Distribution and Evolution Regularity of Reservoir Interlayer in Xijiang 24-1 Area
2018-12-27JiaweiGuo
Jiawei Guo
School of Geosciences, Yangtze University, Wuhan Hubei
Abstract The seepage barrier formed by interlayer played a very important role in controlling the distribution of oil-water movement, especially the formation of remaining oil. The study of interlayers was the key factor to improve oil and gas recovery and develop oil and gas resources efficiently. The results show that the interlayer of Xijiang 24-1 Area has a strong effect on controlling the distribution of remaining oil, and its barrier would result in a large amount of residual oil distribution at the middle and late stages of oilfield development. Well logging interpretation results were used to analyze the major factors controlling the low permeability reservoirs, which could be deployed for clearly identifying the interlayers with calcium, muddy and physical properties.
Keywords Interlayer, Logging Response, Permeability, Distribution Mode, Evolution Regularity
1. 油区地质特征研究
西江24-1区地层包括古近系,新近系文昌组、珠海组、珠江组、韩江组、粤海组、万山组,第四系,含油层段主要分布在新近系珠江组,厚778 m,共划分出23个油层,各油层之间均被较厚的泥岩分开[1][2] [3]。研究区是一个位于主断层控制下的逆牵引背斜构造,形态简单,圈闭面积小,构造幅度低,走向北西-南东向,闭合面积0.87~4.32 km2,闭合高度8~47.5 m [4] [5]。区内发育退积充填低位体系域和海进体系域沉积,包括滨岸体系的滩砂、滩砂水道、沿岸坝、滨砂和辫状三角洲体系的分流河道、水下分流河道、河口坝、风暴席状砂等微相类型,可作为良好的储集层[6] [7]。
2. 隔夹层识别研究
西江24-1区的隔夹层实际上是各油层内部分布的夹层,尽管部分夹层厚度较大、分布面积较广,也构成隔层,但考虑其处在油层之内,所以统称为隔夹层。区内储层物性以中高孔、中高渗为特征,难以借用其他油田隔夹层分析方法和标准来识别该区隔夹层。
储层岩心分析结果表明,当渗透率小于120 mD、孔隙度小于16%时,含油率低于5%,该特征虽不能反映工区储层隔夹层划分标准,但表明在中高孔、中高渗储层中,相对较低的渗透率仍能影响油气的分布。以此为参考,将测井渗透率小于120 mD的层位暂作为低渗透层,将区内的隔夹层分为3类:钙质隔夹层、泥质隔夹层、物性隔夹层。其中,钙质隔夹层的渗透率小于10 mD,钙质质量分数大于10%;泥质隔夹层的渗透率小于10 mD,泥质质量分数大于30%;物性隔夹层的泥质质量分数为19%~31.3%之间,钙质质量分数小于10%。
3. 隔夹层分布模式
3.1. 单层砂体
1) 厚层分流河道砂体顶部常见钙质隔夹层,底部粗砂岩中少见,仅发育一些物性隔夹层,厚度一般为 1~1.5 m。
2) 河口坝砂体主体部位隔夹层不发育(图 1),上部局部发育钙质隔夹层,但厚度小,分布少;侧翼发育钙质或物性隔夹层。
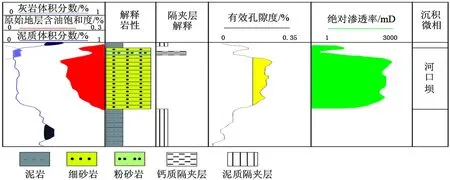
Figure 1. The calcium interlayer developed in the upper part of the sand body (Layer H12 in Well 1X) of estuary dam图1. 河口坝砂体上部发育的钙质隔夹层(1X井H12层)
3.2. 复合砂体
复合砂体常由垂向上多个期次的单砂体叠置而成,可划分为不同成因单元砂体复合和同成因单砂体复合,不同类型复合砂体隔夹层表现形式不同。研究区常见复合砂体有多期河道砂体复合、多期河口坝砂体复合、河口坝与河道砂体复合。多期河道叠加形成泥质隔夹层、物性隔夹层和钙质隔夹层,主河道附近隔夹层发育较薄,河道边缘隔夹层多且厚度大(图 2);河口坝砂体之间形成泥质隔夹层(图 3);河口坝与河道砂体之间形成物性隔夹层,厚度大(图4)。

Figure 2. The interlayer formed by multi-stage channel superposition图2. 多期河道叠加形成泥质隔夹层
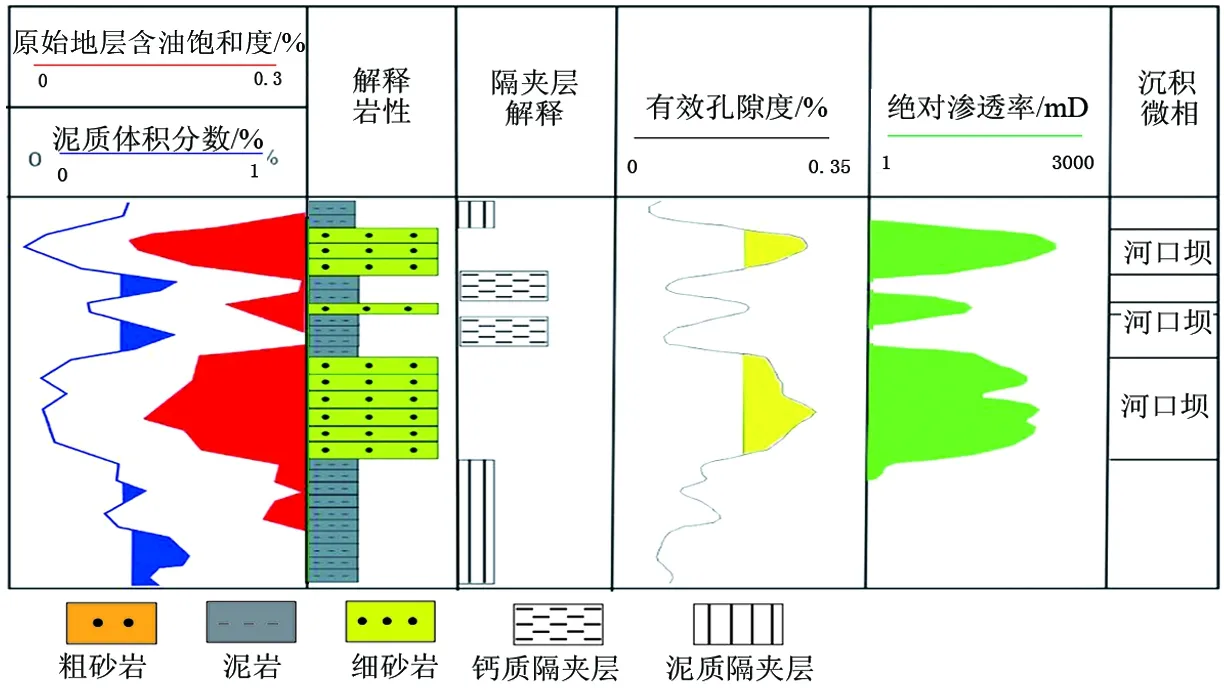
Figure 3. The interlayer formed between the sand bodies of estuarine dams图3. 河口坝砂体之间形成隔夹层

Figure 4. The interlayer formed in the sand bodies between the estuarine dams and channels图4. 河口坝与河道砂体之间形成物性隔夹层
4. 隔夹层演化规律
平面展布上河道分叉区域砂体厚度相对较大,水动力条件和沉积构造组合类型复杂,泥质沉积量大,隔夹层发育。水下分流河道边缘部位的水动力条件弱,使得泥质成分增加,而河道中央水动力运动相对较强,构成泥质沉积缩减。研究区主要在水下分流河道分叉处以及河道边缘发育隔夹层,在单一水下分流河道及河道主流线部位的隔夹层发育较少或不发育。
河口坝沉积早期或河口坝边缘由于沉积能量较弱,往往发育被泥晶碳酸盐胶结的钙质夹层。多期河口坝砂体形成时,每期旋回早期水体较深,三角洲向湖盆推进,形成一套三角洲前缘砂体,同时期可容空间减小,水体变浅;次一级旋回早期水体加深,则可容空间陡然增大,河口位置倒退,在前一期三角洲前缘砂体之上沉积了前三角洲泥岩,形成泥质隔夹层,若被后期改造则易形成物性夹层。河道砂体与河口坝砂体叠加时,易形成物性隔夹层。
5. 结论
1) 西江24-1区储层可识别出钙质、泥质和物性3类隔夹层,并建立了分类识别标准。
2) 单期河道砂体顶部易发育钙质隔夹层,多期河道叠加时,主河道不发育隔夹层,河道边部和前缘易发育泥质、钙质隔夹层。单期河口坝主体无夹层或在顶部发育薄层钙质隔夹层,侧翼易形成钙质隔夹层;多期河口坝叠加易形成泥质或物性隔夹层。河道与河口坝之间易形成物性隔夹层。
知网检索的两种方式:
1. 打开知网页面http://kns.cnki.net/kns/brief/result.aspx?dbPrefix=WWJD下拉列表框选择:[ISSN],输入期刊ISSN:2471-7185,即可查询
2. 打开知网首页http://cnki.net/左侧“国际文献总库”进入,输入文章标题,即可查询
投稿请点击:http://www.hanspub.org/Submission.aspx
期刊邮箱:jogt@hanspub.org
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
石油天然气学报的其它文章
- The Design and Operation of Testing Field of Domestically Made Large-caliber Valves
- Application of Direct Flowback Drilling Fluid in the East of South China Sea
- Study on Oil Washing Agent for the Squeeze Injection System of Scale Inhibitors
- Application of Acidizing Assisted High Energy Gas Fracturing Technique in Well Stimulation in Offshore Oilfield
- Study on Optimized Operation Scheme of Water Injection System
- Design and Application of Positive Pressure Conveying Device for Drill Cuttings in Drilling Platform
