Practice and Enlightenment for International Cooperation on Chang’e 4 Mission
2019-04-05XUEChangbinTANGYuhuaZHANGZheJIAYingzhuo
XUE Changbin ,TANG Yuhua ,ZHANG Zhe ,JIA Yingzhuo
1 National Space Science Center,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190 2 Lunar Exploration and Aerospace Engineering Center,Beijing 100028
Abstract:On January 3,2019,the first lunar farside in-situ exploration mission,China’s Chang’e 4 (CE-4),successfully landed in Von Karman crater within the South Pole-Aitken (SPA)basin.The CE-4 mission provided a host platform and opened its science payload resources to the international community.Science payloads from Germany,Sweden,the Netherlands and Kingdom of Saudi Arabia were aboard CE-4.It has explored effective models of international cooperation,accumulated cooperation experience,and provided a reference for the implementation of broader and deeper cooperation in major projects.This paper summarizes the practical experience of international cooperation on CE-4,analyzes the difficulties and existing problems of science payloads management,explains the current management methods,and puts forward suggestions for the development of broader international cooperation for the future.
Key words:CE-4,international cooperation,experience,suggestion
1 INTRODUCTION
In 2016,the China National Space Administration (CNSA)proposed to conduct international cooperation in China’s deep space exploration for the first time.Through careful evaluation and in-depth communication with countries around the world,Germany’s Lunar Lander Neutrons &Dosimetry (LND),Sweden’s Advanced Small Analyzer for Neutrals (ASAN),the Netherlands’s Netherlands-China Low Frequency Wavelength Explorer (NCLE),and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s lunar camera payload (KLCP)were piggybacked on the Chang’e 4 (CE-4)lander,rover,the Queqiao relay satellite and the Longjiang 2 microsatellite[1].
2 THE PURPOSE AND SIGNIFICANCE OF INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION IN THE FIELD OF LUNAR AND DEEP SPACE EXPLORATION
Deep space exploration missions are technically difficult and require a huge input of human resources and funds.Therefore,only a few major aerospace countries have the basis for implementing deep space missions,including high-thrust launch vehicles,highly reliable spacecraft,and ground-based deep space observation and control networks.In 2007,the success of the CE-1 mission marked China’s entry into the ranks of space powers with the capability to independently complete deep space exploration.Similarly,for some countries’ deep space explorations like the United States,Europe,and India they often carry science payloads from other countries.For example,the Cassini probe of the United States has participation from as many as 27 countries.The International dimension has become one of the important features in the current space science exploration field.
At the same time,through the cooperation with excellent foreign science and engineering teams,we can share science data,which can accelerate the improvement of China’s science research and engineering research in the field of deep space exploration.
3 CE-4 INTERNATIONAL PAYLOAD CONFIGURATION AND PROCESS MANAGEMENT
3.1 International Cooperation Science Payloads on CE-4
NCLE
The NCLE was carried on the CE-4 relay satellite,consisting of three-band monopole antennas that can extend to a maximum length of 5 meters,a low noise amplifier,an electronics box and auxiliary connection cables.China and Netherlands jointly proposed and completed the conceptual design.The University of Nemegen in the Netherlands,the radio astronomy institute ASTRON and ISIS jointly completed the detailed design and processing of the equipment,completed the delivery test and satellite integration with China.The science payload can work in the range of 80 kHz -80 MHz,and its basic science mission was to detect low-frequency radiation signals in the universe,including mapping of space radiation flow in 2 -3 frequency bands between 1 MHz -60 MHz,studying kilometer wave explosions of the Earth and radio explosions of Jupiter as well as developing radio burst detection of stars II,III and IV of the sun.
ASAN
ASAN was carried on the CE-4 rover.Jointly developed by the Swedish Institute of Space Physics and the National Space Science Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NSSC),it consists of a detector and cable assemblies with science objectives to detect energy neutral atoms and positive ions on the lunar surface,including their energy,composition and flux,determining the distribution function of energy neutral atoms and positive ions and the relationship of local time between the distribution function and the lunar surface topography.
LND
Carried on the CE-4 lander,the LND was jointly developed by the University of Kiel in Germany and NSSC.It consists of a detector and frame,electronics box and cable assembly.Its science objectives were to measure the comprehensive particle radiation and the dynamic changes in the lunar surface by determining a comprehensive dose rate,LET spectrum,particle radiation composition and energy spectrum monitoring of neutral and charged particles on the lunar surface.
KCLP
Launched with the Queqiao relay satellite,the Longjiang 2 lunar ultra-long wave astronomical observation microsatellite carried a KCLP.The science payload successfully observed the moon and obtained clear visible images of the lunar surface successfully which have been interpreted.The technical specifications met the requirements of the implementation agreement signed by both parties.
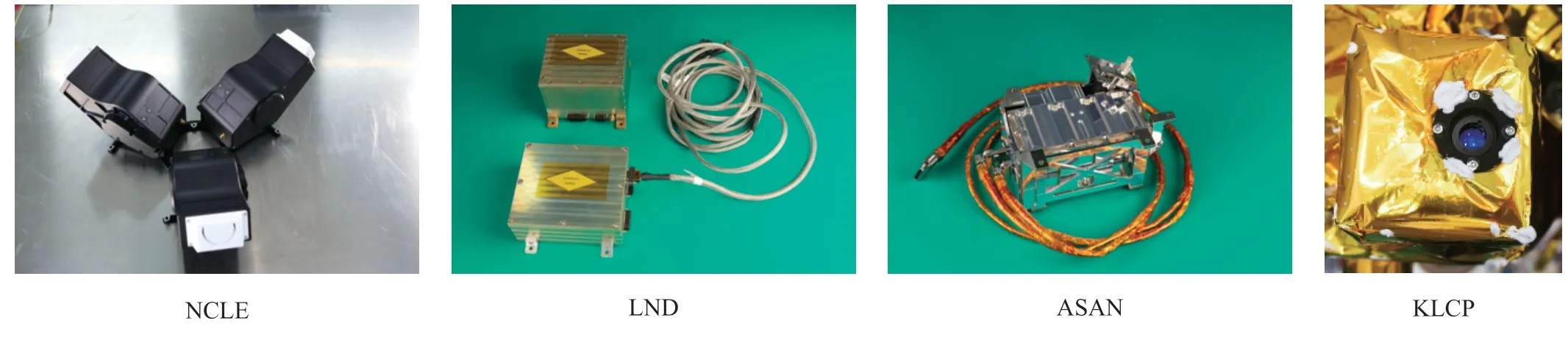

Figure 1 International cooperation scientific payloads on CE-4
3.2 Summary of the International Cooperation Science Payloads Development Process
Through the comprehensive analysis of the similarities and differences between China and foreign countries in the development of aerospace products and procedures,we have formulated a responsibility mechanism for the international cooperation for the CE-4 science payloads.The Chinese and foreign parties jointly put forward science objectives,design schemes and technical indicators,and be responsible for a series of work including joint testing,calibration and environmental testing in the process of product development.After obtaining science data in orbit,the chief expert shall take the lead to carry out research,and jointly share and publish the science results.
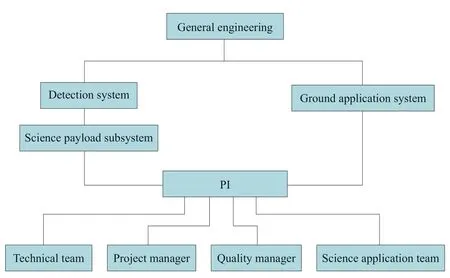
Figure 2 Organization for international cooperation science payloads
CNSA shall be responsible for organizing the demonstration,evaluation and approval of the science objectives proposed by the chief experts of the science payloads,as well as managing science data in accordance with regulations and approve their release.
The“detector system”was responsible for determining the interface state of the international cooperation science payloads,proposing an equipment environment test specification and matrix and the interface compatibility testing after product delivery.
The“science payload sub-system”was responsible for organizing the signing of the technical cooperation agreements between the Chinese team and foreign teams,determining the overall plan and quality requirements for the development of international cooperation science payloads as well as the international product acceptance and sub-system pre-integration testing.
The“ground application system”was responsible for evaluating science objectives,leading the organization of science objectives to achieve thematic research and experimental verification,managing science data according to regulations and conducting research on the applications.
The chief Chinese expert (PI)and the foreign sides jointly put forward the science objectives of international cooperation science payloads and were in charge of evaluating the realization of the objectives.The technical cooperation teams (TCT)of the Chinese-foreign parties jointly formulated the technical and planning processes for the development of the international cooperation science payloads,and clarify the production,insurance standards and application scope.They set up the research team that was responsible for the unit design,development and test of the international payload.
The CE-4 international cooperation science payload team has successfully completed the product development mission,and carried out a number of science explorations and obtained a large column of scientific data which is being analyzed.

Figure 3 Earth and the moon photo taken by KCLP.Xinhua News Agency [2]

Figure 4 The CNSA has delivered the second batch of science data from KLCP to Kingdom of Saudi Arabia [3]

Figure 5 Zhang kejian,head of the CNSA,handed over CE-4’s international cooperation science payload data to Sweden,Germany and the Netherlands [4]
3.3 Risk Analysis and Control
The risks of adopting international cooperation science payloads can be summarized under three aspects:technical risk,management risk and schedule risk.
Technical risk:The development process of CE-4 international cooperation science payloads complies with ESA standards,which are not entirely consistent with China’s requirements.It is necessary for China to strengthen inspection to ensure the interface matching,system compatibility and operation reliability of the international cooperation science payloads.
Management risk:Due to the protection of intellectual property rights,the foreign teams will not provide all the technical documents and information to China,so it is necessary to give flexibility to the role of the Chinese team in international cooperation to strengthen quality control.It is an effective measure for risk control to determine a reasonable and unanimously recognized assessment criteria for international cooperation science payloads,and formulate corresponding operational management methods.
Schedule risk:The schedule delay for an international cooperation science payload has a relatively large impact on the overall schedule of the probe,so risk control measures need to be formulated in advance.Under the premise of ensuring the interface and overall security,the delivery conditions of foreign science payload can be relaxed.
3.4 Experience and Recommendations
1)The project implementation experience and capability of the foreign teams should be evaluated comprehensively while evaluating the science objectives of the international cooperation project;
2)By summarizing the experience of CE-4,the Chinese team for the international cooperation project has a strong foundation for the mission.The Chinese team should not only have top scientists in the field,but also a strong team of engineers;
3)To formulate a reasonable and feasible technical cooperation agreement,on the premise of ensuring interface security,appropriately relax the product margin requirements of international cooperation science payload,that is,properly compress the margin of in-orbit reliability index of product;
4)The main science objectives of the mission should first be based on domestic science payloads to ensure the autonomy and controllability of science objectives.
4 FUTURE PROSPECTS FOR INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION IN THE FIELD OF LUNAR AND DEEP SPACE EXPLORATION
Deep space exploration has always meant the coexistence of competition and cooperation,where strengthening multi-channel and multi-level cooperation between different countries is required[5].Therefore,the main way to conduct extensive international cooperation in the field of lunar and deep space exploration is to give priority to the Chinese side,and appropriate release of some resources to the foreign side.
In April 2019,China officially announced the opportunity for future cooperation in lunar and deep space explorations,opening up its platform and payload resources to the world and welcoming scientists from all over the world to actively participate in the CE-6 mission and the asteroid exploration mission.The CE-6 mission is to achieve unmanned automatic sampling return,which will reserve 20 kg weight for carrying foreign science payload[6,7].In March 2019,China and France reached a cooperation agreement on lunar exploration.France plans to carry about 15 kg equipment on CE-6,including a camera and an analyzer,to research the lunar soil[8].
The asteroid mission will probe near-Earth asteroid 2016HO3 and comet 133P.Eight scientific payloads totaling 66.3 kg were nominated from all over the world,including a medium field color camera,a thermal radiation spectrometer,a visible infrared imaging spectrometer,a multispectral camera,a detection radar,a magnetometer,a charged particle and neutral particle analyzer,plus a dust analyzer.A capacity of 200 kg has been reserved[9].
Extensive international cooperation in space exploration is a further extension of China’s Belt and Road Initiative.The China’s astronauts will make more and more significant contributions to the peaceful use of space and the continuous development of space science,space applications and space technology.
杂志排行
Aerospace China的其它文章
- Relative Navigation of Long-Range Non-Cooperative Targets Based on Monocular Sequence Images
- Application Research of Card-Model-Based Systems Engineering in the Development of Smart Dragon 1
- Analysis of International Commercial Space Market and Policy
- Reflection on Small Satellite Constellation Operations from the Commercial Space Perspective
- A LM-4B Launched China-Brazil Earth Resource Satellite into Orbit
- Twin BeiDou Satellites Launched Aboard a LM-3B/Yuanzheng 1
