滑片型孔轮式水稻精量排种器排种性能数值模拟与试验
2018-11-05朱德泉李兰兰文世昌武立权
朱德泉,李兰兰,文世昌,张 顺※,蒋 锐,武立权
滑片型孔轮式水稻精量排种器排种性能数值模拟与试验
朱德泉1,李兰兰1,文世昌1,张 顺1※,蒋 锐1,武立权2
(1. 安徽农业大学工学院,合肥 230036;2. 安徽农业大学农学院,合肥 230036)
针对现有水稻旱直播机排种器适应性差和排种精度低的问题,该文设计了一种滑片型孔轮式排种器。引用球度表示水稻种子三轴尺寸,利用EDEM软件对3种球度水稻种子在6种排种轮转速下的排种器排种过程进行仿真试验,得到不同球度水稻种子在不同排种轮转速下的排种性能变化规律,分析了排种轮转速和种子球度对排种性能的影响。仿真结果表明:当排种轮转速在15~40 r/min时,冈优898种子的排种性能优于国丰一号种子和冈优3551种子的排种性能;当排种轮转速在15~30 r/min时,3种球度水稻种子的排种合格率在84.01%~87.91%之间;当排种轮转速大于30 r/min时,随着排种轮转速增加,排种合格率显著下降。在此基础上,选用不同球度的5个水稻品种种子为试验材料,选取排种轮转速和种子球度为试验因素,以排种合格率、漏播率和重播率为评价指标,采用二次回归正交旋转组合设计,进行排种器台架试验。利用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件对试验结果数据进行分析,建立排种性能指标与排种轮转速和种子球度之间的回归方程,得到响应面图,并对仿真结果进行验证。根据回归方程进行优化,得到最佳工作参数:排种轮转速为27.12 r/min、种子球度为44.61%,此时,排种合格率为83.90%、漏播率为5.43%、重播率为10.67%,排种性能最佳;排种器台架试验结果与仿真结果基本相同,排种性能随排种轮转速和种子球度的变化规律一致。田间试验结果表明,排种器对各尺寸等级水稻种子的排种性能皆满足水稻精量穴直播的播种要求。研究结果可为滑片型孔轮式精量排种器的结构优化及排种性能提升提供参考。
农业机械;数值模拟;农作物;水稻;排种器;排种性能;滑片型孔轮
0 引 言
水稻精量穴直播作为目前生产上先进的水稻机械直播技术,已得到广泛的推广应用[1-3]。排种器是水稻精量穴直播机的核心工作部件,其排种性能直接影响机械播种质量。型孔轮式排种器是较为常用的机械式排种器,其充种性能直接影响着排种质量[4-10]。
目前,生产上使用的水稻旱直播品种繁多,种子尺寸各不相同,排种器对不同尺寸水稻种子的适应性不一样,高速作业对排种器的充种性能也会产生很大的影响[11-14]。因此,研究水稻种子尺寸及排种轮转速对排种性能的影响,可为精密排种器的结构优化提供参考依据。
随着计算机技术的快速发展,近年来许多学者应用离散元法(discrete element method,DEM)及其数值模拟仿真软件EDEM对排种器的工作性能进行研究分析。王金武等运用EDEM软件对指夹式精量排种器排种性能进行数值模拟与试验[15],廖庆喜等基于EDEM软件对离心式排种器排种性能进行数值模拟[16],鲍秀兰等采用离散元法对窝眼式排种器结构进行优化仿真[17],张涛等使用离散元法对排种器排种室内玉米种群运动规律进行研究[18]。这些应用研究对排种器的结构参数和工作参数优化以及工作性能提升均取得较为理想的研究结果。但上述研究主要针对充种性能较好的表面光滑团粒种子,而水稻种子是表面粗糙的细长粒种子,流动性和充种性较差,实现水稻精少量穴播,亟待提高排种器的排种性能。
因此,针对杂交稻旱穴直播精少量播种的农艺要求,设计一种滑片型孔轮式排种器,建立排种轮充种过程动力学方程,分析充种性能与排种轮转速和种子尺寸的相关性。在此基础上,引用球度表示水稻种子三轴尺寸,使用EDEM软件对滑片型孔轮式排种器进行排种性能仿真试验,根据模拟仿真结果得出排种性能随排种轮转速和种子球度的变化规律。选用不同球度的5个水稻品种种子为试验材料,选取排种轮转速和种子球度为试验因素,以排种合格率、漏播率和重播率为评价指标,采用二次回归正交旋转组合设计,进行排种器台架试验,得到最佳工作参数组合。通过台架试验验证了仿真结果的可靠性,并通过田间试验检验了排种器的工作性能,为滑片型孔轮式精量排种器结构优化及排种性能提升提供了依据。
1 排种器结构与工作原理
滑片型孔轮式排种器主要由排种轮、排种轴、护种滑片、限种板、清种毛刷、法兰盘、罩壳等组成,如图1a所示。工作时,机具行走地轮通过链传动将动力传至排种轴,带动排种轮以及嵌在排种轮上的护种滑片做旋转运动,种子从种箱下落至排种器的充种区后,在自身重力、种群侧压力及排种轮旋转带动作用下充入型孔,完成充种过程。进入清种区,在清种毛刷的作用下,型孔外多余种子被刷出后落回充种区,在护种滑片随排种轮转动至与铅垂方向呈15°角时,即图1b中的点处,护种滑片在右法兰盘内侧圆柱凸轮作用下被推至另一侧,利用护种滑片无孔处封住型孔,形成护种作用,当护种滑片随排种轮转动至与排种口正下方呈15°角时,即图1b中的点处,左法兰盘内侧圆柱凸轮将护种滑片推至初始位置,即护种滑片通孔与排种轮型孔轴线重合。当种子进入排种区后,在自身重力作用下,种子由型孔落入导种管,并下落投入种沟中,实现精量排种作业。

1. 限种板 2. 从动轴 3. 清种毛刷 4. 右法兰盘 5. 圆柱凸轮 6. 罩壳 7. 导种管 8. 护种滑片 9. 排种轮 10. 左法兰盘 11. 排种轴
2 充种过程动力学分析
为了提高排种器的充种性能,对种子在充种区进行受力分析。为简化分析,假设水稻种子为圆球体且规则排列[19],种子所受压力为其上方所有种子重力之和,侧压力为0。根据排种器工作条件可知,种子在自身重力、排种轮对种子的支持力1、种子群之间的推挤力2、排种轮外壁与种子的摩擦力1、种子群内摩擦力2、离心力F的共同作用下充入型孔中,将力系向排种轮截面的法向和切向进行分解,如图2a所示,建立其力学平衡方程式:

式中F为切向合力,N;F为法向合力,N;a为切向加速度,m/s2;a为法向加速度,m/s2;为水稻种子质量,g;为水稻种子角位移,(°);为水稻种子质心到排种轮中心距离,mm;为水稻种子角速度,rad/s;为排种轮转速,r/min;1为排种轮外壁与种子之间的摩擦因数;2为种子间摩擦因数。
整理式(1)可得

分析水稻种子充入型孔的过程可知,种子质心沿排种轮截面法向方向的位移量(即型孔深度)与种子法向加速度a关系为

式中为种子质心充入型孔内时间,s。
由于a在排种转速范围内与实际运动方向相反,可知a<0,结合式(2)和式(3)求得

型孔深度应与每穴播量相适宜,杂交稻穴直播每穴播种(3±1)粒为宜,参考型孔参数设计经验,型孔内种子以2粒平躺和1粒竖立的排列方式居多[20-21]。因此,型孔深度应满足

式中为种子长度,mm;为种子宽度,mm。
为达到较好的充种性能,排种轮型孔直径应不小于种子长度与种子厚度之和[20]。结合水稻种子排种试验研究,确定较为适合的排种轮菱形型孔长对角线长度1和短对角线长度2分别为12 mm和10 mm,型孔深度为8 mm,如图2b、图2c所示。
为保证水稻种子充分充入型孔内,需适当缩短种子进入型孔中的时间。由式(4)、式(5)整理可得:

式中=(2+)cos+22sin。
由式(6)分析可知,在确定水稻种子角位移、种子参数、2以及水稻种子质心到排种轮中心距离后,种子充入型孔中的时间与排种轮转速和种子尺寸有关。

注:Fr为种子离心力,N;F1为排种轮对种子的支持力,N;F2为种子群之间的推挤力,N;G为种子自身重力,N;f1为排种轮外壁与种子的摩擦力,N;f2为种子群内摩擦力,N;h为排种轮菱形型孔深度,mm;l1为排种轮菱形型孔长对角线长度,mm;l2为排种轮菱形型孔短对角线长度,mm。
3 排种性能仿真与分析
3.1 仿真模型构建
3.1.1 排种器模型建立
为减少仿真时间以及运算量,在不影响仿真效果的前提下,将与种子无接触的部件省去,应用三维软件SolidWorks对排种器进行实体建模,并以.igs格式导入EDEM软件中,如图3所示。

图3 排种器几何模型
通过EDEM软件前处理面板,在不影响仿真效果的前提下,简化排种器的运动过程,将运动过程简化为护种滑片随排种轮做圆周运动以及护种滑片在碰到凸轮时的横向进给运动。设置种子模型的泊松比为0.3,剪切模量为1.815×108Pa,密度为1 239 kg/m3。排种轮和护种滑片材料皆为不锈钢,泊松比为0.28,弹性模量为7.9× 107Pa,密度为7 850 kg/m3;清种毛刷材料为塑料,泊松比为0.4,弹性模量为1.0×108Pa,密度为1 150 kg/m3 [22-25]。
3.1.2 水稻种子离散模型建立
为探究种子尺寸在不同排种轮转速下对排种器排种性能的影响,引用球度表示水稻种子与球体之间的差异程度,用以代表水稻种子尺寸[26]。水稻种子球度可由式(7)计算得出。

式中S为种子球度,%;、、分别表示种子长度、宽度和厚度,mm。
选取3个不同种子尺寸等级的水稻品种:国丰一号、冈优898和冈优3551,每个水稻品种随机挑选1 000粒种子,测量其三轴尺寸,取平均值。3个水稻品种种子三轴尺寸及球度如表1所示。

表1 3个水稻品种种子尺寸及球度
按照水稻种子三轴尺寸均值建立其三维模型,并在EDEM软件中通过多球面组合对模型表面进行填充,模拟种子的状态,如图4所示。

图4 水稻种子EDEM模型
3.1.3 仿真参数的设定
由于水稻种子表面无黏附作用,选择Hertz-Mindlin无滑动模型为仿真接触模型[27]。根据充种区的具体情况,设置EDEM颗粒工厂以4 000粒/s的速率,生成总量数为4 000粒,生成种子颗粒总时间1 s,以保证充种区内有足够数量的种子进行仿真,排种轮和护种滑片皆设置为1 s后开始运转,为保证仿真的连续性,设置固定时间步长为4.39×10–6s,为Rayleith时间步长的25%,总时间为15 s(前1 s为充种过程)[28]。
3.2 排种性能虚拟仿真
为了提高排种器的排种性能,运用EDEM软件进行排种性能虚拟试验,分析排种轮转速和水稻种子球度对排种性能的影响。
根据田间实际工作情况,将排种轮转速分别设置为15、20、25、30、35、40 r/min,对3个水稻品种种子分别进行6组仿真虚拟试验。如图5所示,将排种器以网格模型(Mesh=0.3)显示,图中颜色的变化表示其运动速度的变化,可清楚表示水稻种子的运动状态。通过仿真可知,充种区边缘处的水稻种子运动比较明显,排种轮的旋转运动带动靠近排种轮边缘层的种子颗粒运动,其速度逐渐增加,与实际工作情况相符合。仿真中充种和排种过程的水稻种子速度如图5a、图5b所示。

图5 EDEM排种过程种子运动仿真
仿真过程中,排种器排种结果主要是合格、漏播、重播3种状态。为便于观察仿真过程中水稻种子运动形式,设置排种器以实体模型(Filled=0.4)形式显示,如图6所示。型孔中充有2~4粒水稻种子并排出导种口表示排种合格,如图6a所示;有0~1粒水稻种子充入型孔表示漏播,如图6b所示;型孔中充入多于4粒水稻种子并排出导种口表示重播,如图6c所示。

图6 EDEM仿真水稻种子3种排种状态
3.3 仿真结果分析
以排种轮转速和种子球度为因素,运用EDEM软件进行18组虚拟仿真试验。根据GB/T 6973-2005《单粒(精密)播种机试验方法》,选取合格率1、漏播率2和重播率3为试验指标[29-30],其计算公式如下

式中为理论排种数,1为合格排种数,2为漏播排种数,3为重播排种数。
通过EDEM仿真分析得到的数据运用Excel软件进行处理,得到3个水稻品种种子的排种合格率、漏播率和重播率变化曲线,如图7所示。

图7 排种性能EDEM仿真结果
由图7可知,当排种轮转速在15~40 r/min时,冈优898种子的排种性能较优,其合格率最低达80%,冈优3551和国丰一号种子的排种性能次之。排种轮转速在15~ 30 r/min时,随排种轮转速增加,3个水稻品种种子的合格率整体呈上升趋势;当排种轮转速高于30 r/min时,合格率随排种轮转速增加呈显著下降趋势。漏播率随排种轮转速增大呈逐渐增大趋势,重播率随排种轮转速增大整体呈下降趋势。当排种轮转速为 30 r/min 时,冈优 898种子的合格率达到最高为87.91%,漏播率为4.21%,重播率为7.88%;冈优3551种子的合格率为84.01%,漏播率为3.51%,重播率为12.48%;国丰一号种子的合格率为84.52%,漏播率为8.46%,重播率为7.02%;当排种轮转速大于30 r/min时,3个水稻品种种子合格率下降幅度以及漏播率整体增长趋势加快。当排种轮转速为40 r/min时,3个水稻品种种子的漏播率皆超过8%,已不符合水稻精量播种的农艺要求[31]。
结合表1和图7综合分析可知,3个水稻品种中,冈优3551种子长度较小,种子球度较大,其流动性较好,种子容易充入型孔,充种性能较好,漏播率较低;但排种轮转速过低,其重播率较高,当排种轮转速小于20 r/min时,其重播率大于15.53%。国丰一号种子长度大,其球度较小,流动性和充种性能较差,充入型孔的种子粒数较少,会导致漏播率较高,当排种轮转速为40 r/min时,其漏播率达15.20%。由于种子球度过大易导致重播率较高,种子球度过小会造成漏播率较高,从而合格率较低。在供试的3个水稻品种中,冈优898种子球度介于冈优3551和国丰一号种子球度之间,当排种轮转速在15~40 r/min时,其重播率和漏播率均较低,而合格率较高,最高合格率为87.91%。
4 排种性能试验
4.1 台架试验
4.1.1 试验装置
试验地点为安徽农业大学排种性能实验室。试验设备为黑龙江省农业机械研究院研制的JPS-12型排种器性能检测试验台。排种器固定在安装架上,控制电机带动种床带转动,种床带上涂有一定宽度的黏种油,水稻种子由排种口投落至黏种油层上,如图8所示。人工观察统计每穴粒数。

1. 种床带 2. 排种器 3. 传动链条 4. 控制电动机 5. 试验台架
4.1.2 试验设计
通过前文仿真分析,得出不同球度水稻种子排种性能指标随排种轮转速的变化规律,为进一步探究排种轮转速和水稻种子球度对排种器排种性能的影响及其最佳组合,选取不同种子尺寸等级的国丰一号(大)、两优628(大)、冈优898(中)、冈丰188(小)、冈优3551(小)共5个水稻品种种子作为试验材料,其三轴平均尺寸及球度如表2所示。

表2 5个水稻品种种子尺寸及球度
以排种轮转速和种子球度为试验因素,合格率1、漏播率2以及重播率3为性能评价指标,开展2因素5水平二次回归正交旋转组合试验。因受水稻种子尺寸限制,用5个品种的种子球度替代种子球度的5个水平,试验因素编码如表3所示。每组试验重复3次,取平均值,试验结果如表4所示。

表3 试验因素编码及水平设置
注:括号中的数值是不同水稻品种的种子球度实测值。
Notes: Values in brackets are the test values of seed sphericity of different varieties rice.
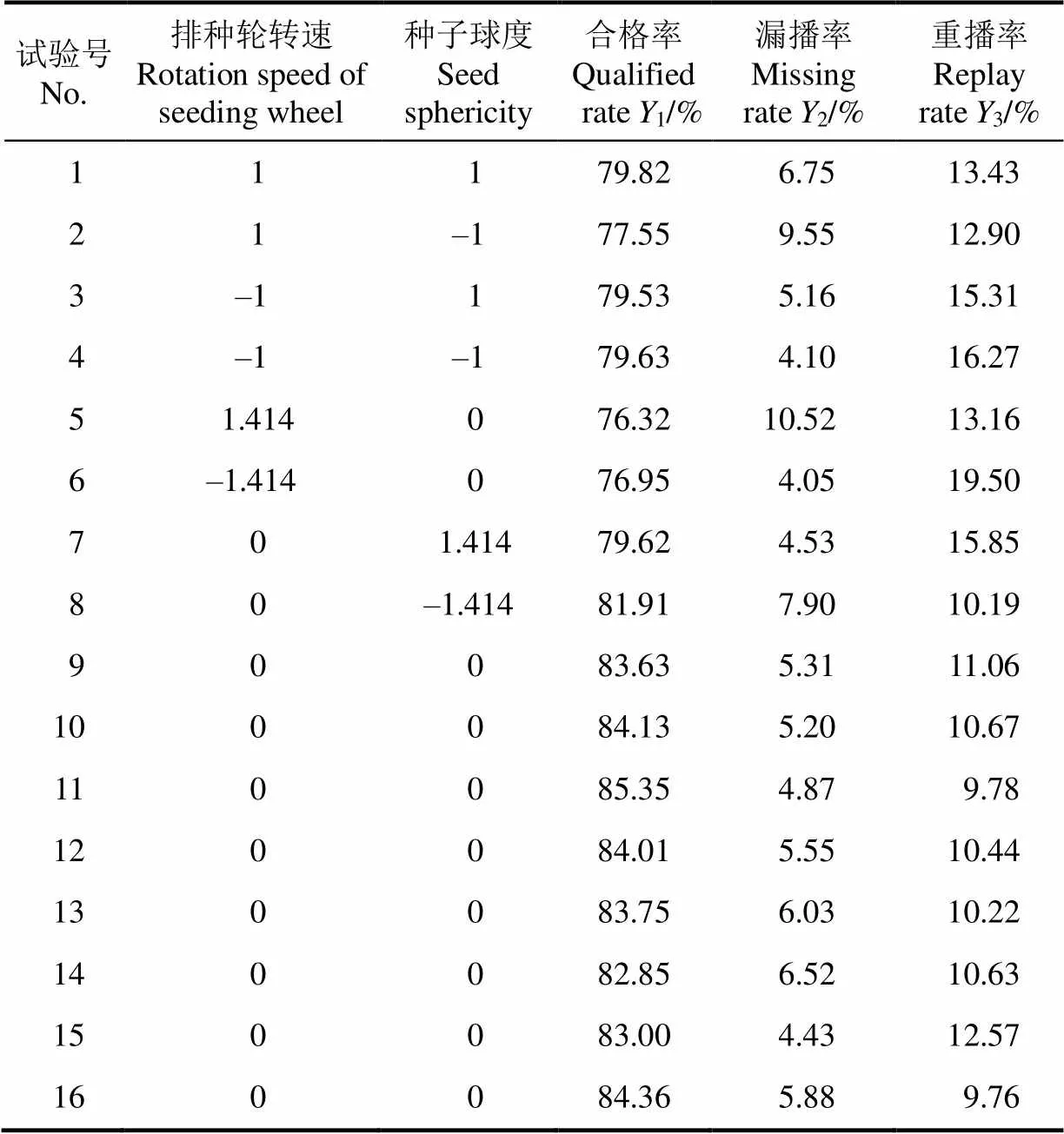
表4 试验设计与结果
4.1.3 试验结果分析
1)回归方程及显著性检验
运用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件对表4的试验数据进行回归分析,分别得到合格率1、漏播率2、重播率3与排种轮转速1和种子球度2之间的回归方程。

对回归方程进行方差分析,如表5所示。由表5可知,排种器的排种合格率1、漏播率2、重播率3的回归方程皆极显著,回归方程的失拟项皆不显著,表明在一定参数范围内,回归模型与实际情况拟合度较高;排种器的排种合格率1、漏播率2、重播率3的决定系数2分别为0.93、0.90以及0.86,说明回归方程的预测值与实际值之间具有较高的相关性,故可用合格率1、漏播率2、重播率3的回归模型对排种器的排种性能进行分析与预测。

表5 回归方程方差分析
注:**表示在0.01水平差异极显著;*表示在0.05水平差异显著。
Note: **indicates the highly significance at 0.01 level; * indicates significance at 0.05 level.
由表5进一步分析可知,对于排种合格率1,回归项12、22影响极显著,回归项1、2以及12皆影响不显著;对于漏播率2,回归项1、2以及12影响极显著,12影响显著,而22影响不显著;对于重播率3,回归项1、12影响极显著,2、22影响显著,12影响不显著。在保证拟合回归极显著、失拟项不显著的前提下对回归方程进行重新拟合,简化后的回归方程为:

式(10)回归模型的<0.000 1,影响极显著;失拟项=0.240 3(>0.05),影响不显著;模型的决定系数=0.91。

式(11)回归模型的<0.000 1,影响极显著;失拟项=0.313 3(>0.05),影响不显著;模型的决定系数²=0.89。

式(12)回归模型的<0.000 1,影响极显著;失拟项=0.081 0(>0.05),影响不显著;模型的决定系数=0.86。
2)试验因素影响效应分析
由表5中各试验因素的检验值可知,影响合格率1的主次因素分别为:12>22>12>1>2;影响漏播率2的主次因素分别为:1>12>2>12>22;影响重播率3的主次因素分别为:12>1>22>2>12。
为更加直观地分析各因素与排种性能之间的关系,利用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件得到种子球度和排种轮转速对排种合格率、漏播率以及重播率影响的响应曲面图,如图9所示。

图9 排种轮转速和种子球度对排种性能指标的影响
响应曲面的等值曲线可直观地反映因素交互作用对试验评价指标的影响程度,圆形曲线表示两因素间交互作用影响不明显,椭圆形曲线则表示两因素交互作用影响显著[32-33]。根据式(9)和图9可知,种子球度与排种轮转速存在交互作用。当排种轮转速一定时,排种合格率随种子球度的增大呈先增大后减小趋势,重播率随种子球度增大呈先减小后增大趋势;当种子球度一定时,合格率随排种轮转速的增大呈先增大后减小趋势,重播率随排种轮转速增大而减小趋势。当排种轮转速以及种子球度变化时,合格率和重播率的变化区间皆较大。因此,种子球度和排种轮转速对排种合格率和重播率的影响程度较为显著。当种子球度一定时,排种器的漏播率随排种轮转速增大而增大,这是因为排种轮转速增大,充种时间减小,囊种的概率降低,导致漏播率增大;排种轮转速变化时,漏播率的变化区间较大。因此,排种轮转速对漏播率的影响程度较为显著。图9所示的排种性能指标随排种轮转速和种子球度的变化规律与仿真结果基本一致。
4.1.4 优化与验证
为确定排种器最佳参数组合,结合各因素边界条件建立排种性能优化模型。其优化模型为

通过Design-Expert 8.0.6软件进行优化求解,得到排种轮转速为27.12r/min、种子球度为44.61%时,排种合格率为83.90%,漏播率为5.43%,重播率为10.67%,排种器排种性能最佳。
在排种轮转速为27.12 r/min时,对5个水稻品种种子分别进行排种器台架试验,每次试验测定种子数不低于1 000粒,分别测定其排种合格率、漏播率和重播率,重复3次,取其平均值,结果如表6所示。

表6 验证试验结果
由表6可知,在排种轮转速27.12 r/min工况条件下,滑片型孔轮式排种器对5个品种水稻种子的排种合格率皆高于80%,均符合水稻精量播种合格率不小于80%的农艺要求[31];其中接近种子球度优化参数的冈优898排种合格率最高,为83.56%,漏播率为5.13%,重播率为11.31%。
4.2 田间试验
为进一步检验滑片型孔轮式水稻精量排种器工作性能,于2017年6月5号在安徽农业大学郭河试验基地开展田间播种试验。试验前采用旋耕机对田块土壤进行耕整,使土壤疏松平整,平均耕深为85 mm,耕深稳定性系数为93.28%,田间土壤平均坚实度为386.6 kPa。水稻种植品种选取国丰一号、两优628、冈优898、冈丰188和冈优3551。将排种器安装于精量旱直播机,配套动力为东方红LX-854型拖拉机,试验参照NY/T 987-2006《铺膜穴播机作业质量》和GB/T 25418-2010《水稻覆土直播机》进行[34-35],试验时机组前进速度约为5.85 km/h,排种器的转动由直播机的地轮带动,排种轮平均转速约为27.12 r/min。每次试验连续统计机组匀速行驶30 m取样长度内各行每穴粒数和穴距,重复3次,取平均值,并由下式求得穴距变异系数CV。


试验数据均依据GB/T 6973-2005《单粒(精密)播种机试验方法》进行统计处理[29],结果如表7所示。

表7 田间试验结果
由表7可知,在排种轮平均转速27.12 r/min、机组前进速度约5.85 km/h工况条件下,滑片型孔轮式水稻精量排种器对5种不同球度水稻品种种子播种合格率皆大于80%,漏播率均小于7.5%,重播率均小于13.5%,平均穴距满足水稻种植株距100~250 mm的范围要求[31],平均穴距在190~230 mm范围内,播种穴距变异系数均小于25%,且各项评价指标均能满足水稻大田精量旱穴直播的一般种植要求。田间播种试验结果与台架排种试验结果有所差距的主要原因可能为:机组田间无规律的振动和地轮打滑导致转速不稳定,对排种器充种和排种具有一定的影响,从而影响机具田间播种质量。
5 结 论
1)建立了滑片型孔轮式水稻精量排种器充种过程动力学模型,分析得到影响排种器排种性能的因素有排种轮转速和种子尺寸。利用EDEM软件对3种球度水稻品种种子进行排种器排种过程仿真模拟试验,结果表明,当排种轮转速在15~40 r/min时,整体上冈优898种子颗粒的排种性能较好,国丰一号和冈优3551种子的排种性能次之;当排种轮转速在15~30 r/min时,3个水稻品种种子的排种合格率整体呈上升趋势;当排种轮转速高于30 r/min时,排种合格率随转速增加而显著降低。
2)排种器台架试验结果表明,在排种轮转速为27.12 r/min、种子球度为44.61%时,排种合格率为83.90%,漏播率为5.43%,重播率为10.67%,排种器的排种性能最佳;排种器台架试验结果与仿真结果基本相同,排种性能随排种轮转速和种子球度的变化规律一致。台架验证试验表明,在排种轮转速为27.12 r/min工况条件下,5种球度水稻种子的合格率皆高于80%,均符合水稻精量播种要求;接近种子球度优化参数的冈优898排种合格率最高,为83.56%。
3)田间播种试验结果表明,在排种轮平均转速为27.12 r/min,机组前进速度约为5.85 km/h工况条件下,滑片型孔轮式水稻精量排种器对5种球度水稻种子排种合格率皆大于80%,漏播率均小于7.5%,重播率均小于13.5%,平均穴距在190~230 mm的范围内,播种穴距变异系数均小于25%,能够满足水稻大田精量旱穴直播的一般种植要求。
[1] 罗锡文,谢方平,区颖刚,等.水稻生产不同栽植方式的比较试验[J].农业工程学报,1999,15(1):136—139. Luo Xiwen, Xie Fangping, Ou Yinggang, et al. Experimental investigation of different transplanting methods in paddy production[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 1999, 15(1): 136—139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 何瑞银,罗汉亚,李玉同,等.水稻不同种植方式的比较试验与评价[J].农业工程学报,2008,24(1):167—171. He Ruiyin, Luo Hanya, Li Yutong, et a1. Comparison and analysis of different rice planting methods in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(1): 167—171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 孙永健,郑洪帧,徐徽,等.机械旱直播方式促进水稻生长发育提高产量[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(20):10—18. Sun Yongjian, Zheng Hongzhen, Xu Hui, et al. Mechanical dry direct-sowing modes improving growth, development and yield of rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(20): 10—18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 罗锡文,蒋恩臣,王在满,等.开沟起垄式水稻精量穴直播机的研制[J].农业工程学报,2008,24(12):52—56. Luo Xiwen, Jiang Enchen, Wang Zaiman, et al. Precision rice hill-drop drilling machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(12): 52—56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 汤楚宙,罗海峰,吴明亮,等.变容量型孔轮式排种器设计与试验[J].农业工程学报,2010,26(12):114—119. Tang Chuzhou, Luo Haifeng, Wu Mingliang, et al. Design and test on seed metering device with variable capacity model-hole roller[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(12): 114—119. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 吴明亮,官春云,高晓燕,等.偏心轮型孔轮式排种器排种油菜极限转速试验[J].农业工程学报,2010,26(6):119—123. Wu Mingliang, Guan Chunyun, Gao Xiaoyan, et al. Test on limit turning speed of eccentric round hole-wheel seedmeter for rape[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(6): 119—123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 施祖强,汤楚宙,官春云,等.转速对偏心轮型孔轮式排种器排种性能的影响[J].湖南农业大学学报:自然科学版,2008,34(3):359—362. Shi Zuqiang, Tang Chuzhou, Guan Chunyun, et al. Effect of rotating speed on seed performance of eccentric round hole-wheel seedmeter[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University: Natural Sciences, 2008, 34(3): 359—362. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 杨文敏,吴明亮,何腾飞,等.型孔轮式排种器排种性能的仿真分析—基于离散元法[J].农机化研究,2015,37(10):34—39. Yang Wenmin, Wu Mingliang, He Tengfei, et al. Simulation analysis for seeding performance of hole-wheel seedmeter—based on discrete element method[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(10): 34—39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 于建群,王刚,心男,等.型孔轮式排种器工作过程与性能仿真[J].农业机械学报,2011,42(12):83—87. Yu Jianqun, Wang Gang, Xin Nan, et al. Simulation analysis of working process and performance of cell wheel metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(12): 83—87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张明华,罗锡文,王在满,等.水稻直播机组合型孔排种器设计与试验[J].农业机械学报,2016,47(9):29—36. Zhang Minghua, Luo Xiwen, Wang Zaiman, et al. Design and experiment of combined hole-type metering device of rice hill-drop drilling machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(9): 29—36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 罗锡文,刘涛,蒋恩臣,等.水稻精量穴直播排种轮的设计与试验[J].农业工程学报,2007,23(3):108—112. Luo Xiwen, Liu Tao, Jiang Enchen, et al. Design and experiment of hill sowing wheel of precision rice direct-seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2007, 23(3): 108—112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 赵永亮,汪润保,李雷霞,等.水稻旱直播机械作业技术[J]. 农业工程,2015,5(4):13—15,18. Zhao Yongliang,Wang Runbao,Li Leixia,,et al. Operation technology of rice dry direct seeding machine[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 5(4): 14—18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 孙永健,郑洪帧,徐徽,等.机械旱直播方式促进水稻生长发育提高产量[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(20):10—18. Sun Yongjian,Zheng Hongzhen,Xu Hui,et al. Mechanical dry direct-sowing modes improving growth,development and yield of rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Societyof Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(20): 10—18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 张绍军,杨宝田,罗阁山.国内外水稻直播机械化的发展研究[J].农业科技与装备,2012(5):61—62. Zhang Shaojun, Yang Baotian, Luo Geshan. Research on the development in direct rice seeding mechanization at home and abroad[J]. Agricultural Science &Technology & Equipment, 2012(5): 61—62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王金武,唐汉,王奇,等.基于EDEM软件的指夹式精量排种器排种性能数值模拟与试验[J].农业工程学报,2015,31(21):43-50. Wang Jinwu, Tang Han, Wang Qi, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment on seeding performance of pickup finger precision seed-metering device based on EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(21): 43—50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 廖庆喜,张朋玲,廖宜涛,等.基于EDEM的离心式排种器排种性能数值模拟[J].农业机械学报,2014,45(2):109—114. Liao Qingxi, Zhang Pengling, Liao Yitao, et al. Numerical simulation on seeding performance of centrifugal rape-seed metering device based on EDEM [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(2): 109—114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 鲍秀兰,孟亮.基于离散元法的窝眼式排种器结构优化仿真[J].江西农业大学学报,2017,39(3):607—614. Bao Xiulan, Meng Liang. Structural optimization simulation of nest type seed metering device based on discrete element method[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Agricultural University,2017,39(3): 607—614. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张涛,刘飞,赵满全,等.基于离散元的排种器排种室内玉米种群运动规律[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(22):27—35. Zhang Tao, Liu Fei, Zhao Manquan, et al. Movement law of maize population in seed room of seed metering device based on discrete element method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(22): 27—35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 田立权,王金武,唐汉,等.螺旋槽式水稻穴直播排种器设计与性能试验[J].农业机械学报,2016,47(5):46—52. Tian Liquan,Wang Jinwu,Tang Han,et al. Design and performance experiment of helix grooved rice seeding device[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(5): 46—52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 中国农业机械化科学研究院.农业机械设计手册(上册)[M].北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2007.
[21] 王在满,黄逸春,王宝龙,等.播量无级调节水稻精量排种装置设计与试验[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(11):9—16. Wang Zaiman, Huang Yichun, Wang Baolong, et al. Design and experiment of rice precision metering device with sowing amount stepless adjusting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(11): 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 杨玲,杨明金,李庆东,等.包衣稻种物理特性的试验研究[J].农业工程学报,2005,21(9):7-11. Yang Ling, Yang Mingjin, Li Qingdong, et al. Experimental study on physical properties of coated rice seed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2005,21(9): 7-11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 张石平,陈进,李耀明.振动气吸式穴盘精量播种装置种子“沸腾”运动分析[J].农业工程学报,2008,24(7):20—24. Zhang Shiping, Chen Jin, Li Yaoming. Analysis of seeds “Boiling” motion on vibrational air-suction tray seeder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(7): 20—24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 李季成,权龙哲,罗立娜.稻米含水率对其弹性模量的影响[J].东北农业大学学报,2008,39(4):1—3. Li Jicheng, Quan Longzhe, Luo Lina. Influences of brown rice grain’s water ratio on elastic modulus[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2008, 39(4): 1—3. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 张锋伟,赵春花,郭维俊,等.基于压痕加载曲线的谷物种子硬度性能测定技术[J].农业机械学报,2010,41(4):128—133. Zhang Fengwei, Zhao Chunhua, Guo Weijun. et al. Testing of grain hardness based on indentation loading curve[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(4): 128—133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 周祖锷.农业物料学[J].北京:中国农业出版社,1994.
[27] van Liedekerke P, Tijskens E, Dintwa E, et al. EDEM simulations of the particle flow on a centrifugal fertilizer spreader[J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 190(3): 348—360.
[28] 胡国明.颗粒系统的离散元素法分析仿真[M].武汉:武汉理工大学出版社,2010.
[29] 单粒(精密)播种机试验方法:GB/T 6973-2005[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2005.
[30] 石林榕,吴建民,孙伟,等.基于离散单元法的水平圆盘式精量排种器排种仿真试验[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(8):40—48. Shi Linrong, Wu Jianmin, Sun Wei, et al. Simulation test for metering process of horizontal disc precision metering device based on discrete element method[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(8): 40—48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 张顺,夏俊芳,周勇,等.气力滚筒式水稻直播精量排种器排种性能分析与田间试验[J].农业工程学报,2017,33(3):14—23. Zhang Shun, Xia Junfang, Zhou Yong, et al. Field experiment and seeding performance analysis of pneumatic cylinder-type precision direct seed-metering device for rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(3): 14—23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 易军鹏,朱文学,马海乐,等.牡丹籽油超声波辅助提取工艺的响应面法优化[J].农业机械学报,2009,40(6):103—110. Yi Junpeng, Zhu Wenxue, Ma Haile, et al. Optimization on ultrasonic-assisted extraction technology of oil from Paeonia Suffruticosa Andr. seeds with response surface analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery. 2009, 40(6): 103—110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 张黎骅,徐中明,苟文,等.滚筒-栅条式银杏脱壳机结构参数的优化[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(10):39—45. Zhang Lihua, Xu Zhongming, Gou Wen, et al. Optimization of structure parameters of cylinder-bar type shelling device for ginkgo biloba[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2012,28(10): 39—45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 铺膜穴播机作业质量:NY/T 987-2006[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2006.
[35] 水稻覆土直播机:GB/T 25418-2010[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2010.
Numerical simulation and experiment on seeding performance of slide hole-wheel precision seed-metering device for rice
Zhu Dequan1, Li Lanlan1, Wen Shichang1, Zhang Shun1※, Jiang Rui1, Wu Liquan2
(1.230036,; 2.230036,)
Precision planting is the advanced technology that sows seeds in the predetermined position of soil accurately and quantitatively by precision planter. Precision seed-metering device is the key component of precision planter and its seeding performance directly affects the quality of rice sowing, which divided into two types according to the working principle. The one is the mechanical metering device, and the other type is the pneumatic seed-metering device. The hole-wheel precision seed-metering device is a kind of mechanical seed-metering device and its seed-filling performance directly affects the seeding quality, which has been increasingly widespread due to its advantages of high planting quality when sowing rice seeds. But it has disadvantages of bad uniformity not to meet the seeding requirement of different size rice seeds. There are many dry direct seeding varieties rice and the sizes of their seeds are different. The adaptability of the seed-metering device to different sizes rice seeds is different. High speed work will also have a great influence on the seed-filling of the seed-metering device. For the problems of poor adaptability and low precision of the current rice drought direct seeding machine, a slide hole-wheel seed-metering device was designed to improve the direct seeding performance for rice. The sphericity was selected as the indicator of 3-dimension size of rice seeds. According to the simulation test by EDEM software for seeding process in 3 varieties of rice seeds with different sphericity (Gangyou 898, Guofeng No.1 and Gangyou 3551) under 6 seed-metering device rotational speeds, the changing laws of seeding performance of rice seeds with different sphericity under different rotational speeds were obtained and the influences of rotational speeds and seed sphericity on seeding performance were analyzed. The simulation results showed that the seeding performance of rice seeds of Gangyou 898 was better than other 2 varieties of rice seeds when the rotational speed of seeding wheel was between 15 to 40 r/min, when the rotational speed of seeding wheel was between 15 to 30 r/min, the seeding qualified rate of those 3 varieties rice seeds floated between 84.01% to 87.91%, and the seeding qualified rate had a increasing trend of overall presentation as the rotational speed of seeding wheel increases, when the rotational speed of seeding wheel was faster than 30 r/min, the seeding qualified rate declined significantly with the increasing of rotational speed. 5 varieties of rice seeds with different sphericity (Guofeng No.1, Liangyou 628, Gangyou 898, Gangfeng 188 and Gangyou 3551) were selected as experimental materials. The rotational speeds of seeding wheel and seed sphericity were selected as influence factors, and seeding qualified rate, missing rate and replay rate were taken as evaluation standards. The bench test was done with the quadratic regression orthogonal combination design method. The regression equation and response surface between the performance index and the rotational speed and seed sphericity were acquired to verify the simulation results after analyzing those data by Design-Expert 8.0.6 software. Finally, the optimal parameter combination was obtained through the regression equation: the rotational speed of seeding wheel was 27.12 r/min and seed sphericity was 44.61%. In this case, the qualified rate is 83.90%, the missing rate is 5.43% and the replay rate is 10.67%, which is the best seeding performance for the seed-metering devices. The results from bench test were in accordance with that from simulation. The changing trends of seeding performance in bench test with rotational speed and seed sphericity were also basically consistent with that in simulation experiments. The field test result showed that, when the average rotational speed was 27.12 r/min and the forward velocity was 5.85 km/h, the seeding performance of seed-metering device could meet the requirements of precision sowing for all size grades of rice seeds. The research results provide a reference for structure optimization and performance improvement of slide hole-wheel precision seed-metering device.
agricultural machinery; numerical simulation; crops; rice; seed-metering device; seeding performance; slide hole-wheel
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.21.003
S223. 91+1
A
1002-6819(2018)-21-0017-10
2018-04-10
2018-08-29
安徽省科技重大专项(17030701045);国家自然科学基金项目(51805005);安徽农业大学青年科学基金重点项目(2016ZR009)
朱德泉,男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事现代农业装备技术研究。E-mail:dqzhu@sina.com
张 顺,男,讲师,博士,主要从事现代农业装备设计及测控研究。Email:shunzhang@ahau.edu.cn
中国农业工程学会高级会员:朱德泉(E041200232S)
朱德泉,李兰兰,文世昌,张 顺,蒋 锐,武立权. 滑片型孔轮式水稻精量排种器排种性能数值模拟与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(21):17-26. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.21.003 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhu Dequan, Li Lanlan, Wen Shichang, Zhang Shun, Jiang Rui, Wu Liquan. Numerical simulation and experiment on seeding performance of slide hole-wheel precision seed-metering device for rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(21): 17-26. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.21.003 http://www.tcsae.org
