Effect of limbal stem cell culture medium on vascular endothelial cell proliferation
2019-03-12XiaoGuangNiuManXu
Xiao-Guang Niu,Man Xu
Abstract AIM:To investigate the effect of cultured limbal stem cells on proliferating of vascular endothelial cells and validate the theory of limbal stem cells.
▪METHODS:The limbal stem cells and epithelium cells of bulbar conjunctiva were cultured and determined by immunohistochemistry staining with AE - 5.The supernatant was collected and added into the cultured human umbilical vein endothelium cells(ECV-304).The negative control was set up.After 24h,MTT was done to detect endothelium cell proliferation.The statistical analysis was done by analysis of Variance.
▪RESULTS:Negative stain of AE-5 can be seen in limbal stem cells and positive stain can be seen in conjunctiva cells.The ratio ofMTT added by limbalstem cell supernatant,conjunctiva epithelium celland negative control were 2.097±0.079,1.981±0.034 and 1.990±0.044,respectively.There were significant difference among the three groups(F=9.169,P=0.000).The proliferate activity of vascular endothelial cells added by supernatant of limbal stem cells was higher than the other two groups(P=0.005 and P=0.007,respectively).
▪CONCLUSION:The supernatant of limbal stem cells can improve the proliferation of vascular endothelium cell.This may be the unique characteristics of limbal stem cells.This study provides more evidences for the theory of limbal stem cells by determining the functional methods. KEYWORDS:limbal stem cells;supernatant;vascular endothelial cells;MTT
INTRODUCTION
S tabilization of ocular surface depends on the structural integrity and normal function of tear film,limbal stem cells,as well as corneal and conjunctival epithelium[1-3].As normal corneal epithelial derived cell,the limbal stem cell has drawn attention increasingly.Human limbal stem cells have been identified to be located in the basal epithelial layer of the limbus,at 1.5 mm to 2 mm wide area that straddles the cornea and bulbar conjunctiva.In the field of severe ocular chemical injury,thermal burns and other diseases resulting in limbal stem cell deficiency,limbal tissue transplantation can achieve a good therapeutic effect[4-6].However,compared with clinical research,fundamental research of limbal stem cell lags significantly.Although anatomical localization and certain biological characteristics of limbal stem cell were studied in many studies,including the lack of the K3/K12 keratin pair in limbal basal cells,but neither the direct evidence of existence of limbal stem cells nor the main biological functions of limbal stem cells was discovered.
Limbal stem cells were morphologically small,had a high nuclear- to - cytoplasm ratio,and are relatively undifferentiated cells with rare cycling and high proliferative capacity.As one kind of stem cell,limbal stem cells not only can differentiate to the corneal epithelial cell,but also possess some other important biological functions.Limbal stem cells deficiency(LSCD)will leads to the inability to sustain corneal epithelial homeostasis[7-8]. Biomicroscopy shows conjunctival hyperemia,loss of the palisades of Vogt,and a“whorled-like”corneal epithelium.How can the biological characteristics of limbal stem cells be realized and maintained?Whether limbal stem cells themselves can play a role has not been reported.
Transplantation of autologous cultures of limbal epithelial stem cells(CLET)was first reported by Pellegrini et al[9]in 1997.Two patients with unilateral LSCD at the severe chronic stage of alkali burns received CLET.Limbal epithelial cells from a 1-2 mm2limbal biopsy sample were expanded in vitro on a feeder layer.Confluent cultured limbal epithelial sheet was placed on a corneal wound bed.The study showed that the regenerated corneal epithelium was stable by 2y follow-up.The culture procedure was then standardized,and to date,more than 270 grafts have been transplanted in different ophthalmological centres throughout Italy,with long-term stability reported in more than 150 patients and with a success rate in 70% -80%of cases.More than 10y of follow-up confirmed the long-term integrity of the engrafted epithelium.This suggests that cultured limbal stem cells have considerable biological functions and is an effective method to reconstruct the ocular surface[11].Therefore,in our study,the effect of limbalstem cell culture medium on endothelial cell proliferation will be investigated by in vitro method,in order to further validate and promote the development of limbal stem cell theory.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
All tissue collection complied with the guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration and was approved by Wuhan Aier Ophthalmology Hanyang Hospital Ethics Committee.
Instruments and ReagentsRPMI-1640 medium(Gibco,USA);fetalbovineserum (Hyclone,USA);human umbilical vein endothelial cells(provided by Cell Biology CenterofShanghai); CO2cellincubator (Heraeus,Germany); mouse anti-human K3 protein monoclonal antibody(AE5);fluorescein-labeled rabbit anti-mouse secondary antibody(Sigma,USA);MTT(thiazole blue)(Sigma,USA);Wellscan MK3 microplate reader.
Experiments
Culture of limbal stem cellsExplant culture method was used[12].Corneal limbal tissue material was from fresh cadaver eyes.A piece of 2 mm wide corneal limbal tissue was cut off along the corneal annulus under sterile condition,and then soaked in 1∶1000 tobramycin solution for 30min.After gently rinsed in Hanks solution,tissue mass of 1×1 mm3was prepared by repeatedly cutting in sterile petri dish.The tissue mass with epithelial surface upward was inoculated into 24-
well plates,and RPMI-1640 medium containing 20%fetal bovine serum was added.Then,the plate was incubated at 37℃ in 5%CO2incubator,after cells grown out around the tissue mass,the culture medium was changed.When cells grown to approximately 30%flat area,the tissue mass was removed under sterile condition and the culture medium was changed.After cells completely formed monolayer,the culture supernatant was collected and stored in-20℃ refrigerator as a standby.The bulbar conjunctival epithelial cells near the corneal limbus were cultured under the same condition as a control,and the supernatant was collected and stored in-20℃ refrigerator as a standby.
Detection of limbal stem cellsIndirect immunofluorescence was used to detect limbal stem cells.After collecting the supernatant,limbalstem cellsand bulbarconjunctival epithelial cells were fixed with 1∶1 95%ethanol and acetone solution for 30min,and then washed with PBS,and then normal goat serum was added and sealed for 20min.Then the serum was discarded,and 1∶100 AE5 monoclonal antibody were added.After incubating at 37℃ for 1h,the specimen was washed 3 times with PBS,5min each time.1∶100 fluorescein-labeled rabbit anti-mouse secondary antibody was added and incubated for 40min,and then the specimen was washed 3 times with PBS,5min each time.The specimen was observed and photographed under a fluorescent microscope.
Culture ofvascularendothelialcellsWhen human umbilical vein endothelialcellswere cultured to 90%confluence,the culture medium was removed and 0.25%trypsin and 0.02%EDTA(2 ∶1)was added to digest the specimen.The culture medium containing 10%fetal bovine serum was added,to adjust the cell number to 1×105/mL,the resulting cell suspension was added to 96-well plates with 100 μL of cell suspension per well.The specimen was divided into three groups,group A was a control,only added with 100 μL cell suspension;group B was bulbar conjunctival epithelial cells control,except 100 μL cell suspension,an equal volume of bulbar conjunctival epithelial cell culture supernatant was added;group C was experimental group,after the addition of 100 μL of cell suspension,an equal volume of limbal stem cells culture supernatant was added.All the 3 groups were incubated at 37 ℃ in 5%CO2incubator.
Detection of vascular endothelial cell proliferation with MTT method Aftervascularendothelialcellsofeach group incubated for 24h,the culture solution was discarded,and then 100 μL culture medium containing 2% fetal bovine serum was added to each well,followed by adding 10 μL MTT of 5 mg/mL(final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL).After incubating in the incubator for 4h,100 μL dimethyl sulfoxide was added.The specimen was oscillated in micro oscillator for 10min,and then analyzed by Microplate Reader to obtain the optical density of 405 nm wavelength.The optical density is proportional to the value of proliferative activity of cell.
Statistical AnalysisAnalysis of variance was used for comparison among 3 groups;q test was used for comparisonbetween 2 groups.All data were analyzed using SPSS13.0 software with P < 0.05 as the difference of statistically significant.
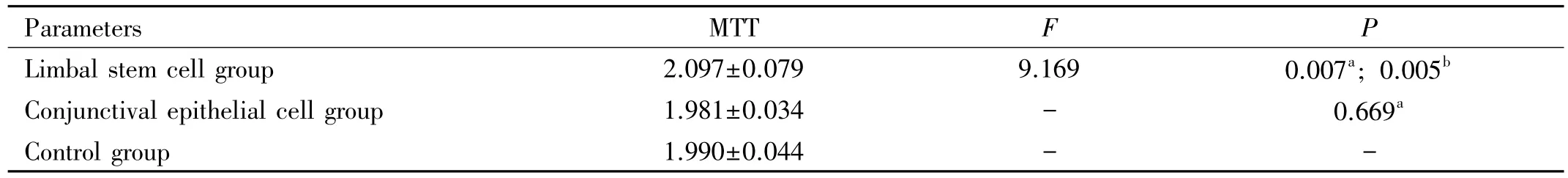
Table 1 MTT value of vascular endothelial cell for three groups
RESULTS
Culture of Limbal Stem CellsAfter cultured 24h,there were oval cells grown out surrounding the tissue explants and forming a“beach-like”transitional zone.After cultured for 1-3d,cells on most tissue explants grown outward from the transitional zone forming one outgrowth,with cells tightly packed and interconnected into a film;the cells grown larger compared with the previous,showing irregular polygon.After cultured for one week, cells achieved 80% confluence,forming a good monolayer.Compared with limbal stem cells,conjunctival epithelial cells can form a good monolayer after incubating for about 5d,and there were no significant differences in cell morphology.
Detection of Limbal Stem CellsImmunohistochemical staining showed thatAE-5 expression in conjunctival epithelial cells was strongly positive,and the cytoplasm was stained(Figure 1);whereas in a majority of cultured limbal stem cells that was negative,and only scattered cells showed a weak positive staining.
Culture of Vascular Endothelial CellsAfter cultured 12h,vascular endothelial cells showed completely adherence,and reached 80% -90% confluence after 24h,with cellular morphology of hexagonal or irregular shape.There were no significant differences in cell growth state and cell morphology among the three groups.
Detection ofVascularEndothelialCellsProliferation ActivityAs can be seen from the MTT value,the proliferation activity of vascular endothelial cells has increased after added limbal stem cells culture supernatant,showing significant difference(P < 0.05) with the group added conjunctival epithelial cells culture supernatant and control group.Whereas there was no significant difference(P>0.05)in proliferation activity of vascular endothelial cell between the group added conjunctival epithelial cells culture supernatant and the control group(Table 1).
DISCUSSION
Normally,the limbal stem cells are the source of corneal epithelial cells proliferation and differentiation,and prevent conjunctival epithelium and blood vessels growing into the cornea,which play an important role in maintaining the dynamic stability of the corneal epithelium and the transparency of the cornea tissue.The limbal stem cells may be destroyed partially or completely resulting in varying degrees of stem cell deficiency with its characteristic clinicalfeatures.These include"conjunctivalization"of the cornea with vascularization, appearance of goblet cells, and an irregular and unstable epithelium.Good results have been achieved not only in treatment of severe ocular surface disease by autologous or allogeneic limbus tissue transplantation[13],but also in treatment of severe chemical injury by amniotic membrane orothercarriercultivated limbalstem cell transplantation[14-18].Although stem cell transplantations are currently introduced into clinical practice,a major challenge for stem cell biologists and clinicians is the identification of stem cells both in vitro and in vivo.No positive markers have been demonstrated to unequivocally identify limbal stem cells,and,currently,limbal stem cells can only be identified by indirect methods.The method used primarily is by detecting the difference of cell surface markers expression which gives indirect evidence.In 1986, Schermer et al[19]detected expression positive in the surface epithelium and fullthickness of corneal limbus using corneal epithelial keratin K3 specific antibody AE-5,accordingly speculated that in corneal limbus the basal cells with unexpressed keratin K3 is limbal stem cells,which was also confirmed by our results.Conjunctival epithelial cells can express keratin K3.Based on this result,we can preliminarily distinguish limbal stem cells and normalconjunctivalepithelialcells.50KD keratin,namely enolase is only expressed in the basal part of the cornea limbus,whereas not expressed in the surface of corneal limbus[20].Some researchers[21-22]found that p63 is only expressed in basal cells of the corneal limbus,whereas not expressed in the surface part and corneal epithelial cells by detecting p63 factor expression level in corneal limbus,hence considered p63 is a mark of limbal stem cell.Recently,Wang et al[23]found IPO13 could serve as a novel potential marker for corneal epithelial progenitor cells.But so far,no specific mark has been found.
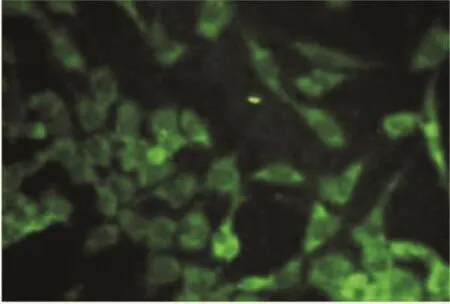
Figure 1 AE-5 positive expression in conjunctival epithelial cells(×200).
Structure and function are two important aspects of cell and tissue,structure is the basis of function,whereas function reflects the specificity ofstructure to acertain extent.Therefore,research in functional aspects,thereby promote the development of limbal stem cell theory may be an important way.However,in previous studies,researchers often focus on the structural characteristics of limbal stem cells,whereas study on its function is apparently lack and not thorough enough.
The main function of stem cell is differentiated to terminal cell,namely corneal epithelial cell.But the author believes there are still many other specific functions have not been discovered.There are some special cellular and extracellular substrates in the corneal limbus,which are involved in the composition of the corneal margin microenvironment and maintain the stability of the corneal limbus microenvironment.For example,corneal limbal fibroblasts participate in the composition of LSC microenvironment and participate in the maintenance and regulation of cell biological characteristics of basal cells,fibroblasts secrete acid secretion protein rich in cysteine,Further studies have found that IL-6 secreted by corneal limbal fibroblasts can cause STAT3 time-dependent phosphorylation,which is mediated by STAT3 pathway to maintain the characteristics of human LSC stem cells.Some scholars have found in mouse experiments that LSCs possess theability to inhibitlymphocyte proliferation and the production of proinflammatory cytokines.In this respect,LSCs are even more suppressive than the classical CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Tregs or MSCs.Pilot experiments showed that the suppression by LSC was mediated by released soluble factors.There are more molecules with antiapoptotic properties that could be expressed in LSCs and could contribute to their resistance to cytotoxicity[24].So,do human corneal limbal stem cells have some other functions?
Rich vascular networks exist in limbal tissue,and their main role is to provide adequate nutrition to the cornea,while also ensure the nutrition limbal stem cell maintaining strong proliferative activity required.Huang et al[25]investigated the function of the limbal microvascular net and the limbal stroma in the maintenance of the limbal epithelial stem cell niche in vivo.Results suggested that limbal epithelial stem cells cannot maintain their stemness or proliferation without the support of the limbal microvascular net microenvironment[25].So how do these vascular networks be maintained?Does limbal stem cells play some role in it?Thus,starting from this issue,we observed the effect of limbal stem cells culture supernatant on vascular endothelial cells proliferation.
It has been discovered that the culture supernatant of limbal stem cells can promote the growth of vascular endothelial cells,The culture solution of bulbar conjunctival epithelial cells had no obvious effect on vascular endothelial cells.We speculated that this promotion effect may be achieved by limbal stem cells secreting a number of pro-angiogenic growth factors.That's because Liu et al[26]detected expression of vascular endothelial growth factor,basic fibroblast growth factor,platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor in the limbus tissue,suggesting that these factors play an important role in maintaining the normal physiological functionality of corneal limbus and corneal.
Thus,according to our findings,we speculated that it is just because of such promotion effect that limbal stem cells brought on cells proliferation of vascular endothelial,limbal tissue can maintain adequate blood supply and adequate growth factors,thereby to maintain a strong growth and proliferation ability of limbus stem cells.But more in-depth research is needed to see if corneal limbal stem cells can secrete specific factors that promote the proliferation of vascular endothelial.
