Liver graft preservation methods during cold ischemia phase and normothermic machine perfusion
2019-04-24KonstantinTchilikidi
Konstantin Y Tchilikidi
Abstract
Key words: Liver graft preservation;Graft preservation solutions;Static cold storage;Hypothermic machine perfusion;Normothermic machine perfusion;Ischemia-reperfusion injury;Marginal grafts;Donation after cardiac death;Extended criteria donors;Transplant complications
INTRODUCTION
This review composed in order to estimate the place of static cold storage,hypothermic and normothermic machine perfusion (NMP) among liver graft preservation techniques.
The potential requirement for donor livers in the world is on constant rise,despite some improvement in organ donation.For example,in the United States of America every year more than 1000 patients die and even more remove from transplant list because of inappropriate state (too sick for transplant) while waiting for donor organ[1].In Germany more than one third among about 1500 patients in transplant list does not receive transplant yearly due to organ shortage[2].
This growing demand for donor organs requires measures to expand donor pool.Several strategies have been studied including split liver transplantation,live donor liver transplantation,and use of extended criteria donors,such as elderly people,steatotic livers,donation after cardiac death,etc.But it has been recognized,that grafts from extended criteria donors are extensively prone to ischemia - reperfusion injury,which in turn leads to early allograft dysfunction and biliary complications[3-7].Besides,some authors reported significant incidence of post-reperfusion syndrome(PRS),which negatively impacts both graft and patient's morbidity and mortality[8,9].Clinical predictors for PRS occurrence are:firs,donor/graft related factors - donation after brain or cardiac death (DBD or DCD),donor age,donor risk index,graft steatosis,second,recipient related factors - elevated MELD (Model of End-stage Liver Disease) score,left ventricular diastolic dysfunction,third,intraoperative and storage related factors - prolonged cold ischemic time (CIT),prolonged warm ischemic time(WIT),intraoperative blood loss[10,11,12].In DCD donation many grafts left not transplanted[13]mainly due to static cold storage insufficiency for these grafts[14].Machine perfusion is actively been studied for marginal grafts listed above.
With organ procurement oxygenated blood flow is terminated that causes inflammation and injury,triggered by deficiency of nutrient factors and ATP(adenosine triphosphate),with lactic acid accumulation in hypoxic anaerobic metabolism.Static cold storage further exaggerates such injurious processes.Disruption of electrolyte cell membrane gradients due to sodium-potassium membrane pumps damage results in cellular edema,with free calcium influx,and subsequent activation of enzyme cascade leading to cell death.Upon restoration of circulation ATP breakdown with accumulation of xanthine oxide generates free radical.Which in turn cause lipid peroxidation with cellular destruction named ischemia-reperfusion injury[15-17].Flushing of cold preservation solution is traditional method of donor liver preservation following organ procurement and interruption of blood supply.This static cold preservation works on diminishing cellular metabolism with temperature decrease (the coenzyme Q10 effect),which limits need for ATP[18].Despite anaerobic metabolism diminishing depletion of ATP reserve continues at low temperatures with accumulation of metabolic waste.All listed above increase risk of primary non-function,initial poor function,and biliary complications such as ischemic cholangiopathy especially in extended criteria donors[19-21].Increasing rate of obesity in modern population and associated steatosis are additional challenges,because such livers already pose increased risk of initial pure function[22,23].Therefore marginal livers are more susceptible to ischemia-reperfusion injury[24,25].
STATIC COLD STORAGE
The mainstay and the golden standard for donated organ preservation is the induction of hypothermia to reduce metabolic requirements.As it has been stated in editorial of Eghtesadet al[26]Alexis Carrel made the initial steps in this area by successfully preserving an artery for several days in chilled Locke's solution.But his work in vascular and transplant surgery overshadowed this event.Mooreet al[27]used ice slush in the donor for simple surface cooling.Another innovation came with Kauppet al[28],who proposed the core cooling concept by flushing cold solution through an aortic cannula for abdominal organs protection.Static cold storage by Collinset al[29]and machine perfusion by Belzeret al[30]developed in late 1960s were the original options in transplantation area and still in use for graft preservation today[26].
The European Liver Transplant Registry started routinely collect data in 1983.Since that point,Collins solution was the unique compound used for static liver preservation in Europe,with 450 transplants as a maximum performed per year[31].The peak of its use came in 1987.However,after the University of Wisconsin preservation solution introduction in 1987 the latter one got to be used in 3750 transplants per year in 2001.In 1990s alternative to University of Wisconsin solution have been developed:histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate solution HTK has been clinically implicated since 1991,Celsior solution CE since 1998,and Institute Georges Lopez solution (IGL-1) since 2003[31,32].Features of Euro-Collins solution which was developed in the 1970s are:it does not contain oncotic agents,but rich in glucose,and potassium-sodium[31].Kidney preservation with relatively less time was very suitable for it,due to renal cells impermeability to glucose.But because glucose can easily enter liver and pancreatic cells,leading to subsequent loss of the osmotic effect,and also anaerobic metabolizing of glucose,inducing intracellular acidosis limited cell preservation in these organs.Later in the University of Wisconsin solution glucose was changed to lactobionate and raffinose.These other larger sugar molecules remain in the extracellular space to preserves their beneficial effect.Jamieson and Belzeret al[30]developed the University of Wisconsin preservation solution in mid-1980s.They conceptualize its features:impermeant and metabolically inert molecules to maintain osmotic concentration,additional administration of oxygen radical scavengers and colloid substrate - hydroxyethyl-starch[31,33].By all the means,organ preservation time with the University of Wisconsin solution got to be prolonged from 6 to 16 h[31,34].During hypothermic storage impermeant substrates in this preservative solution are able to protect graft cell[1,35].In the 1990s when liver transplantations raised in the United States the University of Wisconsin preservation solution became the gold standard for preservation of the liver and other intra-abdominal organs[1,36](Table1).
Besides of the impermeant substances (raffinose,lactobionate) for prevention of edema,the efficacy of the University of Wisconsin preservation solution is based on addition of an ATP precursor (adenosine) and anti-oxidant components (allopurinol,reduced glutathione)[31].On the other hand,oncotic support presented mainly by hydroxyethyl-starch brings higher viscosity and also leads to tissue saturation with the preservation solution.Consequently,this can reduce washout from the graft and therefore interferes with blood flow during reperfusion[37,38].Plus,high concentration of potassium produces activation of voltage-dependent channels with subsequent cellular depolarization[39].Drawbacks due to hydroxyethyl-starch became the reason for development of preservation solutions without oncotic agents such as Celsior and Histidine-tryptophane-ketoglutarate (Custodiol) and others with polyethylene-glycol to substitute hydroxyethyl-starch as oncotic agent,by instance IGL-1 and Tissue and Organ Conservation Solution (SCOT)[31].
Several alternative solutions including listed above with potential benefits have been introduced and utilized in liver transplantation for graft preservation.Histidinetryptophane-ketoglutarate solution was originally developed in the 1970s by H.J.Brettschneider as a cardioplegia solution[33,40]and was successfully implemented in organ transplantation.Its composition is based upon a philosophy of Histidine as a potent buffer,with two substrate amino-acids:Tryptophan and Ketoglutarate.Besides different buffer system compare to University of Wisconsin solution it also contains different electrolytes with low potassium[33].First use of Custodiol for graft protection in liver transplantation started in Europe in the late 1980s,where its efficacy andsafety for liver preservation has been confirmed[41,42].The solution was not implicated in the USA until 2002.First in the United States it has been used in cadaveric and living donor liver transplantation at the University of Pittsburgh[26,43].Histidinetryptophane-ketoglutarate solution with its lower viscosity and potentially better penetration to the liver microcirculation prompted the evaluation of long-term outcome in liver transplantation with particular focus on biliary problems especially in donation after cardiac death (non-heart-beating donors).In addition,low potassium content obviating the need for in situ flush prior to revascularization could be beneficial specifically in the “piggyback” venous reconstruction during live donor liver transplantation[26,44].Some studies demonstrated lower graft survival with histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate solution[26,32,33].Overall,3-year graft survival was higher with University of Wisconsin solution,IGL-1 and Celsior (75%,75% and 73%,respectively),versus histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate solution (69%) (P< 0.0001)[32].Donor age more than 70 years old,cold ischemia time more than 8 h,donation after cardiac death were reported by Stewartet al[45]as potential risk factors for histidinetryptophan-ketoglutarate solution that associated with reduced graft survival when compared to University of Wisconsin solution[12,45].Despite that histidine-tryptophanketoglutarate solution continues to be successfully applied in liver graft preservations,especially taking into account special situations that require its buffer features,low viscosity (with more rapid cooling and better washout of blood elements) and low potassium level (therefore no need for flushing before revascularization)[26,31].For instance,Loet al[46]described Custodiol as a preservation solution in “Transplantation of the Liver” for live donor liver transplant.
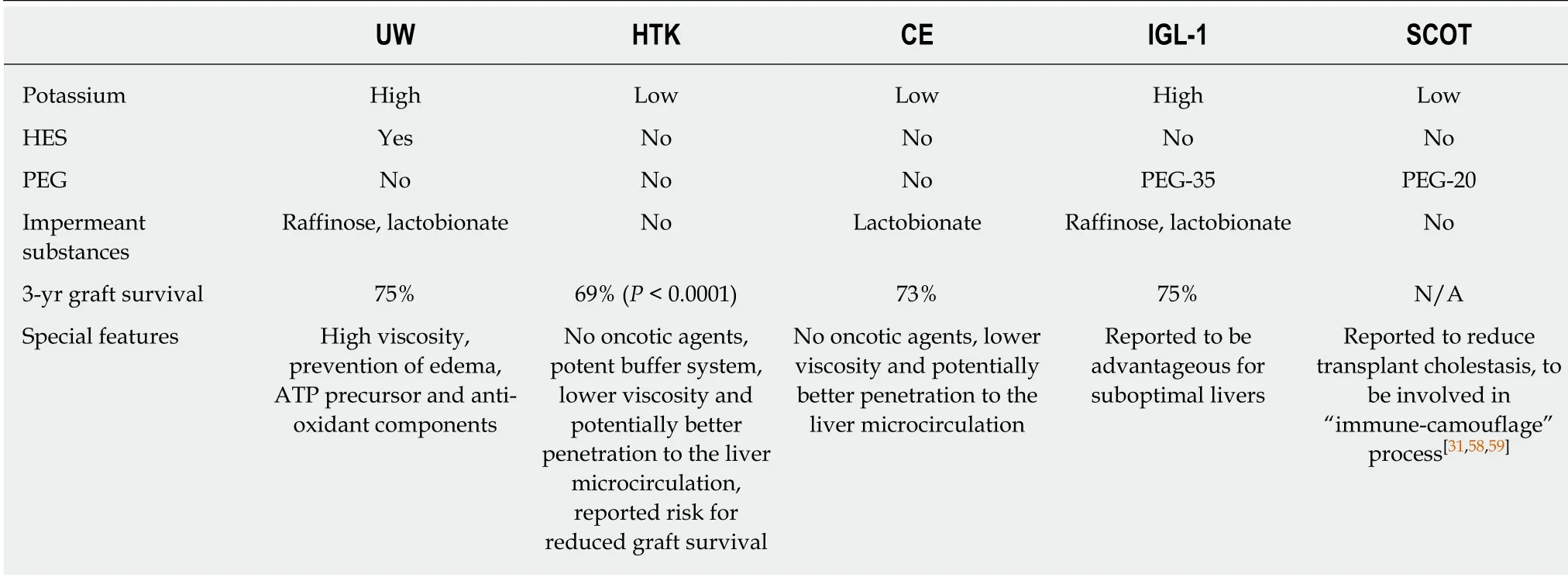
Table1 Graft preservation solutions[31,32,58,59]
Celsior with its low potassium/high sodium composition had also been developed initially for a cardiac preservation in the 1990s.Latter this solution was adopted for the protection of abdominal organ grafts as another alternative to University of Wisconsin solution[31].Particularly in liver transplantation both Celsior and histidinetryptophan-ketoglutarate solution have been widely used in last decade[31,47-49].
There are two main features of the Institute Georges Lopez preservation solution IGL-1:polyethylene-glycol with a molecular weight of 35 KDa (kilodalton) had been used instead of hydroxyl-ethyl-starch by and the high potassium/low sodium ratio had been reversed[31].The beneficial effects of IGL-1 in kidney and liver transplantation have been demonstrated in both experimental[50,51,53]and clinical[52,54]studies in settings of immune response,and against microcirculation dysfunction,endoplasmic reticulum stress,apoptosis.Zaoualiet al[55,56]have shown increased efficacy of the Institute Georges Lopez preservation solution IGL-1 compare to the University of Wisconsin solution of both non-steatotic and steatotic rat liver grafts preservation[31,55-57].Among beneficial effects of the Institute Georges Lopez preservation solution IGL-1 authors found:prevention of mitochondrial injury,oxidative stress and,therefore,hepatic damage.Those had been mediated by nitric oxide production.Though these results need confirmation especially in clinical studies,they made the Institute Georges Lopez preservation solution IGL-1 one of the first reported in static cold storage to be advantageous for suboptimal livers[31].
SCOT is based on polyethylene-glycol of smaller size,particularly with a molecular weight of 20 KDa,and low potassium/high sodium concentrations[31].Bradley and Bejaouiet al[31]showed a higher renal protection in immune response settings of SCOT.Polyethylene-glycol with a molecular weight of 20 KDa supposed to be involved in so called “immune-camouflage” process,which in part is responsible for renal protection described above[31,58].Savieret al[59]in retrospective study reported SCOT with polyethylene-glycol 20 KDa at concentration of 15 g/L (SCOT 15) was able to reduce transplant cholestasisvsUniversity of Wisconsin preservation solution.On the other hand polyethylene-glycol with a molecular weight of 35 KDa as oncotic agent has been shown to be more efficient compare to polyethylene-glycol with a molecular weight of 20 KDa for liver graft preservation[60].That could limit its use in liver transplantation.
Thus,Regular grafts donated after brain death could be safely preserved with convenient static cold storage.Except for prolonged cold ischemia time and extended criteria donors who need additional measures for graft storage and possible graft reconditioning until its implantation.
HYPOTHERMIC MACHINE PERFUSION
Hypothermic machine perfusion provides dynamic organ preservation at 4°C with protracted infusion of metabolic substrates to the graft during theex vivoperiod[61].At the above temperature cellular metabolic demands decrease but does not stop completely.So provision of necessary substrates could potentially decrease amount of harmful metabolites to reduce ischemia/reperfusion stress as an advantage over static cold storage[31].Dutkowskiet al[62]showed hypothermic machine perfusion to protect rodent livers against reactive oxygen species whose accumulation in ischemia causes toxic effects in hepatocytes.It happens due to reduction in glutathione depletion and release of superoxide anion[31,62].In a rat model with diet-induced fatty liver Bessemset al[63]demonstrated improved hepatocellular and endothelial function after hypothermic machine perfusion,as its potential for suboptimal livers[31].Study of Guarreraet al[64]compared hypothermic machine perfusion and static cold storage in human liver transplantation.Hypothermic machine perfusion demonstrated beneficial effect on graft function that diminishes biochemical markers of graft preservation injury[31,64].
Success of liver hypothermic machine perfusion requires oxygen supply,unlike kidney in which oxygenation is not always critical.Oxygenated hypothermic machine perfusion (HOPE) has been shown experimentally to improve quality of liver protection in normal and extended criteria donor livers[65].With oxygenated hypothermic machine perfusion grafts acquire ability to maintain functional integrity of hepatocytes and to restore homeostasis[31].In rodent model of donation after cardiac death Schlegelet al[66]also reported a protective effect of oxygenated hypothermic machine perfusion on biliary system.Oxygenated hypothermic machine perfusion improved immunogenic up-regulation and lowered parameters of hepatocellular injury after transplantation[31,66].
Graft dysfunction in livers from extended criteria donors is caused by ischemiareperfusion injury that negatively affects liver regeneration after surgery including hepatic resections and transplantation[2].In last decades for acceptable preservation allografts from extended criteria donors new strategies have been implicated[67-71].One of them is hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion.It has been studied in preclinical animal experiments[67,23].In those experiments hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion showed positive effect and demonstrated to reduce damage of cellular energy status and mitochondrial,and also the incidence of biliary complications[67].As well as it was in clinical settings.Hypothermic oxygenated organ perfusion over the portal vein performed in the transplant center using an extracorporal organ perfusion system with full oxygen saturation shortly before the actual implantation[67].Dutkowskiet al[72]published first clinical study with hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion in a cohort of patients undergoing liver transplantation with donation after cardiac death allografts.On the other hand the only legally accepted approach for organ donation in many European countries is DBD.And In this settings impact of hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion on early graft function and postoperative complications needs further investigation[2].
Belzer introduced machine perfusion in 1960[30].As well he was one of the authors of the University of Wisconsin preservation solution[73,74].So there is nothing unusual that perfusion solutions used in hypothermic machine perfusion mainly had the same composition as University of Wisconsin solution except for lactobionate which was substituted by gluconate.This solution has been named Belzer-MP solution.And it's still most frequently used perfusion solution[31].
New hypothermic machine perfusion solution,Polysol,has been described by Bessemset al[75].Besides amino acids:histidine,glutamine,tryptophan it has ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol.Their report demonstrated superior ability of Polysol in liver preservation versus Belzer-MP solution,with increased bile production and lower enzyme release[31,75].Another alternative solution for hypothermic machine perfusion is Vasosol[64].Despite it's basically composed on Belzer-MP solution,additional vasodilators (prostaglandin E1 and nitroglycerin),metabolic substrates (αketoglutarate,L-arginine) and antioxidants (N-acetyl-cysteine) are promising.Authors further improved Vasosol with α-tocopherol to enhance antioxidant benefit with hypothermic machine perfusion[76].
Hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion through single (portal vein only) or dual (portal vein and hepatic artery) approach widely discusses in literature[66,77,79,80].Use of dual perfusion is based predominantly on the proposition of better perfusion and biliary preservation leading to reduction of biliary complications in donation after cardiac death transplantation[66,78].However,some experimental data shows effective and sufficient perfusion of liver graft including biliary system through portal vein only approach[70].Also favorable effect of portal vein only approach in hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion has already been successfully demonstrated by Dutkowskiet al[72]in clinical settings.In recent article Schlegelet al[81]discussed possible fields of hypothermic machine perfusion application.Extended criteria donor grafts were among those possible fields.It's based on several previous studies with few hours liver perfusion performed in transplant center before graft implantation.Despite that there is no completed multicenter randomized trial comparing hypothermic machine perfusion and static cold storage to date.
December 21,2018 was starting date of new randomized multicenter clinical trial comparing hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion and static cold storage for extended criteria donor grafts.ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier:NCT03837197.Estimated Primary Completion Date is December 2019.Estimated Study Completion Date is December 2021.
In summary,Hypothermic machine perfusion started in transplant center could be estimated to provide possible positive reconditioning effect for regular grafts donated after brain death with prolonged ischemia time.Use of hypothermic machine perfusion in regular donation instead of static cold storage or in extended criteria donors requires further investigation.Multicenter randomized clinical trial supposed to be completed in December 2021.
NORMOTHERMIC MACHINE PERFUSION
Static cold storage currently is the main method for organ preservation.For high quality liver grafts from healthy donors it works well and brings relatively low rates of early allograft dysfunction,primary non-function,and biliary complications[82,83].Unfortunately static cold storage frequently does not provide successful protection for marginal livers from extended criteria donors,because graft and recipient complications increase unacceptably.NMP delivers oxygen,and nutrition at physiological temperature mimicking regular environment in order to support cellular function.During organ storage continuation of aerobic metabolism would minimize effects of PRS and ischemia/reperfusion injury[84-87].
The NMP concept is based on maintaining physiological support and therefore condition of the liver graft after procurement.That should diminish the risk of organ ischemic injury,because reperfusion has already started by the device,and thereby reduces risk of PRS in recipient[88].Through application of NMP in donation after cardiac death and other marginal grafts this preservation method can protect against ischemic cholangiopathy and other biliary complications[89-91].As it supposed by Jayantet al[92],possibility to establish reliable predictive markers of post-transplant function during the NMP phase,could reveal and eliminate livers at highest risk of primary non-function and initial poor function before implanting into a recipient.That opens a way for screening among increasing number of livers based onex situfunction and exclusion those at higher risk,the number of liver from extended criteria donors could increase significantly.The ability to observe function of liversex situbrings additional advantage in order to improve their condition.Necessary supplements may be added to perfusate solution[92,93-95].Besides that,NMP has already demonstrated significant efficacy in lung transplantation.Also there are testing series in transplantation of kidney and whole pancreas[96,97].
Since preclinical large animal studies of NMP gave promising results in porcine and rodent models[98-101],till date there are 3 commercial normothermic perfusion devices have been used in early clinical trials.Similar principles used in all of them.Differences are in degree of portability,automation,recirculating perfusate pressure and pulsatility,substrate type and delivery,and perfusion through portal vein and hepatic artery[102,103].The first one to be clinically implicated was the Metra device by Peter Friend and colleagues developed in a partnership between the University of Oxford and OrganOx Ltd.company.It is portable,fully automated,works at temperature 37°C,uses whole blood supplemented with plasma expander(Gelofusine),bile salts,parenteral nutrition solution,heparin,insulin,and prostacyclin through a closed perfusion,continuous,non-pulsatile portal vein,and hepatic arterial flow technique[92,104].The second one - Organ Care System follows similar principles of NMP developed by TransMedics (Andover,MA) is also portable and fully automated device[92,105].The third one is semi-automated,with limited portability developed by Organ Assist (Groningen,Netherlands) which has temperatures range from 8°C to 37°C.During liver perfusion hepatic arterial and portal pressures can be modulated to adjust vascular flow[92,106].Until now the importance of device portability is still open problem.Need to transport heavy,complex equipment,provision or on-board generation of oxygen,plus great distances by road transportation or plane pose their own unique technical as well as financial challenges that markedly escalate the technology cost.Due to that more limited intervention in some institutions is now implicated:liver graft NMP since graft's arrival to recipient center.Though it may not fully protect against ischemic cholangiopathy and hepatocyte injury,on the other hand it shows confirmation if liver graft functions before it is implanted.Another possible advantage is some perspective with developments in the future to be more flexible in liver transplantation surgery schedule during daylight hours[92].
Animal studies with pigs (30-40 kg weight) as liver donors included Landrace[107,108]and Yorkshire[109-113].Boehnertet al[114]used only male pigs.Pigs in the study of St Peteret al[108]were gender unspecified.The DCD model has been achieved by cardiac arrest.In turn in the majority of studies cardiac arrest has been induced with potassium chloride injection[107,108,111-113].While Boehnertet al[110]got it via exsanguination.
The only study to compare static cold storage with NMP following a period of static cold storage was Boehnertet al[110]work.In almost all reports the warm ischemia time was 60 min.Only Bananet al[107]had static cold storage group after 40 min of warm ischemia and NMP following 20,40,and 60 min of warm ischemia.Cold preservation solutions were histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate[107,109,111-113],University of Wisconsin[110],or Euro Collins[108].Most studies used dual perfusion through the hepatic artery and portal vein[109,111-113,107].St Peteret al[108]did single arterial flush.In one study dual or single vessel flush has not been specified[110].Also 2 studies flushed liversex situ[111,113],all others - in situ[107-109,110,112].
Duration of NMP was 6[107],8[110],10[109,111-113],or 24[108]h.After that,researchers simulated organ implantation.For this purpose they perfused the whole blood for either 2[107],12[110],or 24[108,109,111-113]h.At the end of the reperfusion stage transaminase levels were investigated.
Bananet al[107]applied a dialysis circuit as a tool for perfusion.Perfusate was delivered:by two centrifugal pumps[107],or a roller pump and a centrifugal pump[109,111-113],or the portal vein passive perfusion and the hepatic artery perfused with centrifugal pump[110,108].Perfusate in 3 studies was whole blood[108,109,111],in 2 studies - diluted whole blood[107,111].One study used acellular perfusate[110].Liuet al[113]compared directly different perfusate solutions:the Steen solution,washed red blood cells plus Steen solution,the whole blood,and static cold storage.The whole blood and washed red blood cells in the Steen solution helped significantly improve liver function and diminish hepatocellular injury and liver function compare to groups where Steen solution was used alone and to livers on static cold storage.Washed red blood cells in Steen solution and group perfused with the whole blood had no significant difference[113].Nostedtet al[115]noted that results with acellular perfusion[110]have not been replicated.Also Liuet al[113]suggested the need for an oxygen carrier.Further studies are needed to determine the optimal solution for NMP[115].
Another weakness of animal studies is heterogeneity.The models of porcine liver transplant differ in longevity of observation period after revascularization (7 d to 8 h).Also in study of Fondevilaet al[116]static cold storage followed a period of NMP and this makes it hardly comparable with other reports.NMP in study of Schönet al[117]has been made with no period of static cold storage,and also 4 h of static cold storage followed 60 min of warm ischemia time made all grafts primary nonfunctional.Keeping in mind that warm ischemia time was 60 min in almost all reports,it supports conclusion of Reddyet al[14]that periods of cold storage can impact positive effects of NMP.On the other hand,in short observation period (8 h) by Boehnertet al[110]static cold storage followed by NMP produced less hepatocellular injury compare to static cold storage alone group.Unfortunately grafts in this study were not assessed in longer follow up.Also in discarded human livers,NMP could improve function of affected livers even after long time cold storage[118].Further research to address NMP's ability to safely recover and transplant DCD grafts following periods of cold storage is needed[115].Ravikumaret al[119]reviewed devices for NMP.And since portable ones are now available,they should be of use to try to eliminate cold storage for such marginal livers during the transplantation procedure.Successful recovery of marginal grafts such as donated after cardiac death by use of NMP even after periods of cold storage could significantly influence its clinical implementation.Besides that,economic impact of this method of liver graft preservation has not yet been estimated although it remains to be important for clinical use of NMP in donation after cardiac death[115].Also gradual rewarming showed promising results for that kind of marginal grafts[106,120-122].So it may play an important role to move forward in utilizing machine perfusion after periods of static cold storage[115].
In clinical settings,Ravikumaret al[104]reported 20 donor livers NMPs plus 40 static cold storages with 4 donations after cardiac death in each group.Bralet al[123]study included 10 (4 - donations after cardiac death) NMPs and 30 (8 - donations after cardiac death) static cold storages.In Selzneret al[124]publication there were also 10 (2 -donations after cardiac death) NMPs and 30 (6 - donations after cardiac death) static cold storages.Liuet al[125]study consisted of 10 (2 - donations after cardiac death)NMPs and 40 (8 - donations after cardiac death) static cold storages.And the largest report has been made by Nasrallaet al[126]with 137 (34 - donations after cardiac death)NMPs and 133 (21 - donations after cardiac death) static cold storages.Also in their report 16 out of discarded 48 donor livers were undergone NMPs,the rest (32) - static cold storage.Among reasons to discard there were prominent cirrhosis in donor liver,increasing lactate level,significant steatosis,intra-operatively found malignancy,more than thirty minutes warm ischemia time,and device related errors[126].Patient'groups in all studies were comparable in donor age,MELD score,time of NMP and static cold storage,with 2 exceptions for Bralet al[123](where NMP lasted 786 minvs235 min of static cold storage) and for Nasrallaet al[126](714 min of NMP and 465 min of static cold storage).In all studies NMP perfusate had been blood based with packed red blood cells ABO group O.Ravikumaret al[104],Bralet al[123],and Nasrallaet al[126]additionally primed the circuit and liver with gelatin-based plasma expander(Gelofusine™,B.Braun,Melsungen,Germany),Selzneret al[124]used Steen solution instead.In all trials liver function characteristics such as hepatic transaminases,INR,pH,lactate level,bile production,hepatic artery,and portal vein flow during NMP were within normal range[104,123-126].In meta-analysis of Jayantet al[92]median patient age was outlined within 48.0-58.0 years (range 14-85) in NMP group and 46.0-58.5 years (range 20-86) in static cold storage group.The median MELD score reported ranged within 12-21 (range 6-40) and 14-23 (range 6-37) in these groups respectively.The reported median NMP time varied considerably,from 558 to 786 min (range 210-1631 min) while median CIT on cold storage was 235-634 min (range 64-967 min)[92].On NMP max medium AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase) level was 417-1252 U/L(range 84-15009 U/L) between days 1 and 7 in all trials.On static cold storage AST was 839-1474 U/L (range 153-8786 U/L).Median INR (International Normalized Ratio) on day 7 in NMP group was 1.05-1.1 (range 0.88-1.6) and 1.03-1.1 (range 0.90-2.2) in static cold storage group.Also on day 7 median bilirubin levels were 25-79 μmol/L (range 8-344 μmol/L) and 30-48 μmol/L (range 9-340 μmol/L) in NMP and static cold storage groups,respectively.Median alkaline phosphatase at day 7 was 139-245 U/L (range 40-626 U/L) on NMP and 147-243 U/L (range 58-743 U/L) at static cold storage[92,104,123-126](Table2).
Only Nasrallaet al[126]reported single primary non-function case in their randomized study in NMP group.Among studies listed above early allograft dysfunction in NMP groups ranged from 10% to 56% and from 23% to 30% in static cold storage groups.As well,Nasrallaet al[126]in donation after cardiac death reported 93% less likelihood of early allograft dysfunction on NMP compare to static cold storage[92,126].Also this randomized trial confirmed earlier data of Bralet al[123]that post reperfusion syndrome occurred less frequently in NMP group than in static cold storage group (15 casesvs32)[92,125,126].
The median intensive care unit stay in reports listed above was 3-4 d (range 0-41 d)for recipients with livers after static cold storage,and for those with livers on NMP -3-16 d (range 1-65 d)[92,104,123,124,126].The median hospital stay for patients with grafts after static cold storage was 13-25 d (range 7-89 d) and 12-45 d (range 6-114 d) for patients with grafts with NMP[92,104,123,124,126].Major complications (Clavien-Dindo score ≥ 3)occurred in 22%-37% and 10%-22% of recipients in static cold storage and NMP groups,respectively[92,104,123,124,126].At 6 mo after liver transplantation biliary complications have been developed in grafts after NMP in study of Ravikumaret al[104]in 20% (4 patients),in study of Nasrallaet al[126]- 10.1% (13 patients).Selzneret al[124]and Bralet al[123]did not report biliary complications at that point.Besides,Bralet al[123]evidenced 14.8% of biliary strictures after static cold storage compare to 0 after NMPand Nasrallaet al[126]in recently published randomized study did not observe any statistical difference between groups for non-anastomotic biliary strictures[92,123,126].

Table2 Results of normothermic machine perfusion and static cold storage[92,104,123-126]
Graft survival at 30 d,3 mo and 6 mo was statistically insignificant between groups 80%-100% in NMP group and 97.5%-100% in static cold storage group[92,104,123,124,126].As well as that was for 30 d mortality.It ranged 2.5%-11% after NMP and 0-2.5% after static cold storage[92,104,123,124].
By the literature,up to one-third of marginal livers are taken in donation after cardiac death despite additional risks[92,107,126-129].In porcine models experimental data demonstrate that NMP application possibly decrease the additional risks of organs donated after cardiac death,but that is almost not proved by clinical practice[107,128].By Brockmannet al[129],porcine donated after cardiac death liver grafts shows better survival and superior function versus static cold storage.In study of Fondevilaet al[116]porcine livers donated after cardiac death with warm ischemia time up to 120 min after NMP survived 100%,and after static cold storage they had 100% mortality[92,116].
Potentially,NMP may help to estimate graft functionality before implantation into a recipient,thus decrease such risks.Currently,assessment of donor liver before implantation could only roughly predict graft survival and function.So,marginal donor livers could potentially be disastrous for recipients,with elevated risk of early allograft dysfunction,primary non-function,or other detrimental complications of ischemia-reperfusion injury,with acute renal injury after PRS[63,92,130-132].
Since NMP has been tested widely,some authors suggested that a combination of metabolic,hemodynamic,and synthetic parameters picked up during the perfusion phase can help to predict viability of the graft by providing its functional assessment[92,99,133].And static cold storage cannot provide such a possibility.The parameters include stability of portal vein and hepatic artery flow and pressure,bile production,some metabolic parameters including ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase),AST,etc.[92,104,123,124,126].Most important predictors of adequate post-transplant liver function are pH stability and repeated bicarbonate corrections,lactate clearance during NMP[92,98,99,134].
The subsequent clinical trials published by Ravikumar,Selzner,Bral,and Nasrallaet al[104,123,124,126]used 20%,20%,40%,and 24.8% livers donated after cardiac death,respectively,and demonstrated similar outcomes to static cold storage controls in donated after cardiac death grafts.Recent study by Nasrallaet al[126](2018) outlined better outcomes with donated after cardiac death livers preserved with NMP in comparison to static cold storage group;however further studies are required to strengthen this outcome owing to limitations of inadequately powered subgroup analysis.
Bralet al[123]did not show significant improvement in opening transaminase levels in the recipients,likely due to their increased proportion of donations after cardiac death and prolonged cold ischemia time while a relatively higher proportion of replaced and accessory hepatic arteries were reconstructed on the back table,and their NMP duration was extended to outer limits often while their small surgical team rested overnight or were engaged in other HPB surgeries[123].
Ischemic injurious impact after static cold storage on hepatocytes and biliary epithelium was well described,despite this method of graft preservation is standard and convenient[92,110,135].So,prolonged cold storage of marginal liver grafts may bring inacceptable risk for recipient[136-141].Among those,primary non-function takes place in up to 5%-8%[142,143].Association between donor risk factors and primary non-function supports its multifactorial nature[137,138],and may also be caused by technical error with inadequate blood flow[136].If emergency re-transplantation is not possible,primary non-function leads to recipient's death.None of the early phase NMP trials have been associated with primary non-function.Only Nasrallaet al[126]reported single primary non-function case in their randomized study in NMP group[92,126,144].
Elevated transaminase levels within first postoperative week most likely indicate early allograft dysfunction,which brings increased risk for the patient[145-147].In the presented studies early allograft dysfunction has been developed in 10%-55.5% after NMP.Bralet al[123]described 4 such events mainly occurred in livers donated after cardiac death[104,123-125].All those grafts finally started to work properly with transaminase levels returned back to normal.Besides,in their recent randomized trial Nasrallaet al[126]in donation after cardiac death reported 93% less likelihood of early allograft dysfunction on NMP compare to static cold storage[92,126,144].
Ischemic cholangiopathy and anastomotic biliary strictures are among the most serious complications in donation after cardiac death liver transplantation.Biliary strictures in liver transplant surgery ranges within 4%-15% for grafts donated after brain death and 30%-40% for those donated after cardiac death[22,92,140].Pathogenesis of this potentially devastating complication includes peribiliary glands' injury due to peribiliary vascular plexus micro-thrombi formation at the time of ischemiareperfusion or a circulatory phase of donation after cardiac death.Later,some reports showed that thrombolytic agent,tissue plasminogen activator infused into hepatic artery dissolved and/or prevented thrombi formation in microcirculations and therefore biliary strictures[92,141,148,149].In porcine models op den Drieset al[99]and Boehnertet al[110]study demonstrated significantly lower rate of complications related to bile duct after NMP.Liuet al[111]reported that differentiation of multipotent stem cells in peribiliary glands into cholangiocytes following NMP in porcine model promotes biliary epithelium regeneration that could prevent formation of biliary strictures[111,150].Results of clinical trials were varying.At 6 mo after liver transplantation biliary complications have been developed in grafts after NMP in study of Ravikumaret al[104]in 20% (4 patients),in study of Nasrallaet al[126]- 10.1% (13 patients).Selzneret al[124]and Bralet al[123]did not report biliary complications at that point.Besides,Bralet al[123]evidenced 14.8% of biliary strictures after static cold storage compare to 0 after NMP and Nasrallaet al[126]in recently published randomized study did not observe any statistical difference between groups for nonanastomotic biliary strictures[92].
Extended criteria donors also include those with steatotic livers.They usually are not used as grafts,because of possibility of primary non-function development[92,134,147].In Spitzeret al[151]study livers with more than 30% of macrosteatosis constituted increased risk of 71% for one-year graft loss versus those with steatosis of less than 15%.Though other reports for macrosteatosis more than 30% demonstrated successful outcomes for donors with age less than 40 year old,cold ischemia time less than 11 h,and not for donation after cardiac death[92,152,153].In animal studies with NMP Jamiesonet al[95]showed substantial decrease of steatosis grade in rat livers.Bananet al[134]and Vogelet al[118]reported improvement in steatosis after NMP and with additional defatting substances.Nagrathet al[154]got reduction in hepatic triglycerides by 65%when used so called “defatting cocktail” for steatotic rat livers to promote oxidation and to esterify hepatic triglycerides.Boteonet al[155]reported their regimen for defatting of primary human hepatocytes which is non-toxic to hepatocytes.cholangiocytes and intrahepatic endothelial cells.But all these studies need clinical confirmation.
Also in a recent publication Scheuermannet al[156]considered that inflammatory molecules accumulated during machine perfusion (so called damage-associated molecular patterns and inflammatory cytokines) can negatively impact liver graft.The accumulation occurs in time dependent manner with noted decrease after a peak.So therapies and optimal time to attenuate them could be beneficial in further improvement of this technology[156].
Dondossolaaet al[157]used NMP to assess marginal liver graft function after hypothermic oxygenated machine perfusion.
To date no clinical recommendations for NMP has been issued even after multicenter randomized trial[126].
Therefore,NMP is actively evaluating promising method for extended criteria donor livers preservation.Potentially,NMP may help to estimate graft functionality before implantation into a recipient.Clinical studies demonstrated at least noninferiority with NMPvsconvenient static cold storage in settings of posttransplant complications,early allograft dysfunction,and primary non-function.At the current level of development possible reconditioning effect of NMP on steatotic livers has not been confirmed in clinics.Future trials are required.
CONCLUSION
Regular grafts donated after brain death could be safely preserved with convenient static cold storage.Except for prolonged ischemia time where hypothermic machine perfusion started in transplant center could be estimated to provide possible positive reconditioning effect.Use of hypothermic machine perfusion in regular donation instead of static cold storage or in extended criteria donors requires further investigation.Multicenter randomized clinical trial supposed to be completed in December 2021.
Extended criteria donors need additional measures for graft storage and assessment until its implantation.NMP is actively evaluating promising method for this purpose.
Future studies are necessary for precise estimation and confirmation to issue clinical practice recommendations.
杂志排行
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery的其它文章
- Management of pancreatic head adenocarcinoma:From where to where?
- Conduit necrosis following esophagectomy:An up-to-date literature review
- Learning curve of enhanced recovery after surgery program in open colorectal surgery
- Single incision laparoscopic fundoplication:A systematic review of the literature
- Laparoscopic celiac plexus ganglioneuroma resection:A video case report
