Measures to Restrain Propeller-Hull Vortex Cavitation and Some Discussions
2018-10-12XUEQingyuHUANGHongboHUANGShuquanWUShenLIUYafei
XUE Qing-yu,HUANG Hong-bo,HUANG Shu-quan,WU Shen,LIU Ya-fei
(1.National Key Laboratory on Ship Vibration&Noise,China Ship Scientific Research Center,Wuxi 214082,China;2.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Green Ship Technology,Wuxi 214082,China)
Abstract:In this paper,the propeller-hull vortex cavitation(PHVC)was observed on a container vessel in the Large Cavitation Channel of CSSRC.Then four vortex-restrained measures were exploited to restrain PHVC using the combination of three new designed propellers and three appendages(vortex generator VG,pre-shrouded vane PSV and wake equaling duct WED).Three of those measures reached the engineering request.According to the above work and accumulated data of ship models,a parameter IHof hydrodynamic interaction intensity was proposed.IH≤3.2 was suggested as a conservative criterion to evaluate the PHVC occurring for further discussion openly.A well designed or controlled inflow of ship propeller permits IH>3.2 without PHVC.
Key words:container vessel;propeller-hull vortex cavitation(PHVC);vortex-restrained measures;hydrodynamic interaction intensity
0 Introduction
When a propeller works under a highly loaded condition with small tip clearance,unsteady line vortex cavitation may happen between it and the hull surface nearby.This phenomenon was first observed by Huse[1]in a laboratory,and was first reported in I.S.P.in 1972 with the name of propeller-hull vortex cavitation(PHVC)showing some experimental results and some hypotheses about possible physical causes of the PHVC.These hypotheses included the starting vortex,the vortices created by the shear flow in the wake field,the vortices created in other regions of the flow field,and the so-called pirouette effect,however,there is not common understanding yet.
Then Shigeki[2]carried out a series of experimental researches on the PHVC,and described how the streamline changed before and after propeller where PHVC occurred.It was demonstrated that the process of the PHVC evolution could be controlled in experimental condition by some critical factors.The different stages of evolution process of PHVC can be found in their following papers.
Some numerical investigations on PHVC were fulfilled by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland and Aalto University[3],the fundamental mechanisms causing the propeller-hull vortex were modelled by using the time-accurate RANS solver.Computations were carried out under seven advance coefficients while keeping the tip clearance constant.It was shown that RANS method seemed to be an effective way to simulate the fundamental mechanisms causing the propeller-hull vortex(PHV),the use of cavitation models would be next step to improve the simulations at full scale.
Recently,in the Large Cavitation Channel of CSSRC,PHVC was observed in a test of a container vessel.As a result,the original design of the propeller had been abandoned,and new designed propellers or necessary appendages were in urgent due to the vessel being constructed already.Finally,three of four exploited measures were confirmed experimentally to successfully eliminate PHVC[4-5],and one of the three was used on the container vessel.There was also some effort of finding a criterion to judge whether PHVC could exist on a ship.
1 PHVC on the studied vessel A
During the cavitation observation and pressure fluctuation measurement of the original propeller of a container vessel A,the PHVC was occurred both at ballast draft condition and design draft condition,for which model propeller rotated at 28 r/s.The detailed test condition is listed in Tab.1 and the PHVC on one blade for different angular position is shown in Fig.1.It seemed random that the PHVC may connect with the edge of back sheet cavitation or with the shed tip vortex cavitation and it jumped from one blade to another when the blades rotated in and out of the wake peak one after another.The fluctuating pressure induced by cavitation was also measured during the test and a section of time history as well as the location of transducers were shown in Fig.2.Without occurrence of PHVC,the fluctuating pressure amplitude was about 3.0 kPa,otherwise it may increase rapidly to 25~30 kPa,which may induce serious hull vibration.
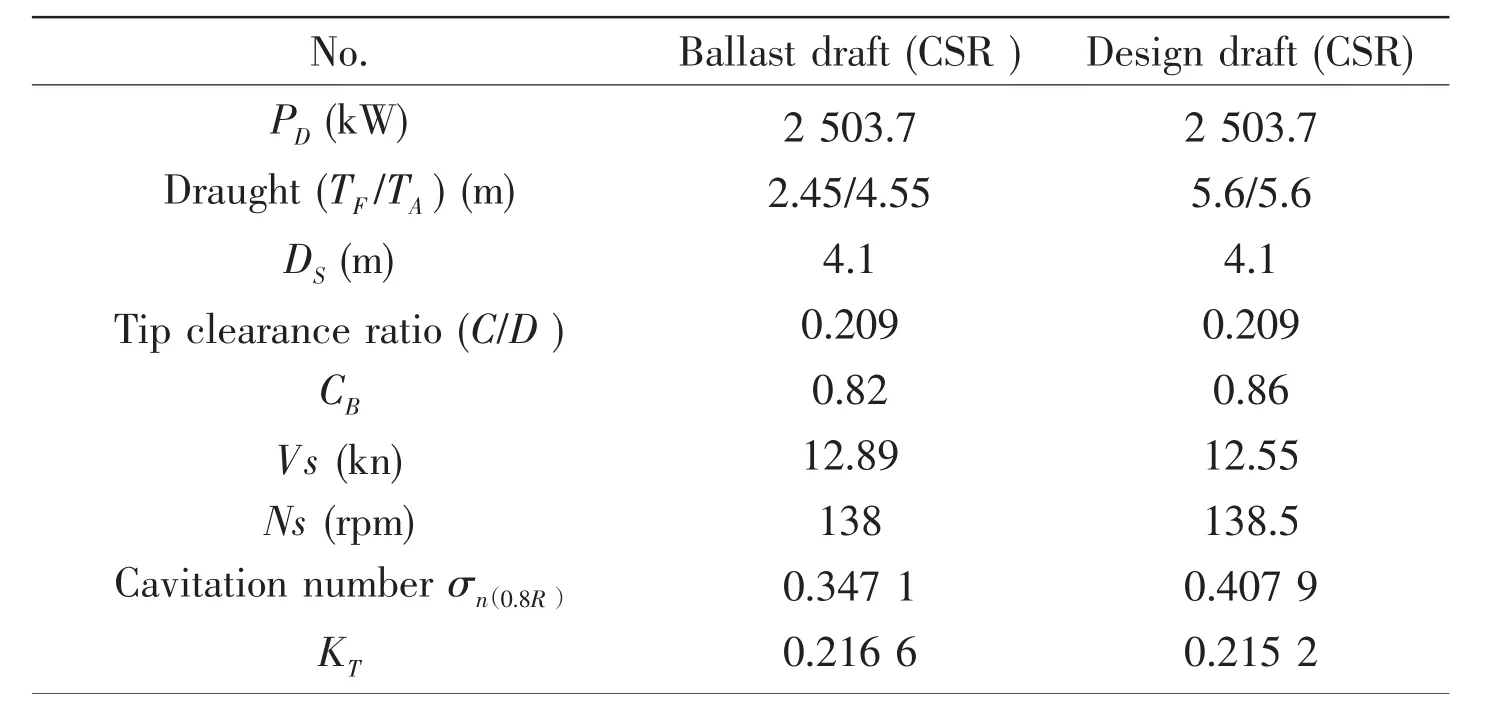
Tab.1 Cavitation test condition of the container ship

Continue Tab.1

Fig.1 The PHVC pattern in different angular position

Fig.2 Fluctuating pressure induced by PHVC
2 Measures to restrain the PHVC and flow analysis
2.1 Measures to restrain the PHVC
Three new designed propellers coupled with three appendages(VG[6-9],PSV,WED)to form four different PHVC restrained measures.Their detailed informations were listed in Tab.2,where Pro.1,Pro.2 and Pro.3 represent the three new designed propellers,D is the diameter of the propeller and Z is the number of the blades of each propeller,C/D is the tip clearance ratio.The idea of these measures was to improve the inflow of the propeller and to increase tip clearance ratio.

Tab.2 Four different PHVC restrained measures and original propeller

Fig.3 Measures and their PHVC restrained results
The tests of each PHVC restrained measure and the corresponding PHVC restrained results were shown in Fig.3.It can be seen from the photos that PHVC was clearly eliminated by measures Pro.1+VG,Pro.1+PSV and Pro.3+WED.But for measure Pro.2+WED,the PHVC still occurred,though it was somehow restrained.It is confirmed by the results that PHVC can be solved by increasing the tip clearance combined with improving the inflow.The difference between Pro.2+WED and Pro.3+WED only lays at 0.8R and 1.0R respectively of propellers where outlet of ducts located.That means the appendages should improve the entire inflow of propellers so as to restrain PHVC.The fluctuating pressure signal corresponding to each PHVC restrained measure was shown in Fig.4.It is demonstrated that for measure Pro.2+WED,the PHVC still existed,which was consistent with what was shown in Fig.3 by cavitation performance.And also the occurrence probability of PHVC was counted according to the cavitation video,and the results were shown in Tab.3.Consistent with what was shown in Fig.4,no PHVC happened in the test of Pro.1+VG,Pro.1+PSV and Pro.3+WED.But for Pro.2+WED,PHVC still happened frequently,though the probability was less than that of the original.

Fig.4 Pressure signal corresponding to each PHVC restrained measure
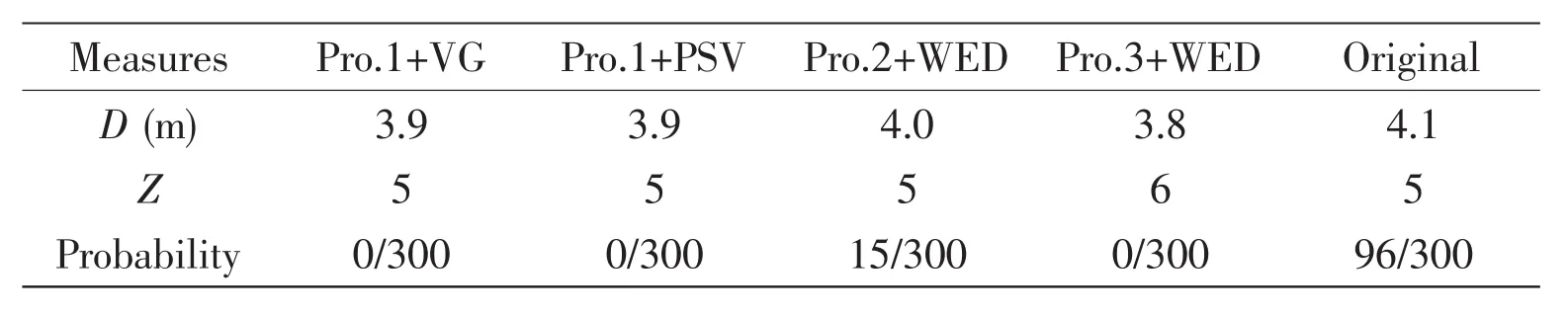
Tab.3 Statistics of probability of PHVC
2.2 Flow analysis of the measures
In order to clarify the mechanism of PHVC happening and restrained,some numerical work was done for measures Pro.1+VG and Pro.1+PSV.The changes inflow on hull surface and in the wake distribution by utilizing VG were shown in Fig.5.It can be seen from Fig.5 that without VG,there were a flow separation on the ship stern and a wake peak on the propeller disc and above.It also can be seen that with VG the flow was improved and the separation disappeared.And also the wake peak on propeller disc weakened and shifted outward distinctively,resulting in increase in axial velocity.It may due to the fact that the appropriate VG created a suitable downstream vortex to weaken the tangent swirling velocity induced by propeller between the stern and the propeller,which greatly improves the inflow in propeller domain.

Fig.5 Inflow improved by utilizing VG
The flow with and without PSV was simulated and the corresponding flow distribution was shown in Fig.6.The color bar represented the axial flow velocity towards propeller disc.It was shown that the PSV increased the velocity of the flow between the blade tip and the foreupward stern.And also it can be concluded that the pre-swirling of fluid by PSV weakened the strength of vortex induced by propeller rotating in flow.All of these acted together and resulted in reducing the risk of PHVC.

Fig.6 The comparison of axial velocity with and without PSV
3 Analysis on main factors and criterion for PHVC
Heavy load usually means relatively larger attack angle,camber and chord length of the propeller,all of these factors lead to a swirling lower pressure area.The small tip clearance represents a more narrow space around the propeller,where wake fraction is higher,shear flow is stronger,and vortices are more complex and stronger consequently.That is why the heavy load and small tip clearance are commonly accepted as apparent reasons of PHVC.Here,a parameter called hydrodynamic interaction intensity is introduced to evaluate the risk of occurrence of PHVC as follows.

where CTis thrust load coefficient,C is distance between the propeller tip and the hull above,D is propeller diameter.
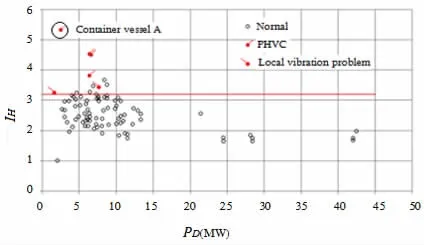
Fig.7 The distribution of IHfor different delivered power of propeller
Based on the above analysis and accumulated experimental data of almost 90 model tests in the Large Cavitation Channel of CSSRC,IH≤3.2 is proposed as a conservative criterion without PHVC.The word‘conservative’means that if there are an excellent stern profile or some effective appendages to cause a very fine wake,the ship could be without PHVC even its IHis larger than 3.2 as did in this paper.In Fig.7,IH=3.2 is a line to divide all test data of 90 models into two parts:definitely without or with(including vibrating model)PHVC.The container vessel A is a good example of exception for IH≤3.2.The hydrodynamic interaction intensities of original and three new designed propellers were listed in Tab.4 and all IHlocated within a circle in top left corner of Fig.7.The tests showed one PHVC and three weaker PHVC respectively in Fig.8.In the test,it was also observed that decreasing the rotation of propeller till the IHcame to about 3.0,the PHVC disappeared immediately,which demonstrated the rationality of IHto judge PHVC occurring.

Fig.8 The cavitation performance of different propellers

Tab.4 Comparison of IHfor different propellers
4 Conclusions
The appendages such as VG,PSV and WED in this paper are very useful to further improve the inflow and wake fraction for a given ship and its propeller.It leads to effectively solve PHVC if the redesigned propeller does not work well.IH≤3.2 is suggested as a criterion of PHVC for a purpose of openly discussion.A well designed or controlled inflow of the ship propeller permits IH>3.2 without PHVC.
杂志排行
船舶力学的其它文章
- Numerical Calculation of Hull Wave-making Resistance by Three-dimensional RANS Method
- Mathematical Representation of a 3-D Translating Source Green Function and its Fast Integration Method
- Evaluation of Turbulence Models for the Numerical Prediction of Time-dependent Cavitating Flow During Water Entry of a Semi-closed Cylinder
- Investigation on Higher-Order Responses of Vortex-Induced Vibration for a Mounted Cylinder
- Dynamic Property and Motion Simulation of Atmospheric Diving Suit
- Experimental Study on Dwell-fatigue of Titanium Alloy Ti-6AL-4V for Offshore Structures
