沉默lncRNA PCA3减少前列腺癌细胞雄激素受体表达抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖和转移
2019-02-20易小敏张珺梁宇沈群山李海波
易小敏 张珺 梁宇 沈群山 李海波
[摘要] 目的 研究沉默lncRNA PCA3对前列腺癌细胞的影响。 方法 选择前列腺癌细胞LNCaP和C4-2细胞,使用siRNA干扰PCA3在细胞内的表达,实时定量PCR法检测干扰效果,检测siRNA干扰PCA3后对前列腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的影响,Western blot法在前列腺癌C4-2细胞内分别检测雄激素受体及其变体7的表达情况。 结果 PCA3特异性的siRNA可明显抑制前列腺癌细胞内PCA3 mRNA的表达,抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭潜能。沉默PCA3后的C4-2细胞内雄激素受体及其变体7表达明显减少。 结论 沉默lncRNA PCA3可减少前列腺癌细胞内AR及AR-V7的表达,从而抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖和迁移等恶性转变。
[关键词] 长链非编码RNA;PCA3;siRNA;前列腺癌;雄激素受体
[中图分类号] R737.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2019)34-0021-05
Effect of silencing lncRNA PCA3 on reduction of prostate androgen receptor expression and inhibition of prostate cancer cell proliferation and metastasis
YI Xiaomin1, 2 ZHANG Jun1 LIANG Yu1 SHEN Qunshan1 LI Haibo1
1.Department of Urology, the 901 Hospital of PLA, Hefei 230031, China; 2.Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, China
[Abstract] Objective To study the effect of silencing lncRNA PCA3 on prostate cancer cells. Methods The prostate cancer cells LNCaP and C4-2 cells were selected, and siRNA was used to interfere with the expression of PCA3 in cells. The interference effect was detected by real-time quantitative PCR, and the effects of siRNA on PCA3 proliferation, migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells were detected. Western blot method was used to investigate the expression of androgen receptor and its variant 7 in prostate cancer C4-2 cells. Results The expression of PCA3 mRNA in prostate cancer cells and the proliferation, migration and invasion potential of prostate cancer cells were significantly inhibited by CA3-specific siRNA. The expression of androgen receptor and its variant 7 in C4-2 cells after silencing PCA3 was significantly reduced. Conclusion Silencing lncRNA PCA3 can reduce the expression of AR and AR-V7 in prostate cancer cells, thereby inhibiting the malignant transformation of prostate cancer cells, such as proliferation and migration.
[Key words] Long-chain non-coding RNA; PCA3; siRNA; Prostate cancer; Androgen receptor
前列腺癌在歐美国家已经成为发病率最高的男性恶性肿瘤,严重危害男性健康。我国前列腺癌的发病率也在不断攀升,患病群体也有年轻化的趋势。早期局限性的前列腺癌可通过手术和放射治疗等综合治疗达到治愈,但在发病早期多数患者并不会出现明显不适。只有在肿瘤迁延进展、侵犯临近组织甚至发生骨转移后,方有可能被患者察觉。通过手术或药物去势的雄激素剥夺治疗是晚期前列腺癌的主要治疗方法,但多数患者在经历大约16个月之后都将转变为去势抵抗性前列腺癌(Castration resistant prostate cancer,CRPC),此时继续行雄激素剥夺的内分泌治疗不再有效[1]。
早期前列腺癌细胞依赖雄激素-雄激素受体信号轴不断增殖是前列腺癌内分泌治疗方案的基础。正常前列腺上皮细胞和前列腺癌上皮细胞在雄激素激活雄激素受体后可产生前列腺特异性抗原(prostate-specific antigen,PSA)并维持存活。前列腺癌的雄激素受体(Androgen receptor,AR)还可出现异常剪接,形成不同的雄激素受体变体(AR Variants,AR-V),而变体同源/异源二聚体化后能够不依赖雄激素实现自激活维持增殖信号[2]。明显升高的雄激素受体变体7(AR-V7)水平直接关系到前列腺癌的治疗效果,也是前列腺癌细胞产生去势抵抗的一个重要因素[3,4]。
非编码RNA在表观遗传学的调控机制中发挥重要作用,非编码RNA(noncoding RNA,ncRNA)是一种不能够翻译为蛋白的功能性RNA序列,常见的具有调控作用的非编码RNA包括小干扰RNA、miRNA、piRNA以及长链非编码RNA。PCA3(Prostate Cancer Associated 3)是一个仅在前列腺组织内特异性表达的长链非编码RNA(long noncoding RNA,lncRNA),其基因座位于9号染色体q21~22。前列腺癌内PCA3的表达水平可达到正常前列腺组织的66倍[5]。不仅如此,PCA3高表达还可增加前列腺癌细胞内雄激素受体的表达水平[6],通过AR信号通路增强前列腺癌细胞的增殖及侵袭能力。尽管PCA3在前列腺癌内的特异性高表达已被熟知,对PCA3在前列腺癌中的调控机制作用尚未阐明。本研究在前列腺癌细胞LNCaP及C4-2内调节PCA3表达,发现沉默PCA3可减少AR及AR-V7的形成,从而抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖和迁移等恶性转变。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞系和细胞培养
人前列腺癌细胞LNCaP购自中国医学科学院基础所细胞中心,前列腺癌细胞C4-2为本实验室保存,使用RPMI1640培养基+10%胎牛血清,于37℃含5% CO2的恒温细胞培养箱内培养。
1.2 瞬时转染
siRNA由上海生工生物合成,靶向PCA3的siRNA(siPCA3)正义链5CUAGCACACAGCAUGAUCAUU-ACGG3,阴性对照序列Scrambled RNA(scrPCA3)正义链5GCACGCUCCUACGAAUGCUAGUAAA3,反义链均为互补。前列腺癌细胞使用siPCA3处理为siPCA3组,使用scrPCA3处理为scrPCA3组。转染前1 d接种前列腺癌细胞至6孔板,转染当天查看细胞贴壁生长良好后,按照Lipofectamine2000转染试剂盒说明书准备siRNA及脂质体的混合物,每孔加入5 μL脂质体及50 pmol的siRNA,终体积用无血清培养基加至2 mL。6 h后轻轻吸去培养基并更换含血清新鲜培养基继续培养30 h后收取样本,使用Trizol(美国Invitrogen公司)试剂盒提取总RNA反转录cDNA进行下一步实验。
1.3 实时定量PCR
使用SYBR绿色荧光标记的SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM试剂盒(Takara公司)及ABIPRISM7300Real-TimePCR仪进行实时定量PCR检测。按如下反应体系进行配置:2×SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM Buffer 10 μL,cDNA 模板50 ng,PCR上下游引物各0.8 μL,(終浓度0.4 μmol/L);ROX Reference Dye(50x)0.4 μL,终体积为20 μL体系。特异性引物序列如下:PCA3 基因:上游:5-AGATTTGTGTGGCTGCAGC-3,下游:5-TCCTGCCCATCCTTTAAGG -3;内参GAPDH基因:上游:5-TGACCCCTTCATTGACCTCA-3,下游:5-AGTCCTTCCACGATACCAAA-3。反应条件为预变性95℃ 10 s,94℃ 5 s、55℃ 20 s、72℃ 31 s(共40个循环)。
1.4 Western blot
使用RIPA裂解液提取实验组细胞总蛋白,12000 r/min离心10 min后,将蛋白上清液转移至新EP管,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,加入上样缓冲液后煮沸5 min。聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳后转PVDF膜,5%脱脂奶粉TBST封闭1 h,分别加入1∶1000的兔抗人AR及AR-V7一抗(英国Abcam公司)4℃过夜,TBST洗3次,加入抗兔二抗(碧云天生物)孵育1 h,TBST洗膜3次后进行显色发光。
1.5 MTT法检测细胞增殖
按照前述操作步骤进行siRNA转染操作后,消化重悬细胞,以每孔5×103的密度将细胞接种于96孔板。分别于0 h、24 h、48 h、72 h在各组选3个复孔更换新鲜培养基100 μL,并加入10 μL CCK-8试剂(日本同仁化学研究所),37℃孵育2 h后,酶标仪检测450 nm OD值并记录。
1.6 细胞迁移和侵袭
前列腺癌细胞接种至Transwell小室的上层,每孔1×104个细胞,加入1% FBS培养基 200 μL,Transwell小室下层加入600 μL含 10% FBS 的培养基。在37℃、5% CO2孵箱中培养24 h后,4%多聚甲醛固定10 min,随后用0.5%结晶紫染色10 min。PBS清洗后棉签擦去上室中的细胞,随机选取5个视野对聚碳酯膜下表面的细胞进行拍照计数,取视野细胞数量进行统计学分析。进行细胞侵袭实验前在Transwell小室的上室内加入50 μL Matrigel基质胶(美国BD公司),放入37℃培养箱6 h,等待胶凝固后加入200 μL无血清培养基37℃培养箱30 min以水化基质胶,其余操作同迁移实验。
1.7 统计学处理
以上实验所获取的数据均使用SPSS 16.0软件进行统计学分析。计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,两组间差异采用t检验进行比较,每次实验至少重复3次,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
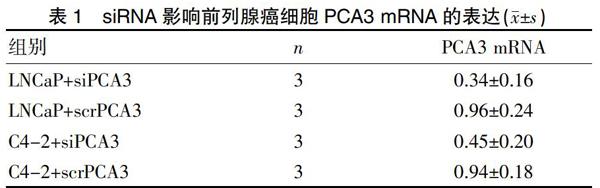
2.1 siRNA干扰前列腺癌细胞内PCA3表达
为明确PCA3对前列腺癌细胞的影响,我们在前列腺癌LNCaP和C4-2 细胞系中使用siRNA干扰PCA3表达。提取总RNA后用Real-time RT-PCR法检测各组PCA3 mRNA的表达情况验证转染效率,以和LNCaP空白对照组的PCA3 mRNA比值进行分析。结果显示转染siPCA3 36 h后,LNCaP细胞及C4-2细胞内PCA3 mRNA表达明显降低(P<0.05);转染scrPCA3后PCA3 mRNA的表达无明显影响,这表明siPCA3可有效干扰前列腺癌细胞内PCA3 mRNA的表达(表1)。siPCA3对LNCaP细胞的干扰效果略高于C4-2细胞组,这可能与C4-2细胞去势抵抗的恶性表型有关。尽管检测结果提示C4-2细胞内的PCA3 mRNA表达有略高于LNCaP细胞对照组PCA3 mRNA表达的趋势,两组间未见明显统计学差异(P>0.05)。siPCA3良好的干扰效果保证了后续对PCA3功能的研究。
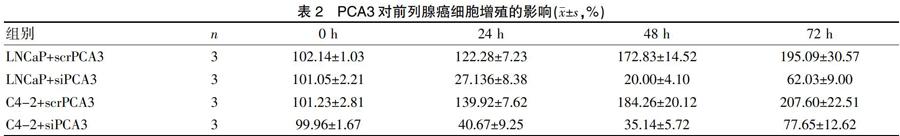
2.2 PCA3对前列腺癌细胞增殖能力的影响
在siPCA3及scrPCA3处理前列腺癌细胞后,我们采用MTT法检测各组细胞在不同时间点的增殖情况(表2)。结果显示与转染scrPCA3的对照组相比,转染siPCA3后的两株前列腺癌细胞增殖明显受到抑制(P<0.05),这种抑制在48 h时更为明显,但在72 h后前列腺癌细胞恢复了大部分的增殖能力,这与siPCA3瞬时转染的起效时间相吻合,表明siRNA的干扰效果是可逆转的。
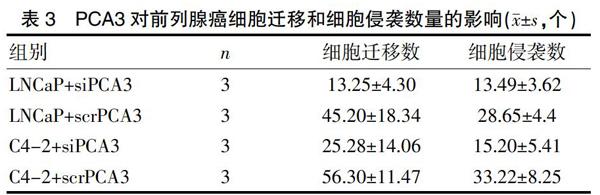
2.3 PCA3对前列腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭数量的影响
采用细胞迁移和侵袭实验检测siPCA3对前列腺癌细胞转移能力的影响(表3)。结果可见siPCA3干扰后的两株前列腺癌细胞迁移及侵袭数量均低于scrPCA3对照组,且差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2.4 PCA3对前列腺癌细胞AR-V7表达的影响
雄激素受体及其变体在前列腺癌细胞的去势抵抗进展中发挥了重要作用。为进一步分析PCA3如何实现对前列腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的影响,本实验用Western blot法检测雄激素不敏感的C4-2细胞内AR及AR-V7的表达,发现scrPCA3处理的C4-2细胞内有少量AR-V7的表达。siPCA3处理组AR的表达较scrPCA3组明显减少(P<0.05),且AR-V7的表达量也明显降低(表4)。这表明PCA3可以通过增加前列腺癌细胞内AR-V7的表达促进前列腺癌细胞增殖和转移等恶性进展。
3 讨论
雄激素受体是激素受体家族的一个重要成员,以配体依赖的方式作为转录因子与不同的DNA位点结合[7,8]。雄激素受体基因位于X染色体q12区域,由8个外显子组成。N端结构域(NTD)内含有转录活化作用的AF1,中间的DNA结合域与糖皮质激素受体和孕激素受体类似,具有两个可识别并结合DNA的锌指结构,其C端含有配体结合区和AF2转录调节结构域[9]。AR蛋白通过一系列的折叠加工后才能拥有配体结合的功能,配体-受体结合后的AR蛋白转位至细胞核内,聚集共活化子并与雄激素应答元件结合,发挥下游基因如PSA和TMPRSS2的转录调控作用[10]。目前已经在去势抵抗性前列腺癌患者中检测出了多种AR变体,这些变体最终形成的截短体蛋白缺失了配体结合域[11,12]。更为重要的是,这些截短体能够在缺少雄激素配体的环境中自我激活并直接調节靶基因的表达[13]。LNCaP为激素敏感性前列腺癌细胞,其自身并无明显的AR-V7表达[14];但异位表达的AR-V7可使LNCaP成瘤裸鼠获得去势抵抗性,敲除AR-V7则能减弱去势抵抗性前列腺癌细胞在裸鼠体内的成瘤能力[1,15,16]。AR-V7高表达增加了患者接受根治性前列腺切除术后生化复发的风险。与雄激素敏感的前列腺癌患者相比,这类患者的预后更差[1,17]。
自Marion首次报道DD3(即PCA3)在前列腺癌内特异性高表达以来,针对PCA3的研究尤其是它作为前列腺肿瘤标记物的研究亦逐渐增加[18]。尿液PCA3检测试剂盒已在2006年获得CE认证,该诊断试剂盒的灵敏度及特异度均高于PSA检测,可用来评价患者是否需要进行前列腺穿刺活检排除前列腺癌,也有研究者使用术前PCA3检测结果来预测前列腺癌患者的预后[19-24]。但PCA3的功能作用仍未彻底阐明,现有研究发现PCA3在雄激素-雄激素受体信号轴中起着重要的调控作用。PCA3基因座位于9号染色体短臂21~22区,与Prune同源基因2(Prune homolog 2 gene,PRUNE2/BMCC1)的6号内含子部分成反义互补,这一特定的结构赋予了它可能在RNA选择性剪接和加尾中的作用[25,26]。
有研究者认为PCA3主要通过调节AR信号通路来促进前列腺癌细胞存活与增殖[27-29]。沉默PCA3后的前列腺癌LNCaP细胞或雄激素不敏感的前列腺癌PC3及DU145细胞后,前列腺癌细胞发生凋亡的比例明显增加,细胞增殖也受到明显的抑制,深入分析雄激素受体的多个靶点基因包括PSA、AR、TMPRSS2、NDRG1、GREB1、FGF8、CDK1、CDK2和PMEPA1表达水平结果显示,这些促进前列腺癌细胞生长增殖的基因表达明显下调[6]。本实验在前列腺癌LNCaP及C4-2的研究结果也证实前列腺癌细胞的增殖与侵袭能力受到明显抑制,同时沉默PCA3表达后AR及AR-V7的表达明显降低,这也表明PCA3在前列腺癌内的表达与AR变体的形成密切相关,从而促使激素依赖性前列腺癌逐渐发展成为去势抵抗性前列腺癌。基于以上结果,我们认为PCA3可能参与了雄激素受体靶基因的调节,对PCA3调控机制的深入研究将有可能实现以PCA3作为前列腺癌靶点的治疗方式。
[参考文献]
[1] Egan A,Dong Y,Zhang H,et al. Castration-resistant prostate cancer:Adaptive responses in the androgen axis[J].Cancer Treat Rev,2014,40(3):426-433.
[2] Xu D,Zhan Y,Qi Y,et al.Androgen receptor splice variants dimerize to transactivate target genes[J].Cancer Res,2015,75(17):3663-3671.
[3] Sharp A,Coleman I,Yuan W,et al. Androgen receptor splice variant-7 expression emerges with castration resistance in prostate cancer[J].J Clin Invest, 2019,129(1):192-208.
[4] Okegawa T,Ninomiya N,Masuda K,et al. AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells cluster as a predictive biomarker of abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide treatment in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients[J]. Prostate,2018, 78(8):576-582.
[5] Hessels D,Klein Gunnewiek JM,van Oort I,et al. DD3(PCA3)-based molecular urine analysis for the diagnosis of prostate cancer[J]. Eur Urol,2003,44(1):8-16.
[6] Ferreira LB,Palumbo A,de Mello KD,et al.PCA3 noncoding RNA is involved in the control of prostate-cancer cell survival and modulates androgen receptor signaling[J].BMC Cancer,2012,12:507-522.
[7] Shafi AA,Yen AE,Weigel NL.Androgen receptors in hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer[J]. Pharmacol Ther,2013,140(3): 223-238.
[8] Bennett NC,Gardiner RA,Hooper JD,et al. Molecular cell biology of androgen receptor signalling[J].Int J Biochem Cell Biol,2010,42(6):813-827.
[9] Ahmed A,Ali S,Sarkar FH.Advances in androgen receptor targeted therapy for prostate cancer[J].J Cell Physiol,2014,229(3):271-276.
[10] Wen S,Niu Y,Lee SO,et al. Androgen receptor (AR) positive vs negative roles in prostate cancer cell deaths including apoptosis,anoikis,entosis, necrosis and autophagic cell death[J]. Cancer Treat Rev,2014,40(1): 31-40.
[11] Yu Z,Chen S,Sowalsky AG,et al. Rapid induction of androgen receptor splice variants by androgen deprivation in prostate cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2014,20(6):1590-1600.
[12] Haile S,Sadar MD.Androgen receptor and its splice variants in prostate cancer[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2011,68(24):3971-3981.
[13] Cao B,Qi Y,Zhang G,et al.Androgen receptor splice variants activating the full-length receptor in mediating resistance to androgen-directed therapy[J].Oncotarget,2014,5(6):1646-1656.
[14] Wilson S,Cavero L,Tong D,et al.Resveratrol enhances polyubiquitination-mediated ARV7 degradation in prostate cancer cells[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(33):54683-54693.
[15] Mediwala SN,Sun H,Szafran AT,et al.The activity of the androgen receptor variant AR-V7 is regulated by FOXO1 in a PTEN-PI3K-AKT-dependent way[J]. Prostate,2013,73(3):267-277.
[16] Krause WC,Shafi AA,Nakka M,et al. Androgen receptor and its splice variant,AR-V7,differentially regulate FOXA1 sensitive genes in LNCaP prostate cancer cells[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol,2014,54(1):49-59.
[17] Sprenger CC,Plymate SR.The link between androgen receptor splice variants and castration-resistant prostate cancer[J]. Horm Cancer, 2014, 5(4): 207-217.
[18] Auprich M,Bjartell A,Chun FK,et al. Contemporary role of prostate cancer antigen 3 in the management of prostate cancer[J].Eur Urol,2011,60(5): 1045-1054.
[19] Wang FB,Chen R,Ren SC,et al. Prostate cancer antigen 3 moderately improves diagnostic accuracy in Chinese patients undergoing first prostate biopsy[J]. Asian J Androl,2017,19(2):238-243.
[20] Tan SJ,Xu LW,Xu Z,et al. The value of PHI/PCA3 in the early diagnosis of prostate cancer[J].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi,2016,96(2):100-103.
[21] Wei W,Leng J,Shao H,et al.High PCA3 scores in urine correlate with poor-prognosis factors in prostate cancer patients[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2015,8(9):16606-16612.
[22] Vlaeminck-Guillem V,Devonec M,Champetier D,et al.Urinary PCA3 to predict prostate cancer in a cohort of 1015 patients[J]. Prog Urol,2015,25(16): 1160-1168.
[23] Tsaur I,Hennenlotter J,Oppermann E,et al.PCA3 and PSA gene activity correlates with the true tumor cell burden in prostate cancer lymph node metastases[J]. Cancer Biomark,2015,15(3):311-316.
[24] TomLins SA,Day JR,Lonigro RJ,et al.Urine TMPRSS2:ERG plus PCA3 for individualized prostate cancer risk assessment[J].Eur Urol,2016,70(1):45-53.
[25] Salameh A,Lee AK,Cardo-Vila M,et al.PRUNE2 is a human prostate cancer suppressor regulated by the intronic long noncoding RNA PCA3[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2015,112(27):8403-8408.
[26] Salagierski M,Verhaegh GW,Jannink SA,et al. Differential expression of PCA3 and its overlapping PRUNE2 transcript in prostate cancer[J].Prostate, 2010,70(1):70-78.
[27] Bourdoumis A,Chrisofos M,Stasinou T,et al. The role of PCA 3 as a prognostic factor in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) treated with docetaxel[J].Anticancer Res,2015,35(5):3075-3079.
[28] Cornu JN,Cancel-Tassin G,Egrot C,et al. Urine TMPRSS2:ERG fusion transcript integrated with PCA3 score,genotyping,and biological features are correlated to the results of prostatic biopsies in men at risk of prostate cancer[J]. Prostate,2013,73(3):242-249.
[29] Altintas DM,Allioli N,Decaussin M,et al.Differentially expressed androgen-regulated genes in androgen-sensitive tissues reveal potential biomarkers of early prostate cancer[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(6):e66278.
(收稿日期:2019-08-16)
