Enterprise Asset-backed Securitization:Legal Structure Is Not So Vulnerable
2018-05-13HuangMengli
Huang Mengli
(School of International Financial Law of East China University of Political Science and Law,Shanghai,200042)
Abstract:The development of asset-based securitization in China is divided into two types:securitization of enterprise assets and securitization of credit assets.The securitization of credit assets adopts trust structure,in which the independence of trust property guarantees the isolation of bankruptcy risk between the underlying assets and the originator,the manager of the special scheme,investors and other investors.And the enterprise asset securitization can only choose the principal-agent relationship to build the relationship between the investor and the program manager in practice.Although the enterprise asset securitization does not have the independent advantage of the trust property stipulated by law,the principal-agent structure adopted by the asset management special scheme is not so vulnerable,compared with the organization form of the company,and can be to able to achieve the bankruptcy risk isolation to a certain extent.
Keywords: Asset-Backed Securitization; Special Scheme on Asset Management; Isolation of bankruptcy;the Principal-Agent Relationship
I.Current Situation of Asset-Based Securitization in China
The current asset management in the new era makes it possible for asset management institutions to compete and cooperate freely, so that banks,securities, insurance companies, fund firms, trust companies and other financial institutions could gradually open business in different ways for free and equal competition[1].
According to the regulatory system of asset-based securitization in China,the market is divided into four sets of systems:the People's Bank of China;the securitization of credit assets under the supervision of China Banking Regulatory Commission (CBRC);the securitization of enterprise assets under the supervision of China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC); the insurance asset-backed scheme under the supervision of China Insurance Regulatory Commission (CIRC);Asset-backed instruments for non-financial enterprises in the inter-bank bond market under the supervision of the Association of Inter-bank Traders.
At present,the asset securitization develops in two main directions:authorized by the“Banking Law”and“Trust Law”,the CBRC shall supervise and administer non-bank financial institutions such as banks and trusts,responsible for the issuance of practice licenses, the subsequent institutional supervision and business supervision.With the legal support of banks and trusts, the credit asset securitization under the supervision of CBRC can develop asset-based securitization with the advantages in both sides: The banking industry provides the abundant underlying assets that can generate future cash flows,and the trust companies act as SPV to achieve the bankruptcy isolation of the trust property.Therefore,the securitized products of credit assets can be used by the banking industry,the financial leasing industry and other financial institutions regulated by the CBRC.
However,when it comes to the securitization of enterprise assets under the supervision of China Securities Regulatory Commission(CSRC),in view of the underlying assets of its assets-based securitization,the service can only be limited to the enterprises.
This paper will focus on the securitization of credit assets under the supervision of CBRC and the securitization of enterprise assets under the supervision of the CSRC.
What is securitization of enterprise assets?Article 2 of the“Regulations on Management of Assets Securitization of Securities Companies and Fund Management Subsidiaries”expounds the concept of asset-backed securitization①Asset-based securitization refers to the business activities of issuing asset-backed securities on the basis of the cash flow generated by the underlying assets as the payment support and credit enhancement through structured means..According to this definition, the securitization of enterprise assets refers to taking the scheme of the enterprise's continuous and stable cash flow as the underlying assets,and the source of securities payment,mainly applicable for the industrial enterprises and other non-financial institutions.Article 4 of the Provisions specifies that a securities company or fund management company shall carry out the securitization businesses of assets through the establishment of a Special Purpose Vehicle(SPV).The CSRC could establish reliable SPV structure for the securitization of enterprise assets,only within its own supervision scope,which mainly includes the special asset-backed scheme established by securities companies or the subsidiaries of the fund management companies for assets securitization business,or other special purpose vehicles(SPV)approved by the CSRC.
The“Management Procedure for Clients Assets Management of Securities Companies”stipulates three types of assets management schemes initiated and established by securities companies②Conduct targeted asset management for single customers;Handle the business of collective asset management for multiple customers;Special purpose asset management for customers..The securitization of enterprise assets is a special asset management business for clients.Therefore,the SPV structure built in the securitization of enterprise assets belongs to the special asset-backed scheme in the special assets management scheme.
II.“Real Sale”and“Bankruptcy Isolation”in Asset Securitization
The two core functions that the asset securitization must have are: real sale and bankruptcy isolation,with which the legal structure could secure the stability and sustainability of the whole structure and the interests of investors.
The SPV is built to achieve these two main core functions.What is SPV?Teacher Hong Yanrong once defined SPV as a vehicle specifically set up in the securitization of assets, which could be used to purchase assets from the initiators,so as to possess and manage the underlying assets and achieve ABS issuance with the cash flow generated from the underlying assets as the payment guarantee.SPV serves at the core of assets securitization,which is closely related to the structure design of asset securitization and the realization of the two core functions[2].The SPV usually exists in the following forms:
(i)The SPV of the Company Form
When SPV appears in the form of a company organization, it is an independent personality in accordance with the law and has the ownership of property because the organization of a company is taken as a quasi-legal person.In the form of a company,the investor becomes the shareholder of the company, and the property invested by the shareholder constitutes the property of the company.The entity of the company,to a certain degree,could realize the bankruptcy isolation between the property of the company and the personal property of the shareholders.So when the investor(shareholder)goes bankrupt,based on the principle of corporate capital maintenance,the investor's creditors are often only required to apply for enforcement of shareholders'equity and may not require enforcement of corporate property.Therefore, to a certain extent, the organization form of the company can effectively ensure the risk isolation of collective funds,so that it would not be affected by the bankruptcy of the investors(shareholders)or the sponsors(managers).
In addition,as the restrictions necessary for financing is stipulated in the business license and articles of association within the form of the company,investors can easily assess the legal risk of assets securitization through information disclosure.But the SPV of the company form has its inherent limitations,such as double taxation, the high cost of the establishment of related organizational structure,the cumbersome procedures and so on.
(ii)The SPV in the Form of Partnership
Partnership is also one of the organizational forms of the SPV in the securitization of assets,but it is rarely used compared with the SPV of the company form,because partnership is usually divided into the limited partnership and the unlimited partnership.In the form of limited partnership,the limited partners shall bear limited liability to the partnership limited by their capital contribution, and the unlimited partners shall be jointly and severally liable for the partnership debts with their full assets.The investors in an unlimited partnership generally act as limited partners,or the originator as an unlimited partner.Since the partnership does not have an independent personality, it does not have ownership of the partnership property.When the partner goes bankrupt,it will have an impact on the capital pool and the partner debtor has the right to claim the enforcement of the partnership property.The form of the partnership is unable to achieve the bankruptcy isolation between partners (investors) and the underlying assets (partnership assets).In addition,the transfer of the shares of the partnership is subject to certain restrictions and requires the consent of other partners,which means that the share of assets held by investors, is restricted during transfer,subject to the consent of other investors.However,the issue may be resolved in advance in the partnership agreement.
(iii)The SPV in the form of trust
Compared with other organizational forms,the SPV in the form of trust is the most widely used and thoroughly risk isolation one.According to the law,the trust property is independent,independent of the trustee (the original shareholder),trustee(manager),and beneficiary (asset-backed securities investor).When these legal entities go bankrupt,their creditors may not apply for the enforcement of trust property,and the trust property shall not be mixed with any form of property of any entity.In addition, the establishment and operation of trust require fewer rules,reducing the cost of SPV establishment and is therefore widely used.
After understanding the several main forms of SPV,let's look at what can we achieve with the two core functions.It is necessary to understand the connotation of“real sale”and“bankruptcy isolation”of the SPV.
What is Real Sale?Real sale means that in the process of the transfer of assets,the initiator transfers the ownership of the underlying assets to the special scheme in the form of sale and transfers all the proceeds and risks related to the underlying assets to the SPV[3].After the completion of the underlying assets,the assets will be owned by the SPV,which makes that the initiator and the creditors are not entitled to exercise control or benefit over the underlying assets.After transferring the underlying assets to the SPV completely and effectively,the originator(the transferor)obtain the fair consideration for the future cash flow and the expected earnings collected in advance.Real sale is the first layer of risk isolation in the securitization of assets,which realizes the effective transfer of the ownership of the underlying assets and the risk isolation between the underlying assets and the originator.Therefore,real sale is the transaction between the originator and the SPV.In terms of law,through real sale the ownership of the underlying assets is fully transferred to the SPV,so as to isolate the underlying assets from the originator and prevent the risk of bankruptcy of the originator from being transferred to the SPV.
What is bankruptcy isolation? There are different views on bankruptcy isolation.Teacher Shen Zhaohui believes that bankruptcy isolation should be bankruptcy segregation between SPV and investors in asset-backed securities, which means that when investors holding asset-backed securities go bankrupt, their creditors cannot enforce the underlying assets under the SPV,which is not part of the investor's bankruptcy property.By contrast,the teacher Hong Yanrong believes that bankruptcy isolation breaks the transmission of the original equity owners and SPV,which is the bankruptcy isolation between the originator and the SPV.
III.Comparison of Risk Isolation Function of Different Forms of SPV between Credit Asset Securitization and Enterprise Asset Securitization
Because of the use of different structures of SPV for the securitization of credit assets and the securitization of enterprise assets, there are differences in the realization of the two functions of“real sale”and“bankruptcy isolation”.
(i)Specific Structure of Securitization of Credit Assets and Securitization of Enterprise Assets
At present,the main structures of securitization of credit assets and securitization of enterprise assets in China are as follows:1)Securitization of credit assets is usually adopted the following methods:the bank (the underlying assets)+the trust company(SPV);2)Strategy of the securitization of enterprise assets under the supervision of CSRC:to bypass the trust and by way of entrusted agent.
Specifically,in the securitization of credit assets with trust as SPV,the underlying assets are the credit assets of the bank,the credit assets as the underlying assets and the repayment of the borrower as the guarantee of payment.In the securitization of credit assets, the trust companies act as SPV and, as mentioned above,make full use of the independence advantages of trust property in the trust system.For example, the originator Bank C signed a trust contract with the trust company and Bank C,as the originator (as well as a loan service institution)transferred the credit assets to the trust company through the assignment of creditor's rights,for real sale and to build a commercial trust.Based on the creditor's rights, the trust companies shall issue asset-backed securities to investors, and the investors shall be entitled to the securities after the investors subscribe for asset-backed securities.The trust company shall pay the investor's subscribed funds to the originator,as the consideration for the assignment of the creditor's rights.
But the securitization of enterprise asset is confronted with a difficult problem: which commercial organization law should be used to build SPV? A trust company is a financial institution licensed and supervised by the CBRC,and is not subject to the supervision of the CSRC.Without the support of the trust system, the enterprise asset securitization under the supervision system of the CSRC, does not have the independence of trust property,and the trust company won't be used as SPV.As mentioned above,there will be a question of double taxation in practice, if the SPV of the company form is taken,because the company is also a tax entity.In the form of partnership organization,the property (the underlying assets of the securitization of enterprise assets) cannot be transferred to the SPV,which is still the property of the partners and cannot be isolated from bankruptcy,which makes that the asset risk is even greater.Therefore, the securitization of enterprise assets under the supervision of CSRC can only rely on the principal-agent system in Civil Law,which means the investors as the truster,the special scheme as the trustee and the legal relationship between the investors and the special scheme as principal-agent relationship.
In the enterprise asset securitization scheme which the author has come into contact with in practice,the statement of the scheme issued by the securities company often agrees that“the purpose of the asset-backed securities issuance is as follows:the special scheme set up by the manager aims to accept the trust of the subscribers,and to purchase the underlying assets with the subscription funds in accordance with the provisions of the special scheme document and to pay the holders of asset-backed securities with the returns of the special scheme generated by the assets”.The special prospectus clearly specifies the relationship between the“The manager accepts the Subscriber's trust”,and there is a principal-agent relationship between the SPV manager and the subscriber.
It can be seen that in the trust SPV and the special asset-backed scheme,at the asset end real sale is achieved through the assignment of creditor's rights,that is,the originator transfers the ownership of the underlying assets just in the form of transfer.
The main difference between the trust SPV and the special asset-backed scheme lies in the capital end, namely, how to deal with the relationship between the SPV and the investors.In the Trust SPV,the investors act as trustee beneficiaries and the scheme manager as the trust managers;however,in the special asset-backed scheme,the fund can only be managed by the investors entrusting the manager through the agreement.
(ii)Legal Entity Status and Legal Relationship in Securitization of Credit Assets and Enterprise Assets
Before analyzing the different types of SPV risk-isolation function,we should firstly figure out the status of the legal entities and the relations between the different entities.
In the securitization of credit assets,we firstly figure out the flow of assets and funds,so as to determine what trust property is.In the securitization of credit assets,the underlying assets are the bank credit assets,and the funds are the consideration paid by the holders of asset-backed securities for the acquisition of securities, i.e.the total amount of investment.From the perspective of the flow of assets,the assets of the securitization of credit assets have gone through the originator to the trust managers(the scheme manager).After the issuance of credit assets,the principal and interest paid by the debtor will be taken as the source of payment,classified as the trust property and used to pay the securities interest to the holders of the securities.From the direction of capital flow,investors in the securitization of credit assets pay the funds to the trustee,who then shall pay the originator as the consideration for the credit assets.It is therefore clear that trust property is credit assets in the securitization of credit assets.
As mentioned above,in the securitization of credit assets, the trust of property rights is established by the originator through the assignment of creditor's rights.As there is no recognition of dual ownership in China, the ownership of the trust property is not clearly defined.
At this time,there may be two legal relations that may exist at the end of the asset transfer:one is the transfer of assets in the Property Law,where the ownership of the assets is transferred to the trustee(the scheme manager) in accordance with the Property Law,and the trustee has the ownership of the underlying assets.However,with the ownership of the underlying assets belonging to the trustee,if the trust is set again, the trustee shall entrust the underlying assets to the self-established trust as the trustee.At this point,the structure of the trust SPV in the securitization of credit assets becomes: the principal is the scheme manager;the trustee is a scheme manager;the beneficiary is the asset-backed securities holder with the trust property as the underlying asset.The second legal relation is the commercial trust mentioned by scholars.And one of its characteristics is that the trustee shall pay the consideration when receiving transfer of the trust property from the truster[4].When a property rights trust is initiated and established by the commercial bank as the truster,it is essentially the establishment of a trust,despite of the assignment of creditor's rights; namely, the originator as the trustee, the scheme manager as the trustee, the holder of asset-backed securities as the beneficiary and the underlying assets as the trust property.At this point,there is no such assignment of property rights in essence as it looks formally,but a trust established with the creditor's rights as the trustee of the other party of the commercial trust,so as to acquire the consideration of the trust property.The author prefers the second understanding of the legal relationship,in which with the underlying assets,the bankruptcy isolation is achieved between the trust property(the credit assets) and the originator based on the establishment of trust, in accordance with the provisions by law on the independence of trust property,instead of being based on meeting the real sale conditions.
In the securitization of enterprise assets,the legal relationship and the status are still analyzed in accordance with the above mentioned thinking order,to start with the funds and assets.At this point,the asset is the underlying assets of an enterprise or other non-financial institution,and the capital remains the consideration for the holder of the securities.Unlike the securitization of credit assets, the underlying assets are transferred directly to the special asset-backed scheme through the assignment of creditor's rights.According to the provisions of law in China,in the securitization of credit assets,since the underlying asset exists as an independent property,for which there is no clear ownership required.However,in the securitization of enterprise assets,there must be an ownership subject of the underlying assets,i.e.the ownership of the underlying assets in the asset-backed scheme.The manager takes care of the underlying assets on its behalf.At the capital end,the investors entrust the manager to operate the fund,that is,the securities company shall specially manage the collective fund for the customer,which shall be invested by the manager into the special asset-backed scheme.Within these legal entities,there is a principal-agent relationship between the investors and the scheme manager,with investors as truster and the manager as trustee;In addition,the originator is the assignor of the creditor's rights,and the special asset-backed scheme as the bond assignee vehicle;It is the investment of the collective fund to the special scheme by the manager,that links the two legal entities together.Therefore, in the securitization of enterprise assets, based on the special asset management of the securities company,the order of legal relationships goes as follows:the principal-agent relationship-the investment relationship (which may occur simultaneously or successively with the assignment of the creditor's rights)-the distribution relationship.However,in the trust relationship,since the trust property rights are based on trust property,the order of legal relationship is the trust principal-agent relationship(based on the provisions of law in China)-the trust benefit relationship(i.e.distribution relationship).
In short,based on the legal arrangement of the form of trust,the independence of trust property,and the vague stipulation of the ownership of trust property in Trust Law in China, there are great differences between the entities status and the legal relationship respectively in the securitization of credit assets and the securitization of enterprise assets.
(iii) Comparison of the Bankruptcy Isolation between the Asset-Based Securitization and Securitization of Credit Assets
The bankruptcy isolation functions on a basis of the commercial organization law to build the SPV,which is based on the function of the assets segmentation of the commercial organization law.A simple comparison can be made between the SPV and corporate form assets segmentation:
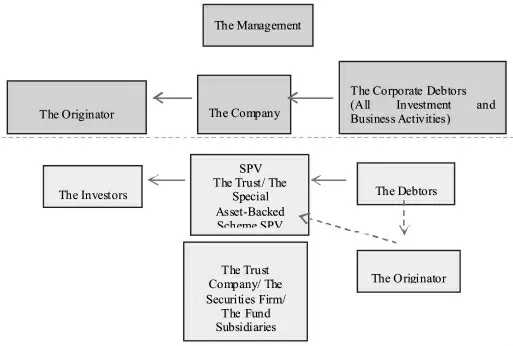
The solid line in the chart above represents the direction of risks.In both forms of SPV,the risk is transferred to the SPV when the debtor is unable to fulfill obligation,which will be ultimately borne by the investors.In the organizational structure of a company,the risk is borne by the company and then transferred to the shareholders of the company,when the company fails to operate or any defaults of the company's debtors.
For the two forms of SPV,it is obviously unable to isolate the bankruptcy risk of the debtors,where the risk of underlying assets exists.Moreover,there is no such discussion mentioned here about the bankruptcy risk of the SPV itself.This paper mainly discusses the impact on the SPV from the bankruptcy risk of investors and that of the scheme manager.
From the perspective of the company as an entity,the impact of the bankruptcy risk of managers on the company,to the greatest extent,will be on the business operations,instead of resulting in the direct reduction of corporate assets.In the event of bankruptcy of the original shareholders of the Company, due to the limited liability of the shareholders and the obligation to pay the capital contribution,the part of the equity may be transferred or auctioned by the bankruptcy administrator,but no matter how the shareholders change,there is no impact on the company's capital.To sum up,the entity is largely insulated the risk of bankruptcy for managers and shareholders.
According to one-to-one correspondence between the subject of the company and the SPV,in the securitization of credit assets, it has been illustrated that the above mentioned credit SPV achieves the bankruptcy isolation for the truster,namely the originator,with respect to the provisions stipulated in Trust Law on the independence of the trust property,instead of by the real sale.On the basis of the independence of the trust assets,we can also concluded the result of bankruptcy isolation for the SPV trustee (namely the scheme manager),and the beneficiary (namely the Investors).The trust property will not be affected even when the three entities go bankrupt,which provides guarantee for investor's income.
However,in the special asset-backed scheme of enterprise, the transaction structure is usually designed as: 1) By signing of a“Subscription Agreement”with the scheme manager,the subscriber obtains the asset-backed securities and becomes the holder through entrusting the subscription fund in the form of special assets management to the scheme manager,who shall be responsible for establishing and managing the special plan.2)The manager shall use the funds for the purchase of underlying assets,as agreed in the stipulations of the“Agreement on Purchase and Sale of Assets”signed with the originator.In addition, under the rights and obligations of the parties in the statements of the scheme,it is often agreed that the obligations of the asset-backed securities holder include the asset-backed securities holder during the term of the special scheme,shall not require the manager to redeem the acquired asset-backed securities acquired or transferred.
It is possible to see that in the special asset-backed scheme,the contracts or agreements are used to achieve“real sale”and“bankruptcy isolation”.“Agreement on Purchase and Sale of Assets”shall be signed between the scheme manager and the originator to achieve the purpose of the real sale;The investor's obligations are stipulated in the statements of the scheme in order to achieve the isolation of bankruptcy risk for the investor,which agrees that the asset-backed securities holder shall not require the manager to redeem his or her asset-backed securities acquired or transferred;In order to meet the bankruptcy isolation of the manager(securities compa ny/fund subsidiary),the CSRC requires a review of whether the manager holds an equity interest in the originator,the originator shares an equity interest in the manager,or whether there is any other significant interests between the two parties.The requirement is essentially to lower the risk of bankruptcy of the asset-backed securities themselves,instead of a measure of bankruptcy isolation.
Real sale may achieve the purpose of isolating the bankruptcy risk for the originator.However,when some investors go bankrupt, the bankruptcy administrator's demand for redemption of asset-backed securities does not have the same strong effect as the corporate entities against shareholders'withdrawal from capital;However,it will not affect the entire special fund management business to a certain extent, if the bankruptcy administrator calls for the transfer of asset-backed securities, and within the prescribed number of persons.In the second point of this section,the bankruptcy isolation of the scheme manager has been explained.Since the manager does not hold the underlying assets,the effect of its bankruptcy on the whole SPV,will be spread on the operation of the asset-backed scheme,and even the duration of the SPV.But it is an inevitable risk even in corporate entities.
IV.Conclusion
Due to its incomparable regulatory advantages,there is a stable structure of risk isolation in the securitization of credit asset.But even for the special asset-backed scheme set up with the principal-agent relationship, the whole legal structure is not so vulnerable.
However,the ambiguity of the supervision in the Trust Law leads to huge differences between the two structures.And the regulatory arbitrage caused by some trust licensing business should be taken into consideration.Since no department or institution should monopolize a form of business organization,trust,just like the form of the company,should be taken good use for commercial activities,without being limited in the financial licensing business.
杂志排行
中阿科技论坛(中英文)的其它文章
- 中国天眼模型结构的技术探究
- SWOT Analysis and the Development Strategy of Goji Berry Industry in Ningxia
- Technical Research on Model Structure of Chinese“Sky Eye”
- 宁夏枸杞产业的SWOT 分析与发展策略
- The Potentials,Challenges and Path for Achieving Science and Technology Cooperation between China and Arab States under the Background of the Belt and Road Initiative
- Study on the Law of the Development Height of Water Flowing Fractured Zone in Shaanxi Guojia River Coal Mine
