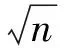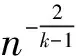随机图中k-独立集的相变性质
2017-12-16卢友军许道云
卢友军 许道云
(贵州大学计算机科学与技术学院 贵阳 550025)
随机图中k-独立集的相变性质
卢友军 许道云
(贵州大学计算机科学与技术学院 贵阳 550025)
(yjlu111@126.com)
相变性质;随机图;k-独立集;临界概率;临界边数
给定一个简单无向图G=(V,E),V表示图G的顶点集合,E表示图G的边集合.一个顶点子集T⊆V称为图G的独立集[1](independent set, IS),是指对任意的顶点u,v∈T都有(u,v)∉E.若顶点子集T的元素个数为k,则我们称该顶点子集T为k-独立集.若独立集T不是其他任何一个独立集S的真子集,则我们称该独立集T为图G的极大独立集.若独立集T是顶点个数最大的独立集,则我们称该独立集T为图G的最大独立集[2](maximum independent set, MIS).MIS问题是指在一个给定的简单无向图G中找一个顶点个数最大的独立集,该问题是组合优化领域中的著名NP-完全问题[3].MIS问题在编码理论[4]、计算机网络以及计算机视觉等领域都有重要应用.
本文的主要工作是研究随机图G(n,p)和随机图G(n,m)中k-独立集出现相变的临界概率和临界边数,其目的是让我们对随机图G(n,p)和随机图G(n,m)中k-独立集的结构有更加深入的理解.
1 基础知识及记号
本节首先给出经典ER随机图模型的定义[16],然后给出基本概念以及与ER随机图有关的一个重要结果.
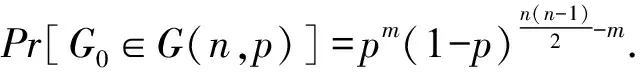
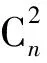
一个图性质Q是指当G∈Q,H∈G(n,p)且G≅H(G同构于H)时有H∈Q,其中,G∈Q表示图G中有图性质Q.若该图性质满足条件:G∈Q并且G⊂H时蕴含H∈Q,则称该图性质Q是单调递增的.
如果F⊆G⊆H且F,H都满足性质Q,则G也满足性质Q,称图G的性质Q是凸的.
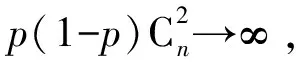
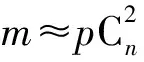
设Q是一个图性质,如果:
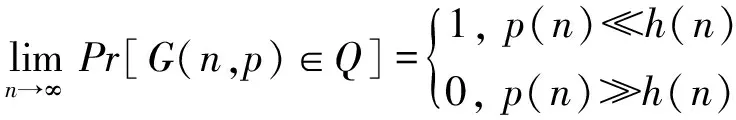
成立,则称函数h(n)是性质Q的一个临界函数.如果对于任意的ε>0,有:
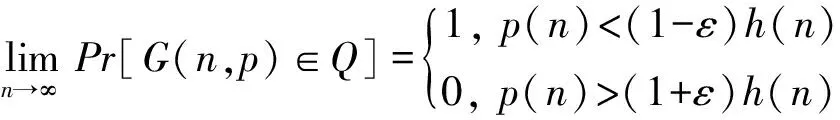
成立,则称函数h(n)是性质Q的一个严格临界函数.
2 k-独立集存在的相变分析

证明. 假设Γ是顶点个数为k的所有顶点子集构成的集合,其元素包含在V(G)中,其中,V(G)表示图G∈G(n,p)的顶点集,其顶点总数为n.为描述方便,用α,β,γ,…表示Γ中的元素.记Jα是关于随机图G(n,p)的示性随机变量.
如果顶点集α是图G∈G(n,p)的一个k-独立集,则Jα=1;否则,Jα=0.
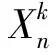
证毕.
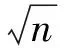
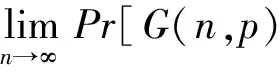
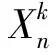
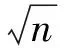
(1)
(2)
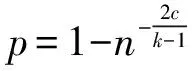
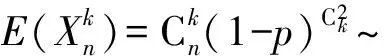
(3)
当c>1时,有
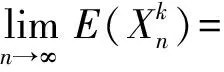
(4)
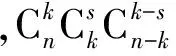
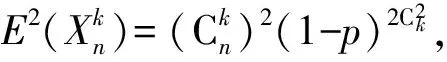
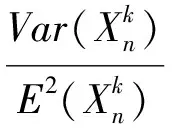
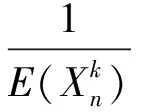
(5)
其中:
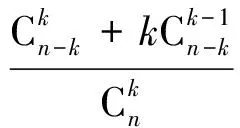
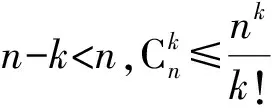
(6)
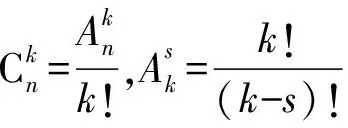
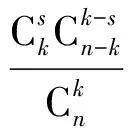
(7)
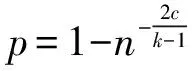
(8)
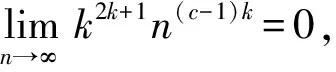
证毕.
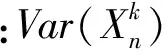
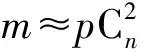
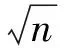
其中,[x]为取整函数.
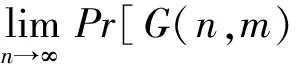
3 独立集算法
给定一个图G=(V,E),V表示图G的顶点集合,E表示图G的边集合.若顶点集合V的顶点子集T中任意2个节点u,v之间都没有边,则称该顶点子集T为图G的独立集.若顶点子集T的元素个数为k,则称该顶点子集T为k-独立集.下面给出独立集的求解算法1[19]:
算法1. 独立集求解算法.
输入:简单无向图G=(V,E),整数k≥2,其中,|V|=n;
输出:独立集|S|≥k,其中|S|表示独立集S中的元素个数.
Step1. 对图G中的每个顶点用数字i=1,2,…,n标记,即V={1,2,…,n}.
Step2. 当i≤n时,初始化独立集Si={i},同时执行I=V-i∪N(i);如果I=∅,此时|Si|=1,那么执行i=i+1,然后转回Step2;否则,转到Step3.
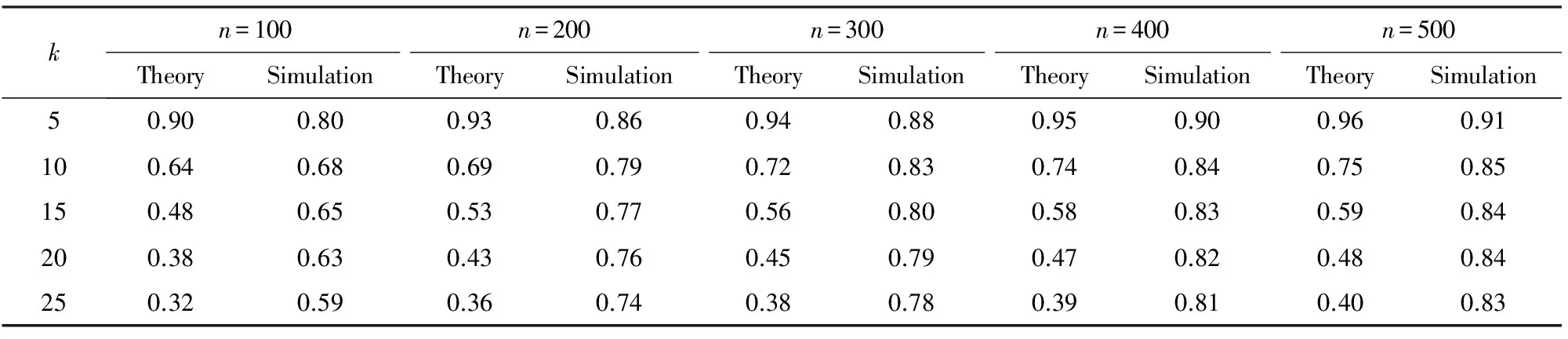
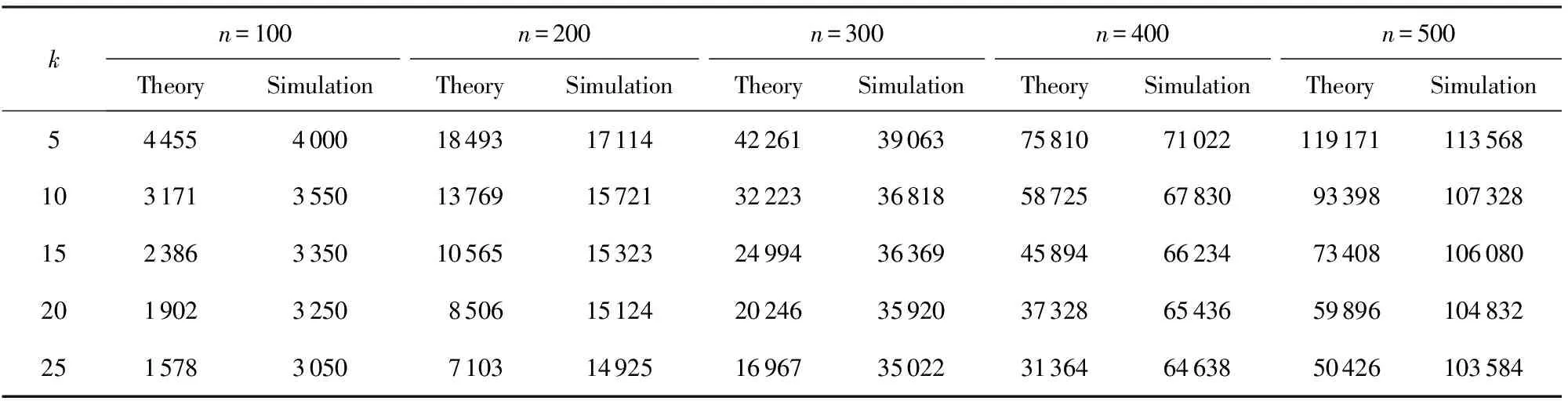
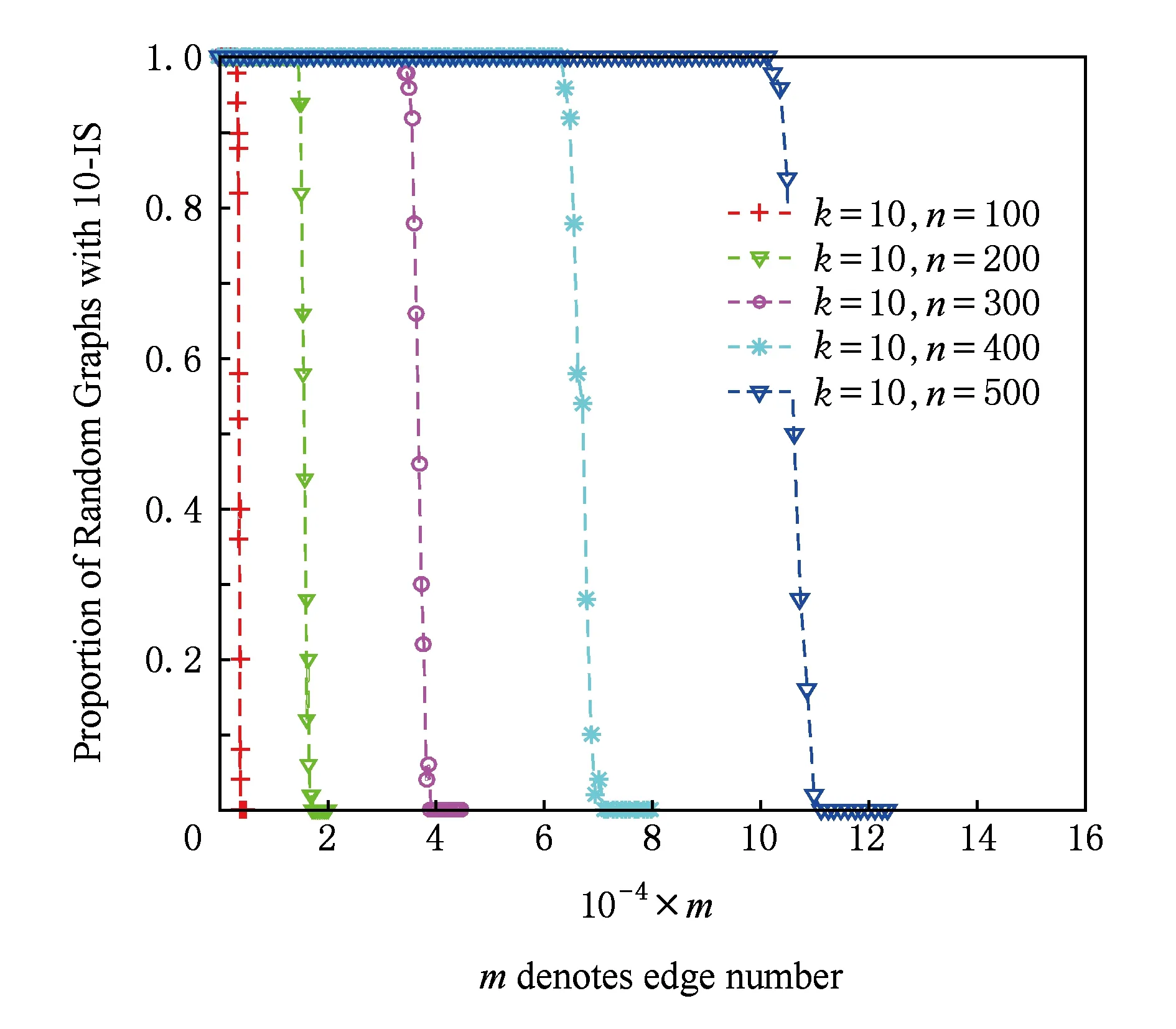
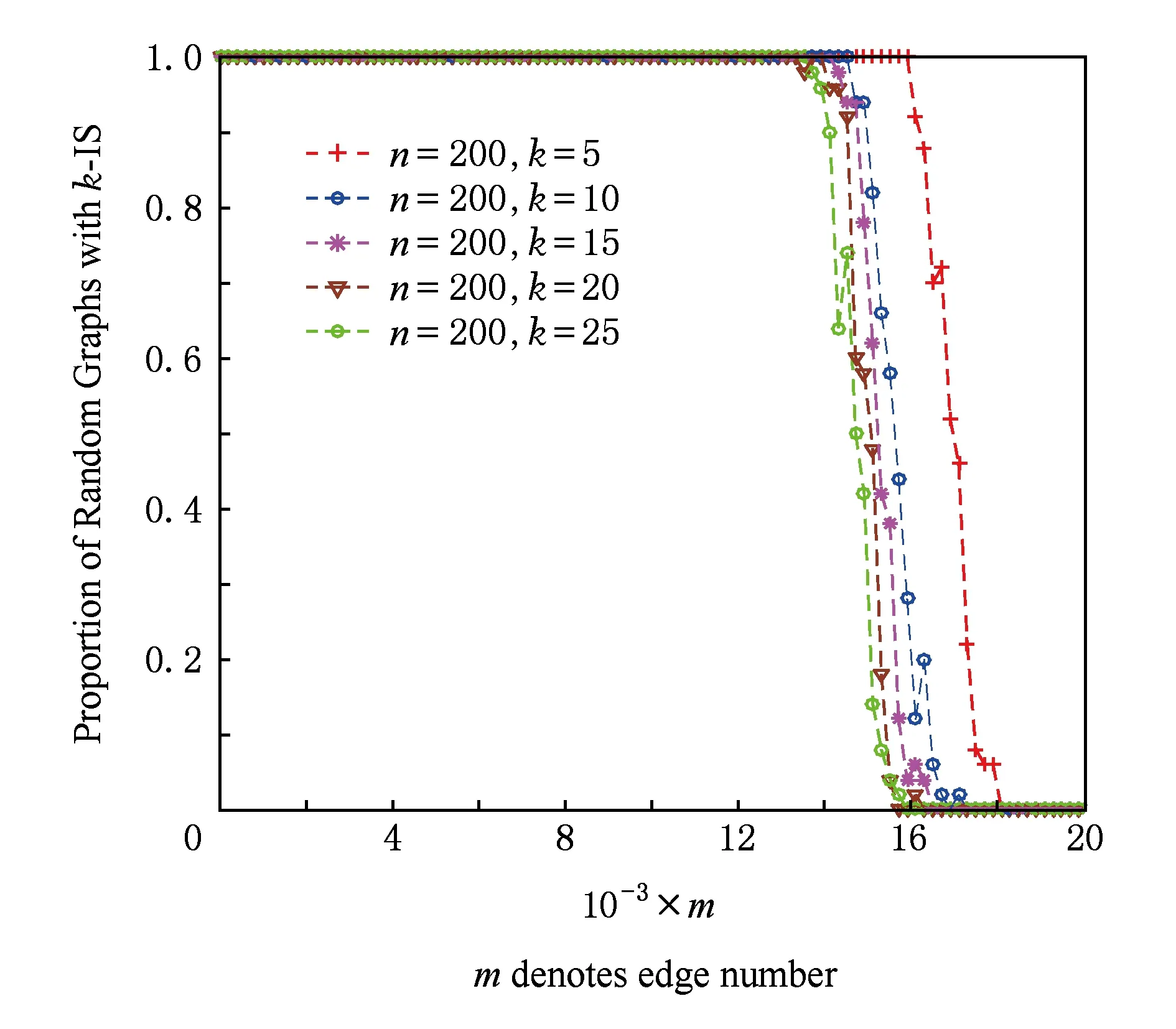
Step3. 当|Si| Step5. 若|Si| Step6. 若|Si|≥k,则输出Si程序终止;否则,转到Step3. 本节的主要工作是进行数值仿真实验分析,该实验主要基于3个算法:1)随机图G(n,p)实例产生算法[6,20];2)随机图G(n,m)实例产生算法[6,20];3)独立集算法[19].数值实验的具体操作方法是首先利用随机图G(n,p)(或G(n,m))算法产生一个随机图实例,然后调用独立集算法判断图G∈G(n,p)(或G∈G(n,m))中是否存在k-独立集.判断方法主要是看独立集算法在图G中是否能找到一个节点数不小于k的独立集,若独立集算法找到的独立集的节点数不小于k,则确定在G∈G(n,p)(或G∈G(n,m))中存在一个k-独立集,否则,我们确定在G∈G(n,p)(或G∈G(n,m))中不存在k-独立集. 从定理1可知,随机图G(n,p)中k-独立集性质出现相变的临界概率pc与节点总数n和独立集节点数k有关.所以,在模拟随机图G(n,p)中k-独立集性质的相变现象时,分别取节点总数n值为100,200,300,400,500,独立集节点数k值为5,10,15,20,25,如表1所示: Table 1 Comparison Between the Theoretical Threshold and the Numerical Simulations for the Existence of k-Independent Set in Random Graph G(n,p) 表1 随机图G(n,p)中存在k-独立集的理论临界和仿真临界的对比 kn=100n=200n=300n=400n=500TheorySimulationTheorySimulationTheorySimulationTheorySimulationTheorySimulation50.900.800.930.860.940.880.950.900.960.91100.640.680.690.790.720.830.740.840.750.85150.480.650.530.770.560.800.580.830.590.84200.380.630.430.760.450.790.470.820.480.84250.320.590.360.740.380.780.390.810.400.83 Fig. 1 Phase transition of 10-IS in random graph G(n,p)图1 随机图G(n,p)中10-独立集的相变 图1给出了当独立集节点数k固定时随机图G(n,p)中存在k-独立集的临界概率pc随节点总数n的变化情况,这里取独立集节点数k=10,节点总数n分别取值为100,200,300,400,500.图1中的每个数据点是对每个给定的概率p和节点总数n利用随机图G(n,p)生成算法生成的100个图G∈G(n,p)实例中存在10-独立集的统计概率. 从图1可以看出,当独立集节点数k=10固定时,随机图G(n,p)中存在10-独立集的临界概率pc随节点总数n的增加而增加,而且临界概率pc向右移动. 图2给出了当节点总数n固定时随机图G(n,p)中k-独立集出现相变的临界概率pc随独立集节点数k的变化情况,这里取节点总数n=400,独立集节点数k分别取值为5,10,15,20,25.图2中的每个数据点是对每个给定的概率p和节点总数n利用随机图G(n,p)生成算法生成的100个图G∈G(n,p)实例中存在k-独立集的统计概率.从图2可以看出,当节点总数n=400固定时,随机图G(n,p)中存在k-独立集的临界概率pc随独立集节点数k的增加而减小,而且临界值pc向左移动. Fig. 2 Phase transition of k -IS in random graph G(n,p)图2 随机图G(n,p)中k-独立集的相变 Table 2 Comparison Between the Theoretical Threshold and the Numerical Simulations for the Existence of k-Independent Set in Random Gandom Graph G(n,m) 表2 随机图G(n,m)中存在k -独立集的理论临界边数和仿真临界边数对比 kn=100n=200n=300n=400n=500TheorySimulationTheorySimulationTheorySimulationTheorySimulationTheorySimulation5445540001849317114422613906375810710221191711135681031713550137691572132223368185872567830933981073281523863350105651532324994363694589466234734081060802019023250850615124202463592037328654365989610483225157830507103149251696735022313646463850426103584 图3给出了当独立集的节点数k固定时随机图G∈G(n,m)中存在k-独立集的临界边数mc随节点总数n的变化情况,这里分别取独立集节点数k=10,节点总数n分别取值为100,200,300,400,500.图3中的每个数据点是对每个给定的边数m和节点总数n利用随机图G(n,m)生成算法生成的100个图G∈G(n,m)实例中存在k-独立集的统计概率.从图3可以看出,当固定独立集节点数k=10时,随机图G(n,m)中存在k-独立集的临界边数mc随节点总数n的增加而增加,临界边数mc向右移. Fig. 3 Phase transition of 10-IS in random graph G(n,m)图3 随机图G(n,m)中10-独立集的相变 图4给出了当节点总数n固定时随机图G(n,m)中k-独立集出现相变的临界边数mc随独立集的节点数k的变化情况,这里分别取节点总数n=200,独立集节点数k分别取值为5,10,15,20,25.图4中的每个数据点是对每个给定的边数m和节点总数n利用随机图G(n,m)生成算法生成的100个图G∈G(n,m)实例中存在k-独立集的统计概率.从图4可以看出,当固定顶点数n=200时,随机图G(n,m)中存在k-独立集的临界边数mc随着独立集节点数k的增加而减小,临界边数mc向左移. Fig. 4 Phase transition of k -IS in random graph G(n,m)图4 随机图G(n,m)中k -独立集的相变 [1]Coja-Oghlan A, Efthymiou C. On independent sets in random graphs[J]. Random Structures & Algorithms, 2014, 47(3): 136-144 [2] Zhao Chunxiao, Wang Guangxing. Aδ-degree-based clustering algorithm in MANET[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2005, 42(5): 818-822 (in Chinese)(赵春晓, 王光兴. 一种δ-度约束的自组网成簇算法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2005, 42(5): 818-822) [3] Garey M R, Johnson D S. Computers and Intractability: A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness[M]. New York: W H Freeman and Company, 1979 [4] Sloane N J A. Unsolved problem in graph theory arising from the study of codes[J]. Graph Theory Notes of New York, 1989, 18(11): 11-20 [5] Erdös P, Rényi A. On random graphs I[J]. Publicationes Mathematicae, 1959(6): 290-297 [6] Wang Xiaofan, Li Xiang, Chen Guanrong. Network Science: An Introduction[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2012: 200-201 (in Chinese)(汪小帆, 李翔, 陈关荣. 网络科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2012: 200-201) [7] Hopcroft J, Kannan R. Computer Science Theory for the Information Age[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2013: 39-72 [8] Zdeborová L, Krzakaa F. Phase transitions in the coloring of random graphs[J/OL]. Physical Review E Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics, 2007, 76(3): Article Number 031131. [2016-09-01]. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.76.031131 [9] Xu Ke, Li Wei. Exact phase transitions in random constraint satisfaction problems[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2000, 12(1): 93-103 [10] Xu Ke, Li Wei. Many hard examples in exact phase transitions[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2006, 355(3): 291-302 [11] Mertens S, Zard M, Zecchina R. Threshold values of random K-SAT from the cavity method[J]. Random Structures & Algorithms, 2006, 28(3): 340-373 [12] Nekovee M, Moreno Y, Bianconi G, et al. Theory of rumour spreading in complex social networks[J]. Physica A Statistical Mechanics & Its Applications, 2008, 374(1): 457-470 [13] Gómezgardees J, Lotero L, Taraskin S N, et al. Explosive contagion in networks[J/OL]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): Article Number 19767. [2016-09-01]. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19767 [14] Culberson J, Gao Yong, Anton C. Phase transitions of dominating clique problem and their implications to heuristics in satisfiability search[DB]. Trier, Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany: DBLP, 2005 [2016-09-01]. http://dblp.org/db/conf/ijcai/ijcai2005.html [15] Nehéz M, Olejár D, Demetrian M. A detailed study of the dominating cliques phase transition in random graphs[C] //Proc of the 9th Annual Int Conf on Theory and Applications of Models of Computation. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 594-603 [16] Bollobasi B. Random Graphs[M]. New York: Academic Press, 2001 [17] Seierstad T G. The phase transition in random graphs and random graph processes[D]. Berlin: Humboldt University, 2007 [18] Nehéz M, Olejár D, Demetrian M. On emergence of dominating cliques in random graphs[EB/OL]. 2008 [2016-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/0805.2105 [19]Dharwadker A. The independent set algorithm[OL]. 2006 [2016-09-01]. http://www.dharwadker.org/independent_set/ [20] Nobari S, Lu X, Karras P, et al. Fast random graph generation[C] //Proc of the 14th Int Conf on Extending Database Technology. New York: ACM, 2011: 331-342 PhaseTransitionPropertiesofk-IndependentSetsinRandomGraphs Lu Youjun and Xu Daoyun (CollegeofComputerScienceandTechnology,GuizhouUniversity,Guiyang550025) phase transition property; random graphs;k-independent set; threshold probability; threshold edge number 2016-09-14; 2016-12-05 国家自然科学基金项目(61262006,61462001,61540050,61762019);贵州省重大应用基础研究项目(JZ20142001);贵州大学研究生创新基金项目(2016047) This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61262006, 61462001, 61540050, 61762019), the Major Applied Basic Research Program of Guizhou Province (JZ20142001), and the Graduate Student Innovation Foundation of Guizhou University (2016047). 许道云(dyxu@gzu.edu.cn) TP301 LuYoujun, born in 1985. PhD candidate. Student member of CCF. His main research interests include computational complexity and complex networks. XuDaoyun, born in 1959. Professor and PhD supervisor at the College of Computer Science and Technology, Guizhou University. Senior member of CCF. His main research interests include computability theory and computational complexity.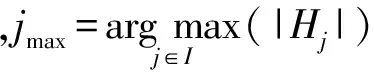
4 数值实验分析

5 结束语