was verified by sequencing.DNA Midiprep kit (E.Z.N.A Endo-Free.mid Mini Kit) was used to prepare plasmid vectors for transfection with Liposome 3000 (Invitrogen).
Subcellular localization,apoptosis,and invasion analysis
In short,cells were immobilized and incubated with a fluorescencein situhybridization (FISH) probe (Guangzhou Reebok Company),and fluorescence detection was performed after the uncoupled probe was washed out.According to the instructions for cell apoptosis detection (Biyuntian C0003),fixed cells were stained,and then sealed for apoptotic fluorescence detection.Meanwhile,cells suspended in serum-free medium were inoculated into the upper chamber of TnWistar (Corelle).After 24 h of cell culture,the surface of cell membrane was cleaned,fixed with 90%ethanol,stained with crystal violet,and observed under a microscope at a magnification of 400 times.
Statistical analysis
Chi-square test andt-test were used for statistical analyses,withP-values < 0.05 considered statistically significant.Each test was repeatedly performed at least three times.The statistical methods used in this study were reviewed by the InformationDepartment of Scimall Biotech Company.
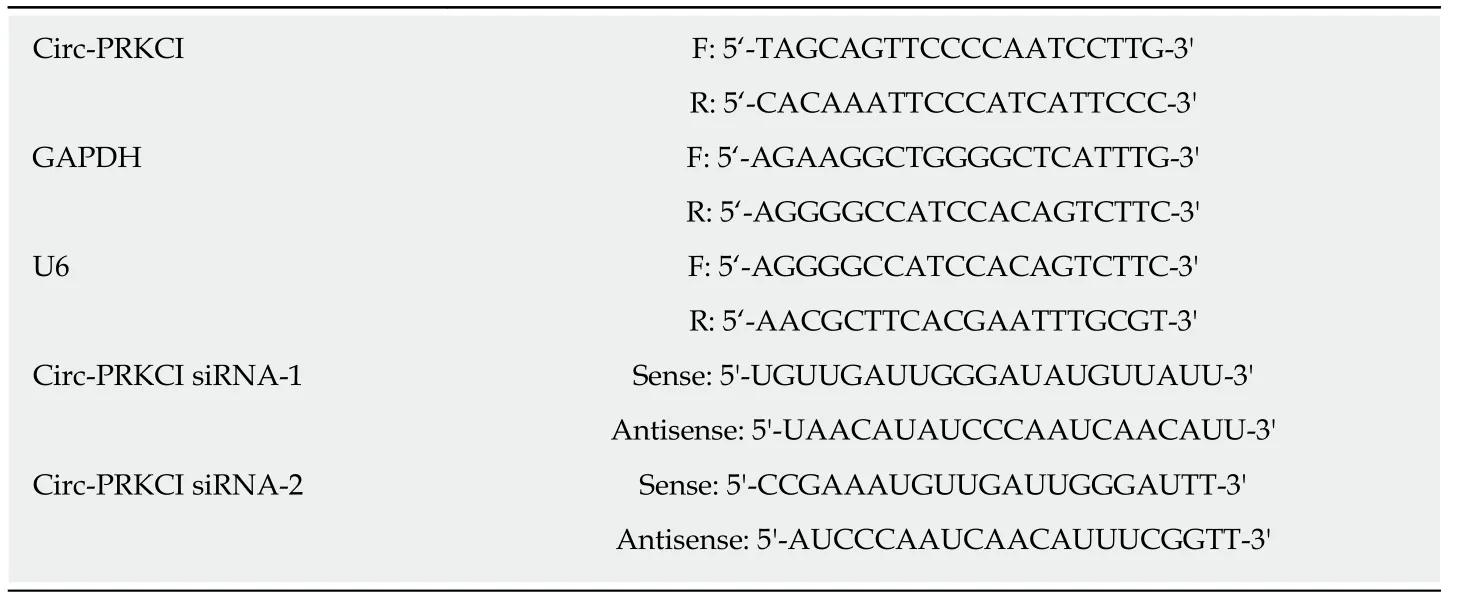
Table1 Primers used for the quantitative real-time PCR and siRNA related experiments
RESULTS
Expression characteristics of circ-PRKCI in HCC
A series of studies have shown that there is circRNA imbalance in many gastrointestinal cancers and other cancer cell lines[13,14].Circ-PRKCI is located on chromosome 3 and is formed by splicing of two exons (Figure 1).To investigate the role of circRNA in digestive system tumors,we first confirmed the endogenous expression of circ-PRKCI.Then,we detected circ-PRKCI levels in liver cancer tissues,adjacent tissues,and blood by qRT-PCR.The results suggested that the expression of circ-PRKCI in tumor adjacent tissues was inferior to that in cancer tissues (Figure 2A),but there was no obvious difference between blood extracted from patients with liver cancer and normal individuals (Figure 2B).We also detected the expression level in esophageal (CaES-17 and EC109),liver (HepG2 and Hep3B),stomach (MKN45 and SNU-5),and colon cancer (SW60) cell lines.It was observed that the expression levels in different tumor cell lines were significantly higher than that in normal cells,and it was highest in HCC cell lines HepG2 and Hep3B (Figure 2C),signifying that circ-PRKCI is generally highly expressed in digestive system tumors.Interestingly,the expression of circ-PRKCI decreased dramatically when cells remained over-confluent(Figure 2D).These results demonstrated that circ-PRKCI is involved in the progression of multiple digestive system tumors,especially HCC,and might be associated with the apoptosis of cancer cells.
Circ-PRKCI affects the growth of HepG2 cells
To investigate whether circ-PRKCI is associated with the growth of cancer cells,the effects of circ-PRKCI knockdown or overexpression on the apoptosis and invasion of HepG2 cells were examined.Circ-PRKCI was silenced with two specific siRNAs(Figure 3A).To avoid the effect of linear PRKCI on the experiment,linear PRKCI was digested with Rnase R enzyme to ensure the specificity of siRNAs and the integrity of circ-PRKCI (Figure 3B).It was observed that apoptosis was enhanced when circ-PRKCI was silenced (Figure 3C).Moreover,the invasiveness of HepG2 cells transfected with circ-PRKCI siRNA or circ-PRKCI overexpressing plasmid (Figure 3D)was detected.The results showed that the invasiveness of cancer cells increased when circ-PRKCI was overexpressed,and decreased significantly when it was silenced(Figure 3E).Further,MTT assay showed that cell proliferation decreased when circ-PRKCI was knocked down,while increased after circ-PRKCI overexpression (Figure 3F).These results indicated that circ-PRKCI is involved in the growth of HepG2 cells through regulating apoptosis and invasion.
Circ-PRKCI regulates cell function via the AKT3 signaling pathway
It has been reported that circRNAs are abundant in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and expressed in a tissue-,time-,and disease-specific manner[15].Therefore,in order to further explore how circ-PRKCI participates in the cellular processes in carcinogenic cells,we first detected the subcellular localization of circ-PRKCI in HepG2 and Hep3B cells by FISH,and found that circ-PRKCI is located in the cytoplasm (Figure 4A).
Previous studies have shown that circ-PRKCI can function as a sponge of miRNA-545 and act as a ceRNA[11].Therefore,we detected the protein level of AKT3 in HepG2 cells with miR-545 overexpression and circ-PRKCI overexpression by Western blot(Figure 4B).Compared with the control group,the overexpression of circ-PRKCI and miR-545 reduced the expression of AKT3,suggesting that circ-PRKCI may regulate the RAC-γ serine/threonine-protein kinase pathway along with miR-545.
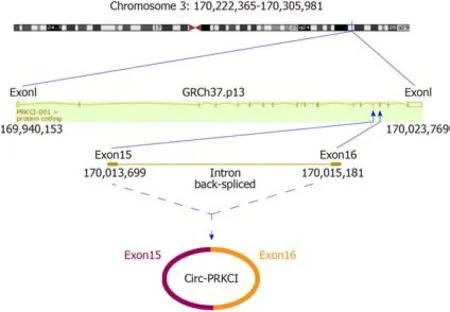
Figure1 The structure and location of circ-PRKCI.
Role of circ-PRKCI in the prognosis of HCC
It has been reported that circ-PRKCI-miR-545-E2F7 has an impact on cancer prognosis[11].Survival analysis showed that E2F7 significantly affected the survival of patients with HCC (Figure 5).The higher the expression level of E2F7,the lower the survival rate and survival time of patients who had liver cancer.Furthermore,we detected circ-PRKCI expression in 40 subjects,including 20 HCC patients and 20 healthy controls.The results showed that the distribution of circ-PRKCI rose with the depth of invasion,lymph node metastasis,distant metastasis,and TNM stage (Table 2),indicating that circ-PRKCI may,to a great extent,affect the survival and prognosis of patients with liver cancer by regulatingE2E7.
DISCUSSION
Recently,a large number of circRNAs have been found in mammalian transcriptomes through bioinformatics and experimental analysis[16],and their function in human diseases has gotten more and more attention[17].Emerging evidence suggests that circRNAs may play an important role in human diseases,such as cancer,neurological diseases,and atherosclerotic vascular disease.Therefore,they may be developed as potential new and stable biomarkers or potential drug targets for disease diagnosis and treatment[18].This study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of circ-PRKCI in the development and progression of digestive system tumors.The results proved that the circ-PRKCI expression in cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in cancer tissues,and especially noticeable in liver cancer.Then,we further clarified that circ-PRKCI can significantly inhibit cell apoptosis and promote cell invasion by a series of functional tests,demonstrating that circ-PRKCI may participate in the cancer development by affecting the growth and metastasis of carcinoma cells.In addition,it was observed that circ-PRKCI is located in the cytoplasm,suggesting that circ-PRKCI may be involved in the process of protein translation and signaling transduction in the cytoplasm[19,20].Furthermore,the effect of circ-PRKCI on the AKT3 signaling pathway were detected.Akt acts as a key signaling node,bridging the connections of carcinogenic receptors to many essential survival-promoting cell functions,and may be the most frequently activated signal transduction pathway in human cancer[21].Our results suggested that circ-PRKCI was able to reduce AKT3 protein expression by forming a ceRNA with miR-545.This regulation of ceRNA has been found by other researchers as well.For example,cir-ZNF609 can also be used as a sponge of miRNA-150-5p to regulate the expression of AKT3 and participate in the pathogenesis of Hirschsprung's disease[22].Circ-PDE8A-miRNA-338 regulates MACC1 and stimulates aggressive growth through the MACC/MET/ERK or AKT pathway[23].Therefore,the reduction of AKT3 expression by circ-PRKCI may be one of the causes of digestive system tumors,especially HCC.
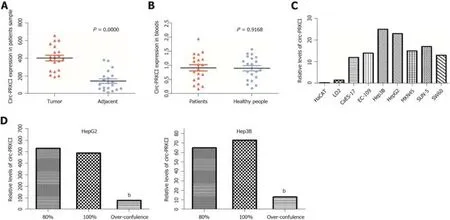
Figure2 The level of circ-PRKCI.
We also predicted the relationship between the ceRNA target geneE2F7and the prognosis of patients with HCC,and found that it was negatively correlated with the survival rate of patients.In addition,circ-PRKCI expression in patients with HCC was detected.The results showed that the distribution of circ-PRKCI increased with the depth of invasion,lymph node metastasis,distant metastasis,and TNM stage,implying the relationship between circ-PRKCI and the prognosis of HCC.In fact,the regulatory role of circRNAs in liver cancer has been studied extensively.CiRS-7 has a certain effect on the clinical manifestations and prognosis of patients with liver cancer[24].Circ-101764 may also play an important role in the occurrence and development of HCC[25].
In summary,circ-PRKCI is obviously involved in the occurrence and development of digestive system tumors.In particular,circ-PRKCI can regulate tumor cell apoptosis and invasion in the pathogenesis of liver cancer.It also has an indicative effect on clinical prognosis of liver cancer and may be a biomarker for clinical detection.This will provide a theoretical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
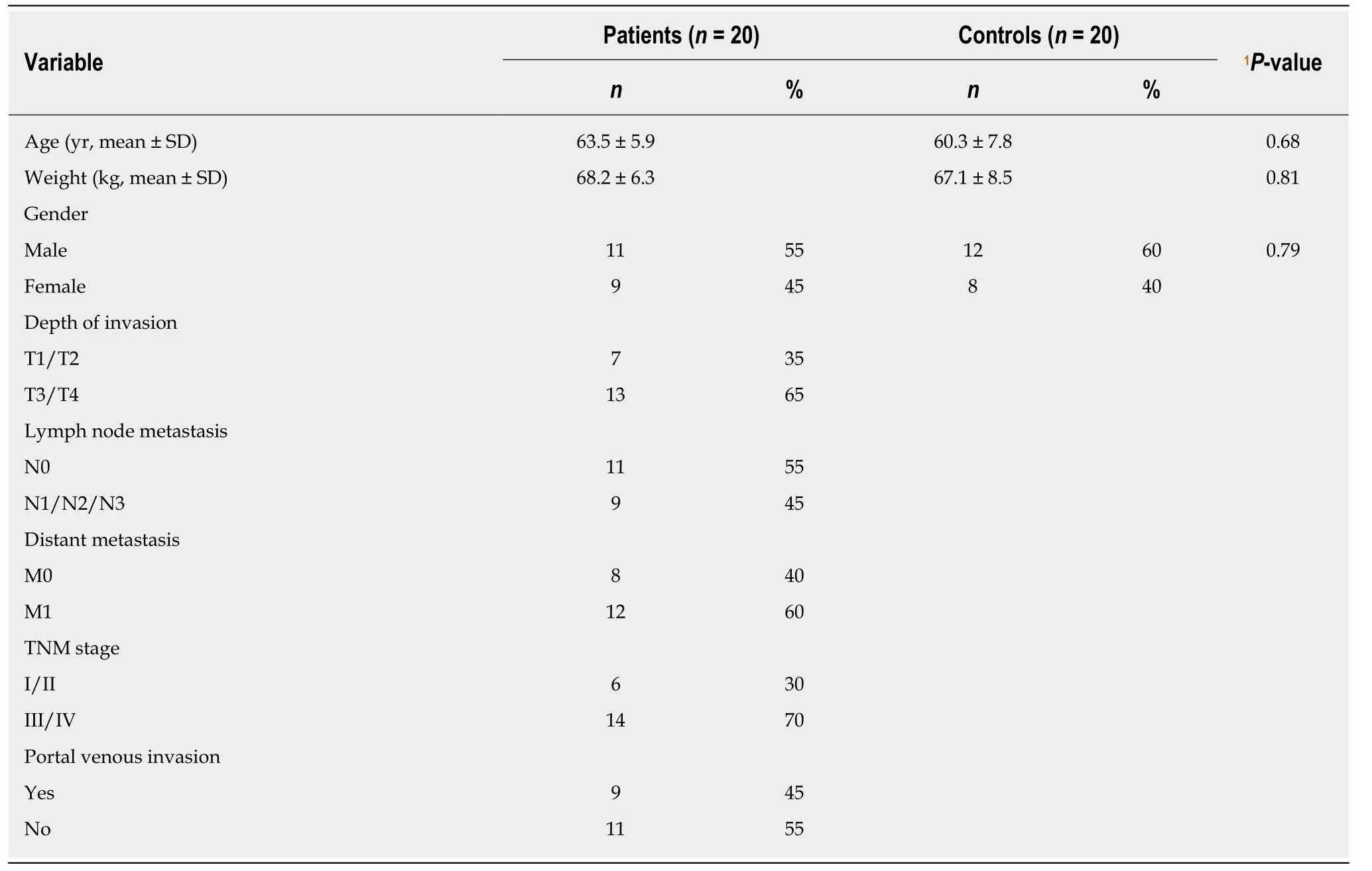
Table2 Characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma patients and control subjects
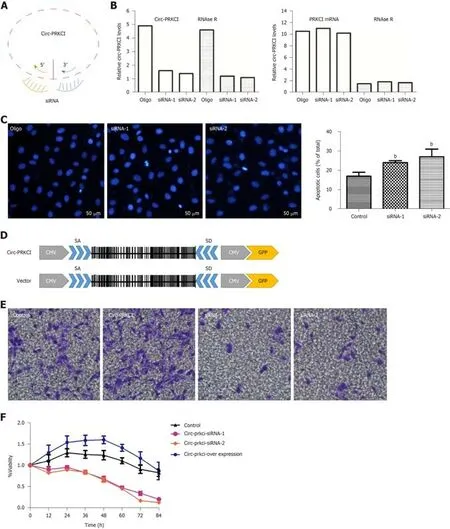
Figure3 Effect of circ-PRKCI on the growth of HepG2 cells.
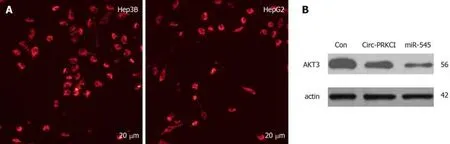
Figure4 Circ-PRKCI regulates cell function through the AKT3 signaling pathway.

Figure5 E2F transcription factor 7 affects survival rate of patients with liver cancer.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Digestive system tumors have high morbidity and mortality and account for a large proportion of all tumors.It has been confirmed that circRNAs are important in the occurrence and development of some digestive system tumors,such as gastric cancer,liver cancer,and colon cancer.
Research motivation
Does circ-PRKCI affect the occurrence and development of digestive tract tumors,especially hepatocellular carcinoma?
Research objectives
To investigate the role and molecular mechanism of circ-PRKCI in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Research methods
This study used quantitative real-time PCR,Western blot,knockdown and overexpression experiments,fluorescencein situhybridization,survival analysis,and statistical analyses.
Research results
The level of circ-PRKCI was significantly higher in HCC tissues than in adjacent tissues.Circ-PRKCI substantially inhibited cell apoptosis and promoted cell invasion.It was found that circ-PRKCI can act as the sponge of miRNA-545 to reduce the expression of AKT3 protein.Circ-PRKCI target geneE2F7can reduce liver cancer patients’ survival rate.Circ-PRKCI was positively correlated with the depth of invasion,lymph node metastasis,distant metastasis,and TNM stage.
Research conclusions
Circ-PRKCI is significantly involved in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Research perspectives
This study provides a new research direction and theoretical basis for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are grateful to Dr.Yan Huang for help in editing the manuscript.
杂志排行
World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Development of Helicobacter pylori treatment: How do we manage antimicrobial resistance?
- Organoids of liver diseases: From bench to bedside
- Upper gastrointestinal tract involvement of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: A pathological review
- Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes the Warburg effect possibly by inducing pyruvate kinase M2 phosphorylation in liver precancerous lesions
- Immune response pattern varies with the natural history of chronic hepatitis B
- Comparison of decompression tubes with metallic stents for the management of right-sided malignant colonic obstruction
