一氧化氮的海洋生物地球化学研究进展❋
2018-03-16刘春颖姜源庆李培峰简慧敏张升辉
刘春颖, 田 野, 姜源庆,李培峰, 简慧敏, 张升辉
(1.中国海洋大学海洋化学理论与工程技术教育部重点实验室, 化学化工学院, 山东 青岛 266100;2.国家海洋局 烟台海洋环境监测中心站,山东 烟台 264006)
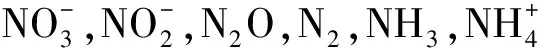
1 海洋中NO的测定方法研究
由于NO的不稳定性、易逸性、低含量,目前关于海水中NO测定方法的报道不多(见表1),主要有电化学方法[11-13],荧光法[14-16]和化学发光法[17-19],这些方法可用于NO的光解产生和生长调控作用机制的研究。而能用于现场NO观测的只有吹扫-捕集荧光法[19]和吹扫-捕集化学发光法[17-18],可分别用于近海和大洋的NO分布和产生速率的观测。吹扫-捕集化学发光法也逐渐从大体积开放式变成小体积密闭式。除了测定方法,NO的采样过程对测定结果有一定的影响,用传统的Niskin采水器采样可能有一定的误差,用水泵直接采水测定更为准确[18]。

表1 海水中NO的测定方法
2 海洋中NO的来源与分布
海水中NO的产生途径有光化学过程[22]、大气交换[23]、热过程[24]、生物学过程[25]含硝化与反硝化过程[2]、化学过程等。目前关于海洋NO的确切来源和转化还不清楚[26],研究较多的是光降解过程,微生物硝化与反硝化过程和浮游植物生长过程(见图1)。

图1 NO的海洋生物地球化学过程[1-3,11-14]Fig.1 Marine biogeochemistry process of nitric oxide
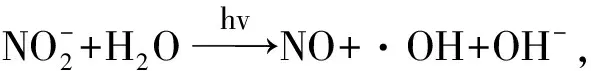

海洋中生物体释放NO的研究主要集中在植物上。Morrall等[32-33]研究表明,热带海洋中银莲花的一氧化氮合成酶(NOS)活性明显受到环境温度、铜离子浓度的影响。在深海或表面水的大量浮游植物(藻类)生长处,因缺氧条件而产生NO[17]。Kim等[34-35]观测到Chattonellamarina,C.ovata和Heterosigmaakashiwo三种海洋赤潮藻释放NO的现象。刘春颖等[1]对海洋微藻Platymonassubcordiformis、Skeletonemacostatum、Gymnodiniumsp.和Chaetoceroscurvisetu藻液中NO的浓度和来源进行了初步研究,结果表明,不管是赤潮藻还是非赤潮藻体系都发现NO的客观存在,浓度大约在10-8~10-9mol/L;NO是微藻生长状况的信息因子,也是微藻应激反应的信号分子;藻密度达最大值之前,伴随着NO浓度曲线也出现一个峰值,此现象为赤潮化学预报研究提供了实验基础。除了实验室的观测,在野外藻类培养池中也检测到NO的存在[20,34-35]。此外,海洋动物产生NO的研究也开始有报道。Jeong等[37]发现潮间带桡足类虎斑猛水蚤受到免疫挑战时可诱发体内的NOS;Xian等[38]检测到对虾不同部位血细胞中NO浓度有所不同。
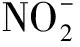
3 海洋中NO的迁移与转化

4 NO在海洋生态系中的作用
研究表明,生物体不仅自身会产生NO,同时会对外界的NO做出不同的响应,当然这依赖于浓度的大小[20, 43-45],并有种间差异。Yoshihara等[46]和Nagase等[11]报道绿藻在吸收利用炉气时,能吸收其中的NO,在NO与炉气的体积比为(100~300)×10-6的气体中,绿藻能正常生长。从20世纪80年代后期开始,由于生物化学和分子生物学的研究发展,逐渐发现和证实NO是生物体内一种重要的信使分子和效应分子,在生命过程中起着举足轻重的作用。外源NO对海洋浮游植物的生长有显著的影响,它可能是浮游植物(藻类)生长的一种信息因子[8, 11, 46-47];NO能参与调节微藻的其他生理活动[48-50];并能在一定程度上抵御非生物的生长胁迫[51],包括金属,非金属,紫外照射,农药等的胁迫。NO在水产养殖生物病害方面具有抵抗病原体的作用[7];Chen等[52]报道了热带海参体内NO参与调节钙调素的证据;越来越多的证据表明,NO在海洋生态系扮演着重要的角色。
5 NO在大气中转化与作用
在平流层臭氧光化学过程中,NO通过反应NO+O3→NO2+O2直接破坏臭氧;另一个反应NO2+O→NO+O2不仅使大气中氧原子减少,不利于O3形成,同时还产生NO,进一步破坏O3。另一方面,平流层NO2还可以光化分解为NO和氧原子。NOx在对流层中的化学行为较为复杂,NO和NO2可转化为HNO2、HNO3、HO2NO2、NO3、N2O5和有机硝酸盐,它们当中大部分分子又被光解和热分解为NOx。观测表明,NO和NO2主要转化为HNO3、过氧乙酰硝酸酯(Peroxyacetyl Nitrate,PAN)和颗粒物硝酸盐。HNO3在白天很快被光解,在晚上能和NO2生成N2O5,而N2O5的湿清除可能是NOy(NOy=NOx+HNO2+HNO3+HO2NO2+NO3+2N2O5+PAN+颗粒物硝酸盐)的一个重要的汇。HNO3再以其高度水溶性溶入雨滴降落地面,也可能粘结在气溶胶或悬浮颗粒上,最后干降于地表,所以NOx最终的汇是地面或地面水系。NOx既能生成二次无机气溶胶,也能生成二次有机气溶胶(SOA)[53]。人类活动排放的CH4、CO、NMHC等气体和大气中的OH和O2反应生成过氧基,这些过氧基使大气中的NO转化为NO2。NO2光解生成O原子,基态氧原子和O2反应生成O3,诱发城市光化学烟雾。工业革命后对流层中O3浓度每年以2%~4%的速度增长,研究发现,这主要是由于人类活动排放的NOx所致的。由于NOx在对流层大气化学过程中的重要地位,所以近些年来对NOx在对流层中的分布及变化规律进行了许多测量和研究。观测表明,白天NOy的15%~30%是以(HNO3+PAN+NO3(p))形态存在的,夜晚90%以上的NOy是以(NO+NO2)的形态存在的。白天硝酸占有较高的比例,是因为NOx的光化学反应所致;在夜间有雾的情况下,40%的NOy是以硝酸盐的形态存在的。大气中NOx的浓度取决于NOx的排放与输送,在城市和工业区主要是人为的排放,浓度范围为1×10-9~10×10-9(v/v);沿海地区为0.1×10-9~1.0×10-9(v/v);在没有受到人为影响的远海和极地地区NOx的浓度为0.001×10-9~0.01×10-9(v/v)。洋面上NOx的浓度从海平面到平流层顶随着高度的增加而增大,这与陆地上NOx垂直梯度的变化正相反。夏季NOx的寿命主要由NO2和OH的反应所决定,且随着NOx浓度的变化而变化,同时也取决于NOx和NMHC的比值。当NOx的浓度在1×10-9(v/v)时,NOx的寿命约为0.5天,冬季NOx的寿命很不确定,约为1~2天[54]。卫星返回的数据可以检测到大气中NO2浓度变化,目前陆地上空的观测较多,而海洋上空的观测还未深入开展。
6 结论
综上所述,NO对全球气候与环境有着重要影响,海洋生态系释放NO越来越受到人们的重视;此外,NO在海洋生态系中扮演着重要的角色,对海洋生物生长具有重要的调控作用。然而NO的海洋生物地球化学研究刚刚起步,许多重要的科学问题和研究手段尚待解决。
(1)建立起适合于现场观测的易操作、高灵敏、低检出限的NO分析方法,才能广泛开展NO的海洋生物地球化学研究。目前还没有一套大家认可的NO分析方法。
(2)随着人们对NOx危害的重视以及化石燃料的减排,生态系统释放NO的问题越来越受到人们的关注。开展海洋尤其是近岸海域释放NO的过程及机制研究,才能完善海洋氮循环的研究,进一步对全球氮的收支平衡做出定量评估,为应对全球气候和环境变化提供参考数据。
(3)开展海洋生态系中NO的产生途径、释放速率及浓度范围,才能进一步认识NO的生态效应。
(4)深入研究NO对海洋生物生长,抗逆抗病等作用规律和机制,才能认识NO在海洋生态系中的地位与作用。
[1] 刘春颖. 海水中一氧化氮对浮游植物生长影响的规律研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2006.
Liu C Y. Studies on the Effect Laws of Nitric Oxide on the Phytoplankton Growth in Seawater [D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2006.
[2] Law C S. Air-Sea Transfer: N2O, NO, CH4, CO. Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences [M]. San Diego, USA: Academic Press, 2001.
[3] Huang Y, Li D. Soil nitric oxide emissions from terrestrial ecosystems in China: A synthesis of modeling and measurements [J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 7406.
[4] Leshem Y Y. Nitric oxide in biological systems [J]. Plant Growth Regulation, 1996, 18(3): 155-159.
[5] Yu M, Lamattina L, Spoel S H, et al. Nitric oxide function in plant biology: a redox cue in deconvolution [J]. New Phytologist, 2014, 202(4): 1142-1156.
[6] Corpas F J, Leterrier M, Valderrama R, et al. Nitric oxide imbalance provokes a nitrosative response in plants under abiotic stress [J]. Plant Science, 2011, 181(5): 604-611.
[7] 姜国建, 于仁诚, 周名江. 活性氮中间体和一氧化氮合成酶系统在水产养殖生物病害防御中的作用[J]. 海洋科学, 2006, 30(3): 90-93.
Jiang G J, Yu R C, Zhou M J. Role of reactive nitrogen intermediates (RNIs) and nitric oxide synthase in disease resistance of maricultured organisms[J]. Marine Sciences, 2006, 30(3): 90-93.
[8] Zhang Z, Lin C, Liu C, et al. Study on patterns and chemical features of NO effect on marine phytoplankton growth[J]. Science China (Chemistry), 2005, 48(4): 376-384.
[9] Chen J, Wu F H, Xiao Q, et al. Diurnal variation of nitric oxide emission flux from a mangrove wetland in Zhangjiang River Estuary, China [J]. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2010, 90(4): 212-220.
[10] Martens-Habbena W, Qin W, Horak R E A, et al. The production of nitric oxide by marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea and inhibition of archaeal ammonia oxidation by a nitric oxide scavenger [J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 17(7): 2261, 2274.
[11] Nagase H, Yoshihara K, Eguchi K. Uptake pathway and continuous removal of nitric oxide from flue gas using microalgae [J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2001, 7(3): 241-246.
[12] 罗超, 周秀骥. 氮氧化物(NOx)在对流层中的收支与循环的研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 1993(1): 92-99.
Luo C, Zhou X J. The study of the cycle of nitrogen oxides in the troposphere [J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 1993 (1): 92-99.
[13] Schreiber F, Polerecky L, De B D. Nitric oxide microsensor for high spatial resolution measurements in biofilms and sediments [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 80(4): 1152-1158.
[14] Olasehinde E F, Takeda K, Sakugawa H. Development of an analytical method for nitric oxide radical determination in natural waters [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(16): 6843-6850.
[15] 丰卫华, 刘春颖, 杨桂朋, 等. 海水中一氧化氮的化学发光法测定[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(6): 93-99.
Feng W H, Liu C Y, Yang G P, et al. Chemiluminescence detection of nitric oxide in seawater [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2011, 33(6): 93-99.
[16] Liu X, Shang L, Sun Z, et al. Direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin in dimethyldioctadecyl ammonium bromide film and its electrocatalysis to nitric oxide [J]. Journal of Biochemical & Biophysical Methods, 2005, 62(2): 143-151.
[17] Ward B B, Zafiriou O C. Nitrification and nitric oxide in the oxygen minimum of the eastern tropical North Pacific [J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1988, 35(7): 1127-1142.
[18] Lutterbeck H E, Bange H W. An improved method for the determination of dissolved Nitric Oxide (NO) in seawater samples [J]. Ocean Science Discussions, 2015, 12(3): 959-981.
[19] Liu C Y, Zhao M, Ren C Y, et al. Direct measurement of nitric oxide in seawater medium by fluorometric method [J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 37(10): 1463-1467.
[20] Zhang Z B, Xing L, Wu Z Z, et al. Discovery of nitric oxide in marine ecological system and the chemical characteristics of nitric oxide[J]. Science in China Series B: Chemistry, 2006, 49(5): 475-480.
[21] Zafiriou O C, Mcfarland M. Nitric oxide from nitrite photolysis in the central equatorial Pacific [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 1981, 86(C4): 3173-3182.
[22] Zafiriou O C, True M B. Nitrate photolysis in seawater by sunlight [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1979, 8(1): 9-32.
[23] Zafiriou O C. Marine organic photochemistry previewed [J]. Marine Chemistry, 1977, 5(4-6): 497-522.
[24] 杨桂朋. 海水中自由基的产生过程及其化学反应[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1990 (1): 70-76.
Yang G P. Production of free radicals in seawater and their chemical reactions [J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1990 (1): 70-76.
[25] Lipschultz F, Zafiriou O C, Wofsy S C, et al. Production of NO and N2O by soil nitrifying bacteria [J]. Nature, 1981, 294: (641-643.
[26] 刘春颖, 张正斌, 邢磊, 等. 一氧化氮的海洋生物地球化学[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 34(sup.): 16-22.
Liu C Y, Zhang Z B, Xing L, et al. Marine biogeochemistry of nitric oxide [J]. Periodcial of Ocean University of China, 2004, 34(sup. ): 16-22.
[27] 李培峰, 李文帅, 刘春颖, 等. 水体中亚硝酸盐的光降解[J]. 环境化学, 2011, 30(11): 1883-1888.
Li P F, Li W S, Liu C Y, et al. The photodegradation of nitrite in water [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2011, 30(11): 1883-1888.
[28] Riley J P, Skirrow. Chemical Oceanography [M]. London: Academic Press, 1983.
[29] Voss M, Bange H W, Dippner J W, et al. The marine nitrogen cycle: recent discoveries, uncertainties and the potential relevance of climate change [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2013, 368(1621): 91-97.
[30] Watmough N J, Butland G, Cheesman M R, et al. Nitric oxide in bacteria: synthesis and consumption [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1999, 1411(2-3): 456-474.
[31] Ren T, Roy R, Knowles R. Production and consumption of nitric oxide by three methanotrophic bacteria [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2000, 66(9): 3891-3897.
[32] Morrall C E, Galloway T S, Trapidorosenthal H G, et al. Characterisation of nitric oxide synthase activity in the tropical sea anemone Aiptasia pallida [J]. Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology Part B Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 2000, 125(4): 483-491.
[33] Morrall C E, Trapido-Rosenthal H G, Knap A H, et al. Development of nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase as ecotoxicological biomarkers in the tropical marine environment [J]. Marine Environmental Research, 1998, 46(1): 429-432.
[34] Kim D, Yamaguchi K, Oda T. Nitric oxide synthase-like enzyme mediated nitric oxide generation by harmful red tide phytoplankton,Chattonellamarina[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2006, 28(6): 613-620.
[35] Kim D, Kang Y S, Lee Y, et al. Detection of Nitric Oxide (NO) in marine phytoplankters [J]. Journal of Bioscience & Bioengineering, 2008, 105(4): 414-417.
[36] Tang X, Chen J, Wang W H, et al. The changes of nitric oxide production during the growth ofMicrocystisaerugrinosa[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(12): 3784-3792.
[37] Jeong C B, Kang H M, Seo J S, et al. Identification and molecular characterization of Nitric Oxide synthase (NOS) gene in the intertidal copepodTigriopusjaponicas[J]. Gene, 2016, 577(1): 338-345.
[38] Xian J A, Guo H, Li B, et al. Measurement of intracellular Nitric Oxide (NO) production in shrimp haemocytes by flow cytometry [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2013, 35(6): 2032-2039.
[39] 薛超. 黄渤海和胶州湾一氧化氮的分布、通量及生产速率的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.
Xue C. Distribution, Flux and Release rate of Nitric Oxide in China’s Coastal Waters [D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012.
[40] Lewis R S, Deen W M. Kinetics of the reaction of nitric oxide with oxygen in aqueous solutions [J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 1994, 7(4): 568-574.
[41] Carpenter L J, Nightingale P D. Chemistry and release of gases from the surface ocean [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2015, 115(10): 4015.
[42] IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [R]. Sweden Stockholm:American Geophysical Union, 2013.
[43] Zheng X X, Wang M X, Wang Y S, et al. Mitigation options for methane, nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emissions from agricultural ecosystems [J]. Advances in Atmosphere Sciences, 2000, 17(1): 83-92.
[44] Beligni M V, Lamattina L. Nitric Oxide: A non-traditional regulator of plant growth [J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2001, 6(11): 508-509.
[45] Yamasaki H, Sakihama Y. Simultaneous production of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite by plant nitrate reductase: in vitro evidence for the NR-dependent formation of active nitrogen species [J]. FEBS Letters, 2000, 468(1): 89-92.
[46] Yoshihara K I, Nagase H, Eguchi K, et al. Biological elimination of nitric oxide and carbon dioxide from flue gas by marine microalga NOA-113 cultivated in a long tubular photobioreactor [J]. Journal of Fermentation & Bioengineering, 1996, 82(82): 351-354.
[47] Zhang Z, Lin C, Liu C, et al. The effect of nitric oxide on the growth of marine phytoplankton [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2003, 2(2): 185-188.
[48] Zhang Z B, Liu C Y, Wu Z Z, et al. Detection of nitric oxide in culture media and studies on nitric oxide formation by marine microalgae[J]. Medical Science Monitor International Medical Journal of Experimental & Clinical Research, 2006, 12(2): 75-85.
[49] Liu C Y, Zhang Z B, Chen X R. Mutual effects of nitric oxide and iron on the growth of marine algae [J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2005, 24(5): 100-109.
[50] Liu C Y, Kieber D J, Yang G P, et al. Evidence for the mutual effects of dimethylsulfoniopropionate and nitric oxide during the growth of marine microalgae[J]. Nitric Oxide, 2014, 42: 54-61.
[51] Lobysheva I I, Vanin A F, Sineshchekov O A, et al. Nitric oxide modulates phototaxis ofChlamydomonasreinhardtii[J]. Biophysics, 1996, 41(2): 538-541.
[52] Li P, Liu C Y, Liu H, et al. Protective function of nitric oxide on marine phytoplankton under abiotic stresses [J]. Nitric Oxide Biology & Chemistry, 2013, 33(9): 88-96.
[53] Chen T, Ren C, Li W, et al. Calmodulin of the tropical sea cucumber: gene structure, inducible expression and contribution to nitric oxide production and pathogen clearance during immune response [J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 2015, 45(2): 231-238.
[54] Presto A A, Miracolo M A, Donahue N M, et al. Secondary organic aerosol formation from high-NOx photo-oxidation of low volatility precursors: n-Alkanes [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(6): 2029-2034.
