Experimental and simulation studies on delamination strength of laminated glass composites having polyvinyl butyral and ethyl vinyl acetate inter-layers of different critical thicknesses
2018-08-25AjitanshuVedrtnam
Ajitanshu Vedrtnam
aDepartment of Applied Mechanics,Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad,Allahabad,UP,211004,India
bDepartment of Mechanical Engineering,Invertis University,Bareilly,UP,243001,India
Keywords:Delamination strength Composite material PVB Laminated glass Finite element analysis
A B S T R A C T The laminated glasses(LGs)composites are gaining popularity as protective structural material.Delamination strength(DS)of(LGs)with different inter-layers and their different nominal thicknesses were compared.The effect of inter-layer thickness,delamination load,and inter-layer type on DS is clearly observed from this brief study.It is concluded that inter-layer thickness has the significant role in determining the DS of LGs.The statistical analysis confirmed the strong association of DS with inter-layer thickness and the interlayer type.It was found that the LG-PVB composite has the comparatively lower DS than LG-EVA composite and inter-layer thickness has the prominent role in the determination of DS in the LG-EVA composite.There is an increment in DS with an increment in critical inter-layer thickness in both LG-EVA and LG-PVB composites.The increment in the inter-layer thickness from 0.38 mm to 0.76 mm increases DS significantly;whereas,the further increment in the inter-layer thickness to the higher value has a lesser effect.The finite element model was constituted(without considering the effect of temperature)for determining DS of LG composite.The simulation results were in a good match with experimental results.The results of the present work can be utilized by the design engineers while selecting LG for structural applications.
1.Introduction
LG is a sandwiched composite material,composed of two pieces of outer glass layers(LG panels can have more than 2 glass layers)and one or more pieces of the interlayer sandwiched in-between the glasses.Inter-layer modifies the fracture pattern of LG,improves the post-breakage performance,and keeps together the wrecked pieces of glasses that can possibly cause hazardous incidents[1-4].The properties of the LG are generally determined by bending test(impact and blast performance are also widely discussed)of LG[1-24];acoustics[25],hardness[26],ringon ring[27]are also discussed in the cited literature.An experimental study on delamination strength(rare in cited literature)is reported in the present work.Delamination is the mode of failure in LG composites in which shear,fatigue or impact loading causes separation of glasses and polymer interlayer[1].
Hooper has reported a mathematical model for four-point loading bending test of simply supported LG beams[8].Behr et al.have performed experimentation for determining bending strength of the monolithic and LG beams[9].Edel has reported the effect of temperature on the bending strength of LG[10].Norville et al.reported a multilayer model for describing the bending behavior of LG[11].Asik and Tezcan presented the three coupled non-linear differential equations for analyzing LG beams with different boundary conditions[12].Viciusa et al.compared load bearing ability of LG with Polyvinyl butyral(PVB),Ethyl vinyl acetate(EVA),and Sentry Glass(SG)inter-layers with at different temperatures using four-point bending test and found that SG inter-layer has more load bearing ability compared to LG-PVB and LG-EVA[13].Louter et al.reported the effects of humidity,temperature,thermal cycling,and load period on LG-SG performance[14,15].Belis et al.found that failure mechanism of LG-SG was considerably different from LG-PVB[16].Seshadri et al.reported dependence of the post fracture performance of LG on the polymer inter-layer[17].Biolzi et al.reported the difference between the gradual breakage of the LG-SGP and LG-PVB[18].Ivelin and Ivanov reported that the bending stress in glass layers decide load bearing ability of the LG and the inter-layer of LG should be thinner than the external glass layer under external pressure for the lightweight structural design[19].Galuppi and Carfagni have found the inconsistency in EN-standards and suggested that Enhanced Effective Thickness(EET)method can be effectively applied for LG constructions[20].Nhamoinesu and overend have presented a FE based model for the post-breakage behavior of the LG and compared it with experimental results obtained a four-point bending test of the LG[21].Calderone et al.found that the effective thickness technique has been an efficient method for calculating the glass stress and deflection of the LG[22].Serafinavičius et al.experimentally investigated long-term bending strength of LG,by conducting four-point bending test on LG with PVB,EVA and SG inter-layers at different temperatures[23].Galuppi et al.also evaluated the enhanced effective thickness for multi-layered LG[24].The fatigue strength of rectangular glass specimen subjected to cyclic-torsion depends on the ratio of specimen width to specimen thickness[28].A few studies on torsional buckling of LG were reported in the cited literature[29-32].Belis and Luible[31]evaluated an existing model for lateral torsional buckling analysis of the LG-PVB beams using simulations and the experiments.Amadio and Bedon[32]investigated the out-of-plane bending by developing an analytical model based on Newmark's theory.Additionally,few buckling curves were also proposed to find the effect of different aspects[33].The fatigue strength of laminated composites is discussed widely[34-37],but DS of LG composite with the variety of the interlayers(types and thickness)considered in the present work along with the presented experimental setup was not cited in literature.
DS of LG having PVB/EVA inter-layers with different nominal thicknesses(0.38/0.76/1.52mm)is evaluated in the present work.The results of the experimentation were validated by the statistical analysis using MINITAB.A finite element(FE)model was constituted for determining the effect of interlayer thickness on DS of LG composites.An additional objective of the present work includes determining the suitability of the type of LG for different structural applications.
2.Material and methods
The LG specimens were prepared by combining two annealed float soda lime glasses(5mm thick)with an inter-layer of PVB/EVA of 0.38/0.76/1.52mm thickness.The LG-PVB and LG-EVA samples are prepared at Hindustan Glass Works Ltd,Allahabad,India and at Mehr Image Pvt.Ltd.,Delhi,India respectively.The shear test was conducted on the LG-PVB and LG-EVA specimens having three different critical inter-layer thicknesses(0.38 mm,0.76mm and 1.52 mm)following ASTM D3163.The test method ASTM D3163 is an extension for ASTM D1002 and used for rigid plastic adherents.The test method is useful for generating comparative shear strength data for joints made from a number of plastics.The test method includes the following steps:
1)Firstly,the specimens were heated up to 100-120°C for LG-EVA composite and 150-160°C for LG-PVB composite in a hot air oven for the softening of inter-layer (causing partial delamination).
2)Further,the softened partially delaminated LG samples placed inside the shear testing machine.
3)Further,the LG specimens were fixed in the grips of the testing machine such that the applied load coincides with the long axis of the test specimen.The specimen was loaded at a rate of 8.3-9.7MPa(1200-1400 psi)of shear area per minute(at 0.05 in./min cross head speed)up to the failure of the specimen.
4)Finally,the shear stress at which failure occurred is noted.Fig.1 shows the steps of experimentation and schematic diagram of delamination process diagrammatically.The schematic diagram reflects the way LG composite is fixed and loading is applied inside the shear testing machine.
3.Results and discussion
The result and discussion section is divided into three parts:the first part reports experimental results and discussion on same.Further,the statistical analysis is reported for ensuring the validity of experimental results.Finally,the FE simulation results are reported.
3.1.Experimentation
Table 1 shows the results obtained from the testing of 60 samples having different inter-layers and different thicknesses.
The result obtained from testing of 10.38mm thick LG-PVB shows that a maximum DS is 6N/mm2whereas the minimum DS is 63.5N/mm2.The variation in the observed values are due to the non-uniform behavior of glass due to non-uniformity of the chemical composition,surface(crack)and edge defect,the duration of the loading,glass manufacturing techniques(including heat treatment,environmental parameters),the geometry production,storage,cutting,and transportation of the LG sample,which requires further intensive investigation[38].The results obtained from the testing of 10.38mm thick LG-EVA shows that a maximum DS is 79.72 N/mm2whereas the minimum DS is 70.55N/mm2.The DS of LG-EVA samples are higher at an average from LG-PVB samples.Results obtained from the testing of 10.76 mm thick LGPVB reflects the maximum DS is 98.63 N/mm2whereas the minimum DS is 85.25 N/mm2.It clearly indicates that increasing the inter-layer thickness increases the DS.Testing of LG-EVA 10.76mm thick samples shows that a maximum DS is 97.73 whereas the minimum DS is 95.55 N/mm2.The LG-EVA 11.52 mm thick samples have maximum 129.21 N/mm2whereas the minimum DS is 126.15N/mm2.The testing of 11.52 mm thick LG-PVB shows that a maximum DS is 117.32N/mm2where as the minimum DS is106.47 N/mm2.From the experimental results,it can be safely concluded that increasing the interlayer thickness increases the DS and LG-EVA is having comparatively higher DS than LG-PVB.
3.2.Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis is conducted using MINITAB software for the validation and description of experimental results.The F value shows the dependency of DS on inter-layer thickness.The higher F-value of LG-EVA also reflects that LG-PVB is having comparatively lower DS and inter-layer thickness has more prominent role in the determination of DS in case of LG-EVA.A general linear model of Analysis of variance(ANOVA)is constituted for the DS considering inter-later thickness and inter-layer type using an adjusted sum of square for the test.
3.2.1.Analysis of variance(ANOVA)
ANOVA includes a general linear model preferable for factorial designs,in which main effects and interactions between one or more factors are to be determined.In the present work,ANOVA is one of the most suitable way to establish the dependency of DS on interlayer type and inter layer thickness.Table 2(a)shows the factors with their different levels considered in the present study.Table 2(b)shows the result of ANOVA.
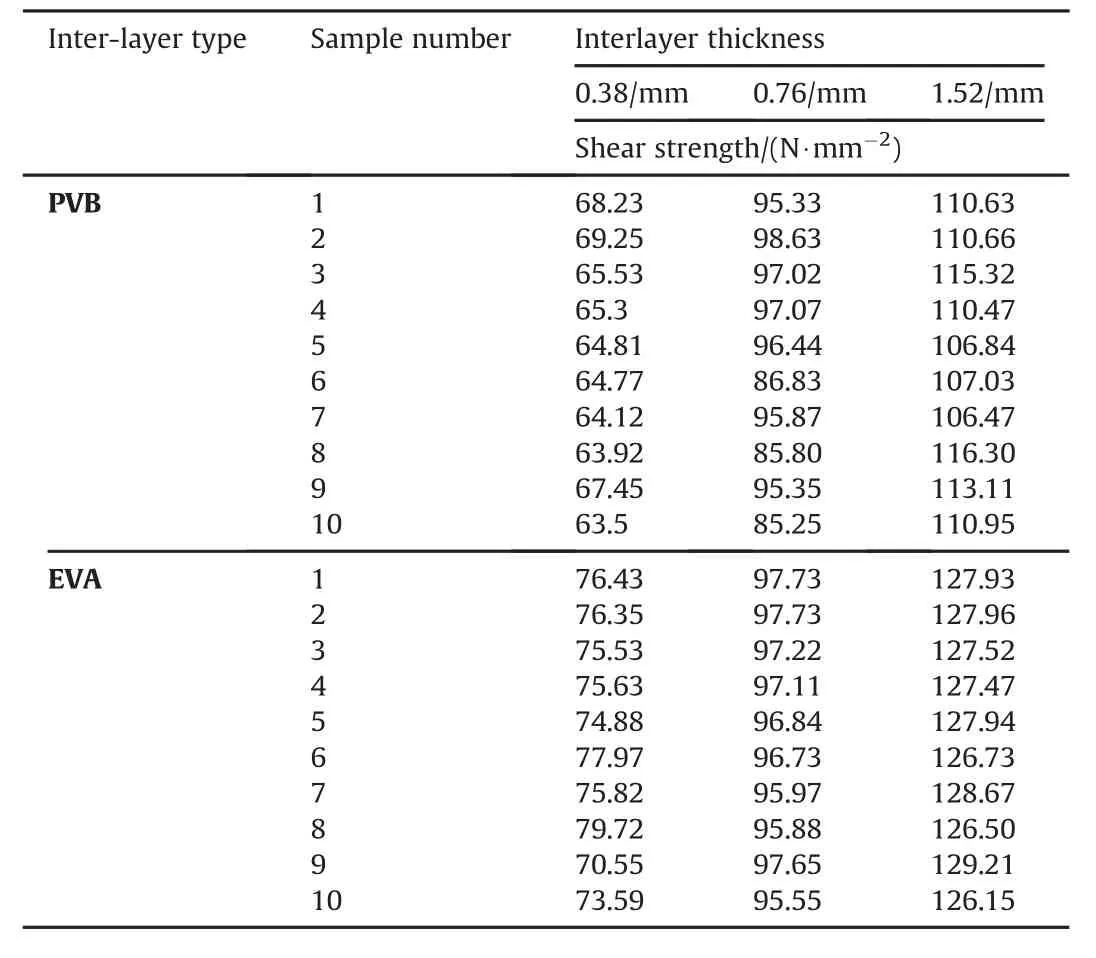
Table 1 Results of DS test.
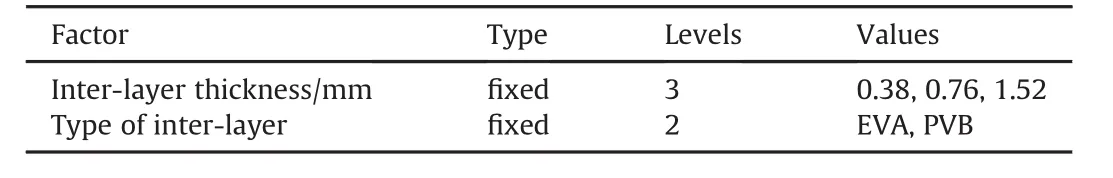
Table 2(a)Factors with their levels for ANOVA.
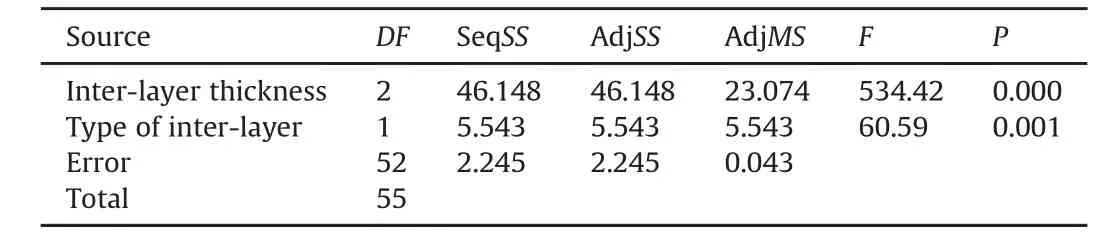
Table 2(b)Results of ANOVA.
ANOVA clearly reflects that the number of cycle withstand by the LG samples depends most significantly on inter-layer thickness followed by type of interlayer.
Fig.2 shows the residue plots obtained from ANOVA.The pencil thickness plot shows that the data qualifies the pencil thickness test,thus,data is normally distributed.It also reflects that an error is within the considerable limits.
3.2.2.Regression analysis
The regression analysis is conducted for LG-PVB samples.LGEVA samples follow the similar patterns as LG-PVB samples,however,with higher DS values.Table 3(a),Table 3(b),and Table 3(c)shows the results of regression analysis of LG samples.
It is safe to conclude from the regression and ANOVA output that the errors in interpretations of the experimentation results are within considerable limit.The DS of LG composite significantly depends on the interlayer thickness[2,3].
3.3.Numerical simulation
A numerical model is presented to predict the effect of interlayer thickness on delamination strength of laminated glass.The principle of numerical modelling is presented in Fig.3.The simulation was performed considering the experimental set-up used.The loading conditions were simulated assuming the similar boundary and the loading condition as used in experimentation.
The maximum load at which delamination of LG composite took place(116.3N)was applied as line load at the centre of specimen and one side of LG sample.The samples were kept fixed at one of the end(lateral face of the sample)using nodal restraints.The linear elastic material model is followed during simulation[1-3].The tetrahedron, fine mesh(number of nodes-24872,number of elements-5866)was used,grid refinement study was also conducted but no significant changes were observed in the response.The properties of Glass and inter-layers(Table 4)were taken from Refs.[1,2].
Fig.4 shows the sample output of simulation results.The Fig.4 clearly shows that the interlayer thickness has the significant effect on DS.The maximum deflection(resulted after separation of glasses)is 86.81%lesser in LG composite having 11.52mm interlayer than the LG composite having 10.38 mm interlayer at 116.3 N delamination load.The LG composite having 10.76mm thick interlayer has 57.6%less deflection after delamination than the LG composite having 10.38 mm thick interlayer.The DS of LG increases with the interlayer thickness as reflected by the experimentation results.It is also reflected by simulation results that increment from 0.38mm to 0.76mm has more significant than the further increment in the interlayer thickness.However,results of experimentation and simulation can't be compared,as the effect of temperature is not considered in the simulation.

Table 3(a)Regression statistics.
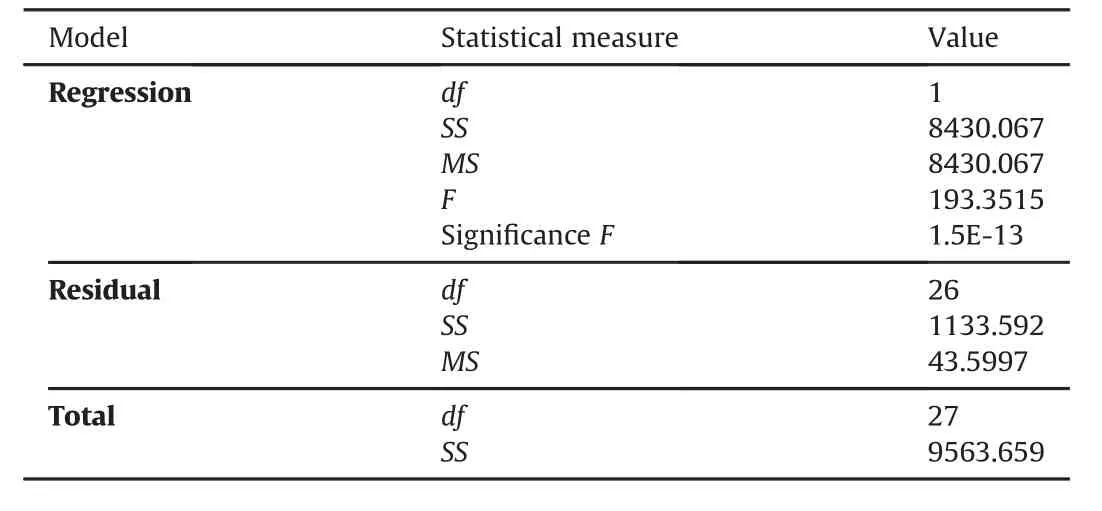
Table 3(b)Results of regression analysis.
4.Conclusions
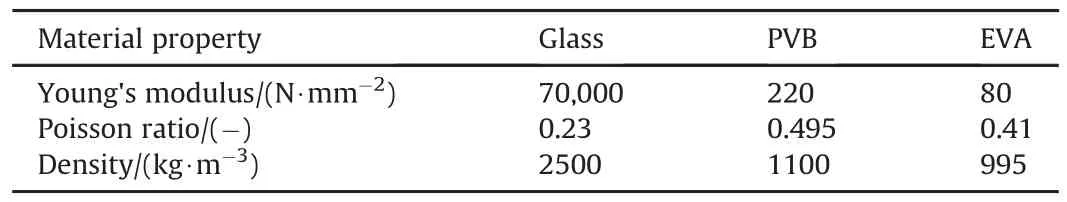
Table 4 Material properties used in simulation.
The interlayer type and interlayer thickness have a significant effect on DS.LG-EVA has higher DS when compared to LG-PVB for same critical inter-layer thickness.The statistical analysis(highF-statics value)confirmed the dependability of DS of LG on the interlayer type and inter-layer thickness.Pvalue shows that the error in the analysis is within considerable limits.Inter-layer thickness has a more prominent role in the determination of DS in the case of LGEVA,however,the effect of inter-layer type is also significant on DS.An increment in inter-layer thickness results in an increment in average DS before fracture.DS significantly increases when the inter-layer thickness increases from 0.38mm to 0.76 mm but the further increment of interlayer thickness to 1.52 mm reported lesser increment in DS.The results of present work reflected that the experimentation along with the use of the statistical techniques gives the conclusive results for designing the LG structures.Aparallel comparison of experimental results,FE method with other computational methods like boundary element analysis can be performed in future for further accurate prediction of the DS of LG by theoretical means.The shortcoming of present work includes selecting the linear elastic material model and not considering the effect of temperature during simulation.The experimental results can be utilized for developing a further specialized numerical model(utilizing other means than FE method)that can predict the performance and DS of LG in structural,automotive,and other applications adequately.

Table 3(c)Results of ANOVA.
Acknowledgement
Present work is supported by Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme(TEQIP-II)of Motilal Nehru National Institute of Technology Allahabad,Allahabad(U·P.),India financially and also by Invertis University,Bareilly,(U·P.),India.
杂志排行
Defence Technology的其它文章
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Defence technology:Special issue on“composite materials in defence technology”
- Thermal,corrosion and wear analysis of copper based metal matrix composites reinforced with alumina and graphite
- Age hardening process modeling and optimization of aluminum alloy A356/Cow horn particulate composite for brake drum application using RSM,ANN and simulated annealing
- Vertex angles effects in the energy absorption of axially crushed kenaf fibre-epoxy reinforced elliptical composite cones
- A review on machinability of carbon fiber reinforced polymer(CFRP)and glass fiber reinforced polymer(GFRP)composite materials
