Efficacy of high-flow nasal cannula on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:A meta-analysis
2019-04-05YingMingSunMinZhangNaSunZhiGuanYingWang
Ying-Ming Sun ,Min Zhang ,Na Sun ,Zhi Guan ,Ying Wang
1Graduate School,Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,3001617,China;
2Department of Nursing Administration,Tianjin First Centre Hospital,Tianjin,300192,China.
Abstract Objective:To systematically evaluate the efficacy and feasibility of high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC)on patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD).Methods:Systematic searches on PubMed,Web of Science,the Cochrane Library,Embase,CBM (Chinese Biomedicine Database),CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure),Wanfang Database and VIP were performed for randomized controlled trials (RCTs)which explored the effects of HFNC on patients with AECOPD.The retrieval time was from the establishment of each database to July 2019.RevMan5.3 software was used for statistical analysis.Results:A total of 12 articles were included,involving 812 patients.The results showed that:(1)Compared with conventional oxygen therapy,HFNC could improve patients' arterial partial oxygen pressure (PaO2)(MD=12.70,95% CI (7.00,18.40),Z=4.37,P < 0.0001),reduce partial arterial blood carbon dioxide (PaCO2)(MD=-10.99,95% CI (-14.42,-7.55),Z=6.26,P < 0.00001)and reduce endotracheal intubation rate (OR=0.19,95% CI (0.04,0.93),Z=2.05,P=0.04),shorten the hospitalization time (SMD=-0.74,95% CI (-1.11,-0.37),Z=3.95,P <0.0001).(2)Compared with non-invasive positive pressure ventilation,it has fewer adverse reactions (OR=0.18,95% CI (0.09,0.35),Z=5.08,P < 0.00001)and shorter hospital stay (SMD=-0.57,95% CI (-0.90,-0.23),Z=3.33,P=0.0009).Conclusion:HFNC can improve the patients' hypoxia symptoms and CO2retention,reduce the rate of tracheal intubation,and alleviate adverse reactions.However,Limited by the quality and region of the included studies,more high-quality are needed to test it.
Keywords:High-flow nasal cannula,AECOPD,Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation,Conventional oxygen therapy,Meta-analysis
Introduction
Acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (AECOPD)refers to rapid deterioration of respiratory symptoms at the original basis of COPD.It is characterized by lack of oxygen and carbon dioxide retention which lead to need additional treatment [1].AECOPD is easy to merge with typeⅡrespiratory failure,with high mortality and poor prognosis.It's an important factor in hospitalization and death of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[2].Oxygen therapy is a key part of hospitalization for AECOPD patients and improves patient survival.Highflow nasal cannula (HFNC)is a new type of oxygen therapy that provides a relatively constant oxygen concentration (21%~100%),high airflow (8~80L/min)gas for human airway temperature and humidity,which is applied and promoted in clinical practice [3].
HFNC was originally applied to neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome.In recent years,the effectiveness and feasibility of HFNC in patients with hypoxemic respiratory failure or post-extubation have been confirmed by relevant studies.Research performed on patients diagnosed with COPD have shown that HFNC can reduce the frequency of acute exacerbation,PaCO2 and the number of hospital stays compared with conventional oxygen therapy [4].However,some studies indicate that the application of HFNC in patients with AECOPD complicated with type II respiratory failure may cause respiratory acidosis,thereby increasing the mortality rate of patients[5].The efficacy of HFNC in patients with AECOPD remains controversial.Therefore,this study conducted a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of HFNC versus conventional oxygen therapy (COT)and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV)in patients with AECOPD to explore it's therapeutic effects.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
1.1.1 Study Design:
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs)of HFNC were applied to patients with AECOPD.
1.1.2 Subjects:
The participants were adults at least 18 years old and diagnosed with AECOPD based on the guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of COPD [6].
1.1.3 Interventions:
Patients were divided into experimental group,in which HFNC oxygen therapy was applied.In control group,they were assigned to receive COT or NIPPV.
1.1.4 Outcome:
The primary outcomes included partial oxygen pressure(PaO2),partial arterial blood carbon dioxide (PaCO2),and endotracheal intubation rate.
The secondary outcomes included but not limit to hospitalization time and adverse reactions.
1.1.5 Exclusion criteria:
(1)AECOPD patients undergoing sequential treatment after tracheal intubation and extubation.
(2)Duplicate literature,literature with incomplete information,no data available for analysis and review.
1.2 Literature search
A systematic and comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed,Web of Science,the Cochrane Library,Embase,CBM (Chinese Biomedicine Database),CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure),Wanfang Database and VIP for eligible studies published up to July 2019.Search terms included:(“high flow nasal cannula”OR“HFNC”OR“high flow nasal oxygen”OR“high-flow oxygen therapy”OR“HFOT”OR“humidified high-flow nasal cannula”OR“heatedand humidified high-flow nasal oxygen”)AND(“chronic obstructive pulmonary disease”OR“acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease”OR“AECOPD”).Chinese terms included:(“ 经 鼻 高流量氧疗”OR“经鼻高流量湿化氧疗”OR“经鼻高流量加温加湿吸氧”OR“高流量加温加湿氧疗”OR“湿化高流量氧疗”OR“高速流鼻插管”OR“高速流氧疗法)AND (慢性阻塞性肺疾病”OR“慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期”OR“慢阻肺急性加重期).We also manually searched the related articles and reviewed the references listed in each identified article to ensure all eligible studies.
1.3 Literature screening and data extraction
(1)All the searched studies were imported into Note Express literature management software for preliminary repeated screening.According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria,two researchers independently read the title and abstract to screen the literature,read the full text further,cross-check the literature screening results.Differences in opinion were settled by consensus or after consultation with a third investigator.The extracted information mainly includes:Basic information (the title of included studies,first author,publication time,national),research type,basic patient type,sample size,interventions,outcomes,etc.
1.4 Assessment of literature quality
According to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions,Version5.1.0,included literatures were independently evaluated by two researchers.Seven items examined are as follow:generation of the allocation,concealment of allocation,blinding participants and personnel,blinding outcome assessment,incomplete outcome data,selective outcome reporting and other sources of bias.Two investigators conducted the quality assessment for the study methodology,independently and separately.Any divergence was resolved by consensus through expert advice or a third investigator.
1.5 Statistical analysis
The meta-analysis was accomplished by using Revman version 5.3.An initial test for statistical heterogeneity among studies was conducted and we used Chi-square(X2)test and I-squared (I2)statistics (P>0.05 or I2< 50%)to indicate significance.Fixed-effects model was applied in the absence of statistical heterogeneity;Otherwise,tracing the source of heterogeneity,randomeffects model was used unless it's for clinical reasons.When the heterogeneity is obvious,subgroup analysis,sensitivity analysis or descriptive analysis would be used.Mean difference (MD)was used to describe continuous data,while the risk ratio (RR)was used to describe dichotomous data.And 95% confidence interval (95% CI)was given.The hypothesis test level of the meta-analysis is α=0.05 and the results were displayed in Forest plots.
2 Results
2.1 Literature screening process and results
Initially 204 articles have been collected,of which 199 were extracted from electronic databases and 5 were extracted from reference lists review.Eventually 12 trials were enrolled in our final analysis.The total sample size was 812,including 405 in HFNC group and 407 (COT 136,NIPPV 271)in control group.The screening process is shown in Figure 1.The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
2.2 Bias risk assessment results of the included studies
Quality assessment of the 12 enrolled studies showed that there was no bias in incomplete outcome data or selective outcome reporting.4 literatures have introduced the generation of random sequences.Results of bias risk assessment were presented in Table 2 and Figure 2.
2.3 Meta-Analysis Results
2.3.1 Effect of HFNC on PaO2 of AECOPD
(1)A total of 4 studies [7-10]were included,involving 248 patients.The meta-analysis of the random model showed the PaO2 of AECOPD in HFNC group was higher than the COT group,and the difference was statistically significant (MD=12.70,95% CI (7.00,18.40),Z=4.37,P< 0.0001)(Figure 3).
(2)Compared with the NIPPV group,only 5 studies[11-15]involving 392 patients reported the effect of HFNC on PaO2.The use of HFNC was not associated with statistically significant (MD=0.06,95% CI (-1.35,1.46),Z=0.08,P=0.94)(Figure 4).
2.3.2 Effect of HFNC on PaCO2 of AECOPD
Compared with COT group,four studies [7-10]reported a statistically significant decrease in PaCO2 in the patients managed with HFNC (MD=-10.99,95%CI (-14.42,-7.55),Z=6.26,P< 0.00001).On the contrary,seven other studies [11-18]failed to show any difference.No statistically significant difference is found (MD=-0.34,95% CI (-2.10,1.43),Z=0.37,P=0.71)(Figure 5).
2.3.3 Effect of HFNC on endotracheal intubation rate of AECOPD
Results from 6 trials [8,10-12,15,17]were available to examine the reduction in the incidence of intubation,Two [8,10]of which describe the comparison of HFNC with COT,and the other studies [11,12,15,17]is with NIPPV.A low level of heterogeneity was found among the identified comparisons (P=0.72,I2=0%)(P=0.37,I2=0%),so we both used a fixed-effect model for pooled analysis.The results showed that the endotracheal intubation rate of the patients in the HFNC group was lower than that of the COT group.Significant difference in the endotracheal intubation was found in HFNC treatment compared with COT(OR=0.19,95% CI (0.04,0.93),Z=2.05,P=0.04).But compared with NIPPV,the difference was not statistically significant (OR=0.84,95% CI (0.42,1.68),Z=0.50,P=0.62)(Figure 6).
2.3.4 Effect of HFNC on adverse reactions of AECOPD
In terms of the incidence of adverse reactions,the adverse reactions caused by different oxygen therapy methods in various literatures specifically refer to:nasal injury,bronchospasm,dryness of the respiratory tract,drainage disorder,flatulence,etc.Four studies[11-14]reported the effect HFNC on adverse reactions compared with the NIPPV group,there was no heterogeneity between studies (P=0.91,I2=0%),so we used a fixed-effect model for Meta-analysis.The results showed that the incidence of adverse reactions in HFNC group was lower than that in NIPPV group,and the difference was statistically significant (OR=0.18,95% CI (0.09,0.35),Z=5.08,P< 0.00001)(Figure 7).
2.3.5 Effect of HFNC on hospitalization time of AECOPD
Hospitalization time was reported in four trials,Two of which [12,15]describe the comparison of HFNC with COT,and the other studies [8,10]is with NIPPV.The results of the fixed model showed that the difference in hospitalization time between the HFNC group and NIPPV/COT was statistically significant (SMD=-0.57,95% CI (-0.90,-0.23),Z=3.33,P=0.0009);(SMD=-0.74,95% CI (-1.11,-0.37),Z=3.95,P< 0.0001)(Figure 8).
2.4 Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
When the number of meta-analyzed studies is ≥ 10,the funnel plot is used for analysis.However,there were less than 10 articles in the outcomes of the HFNC compared with the COT/NIPPV,and the funnel plots could not be drawn for publication bias analysis.The possibility of publication bias could not be ruled out.
When the data of a single study is excluded,the corresponding combined effect quantity has no essential change to the original result,suggesting that the research result is robust.The sensitivity analysis was eliminated one by one for each study result.The results showed that there was no significant change in the results after the combined effect.Therefore,the results of the meta-analysis are more robust and reliable.
3 Discussion
3.1 Effect of HFNC on the effectiveness of AECOPD patients
AECOPD is a typical type of disease characterized by type II respiratory failure.It is mainly characterized by decreased ventilation efficiency and ineffective triggering inspiratory difficulty [19].Studies have found that patients with AECOPD managed HFNC can help improve breathing difficulties and the efficiency of ventilation [20].The meta-analysis is consistent with its findings:HFNC compared with conventional oxygen therapy can significantly improve the patients'PaO2 and lower PaCO2.This potential benefit can be explained by the following mechanisms:(1)HFNC can continuously improve the patient's hypoxia symptoms and correct CO2 retention by providing continuous high-flow gas and flushing CO2 remaining in the upper respiratory tract anatomy dead space [21].(2)HFNC can provide high flow rate gas that exceeds the peak inspiratory flow of the patient.It is rarely affected by the patient's respiratory rate and tidal volume,ensuringa constant oxygen concentration,thus effectively reducing the symptoms of dyspnea [22].Therefore,the application of HFNC in AECOPD patients can have the potential advantage to replace conventional oxygen therapy.However,compared with noninvasive positive pressure ventilation,the current evidence is not sufficient to demonstrate the significant advantages of HFNC in improving patients with hypoxic symptoms and CO2 retention.while for patients with Type Ⅱrespiratory failure may try to use HFNC carefully,remain to be multi-center,high-quality research confirmed.
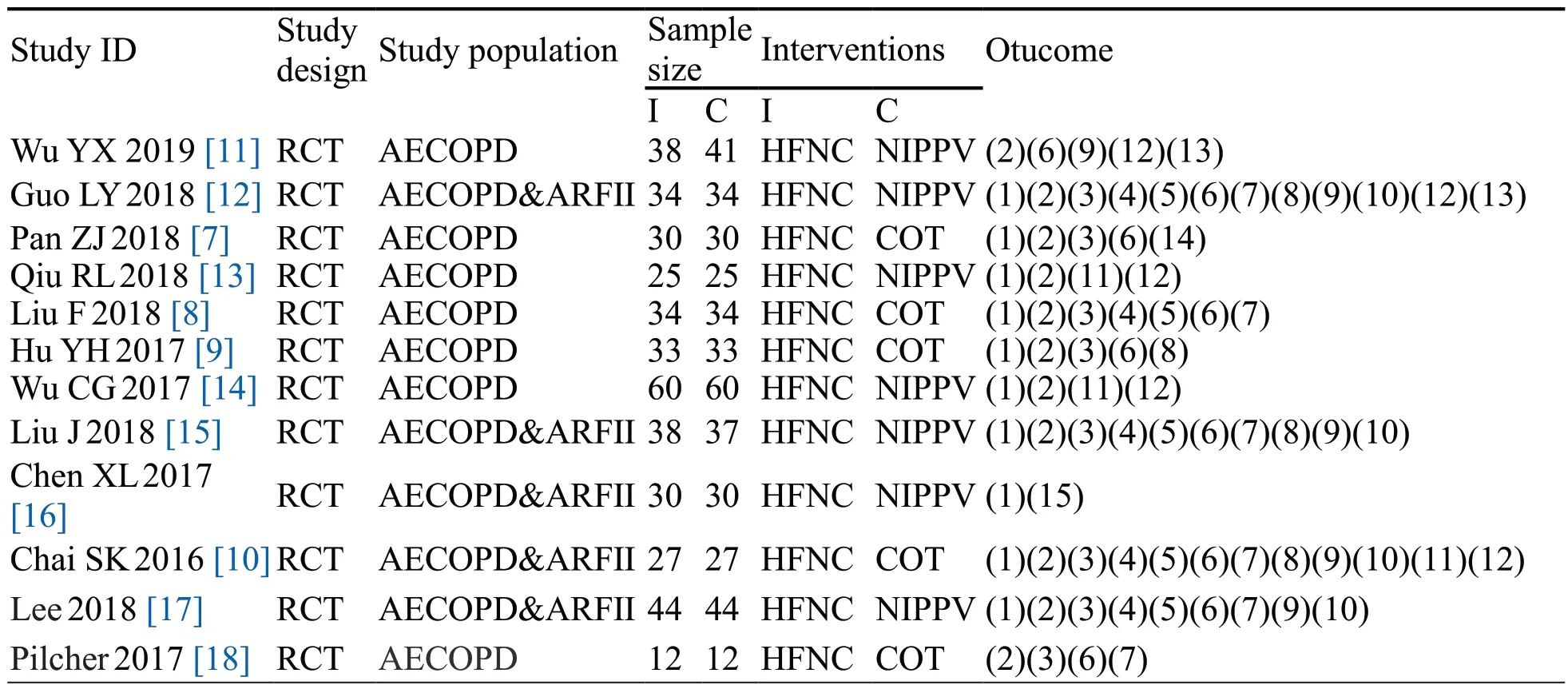
Table 1 The basic characteristics of included studies
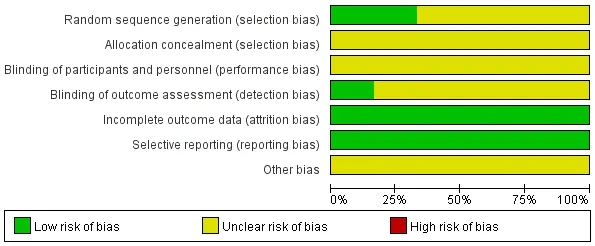
Figure 2 Risk of bias summary and graph

Figure 3 Forest plot shows the effect of HFNC vs COT on PaO2of AECOPD patients
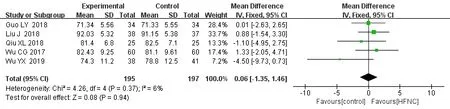
Figure 4 Forest plot shows the effect of HFNC vs NIPPV on PaO2of AECOPD patients
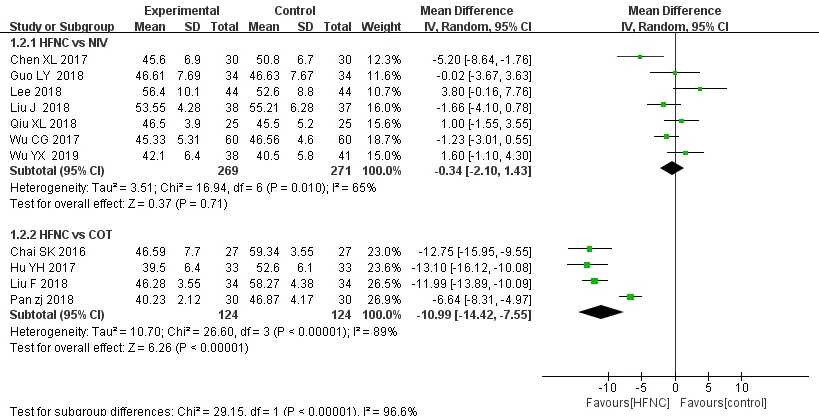
Figure 5 Forest plot shows the effect of HFNC on PaCO2of AECOPD patients
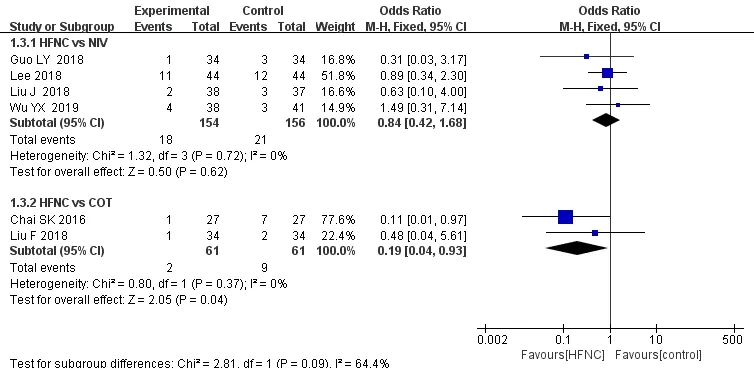
Figure 6 Forest plot shows the effect of HFNC on the incidence of intubation of AECOPD patients
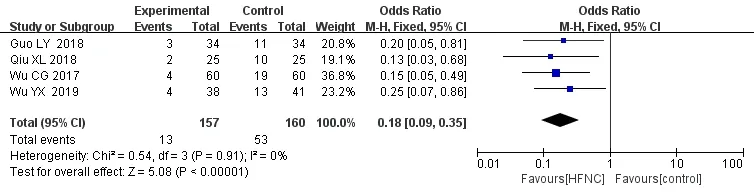
Figure 7 Forest plot shows the effect of HFNC on the incidence of adverse reactions of AECOPD
3.2 Effect of HFNC on the feasibility of AECOPD patients
For AECOPD patients,inspired oxygen concentration should be strictly controlled oxygen therapy in order to avoid the phenomenon of carbon dioxide anesthesia.However,the high-flow oxygen provided by HFNC is not equivalent to high-concentration oxygen.The separate regulation of oxygen flow rate and oxygen concentration can reduce PaCO2 by high-flow scouring,while avoiding the respiratory inhibition of highconcentration oxygen in AECOPD patients.The results of this study indicate:Compared with conventional oxygen therapy,HFNC can reduce tracheal intubation rate and reduce hospitalization days;Compared with noninvasive positive pressure ventilation,HFNC is better tolerated,reducing the incidence of adverse reactions and shortening the length of hospital stay.Analysis reasons are as follows:(1)HFNC can produce flow-dependent positive airway pressure against endogenous positive end-expiratory pressure,increase alveolar ventilation,promote pulmonary physiologic recruitment and reduce upper airway resistance and respiratory work,which can effectively alleviate dyspnea symptoms,thereby reducing invasive mechanical ventilation rate.To a certain extent,it can reduce medical expenses and the hospitalization time.(2)The warm and humid gas provided by HFNC enhances patient comfort and the ease of use of HFNC does not affect the patient's daily activities.In summary,HFNC has a good clinical application prospect in AECOPD patients,especially in reducing the economic burden of patients.
3.3 Limitations and inspiration of this research
(1)There are few articles included in each outcome indicator,and it's impossible to determine whether there is publication bias.(2)There is a certain heterogeneity in the literature,and the reasons for the analysis may be:the parameter indicators set by the intervention and the variation of the treatment duration,the patient's baseline data is not clear,etc.(3)Small sample size,the included literature is publicly published and some articles cannot obtain the full text.(4)Laboratory test indicators are often used in existing research outcome.Reported that there are few endpoints related to lung function and quality of life in patients with AECOPD.Due to the limitations in quality and quantity of this study,it is suggested that future research should further improve experimental design and methodological quality.Comparisons can be made according to different clinical severity levels of the study subjects,in order to provide individualized oxygen therapy strategies for patients.It is also possible to explore the clinical application value of different oxygen therapy devices in terms of medical expenses,and to explore the oxygen therapy methods that are more in line with their own needs from the perspective of patient interests.
4 Conclusion
This study shows that HFNC as a new type of oxygen therapy,compared with conventional oxygen therapy,can improve the symptoms of hypoxia and CO2 retention in patients with AECOPD and can reduce the rate of tracheal intubation in patients.Compared with noninvasive positive pressure ventilation,HFNC can reduce the incidence of adverse reactions in patients,which is better tolerated and can reduce the economic burden of patients to some extent.A multicenter,large sample,high quality RCT study is needed to further validate these findings in order to better determine the clinical value of HFNC in AECOPD patients in the future.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Medical Data Mining的其它文章
- Identification of core compositions of traditional Chinese medicine for Seborrheic Dermatitis using data mining techniques
- The law of oral traditional Chinese medicine for insomnia based on Chinese medical code
- Regularity of syndrome differentiation and treatment of traditional Chinese medicine for Henoch-Schonlein purpura based on data mining techniques
