基于文献计量分析的蒿属植物研究进展
2017-12-22陈林宋乃平王磊杨新国李学斌苏莹李月飞
陈林,宋乃平*,王磊,杨新国,李学斌,苏莹,李月飞
(1.宁夏大学西北退化生态系统恢复与重建教育部重点实验室,宁夏 银川 750021;2.宁夏大学西北土地退化与生态恢复国家重点实验室培育基地,宁夏 银川 750021;3.宁夏大学科学技术处,宁夏 银川 750021)
基于文献计量分析的蒿属植物研究进展
陈林1,2,宋乃平1,2*,王磊1,2,杨新国1,2,李学斌3,苏莹1,2,李月飞1,2
(1.宁夏大学西北退化生态系统恢复与重建教育部重点实验室,宁夏 银川 750021;2.宁夏大学西北土地退化与生态恢复国家重点实验室培育基地,宁夏 银川 750021;3.宁夏大学科学技术处,宁夏 银川 750021)
为深入了解蒿属植物相关研究的全球状况和前沿动态,客观反映相关研究国家、机构和个人在该研究方面的科学能力和影响力,采用Web of Science核心合集数据库中1986-2016年间收录的有关蒿属植物研究的相关文献,基于信息计量学分析方法进行了统计分析。结果表明,关于蒿属植物全球发文量总体呈上升趋势,中国的发文量居榜首,其次为美国,但在国际合作水平来看,美国的合作贡献最大,与中国有着密切合作关系的是英国。中国科学院占据总发文量、一作总数和一作被引次数的首位,香港大学在总被引用次数和一作被引次数方面排名最高。该研究方面发文的主要期刊有Planta Medica,Phytochemistry,Journal of Natural Products等,平均被引次数最高的是顶级期刊Nature。从学科分布来看,植物科学、化学和药理学/配药学位居相关研究的前三;从类别来看,理学占排名前10学科的50%;从科学层次来看,基础和技术科学占比较大,工程科学的相关发文量有待提高。香港大学的Sy在黄蒿提取物方面的系列研究具有较高的影响力,西班牙瓦伦西亚大学Marco和北京大学Wen两位学者的相关研究被引频次较高。在研究前沿趋势方面,蒿属植物的化学成分及其医药用途方面是研究热点。
蒿属植物;Web of Science;文献计量分析;Citespace;研究进展
蒿属(Artemisia)属于菊科(Compositae)春黄菊族(Anthemideae)蒿亚族(Artemisiinae)[1-2],是该族中最大的属之一[3-5],为一、二年生或多年生草本,少数为半灌木或小灌木,常有浓烈的挥发性香气[6],在全世界约有380种,我国分布有180余种和44个变种[7]。蒿属植物分布很广,主要分布在北半球,且多数集中在亚欧大陆,而在南半球鲜有分布[8-9],很多蒿属植物对生物或非生物因子胁迫具有良好的抗性[1],在温带和热带山区、草原、荒漠、高山和亚高山草原等地区均有分布,多成为干旱半干旱地区的优势种。在食物、医药、牧草、装饰等方面具有较高的经济价值[9],为中医药以及民间常用药材[10]。自1972年从该属植物黄花蒿(Artemisiaannua)中分离出抗疟有效单体——青蒿素,研发出我国首创的抗疟新药[11],并在有关研究获得诺贝尔奖[12]和国家最高科学技术奖[13]以来,对蒿属植物化学成分的研究日趋广泛和深入。
近年兴起的文献计量学(Bibliometrics)研究方法为客观的可视化综述研究提供了全新的支撑[14],其概念由英国情报学家Pritchard[15]于1969年提出,是一种基于数理统计的定量分析方法[16-17]。文献计量分析可在某一领域内系统地评估科研结果的相对重要程度,预示该领域近一段时期的发展方向,表征该项研究的分布情况[18]。近年来,知识图谱作为科学计量学的新方法和新领域在我国勃然兴起[19],其以显著的客观性、定量化、模型化的宏观研究优势已被不少学科采用[20]。Citespace是一款应用于科学文献中识别并显示科学发展新趋势和新动态的软件,它能够通过分析文献的引用关系,有效地找出一个学科发展过程中产生关键影响的文献,显示一个学科或知识域在一定时期发展的趋势与动向,形成若干研究前沿领域的演进历程[21],继而发现新兴的分支学科。所绘制的知识图谱由于其“一图谱春秋,一览无余;一图胜千言,一目了然”的优势特征得到了广泛应用[19,22-25]。
针对全球蒿属植物研究热点和相关研究论文数量快速增加,目前对该方面的研究态势进行较为全面和系统的定量分析还未见相关报道,本研究基于信息计量学分析方法,利用Citespace V工具对全球蒿属植物相关研究的文献进行计量分析,以便准确掌握不同时期内容热点、研究现状和前沿动态,有助于研究者了解该领域在全球发展的情况,廓清研究知识基础,明确未来的学科发展和研究方向,旨在为国内外该领域的科研工作者和管理者提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 数据来源
Web of Science数据库是由美国科技信息所(Institute for Scientific Information,ISI)推出的引文索引数据库,是目前提供引文回溯数据最深的数据库,所收录的文献覆盖了全世界最重要和最有影响力的研究成果,已成为国际公认进行科学统计与科学评价的主要检索工具[18]。本研究以Web of ScienceTM核心合集数据库为数据源,采用基本检索方式,以“Artemisia”为检索主题,检索时间跨度为1986-2016年,数据检索时间为2017年1月19日,共检索文献790篇,其中首篇论文出版发表于1987年。
1.2 分析方法
1.2.1文献计量方法 本研究利用“文献计量在线分析平台”对文献产出时间、国家、机构、期刊等方面进行分析[26]。
1.2.2内容分析方法 本研究所应用的软件为Citespace,该软件由美国德雷克赛尔大学陈超美博士团队开发的基于Java平台的信息可视化软件,是用来分析和可视共被引网络的应用程序,是一款功能十分强大的可视化文献分析软件。该软件免费向外界开放,可从陈超美个人网站自由下载,最新版本为Citespace V (5.0.R2 SE)[27]。因此,本研究采用Citespace V来构建蒿属植物研究学科分布、高被引频次论文和研究热点趋势的知识图谱。研究前沿的析出方法:用共引(现)词频(keyword)+术语词组(noun phraces)分析,从分析网图揭示研究前沿。新兴研究前沿析出方法:利用突现词频(burst term)+共引(现)词频,分析网络揭示新兴前沿。知识图谱中节点表示被引用历史状况,节点的圆圈层被称为年轮,不同的颜色代表不同的年份。如文献共被引知识图谱中圆圈层被称为引文年轮,表示该文献发表至今被引用的历史,引文年轮采用不同颜色标识,每一年轮代表当年被引用的情况,而被引次数多的年限圆环的厚度大,因此,从引文年轮的大小、颜色能判断出该文献在研究发展过程中的学术贡献度[28],其他图谱类同。
1.2.3主要指标 发文量:即论文的产出篇数,发文量在文献计量学中一直是一个测度科研生产能力的重要指标[18]。
被引频次:论文被其他论文作为参考文献的次数,论文被引频次越高,反映出该论文在该领域被关注的程度越高、该论文的价值也越高[18]。
研究前沿:指临时形成的某个研究课题及其基础研究问题的概念组合,也是正在兴起或突然涌现的理论趋势和新主题,代表一个研究领域的思想现状[29]。
研究热点:是某一时期内,有内在联系的,数量相对较多的一组文献共同探讨的科学问题或专题[29],频次较高的关键词在一定程度上可以看作是该领域的研究热点[30-31]。
突变词:是指某些年份发表文献中骤增的专业术语[32],适合表征研究前沿及发展趋势[33]。
2 结果与分析
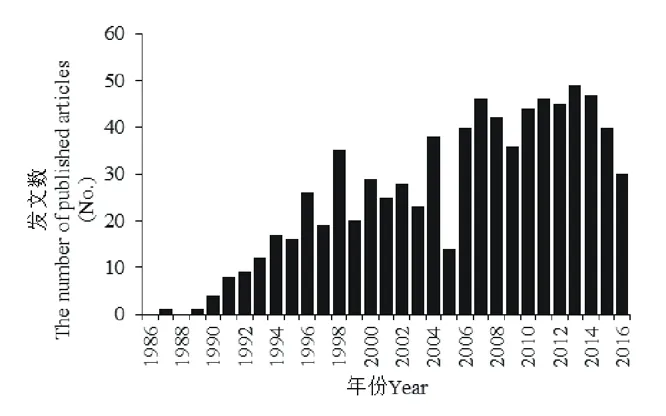
图1 蒿属植物相关研究发文量时间序列变化Fig.1 Temporal trends of the number associated with Artemisia papers
2.1 文献产出时间序列分析
时间是投射客观存在的一个普遍维度[34],一些理论在时间发展序列中会表现出规律性[35],因此许多问题都可以放在时间维度内来进行讨论。从时间上来看,在1987-2016年的30年间,Web of Science的核心合集数据库中,全世界有关蒿属植物研究的论文共790篇,总体来看呈上升趋势(图1),增长趋势符合科技论文数量普遍增长的大趋势[36],这与SCI期刊数的增长也有关系[37]。在1986-2016年期间的关于蒿属植物相关研究的首篇论文出现于1987年,而当年仅有1篇蒿属植物相关研究,从1990年后数量增加迅速;1996-2004年的9年间,文章数呈缓慢的波动式增长,最大差幅为19篇/年,年均论文数量为27篇;2005年有较大降低,仅发文14篇;2006-2015年间,发文数增长迅速,年均论文数量43.5篇,最大值出现在2013年,发文量为49篇;2016年较2015年下降了10篇,发文数为30篇。
2.2 国家及合作关系
论文被SCI收录的数量一定程度上反映了一个国家在某一研究领域的科研实力和影响力,基于文献计量在线分析平台,蒿属植物相关论文发表总量前10的国家从高到低依次为:中国(148篇)、美国(139篇)、韩国(38篇)、意大利(37篇)、英国(37篇)、德国(34篇)、伊朗(29篇)、西班牙(29篇)、日本(26篇)和印度(25篇),占全球发文量的50%以上,达到68.61%。其中,中国和美国2个国家的发文量明显高于其他国家,分别占全球发文量的18.73%和17.59%(图2)。
从发文量来看,中国对蒿属植物的研究大体可划分为3个阶段:1986-1994年基本为研究的空白期,仅在1991年,兰州大学化学系的Tan以第二作者在Phytochemistry杂志上发表了1篇文章;1995-2008年为研究起步阶段,发展相对缓慢,14年间有59篇文章被收录,年均发文量仅为4.2篇;2009-2016年进入相对快速发展阶段,8年间发表论文88篇,年均发文量为11篇。

图2 蒿属植物论文发表量居前10的国家年发文趋势Fig.2 Tendency of publishing papers per year on Artemisia of top 10 countries
随着科技全球化的发展,国际合作成为科技领域不可或缺的重要支撑,而最为有效且直观的评价模式就是国际合著论文[37]。从图3A中可以看出,在蒿属植物论文发表方面,各个国家间均有不同程度的合作,这也反映了在本研究方面的国际合作水平。总体来看,美国的合作贡献最大(图3B),与中国、日本、德国和英国的合作关系最强。中国排名第2,与英国合作最密切,有着较强的合作关系,其次为与美国、加拿大、日本和德国合作(图3C),但合作国家数量低于美国。之前有研究得出地理分布上的邻近关系是影响国际合作的重要因素[38],但随着信息化和网络的发展,不同国家科技合作制度的出台,这种地理邻近性已不成为决定因素。
2.3 研究机构影响力
发文量前10的机构中国有4个,韩国有2个,其他各1个(表1)。排名前3的研究机构分别是中国科学院、香港大学和北京大学,中国科学院以35篇的数量居首,占前10研究机构发文量的24.65%。总被引用次数方面,香港大学则以133列于第1位,中国科学院排名第2位,北京大学和南京大学分列第3和第4位。在一作总数和一作被引次数方面,中国科学院一作总数位居第1,与一作被引次数和一作发文总数略低的北京大学相同,均远低于香港大学的一作被引次数。
2.4 期刊
统计分析刊载相关研究文献的期刊分布情况,可确定该领域的核心期刊,有助于研究人员选择重点期刊进行文献查阅和研究成果的发表[18]。从表2中可以看出,刊载发文量排名第1位的是Planta Medica,刊登蒿属植物相关研究的文献最多,为63篇,占全部发文量的7.97%,Phytochemistry期刊发文量为49篇,排名第2位,占全部发文量的6.20%,Journal of Natural Products期刊发文量排名第3位;但从总被引用次数来看,Phytochemistry期刊以绝对优势(110次)占据榜首,Tetrahedron排名第2位,Journal of Natural Products期刊排名第3位;平均被引次数排名第1位的是Nature期刊(未出现在表2中),其刊载文章总数仅为1篇,总被引用次数为5次,Tetrahedron期刊排名第2位,Journal of Natural Products和Phytochemistry期刊分别排名第10和第11位。总体来看,以上期刊均在蒿属植物相关研究领域中有着重要地位。

图3 蒿属植物论文发表国家间合作(A)及与美国(B)、中国(C)合作国家的网络关系Fig.3 Correlations of the countries (A) and corporations with the USA (B) and China (C) in Artemisia papers
2.5 学科分布
数据导入到Citespace V中运行,经过96次迭代后,分析得到82个节点(nodes),114条连线(links),其中植物科学占据首位,其次为化学学科,而药理学/配药学占据第三位(图4)。在排名前10的学科中,从学科类别来看,涉及理学、医学、农学和工学类,其中理学占50%,其次医学类占30%,农学和工学各占10%(表3)。从学科层次的划分来看,参考屈天鹏[39]的研究,基础科学占50%,其次为技术科学占40%,工程科学仅占10%,形成了基础科学-技术科学-工程科学较为完整的体系。但工程科学发文量还有待进一步提高,应将基础科学研究和技术科学成果转化为工程科学应用,加大基础科学和技术科学对工程科学的支持力度。
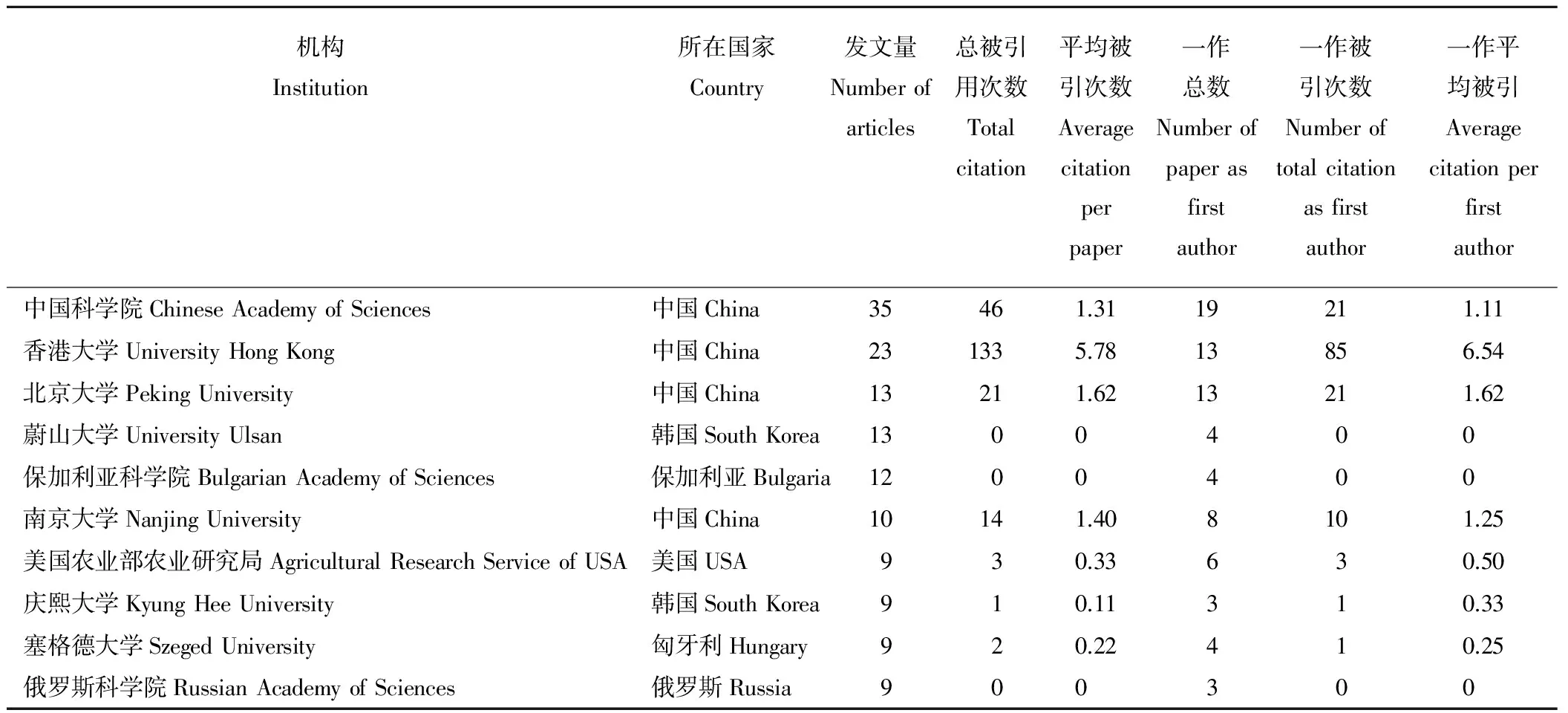
表1 发文量前10的研究机构统计Table 1 Top 10 research institutions in number of articles published

表2 刊载发文量前10的期刊统计Table 2 Top 10 journals in number of articles published
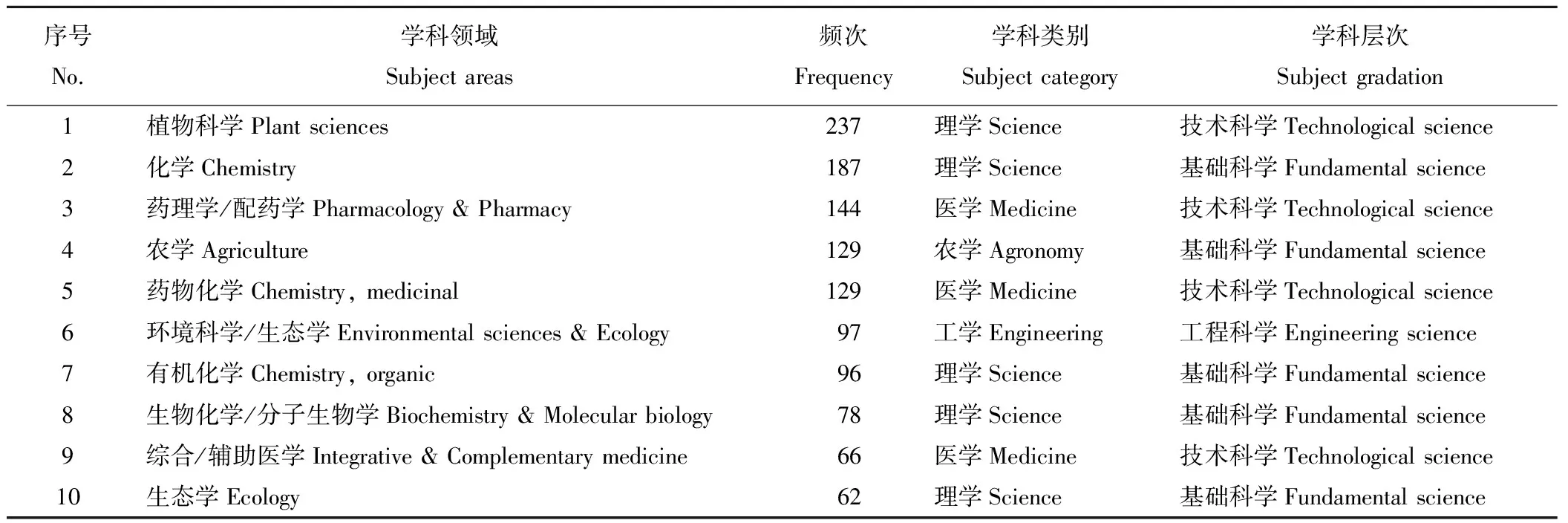
表3 蒿属植物研究排名前10的学科分布情况Table 3 Top 10 of subject areas for Artemisia researches

图4 蒿属植物研究文献的主要学科分布Fig.4 Distribution of subject categories for Artemisia researches Citespace设置为时间分片Time slicing:1986-2016;每个分片的年数Year per slice:1;限定类型Term type:名词短语Noun phrases;节点类型Node types:类别Category;选择前N的标准Selection criteria-top N:选择引用最多的前50或者每个分片相关的主题Select top 50 most cited or occurred items from each slice;前N% Top N%:选择引用最多的前10%或者每个分片相关的主题 Select top 10% of most cited or occurred items from each slice;裁剪 Pruning:路径选择,修剪融合的网络 Pathfinder, pruning the merged network;可视化 Visualization:静态聚集可视,显示融合的网络 Cluster view-static,show merged network;其他采用默认设置。The other defaulted settings.图中每个节点表示一门学科,节点的大小与学科的次数呈正比,红色内核表示该学科在近年出现频次突然增多;节点之间的连线表示不同学科间共被引的关系,其粗细表明共被引的强度,连线的颜色则表示第一次共被引的时间,节点和连线的颜色从冷色调(蓝色)到暖色调(红色)的变化表明时间由远及近的变化。Each node in the graph represented a subject, the subject was proportional to the size of the number of nodes, red kernels represented a sudden increase of frequency in recent years, the line between the nodes represented co-citation relationship of different subjects, the thickness showed that the co-citation strength, the color of lines represented the first time of co-citation, the color of nodes and lines represented from the cold colors (blue) to warm colors (red) signified the time change from far and near.Health care sciences & services:保健科学;History & philosophy of science:历史和哲学科学;History:历史;Food science & technology:食品科学和技术;Agriculture, multidisciplinary:多学科农业;Medicine, general & internal:普内科;Integrative & complementary medicine:综合医学;Chemistry, medicinal:药物化学;Pharmacology & pharmacy:药物学;Horticulture:园艺学;Plant sciences:植物科学;Agriculture:农学;Agronomy:农艺学;Biotechnology & applied microbiology:生物技术;Geosciences, multidisciplinary:地球科学;Physical geography:自然地理;Geology:地质学;Soil science:土壤学;Geography, physical:地球物理学;Agricultural engineering:农业工程;Green & sustainable science & technology:绿色可持续发展科学和技术;Science & technology-other topics:其他主题的科学和技术;Oncology:肿瘤学;Reproductive biology:生殖生物学;Developmental biology:进化生物学;Obstetrics & gynecology:产科学和妇科医学;Cell biology:细胞生物学;Peripheral vascular disease:末梢血管病学;Multidisciplinary sciences:多学科;Life sciences & biomedicine-other topics:其他主题的生命和生物医学;Hematology:血液学;Forestry:林学;Cardiovascular system & cardiology:心血管和心脏学;Biology:生物学;Environmental sciences:环境科学;Materials science, multidisciplinary:多学科材料学;Materials science:材料学;Physics:物理学;Environmental sciences & ecology:环境科学和生态学;Ecology:生态学;Physics, applied:应用物理学;Engineering, environmental:环境工程;Engineering:工程学;Zoology:动物学;Biodiversity & conservation:生物多样性和保护;Engineering, chemical:化学工程学;Chemistry, multidisciplinary:综合化学;Biochemistry & molecular biology:生物化学和分子生物学;Engineering, mechanical:机械工程学;Endocrinology & metabolism:内分泌学和代谢学;Engineering, biomedical:生物医学工程;Engineering, electrical & electronic:电气电子工程;Optics:光学;Biochemical research methods:生物化学研究方法;Chemistry:化学;Chemistry, applied:应用化学;Public, environmental & occupational health:公共环境和职业保健;Chemistry, organic:有机化学.

图5 蒿属植物研究文献被引用时区视图Fig.5 The time-zone view of the cited references Citespace设置为时间分片Time slicing:1986-2016;每个分片的年数Year per slice:2;限定类型Term type:名词短语Noun phrases;节点类型Node types:引用文献Cited reference;选择前N的标准Selection criteria-top N:选择引用最多的前200或者每个分片相关的主题Select top 200 most cited or occurred items from each slice;前N% Top N%:选择引用最多的前10%或者每个分片相关的主题 Select top 10% of most cited or occurred items from each slice;裁剪 Pruning:路径选择,修剪融合的网络 Pathfinder, pruning the merged network;可视化 Visualization:静态聚集可视,显示融合的网络 Cluster view-static, show merged network;其他采用默认设置。The other defaulted settings.图中每个节点表示一篇参考文献,节点的大小与该文献的被引频次呈正比,红色内核表示该文献在近年被引频次突然增多;节点之间的连线表示两篇文献共被引的关系,其粗细表明共被引的强度,连线的颜色则表示第一次共被引的时间,节点和连线的颜色从冷色调(蓝色)到暖色调(红色)的变化表明时间由远及近的变化。Each node in the graph represented a reference, the cited times of reference was proportional to the size of nodes, red kernels represented a sudden increase of frequency in recent years, the line between the nodes represented co-citation relationship of references, the thickness showed that the co-citation strength, the color of lines represented the first time of co-citation, the color of nodes and lines represented from the cold colors (blue) to warm colors (red) signified the time change from far and near.
2.6 高被引频次论文
文献的被引次数是衡量其学术价值的重要参数,也是科研成果得到同行认同的反映[40],经典文献反映研究领域的知识基础[41]。Citespace软件中的研究前沿时区视图是依据前沿热点的交互关系和演进路径设计的[42],能反映某个研究领域的文献被引概况和学术共同体[14]。经过622次迭代后,分析得到251个节点(nodes),430条连线(links)(图5),其中被引频次最多的是1998年由Sy等[43]发表在《Tetrahedron》上的“A novel endoperoxide and related sesquiterpenes fromArtemisiaannuawhich are possibly derived from allylic hydroperoxides”,提出从黄蒿中提取的一些新的倍半萜类化合物可以通过从二氢青蒿酸氧化氢过而形成(表4)。其后续相关研究结果分别在2001年[44]和2002年[45]发表在《Tetrahedron》上,同样具有较高的被引频次。其次是Marco等[46]1990年在《Studies in Natural Products Chemistry》上发表的“Natural products from the genusArtemisiaL.”。而近几年被引频次较高的是Wen等[47]从奇蒿的地上部分分离出的几种化学成分并对它们的结构进行了化学和光谱分析测定,同时对细胞毒活性的效果进行了评价,研究结果2010年在《Journal of Natural Products》上以“Dimeric guaianolides and sesquiterpenoids fromArtemisiaanomala”题目发表。
2.7 研究前沿趋势分析
通过对研究前沿趋势分析,能够把握研究变化动态,预测未来研究动向[41]。综合分析研究前沿时区视图、突变词和具体学术文献,有助于掌握了解该研究领域的前沿趋势。本研究采用Citespace提供的对突变词探测的技术[23], 对蒿属植物研究领域进行趋势分析。图6的研究前沿时区视图是依据前沿热点的交互关系和演进路径设计的,是Citespace软件区别于其他可视化软件的独特功能[42]。经过287次迭代后,分析得到207个节点(nodes),323条连线(links),其中出现频次较高的关键词有倍半萜内酯(sesquiterpene lactone)、青蒿素(Artemisiaannua或Artemisinin)、组成的(constituent)、衍生的(derivative)、香精油(essential oil)、菊科(Asteraceae或Compositae)、疟疾(malaria)、生物合成(biosynthesis)、愈创木内酯(guaianolide)、生长(growth)、酸(acid)、三齿蒿(Artemisiatridentata)、类黄酮(flavonoid)、药用植物(medicinal plant)、桉烷醇甙(eudesmanolide),可以看出,关于蒿属的研究热点和演进主要围绕着化学成分和医药方面的内容进行。

表4 蒿属植物研究排名前10的高被引频次分布情况Table 4 Top 10 of references with high citation for Artemisia researches
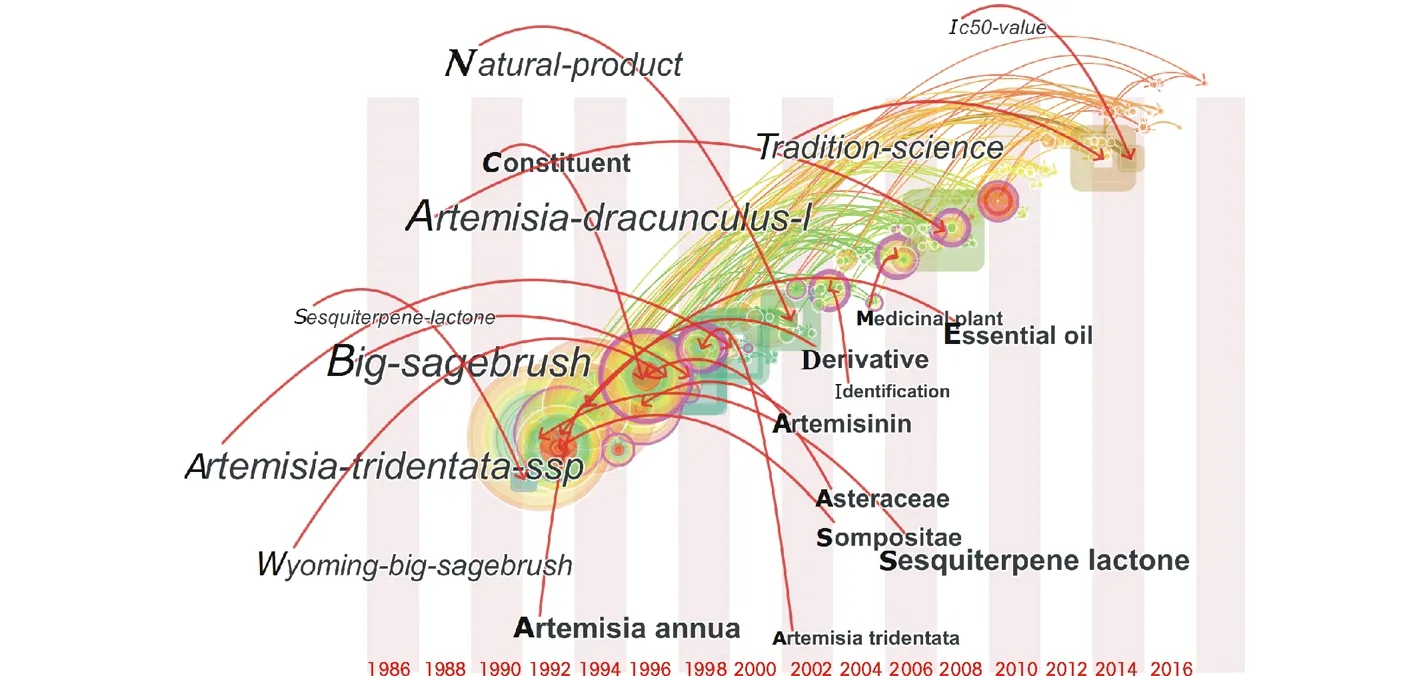
图6 研究前沿时区视图Fig.6 The zone view of research frontier Citespace设置为时间分片Time slicing:1986-2016;每个分片的年数 Year per slice:2;限定类型 Term type:名词短语,突增条件 Noun phrases, burst terms;节点类型 Node types:关键词 Keyword;选择前N的标准 Selection criteria-top N:选择引用最多的前30或者每个分片相关的主题 Select top 30 most cited or occurred items from each slice;前N% Top N%:选择引用最多的前10%或者每个分片相关的主题 Select top 10% of most cited or occurred items from each slice;裁剪 Pruning:路径选择,修剪融合的网络 Pathfinder, pruning the merged network;可视化 Visualization:静态聚集可视,显示融合的网络 Cluster view-static, show merged network;其他采用默认设置。The other defaulted settings.图中黑色斜体字体表示突现关键词,黑色加粗字体表示引文关键词;方形节点代表突现词语,方形大小表示突现词的权重,方形位置体现突现词出现的时间;圆形节点反映高被引论文,圆形大小反映该论文被引频次,通过高被引论文作为参照,可以反映出该突现词出现的背景特征;红色内核表示该关键词在近年被引频次突然增多。The black and italic fonts represented emergent keywords, the black and bold fonts for citation keywords. Square nodes represented emergent words, the size of nodes represented the weight of emergent words, and the position of nodes reflected the emergence time of the emergent words. The circular nodes reflected highly cited papers, the size of circle reflected the citation frequency of the paper. Through the highly cited papers as a reference, it could been reflected the characteristics of the emergent keywords.Natural-product:自然产物;Ic50-value:半数最大抑菌浓度值;Constituent:成分;Tradition-science:传统科学;Artemisia-dracunculus-L:龙蒿;Sesquiterpene-lactone:倍半萜内酯;Big-sagebrush:三齿蒿;Artemisia-tridentata-ssp:三齿蒿;Medicinal plant:药用植物;Essential oil:香精油;Derivative:衍生物;Identification:鉴定;Artemisinin:青蒿素;Asteraceae:菊科;Compositae:菊科;Sesquiterpene lactone:倍半萜内酯;Wyoming-big-sagebrush:怀俄明大鼠尾草;Artemisia annua:青蒿素;Artemisia tridentata:三齿蒿.
图7为12个重点突变关键词,蒿(俗称)(Artemisiavulgaris)为关键词的新兴研究热点,从1986-1997年持续了10年,而类黄酮则是近几年的热点关键词。结合图6和图7,随着时间的变化,关于蒿属研究的突变词,从新兴的大类基础调查研究[菊科、大蒿(Big-sagebrush)、三齿蒿]到细微的成分及其作用研究[倍半萜内酯、大根香叶内酯(germacranolide)、单萜(monoterpene)、类黄酮、抗氧化剂活性(antioxidant activity)、抑菌浓度(Ic50-value)],可以看出,目前新兴研究前沿是围绕蒿属植物的化学成分及其作用方面的内容开展进行。

图7 蒿属植物研究引用频次突增关键词Fig.7 Keywords with the strongest citation bursts of Artemisia
3 结论及展望
在1986-2016年期间,关于蒿属植物全球发文量随时间总体呈上升趋势,这与其他研究方向的论文增长规律也是一致的[48-50]。但发文总的数量仅为790篇,远低于其他领域研究上万篇的数量,且多集中在基础科学和技术科学研究方面。中国发表文献起步较晚,发文量增长较快,从发文量和研究机构影响力方面来看,中国在蒿属植物方面研究具有一定的领先地位,但在顶级期刊和高质量文献发表方面有待进一步提高,且在国际合作的国家数量上低于美国,随着科技全球化,应加强与不同国家间的科技合作。
尽管有关蒿属植物研究的文献已有很多,但通过分析发现,已产出研究内容、研究热点和新兴研究前沿多集中在化学成分分析和作用以及医药利用等方面。同一研究对象的研究内容、研究方法和研究结果的多元化将有助于学科的发展,因此建议今后应加大对蒿属植物在不同学科、内容、方法等方面的研究。
此外,可以看出,利用Citespace软件,可以直观地表达该领域的发展路径与发展趋势,结合具体分析方法,为目标对象领域的科学研究与学科建设深入探索提供了有益参考。但以Artemisia为主要检索主题,仅以Web of ScienceTM核心合集数据库为文献数据源,加之数据库在不断更新,尽管有一定的研究局限性,但分析结果一定程度上吻合相关研究的主题内容和社会大背景需求,且收录发表文献的作者多是当时从事该领域理论与实践研究的主体,研究成果基本能够反映蒿属植物研究的问题导向和社会需求导向。结合本文分析结果,建议今后增强有关工程科学方面的研究成果产出,应将基础科学研究和技术科学成果极大化的转化为工程科学应用,进一步完善学科体系。
References:
[1] Li Z, Chen S M, Chen F D,etal. Distribution of 45S rDNA sequence on chromosomes of five species inArtemisia. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2011, 38(2): 353-360.
李真, 陈素梅, 陈发棣, 等. 45S rDNA在蒿属5种植物染色体中的分布. 园艺学报, 2011, 38(2): 353-360.
[2] Zhou L J, Sang X Q, Sun Y Y,etal. Pesticidal activities and active ingredients ofArtemisia. Acta Agriculturae Universities Jiangxiensis, 2012, 34(4): 699-705.
周利娟, 桑晓清, 孙永艳, 等. 蒿属植物的农药活性及其有效成分. 江西农业大学学报, 2012, 34(4): 699-705.
[3] Kirschner J,těp N J. The plant book. Folia Geobotanica et Phytotaxonomica, 1990, 25(3): 226.
[4] Lin Y R. On the system of the genusArtemisiaLinn. and the relationship with its allies. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 1982, 2(2): 1-60.
林有润. 论蒿属的演化系统兼论蒿属与邻近属的亲缘关系. 植物研究, 1982, 2(2): 1-60.
[5] Bremer K, Humphries C J. Generic monograph of the Asteraceae-Anthemideae. Bulletin of the Natural History Museum Botany, 1993, 23: 71-77.
[6] Yue Y X, Shi B L, Zhang P F,etal. Recent advance in study on biological action ofArtemisiaLinn plants in animal production. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2015, 51(15): 79-82.
岳远西, 史彬林, 张鹏飞, 等. 蒿属植物对动物的生物学作用研究进展. 中国畜牧杂志, 2015, 51(15): 79-82.
[7] Ji M F, Ding D L, Wu S F,etal. Comparison of two photosynthesis-light response curve-fitting models of fourArtemisiaspecies. Pratacultural Science, 2013, 30(5): 716-722.
姬明飞, 丁东粮, 吴寿方, 等. 4种蒿属植物的光合光响应曲线及其拟合模型. 草业科学, 2013, 30(5): 716-722.
[8] Torrell M, Vall S J. Genome size in 21ArtemisiaL. species (Asteraceae, Anthemideae): systematic, evolutionary, and ecological implications. Genome, 2001, 44(2): 231-238.
[9] Vallès S J, McArthur E D.Artemisiasystematics and phylogeny: Cytogenetic and molecular insights. Department of Agriculture Forest Service, 2001, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242411940, 67-74.
[10] Wu Y H. Comparative study on antibacterial effect about plant extracts of six species ofArtemisiaL. plants. Northern Horticulture, 2014, (19): 121-125.
武月红. 六种蒿属植物提取物抑菌效果的比较研究. 北方园艺, 2014, (19): 121-125.
[11] Yang L X, Wang B S, Wu B F,etal. Study on special toxicity of Artemisinin. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 1985, 208-209.
杨立新, 王宾生, 邬碧芳, 等. 青蒿素特殊毒性的研究. 中药药理与临床, 1985, 208-209.
[12] Zhang C G. Artemisinin research and revelation of Tu Youyou’s Nobel prize. Science & Technology Review, 2015, 33(20): 86-89.
张成岗. 青蒿素研发及屠呦呦获得诺贝尔奖的启示. 科技导报, 2015, 33(20): 86-89.
[13] The Sate Council. The State Council’s award decision of the national science and technology on 2016. (2017-01-09)[2017-01-19]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-01/09/content_5158017.htm.
国务院. 国务院关于2016年度国家科学技术奖励的决定. (2017-01-09)[2017-01-19]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-01/09/content_5158017.htm.
[14] Gui Q C, Liu C L, Dong L Y,etal. Knowledge visualization and dynamics of foreign transport geography research. Human Geography, 2016, 31(6): 10-18.
桂钦昌, 刘承良, 董璐瑶, 等. 国外交通地理学研究的知识图谱与进展. 人文地理, 2016, 31(6): 10-18.
[15] Pritchard A. Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics. Journal of Documentation, 1969, 25(4): 348-349.
[16] Nederhof A J. Bibliometric monitoring of research performance in the Social Sciences and the Humanities: A Review. Scientometrics, 2006, 66(1): 81-100.
[17] Zhang Y, Gong J, Ma X C,etal. Research progress on the impact of land use on soil organic carbon based on the bibliometric method. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(2): 480-488.
张影, 巩杰, 马学成, 等. 基于文献计量的近20多年来土地利用对土壤有机碳影响研究进展与热点. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(2): 480-488.
[18] Wu J, Wang M, Jin Z H,etal. Review and prospect of research on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil environment: a bibliometric analysis based on megadata of Web of Science. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5): 1085-1096.
吴健, 王敏, 靳志辉, 等. 土壤环境中多环芳烃研究的回顾与展望——基于Web of Science大数据的文献计量分析. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5): 1085-1096.
[19] Zhang H W, Li Q Z, Xu S Y. The literature knowledge map of China’s clothing digital technology based on CiteSpaceⅢ. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-tech University (Social Science Edition), 2016, 36(4): 354-360.
张会巍, 李启正, 徐石勇. 基于CiteSpaceⅢ的我国服装数字化技术文献知识图谱. 浙江理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2016, 36(4): 354-360.
[20] Qiu J P, Duan Y F, Chen J Q,etal. The retrospect and prospect on bibliometrics in China. Studies in Science of Science (Social Science Edition), 2003, 21(2): 143-148.
邱均平, 段宇锋, 陈敬全, 等. 我国文献计量学发展的回顾与展望. 科学学研究, 2003, 21(2): 143-148.
[21] Qian F K, Wang W W, Zhang J Y,etal. Analysis on land use research progress by Citespace. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(Supp.2): 344-351.
钱凤魁, 王卫雯, 张靖野, 等. 基于Citespace的土地利用领域研究态势分析. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(S2): 344-351.
[22] Synnestvedt M B, Chen C, Holmes J H. CiteSpace II: Visualization and Knowledge Discovery in Bibliographic Databases. AMIA Annual Symposium proceedings/AMIA Symposium AMIA Symposium, 2005: 724-728.
[23] Chen C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 2006, 57(3): 359-377.
[24] Chen C, Hu Z, Liu S,etal. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 2012, 12(5): 593-608.
[25] Wei F, Grubesic T H, Bishop B W. Exploring the GIS knowledge domain using CiteSpace. Professional Geographer, 2015, 67(3): 1-11.
[26] Zheng Y, Liu J Y, Zuo X,etal. Research situation of transgenic corn based on bibliometrics and content mining. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(12): 203-213.
郑莹, 刘家益, 左璇, 等. 基于文献计量和内容挖掘的转基因玉米科研态势研究. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(12): 203-213.
[27] Chen C M. Citespace: visualizing patterns and trends in scientific literature. (2016-10-03)[2017-01-19]. http://cluster.ischool.drexel.edu/~cchen/citespace/download.
[28] Zhao H S, Li X T, Wang J L. The Mapping knowledge domains about development of domestic regional tourism research during 1998-2014: Bibliometric analysis based on CiteSpace. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2016, 30(4): 203-208.
赵慧莎, 李向韬, 王金莲. 1998-2014年国内区域旅游研究发展知识图谱——基于CiteSpace的科学计量分析. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016, 30(4): 203-208.
[29] Zu Y H, Zhang H, Fu Q,etal. Visualization analysis about hot research topics and fronts based on Citepace——Take the field of liquid fuels in catalytic chemistry as an example. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 55(4): 527-533.
祖艳红, 张慧, 傅倩, 等. 基于CiteSpace的学科领域研究热点与前沿可视化分析——以液体燃料在催化化学领域为例. 复旦学报(自然科学版), 2016, 55(4): 527-533.
[30] Bailón-moreno R, Jurado-alameda E, Ruiz-baos R,etal. Analysis of the field of physical chemistry of surfactants with the Unified Scienctometric Model. Fit of relational and activity indicators. Scientometrics, 2005, 63(2): 259-276.
[31] Belvaux G, Wolsey L A. bc-prod: A specialized branch-and-cut system for lot-sizing problems. Management Science, 2000, 46(5): 724-738.
[32] Chen C, Morris S. Visualizing Evolving Networks: Minimum Spanning Trees Versus Pathfinder Networks. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Information Visualization, 2003: 67-74.
[33] Jiang C L, Liu S B, Ding K. The hot spot of research on Chinese Journal of Scientific and Technical Periodicals and its evolution. Chinese Journal of Scientific and Technical Periodicals, 2008, 19(6): 954-958.
姜春林, 刘盛博, 丁堃. 《中国科技期刊研究》研究热点及其演进知识图谱. 中国科技期刊研究, 2008, 19(6): 954-958.
[34] Li J, Liu Y H, Huang C,etal. Remolding the policy text data through documents quantitative research: the formation, transformation and method innovation of policy documents quantitative research. Journal of Public Management, 2015, (2): 138-144, 159.
李江, 刘源浩, 黄萃, 等. 用文献计量研究重塑政策文本数据分析——政策文献计量的起源、迁移与方法创新. 公共管理学报, 2015, (2): 138-144, 159.
[35] Sun Y Z, Shen L. Bibliometric analysis on research progress of four footprint methodologies in China. Journal of Natural Resources, 2016, 31(9): 1463-1473.
孙艳芝, 沈镭. 关于我国四大足迹理论研究变化的文献计量分析. 自然资源学报, 2016, 31(9): 1463-1473.
[36] Larsen P O, Ins M V. The rate of growth in scientific publication and the decline in coverage provided by Science Citation Index. Scientometrics, 2010, 84(3): 575-603.
[37] Wang C, Liu Y, Li X H,etal. Advances in the study of the genera of the genera of amylose based on bibliometrics. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(16): 5276-5283.
王超, 刘杨, 李新辉, 等. 基于文献计量学的直链藻属的研究进展. 生态学报, 2016, 36(16): 5276-5283.
[38] Wang C, Liu Y, Li X,etal. A bibliometric analysis of scientific trends in phytoplankton research. Annales de Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology, 2015, 51(3): 249-259.
[39] Qu T P. Mapping the Subject Distribution and Collaboration Networks of Natural Science of Universities in Liaoning Based on SCI. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2009.
屈天鹏. 基于SCI的辽宁省高校自然科学学科分布与合作网络知识图谱. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2009.
[40] Li J, Guo X H, Jiang K,etal. Preliminary study of knowledge map of safety science——Base on data of Safety Science. China Safety Science Journal, 2013, 23(4): 152-158.
李杰, 郭晓宏, 姜亢, 等. 安全科学知识图谱的初步研究——以《Safety Science》期刊数据为例. 中国安全科学学报, 2013, 23(4): 152-158.
[41] Xiang G P, Ning P, Huang W,etal. The migration footprint of industrial ecology research: visualized research based on Citespace II. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(22): 7168-7178.
项国鹏, 宁鹏, 黄玮, 等. 工业生态学研究足迹迁移——基于Citespace Ⅱ的分析. 生态学报, 2016, 36(22): 7168-7178.
[42] Zhang X, Su N, Yang H G,etal. Knowledge mapping of research on international E-government during 2000-2010 based on Citespace and VOSviewer. Journal of Information, 2012, (12): 51-57.
张璇, 苏楠, 杨红岗, 等. 2000-2011年国际电子政务的知识图谱研究——基于Citespace和VOSviewer的计量分析. 情报杂志, 2012, (12): 51-57.
[43] Sy L K, Brown G D, Haynes R. A novel endoperoxide and related sesquiterpenes fromArtemisiaannuawhich are possibly derived from allylic hydroperoxides. Tetrahedron, 1998, 54(17): 4345-4356.
[44] Sy L K, Zhu N Y, Brown G D. Syntheses of dihydroartemisinic acid and dihydro- epi -deoxyarteannuin B incorporating a stable isotope label at the 15-position for studies into the biosynthesis of artemisinin. Tetrahedron, 2001, 57(40): 8495-8510.
[45] Sy L K, Brown G D. The role of the 12-carboxylic acid group in the spontaneous autoxidation of dihydroartemisinic acid. Tetrahedron, 2002, 58(5): 909-923.
[46] Marco J, Barbera O. Natural products from the genusArtemisiaL.. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, 1990, 7: 201-264.
[47] Wen J, Shi H, Xu Z,etal. Dimeric guaianolides and sesquiterpenoids fromArtemisiaanomala. Journal of Natural Products, 2010, 73(1): 67-70.
[48] Zhang G, Xie S, Ho Y S. A bibliometric analysis of world volatile organic compounds research trends. Scientometrics, 2010, 83(2): 477-492.
[49] Liao J, Huang Y. Global trend in aquatic ecosystem research from 1992 to 2011. Scientometrics, 2014, 98(2): 1203-1219.
[50] Li L L, Ding G, Feng N,etal. Global stem cell research trend: Bibliometric analysis as a tool for mapping of trends from 1991 to 2006. Scientometrics, 2009, 80(1): 39-58.
AbibliometricappraisalofresearchonArtemisiafrom1986-2016
CHEN Lin1,2, SONG Nai-Ping1,2*, WANG Lei1,2, YANG Xin-Guo1,2, LI Xue-Bin3, SU Ying1,2, LI Yue-Fei1,2
1.BreedingBaseforStateKeyLaboratoryofLandDegradationandEcologicalRestorationinNorthwestChina,NingxiaUniversity,Yinchuan750021,China; 2.KeyLaboratoryforRestorationandReconstructionofDegradedEcosysteminNorthwestChinaofMinistryofEducation,NingxiaUniversity,Yinchuan750021,China; 3.DepartmentofScienceandTechnology,NingxiaUniversity,Yinchuan750021,China
In order to identify the location of centres of excellence and better understand the global status of research onArtemisiaand to objectively assess scientific capability and influence of countries, institutions and individuals undertaking research onArtemisia, a bibliometric analysis was conducted. Our study surveyed literature published from 1986 to 2016 and included in the core collection of the Web of ScienceTMdatabase. The number of publications onArtemisiashows a rising trend. In terms of article number, China ranks first, followed by the United States, but from the viewpoint of international cooperation the United States has made the greatest contribution, and Britain also cooperates closely with China. Among research institutions worldwide, the Chinese Academy of Sciences heads the list for article number, first-author papers, and citations of first-author papers. The University of Hong Kong is the institution with the highest total citation count and number of citations of first-author papers. Articles onArtemisiaare mostly published in the journals Planta Medica, Phytochemistry, and Journal of Natural Products, but the highest average number of citations per paper appears in the journal Nature. Plant science, chemistry and pharmacology & pharmacy are the top 3 disciplines within which the research has been conducted. Approximately 50% of identified articles were categorized as scientific studies, with fundamental science and technological science accounting for a larger amount, and engineering science a smaller share. Among individuals, Prof. L. K. Sy of Hong Kong University is a leading author of studies on the extraction ofArtemisiaannua; J. A. Marco Valencia University in Spain, and J. Wen of Peking University have the highest citation frequency. The chemical composition and medicinal application are two commonly studied topics in research onArtemisia.
Artemisia; Web of Science; bibliometric analysis; Citespace; research progress
10.11686/cyxb2017082http//cyxb.lzu.edu.cn
陈林, 宋乃平, 王磊, 杨新国, 李学斌, 苏莹, 李月飞. 基于文献计量分析的蒿属植物研究进展. 草业学报, 2017, 26(12): 223-235.
CHEN Lin, SONG Nai-Ping, WANG Lei, YANG Xin-Guo, LI Xue-Bin, SU Ying, LI Yue-Fei. A bibliometric appraisal of research onArtemisiafrom 1986-2016. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(12): 223-235.
2017-03-02;改回日期:2017-05-17
国家自然科学
基金项目(31460123,31460161,41461046)和国家重点研发计划(2016YFC0500709)资助。
陈林(1983-),男,湖南湘乡人,助理研究员,在读博士。E-mail: chenlin198388@163.com*通信作者Corresponding author. E-mail: songnp@163.com
