Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles of Rice Mutant SLR1 Based on Microarray Data
2019-02-18,,,,,,*
, , , , , , *
1. Institute of Food Crops, Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Kunming 650205, China; 2. Institute of Biotechnology and Germplasm Resources, Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Kunming 650205, China
Abstract Gibberellins are an important class of plant hormones. They play an important regulatory role in all stages of growth and development of higher plants. The use of mutants to study gibberellin metabolism and signal transduction pathways is currently a research hotspot. This article takes the data of Affymetrix chips of rice as an example, bioinformatics method was used to study rice SLR1 mutant and mine differentially expressed wild-type genes, thus exploring the expression regulation network of gibberellin signaling pathway-related genes.
Key words Gibberellin, Gene chip, Data mining
1 Introduction
Gibberellins (GAs) are an important class of plant hormones, belonging to diterpenoid compounds. Up to new, more than 100 kinds of GAs have been discovered from different higher plants. However, only some of them have biological activities regulating plant growth. GAs play an important role in all stages of the plant’s life cycle, such as seed germination, root growth, stem elongation, flowering, seed development and fruit formation[1-2]During plant growth and development, it is desirable to synthesize and accumulate the appropriate level of active GA. Plants can transport GAs from synthetic sites to tissues and organs that require GAs. The NPF protein family and the SWEET protein family play an important role during the transport of GAs[3]. In recent years, with the research and utilization of various mutants with the developments of advanced molecular biology and functional genomics, great progress has been made in the study of signal transduction pathways of GAs and their regulation of plant growth and development. The GA signaling pathways are relatively conserved in plants. The DELLA proteins located in nuclei are negative regulators of the GA signaling pathways. RiceSLR1 is a DELLA protein. After the GA signaling pathway is activated, the active GA binds to the receptor GID1[4-5], promoting the interaction between GID1 andSLR1. The GID1-SLR1 complex is recognized and bound by GID2, which causesSLR1 to be degraded by ubiquitination, releasing its negative regulation, thereby activating GA signals and regulating plant growth and development[6-8]. The objective of this study was mining of the microarray data of riceSLR1 mutant and its wild-type rice plant Taichung 65 as well as analyses of the differentially expressed genes between the two.
2 Materials and methods
2.1SourceofmaterialIn NCBI’S GEO database, search was conducted by keyword "rice gibberellin signaling pathway". In the results, the GSE15046 chip data were selected for analysis. The chip data was submitted by Sakakibaraetal., a total of 12 samples. The samples of riceSLR1 mutant and wild-type rice plant Taichung 65 were selected[9]. This experiment used the Affymetrix Rice Genome Array chip platform.
2.2DataprocessingandscreeningofdifferentialgenesData processing was performed using R software and the Bioconductor project[9]. The data set was subjected to background correction, standardization and log2 transformation using RMA (Robust Multichip Averaging) algorithm. If multiple probes corresponded to the same gene, the average was used. The two groups of samples were compared using the limma package[10]to find the differentially expressed genes between theSLR1 deletion mutant and the wild-type plant Taichung 65.
2.3BioinformaticsanalysisofdifferentialgenesAfter finding these differentially expressed genes, they were subjected to Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and metabolic pathway analysis using the Plant MetGenMAP online analysis system[11].
3 Results and analysis
3.1ScreeningofdifferentiallyexpressedgenesinexpressionprofilesAfter comparing of the two samples groups using Bioconductor’s limma toolkit, a total of 228 differentially expressed genes were found. Among them, 130 genes were up-regulated and 98 genes were down-regulated.
3.2GeneOntologyanalysisofdifferentiallyexpressedgenes
Cluster analysis was conducted using GO analysis in the Plant MetGenMAP database. The molecular functions of the differential genes and the involved biological processes (Process) were checked. The results of the GO analysis are shown in Fig.1 and Fig.2. The Gene Ontology analysis can help to better understand the changes in gene expression afterSLR1 deletion. The GO analysis showed that the molecular function of genes differentially expressed in riceSLR1 deletion mutant is mainly related to catalytic activity. The biological processes involved include mainly cellular process, metabolic process, response to stimulus,etc. This lays a foundation for further study of the molecular mechanism of action of GAs in rice.

Fig.1Numberofgeneswithdifferentmolecularfunction
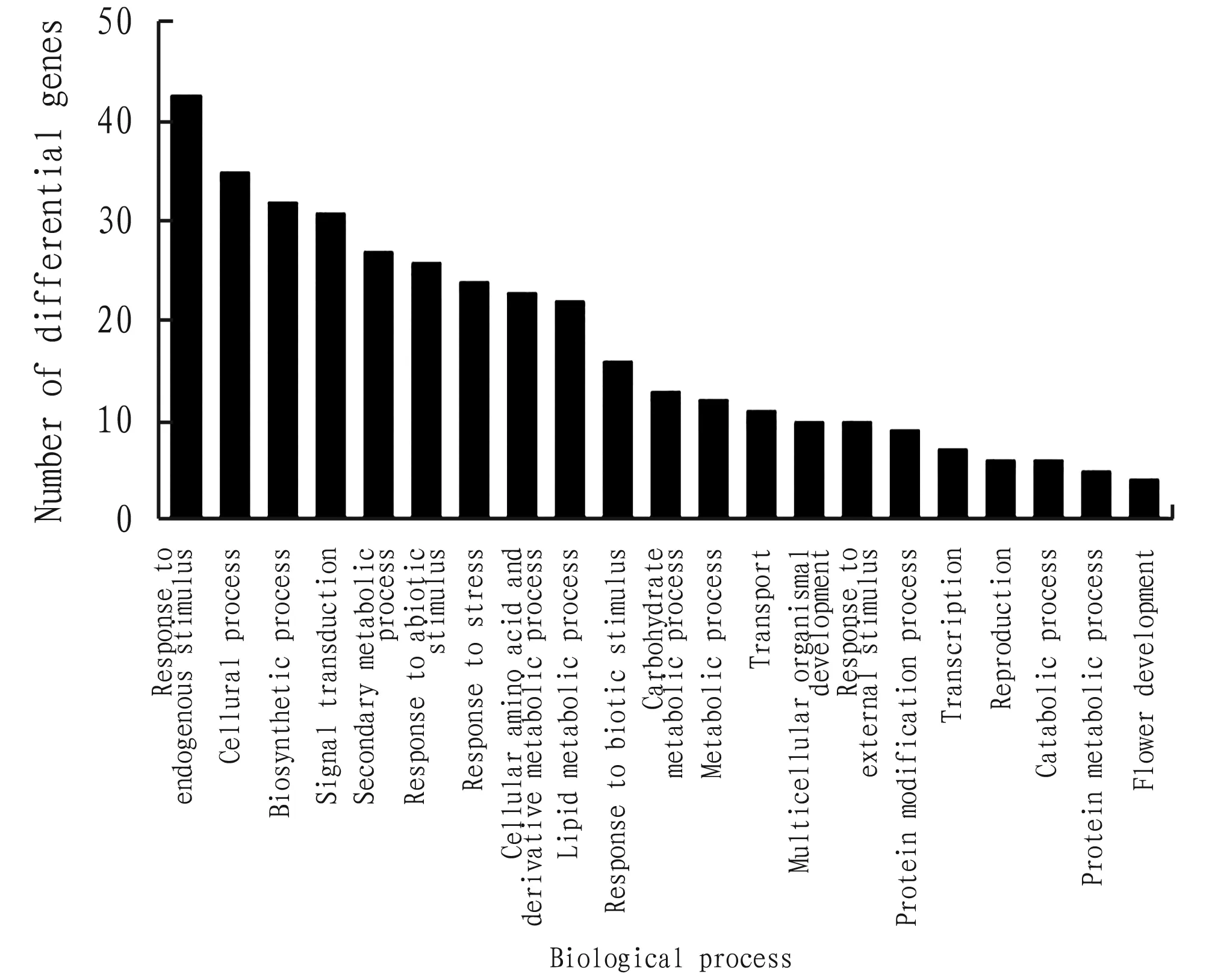
Fig.2Numberofgeneswithdifferentbiologicalprocess
3.3ChangesinmetabolicpathwaysThe changes in rice metabolic pathways were analyzed using the "Significantly changed pathways" in Plant MetGenMAP. As shown in Table 1, there are significant differences in multiple metabolic pathways between riceSLR1 detection mutant and wild-type plant. This result suggests that GAs may be involved in the regulation of these metabolic pathways.
Table1Changesinmetabolicpathways
4 Discussions
Since the "green revolution" in the 1960s, breeders have cultivated a number of new crop varieties, such as semi-dwarf, lodging-resistant high-yielding rice and wheat. This has greatly increased the yield of major crops worldwide[10]. Research has shown that the semi-dwarf mechanism of crops in the "green revolution" is closely related to the gibberellin signaling pathway[10-12], such as sd1 in rice and Rht in wheat. Ricesd1 gene encodes GA20OX2 oxidase. Loss of function of this gene hinders the conversion of GA53 to GA20 in the gibberellin synthesis pathway, which ultimately leads to a decrease in GA and a semi-dwarf phenotype of the plant[11]. The DELLA protein encoded by the wheatRht1 gene is a negative regulator of the gibberellin signaling pathway, which inhibits gene expression in the GA pathway and inhibits plant growth[12].
In rice, SLR1 is a DELLA protein. In wild-type rice,SLR1 encodes a protein consisting of 625 amino acids. It is highly homologous with wheat RHT-D1, maize D8, and arabidopsis GAI. The SLR1 protein contains a DELLA configuration and is a nuclear localization signaling protein. Rice SLR1 protein is an important negative regulator of GA signaling. It prevents the GA signal from being conducted downward. Ikedaetal. believe that the continuous activity of theSLR1 gene during signal transduction promotes endogenously antagonized ABA level,i.e., promotes ABA synthesis and inhibits GA synthesis[13]. The slr phenotype is characterized by weak stems, elongation at the base, shortened root length, and reduced number. Recent research has shown that DELLA-mediated GRF4 is involved in the coordinated regulation of crop growth and nitrogen metabolism in rice, improving nitrogen use efficiency and yield while maintaining rice semi-dwarf excellent trait[14].
In this article, bioinformatics method was used to mine the expression profiles chip data of riceSLR1 mutant and its wild-type rice plants. After analysis, a total of 228 differentially expressed genes were found between the two groups of materials. Compared with wild-type plants, 130 genes are up-regulated and 98 genes are down-regulated inSLR1 mutant. The GO analysis showed that the molecular function of genes differentially expressed in riceSLR1 deletion mutant is mainly related to catalytic activity, and the biological processed involved mainly include cell process, metabolic process and response to stimulus,etc. This study lays a foundation for further study of the molecular mechanism of action of GAs in rice.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Research Progress of Adansonia digitata
- Overlapped Tray Seedling Raising Model for Mechanical Transplanting of Rice
- Reform of Rural Planting Structure in China since the Reform and Opening-up and Its Main Problems
- Effects of Different Seedling Raising Substrates on Quality of Rice Seedlings
- Cucumber Downy Mildew: Research Progress and Registered Fungicides
- Safety Assessment and Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metal Pollutants in Livestock and Poultry Meat from Different Regions of China
