基于CDS的分布式协作共识频谱感知方法
2017-11-21黄庆东闫乔乔
黄庆东,孙 晴,闫乔乔
基于CDS的分布式协作共识频谱感知方法
黄庆东,孙 晴,闫乔乔
(西安邮电大学通信与信息工程学院,信息与通信技术国家级实验教学中心 西安 710121)
针对原有全网络分布式协作共识方法信息交互量大、收敛速度慢、共识收敛结果不稳定的问题,本文在分布式协作共识频谱感知方法的基础上,提出了基于连通支配集的分布式协作共识频谱感知方法。该方法通过网络连通支配子集进行网络频谱感知信息的收集和共识计算,获得稳定的共识结果,再将共识结果分享给网络其他非支配集节点,实现全网络快速共识收敛。与原有分布式协作共识方法相比,降低了网络节点间的信息交互量,并且能快速收敛到稳定、精确的共识结果,仿真结果验证了算法的优良特性。
认知无线电; 连通支配集; 协作频谱感知; 共识
认知无线电(cognitive radios, CRs)主要用于克服无线通信频谱资源的短缺问题,使次用户在不干扰主用户的情况下获得对空闲频谱资源的使用。CRs中谱感知方式可通过非协作或协作的方式实施,本文研究的是一群次用户通过协作的方式实施频谱感知的情况。协作方式可以避免和改善影深和遮掩衰落对检测结果的影响,另外空间分布的用户具有更好的区域覆盖性,有助于提高准确度。
CRs中频谱感知[1]主要有3种方式:匹配滤波理论最优,但需要主用户先验信息;能量检测次优,它简单易实施,对主用户没有太多要求;循环平稳特征检测方法能够检测信噪比(signal to noise ratio, SNR)很低的信号,但它也需要主用户的先验知识[2]。文献[3]提出了分布协作感知,通过分布的次用户协作达到共识并最终判决,特别适应网络中无线衰落严重的用户检测,但是并没有考虑和利用网络拓扑资源。随着无线通信的发展,CRs技术和应用得到广泛关注,文献[4]研究了时变衰落信道下认知无线电技术;文献[5]利用CRs技术改善工业环境中干扰的影响;文献[6]研究了CRs协作信息传递时的信息碰撞问题。近年来,网络拓扑可知理论用于改善网络性能,得到关注和研究[7-9]。连通支配集(connected dominating set, CDS)是网络拓扑的重要方面。文献[9]研究了无线ad hoc网络高效路由机制,提出了连通支配集的简单有效计算方法,以及拓扑改变时的动态更新/重算方法。
本文将文献[3]与文献[9]中的方法相结合,在原算法中考虑了网络拓扑的有利因素,提出基于连通支配集的分布式协作共识频谱感知方法。
1 感知模型及其分布式实现
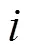
1.1 频谱感知模型




图1 能量检测方块图

1.2 网络模型和共识概念

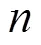
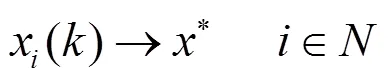
1.3 分布式协作共识频谱感知
1) 对于固定连通网络模型,网络拓扑不发生改变的情况
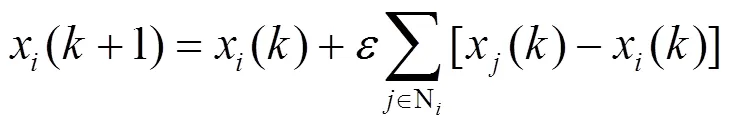
其中,

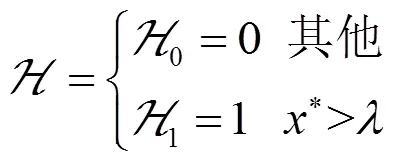
2) 对于随机网络模型,网络拓扑发生随机改变的情况
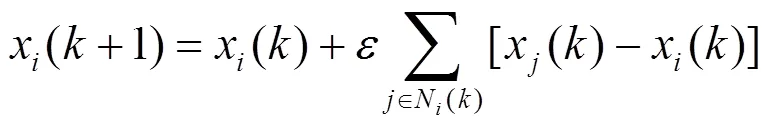
2 连通支配集分布式共识频谱感知
分布式协作共识虽然能够达到一致收敛,但没有借助拓扑结构提升共识速度。实际上可以采用全网络节点分布式协作,并在连通支配集上快速形成稳定共识,然后将结果分享给其他非支配集节点来提升网络共识状态的收敛速度,且最终一致收敛结果不变。
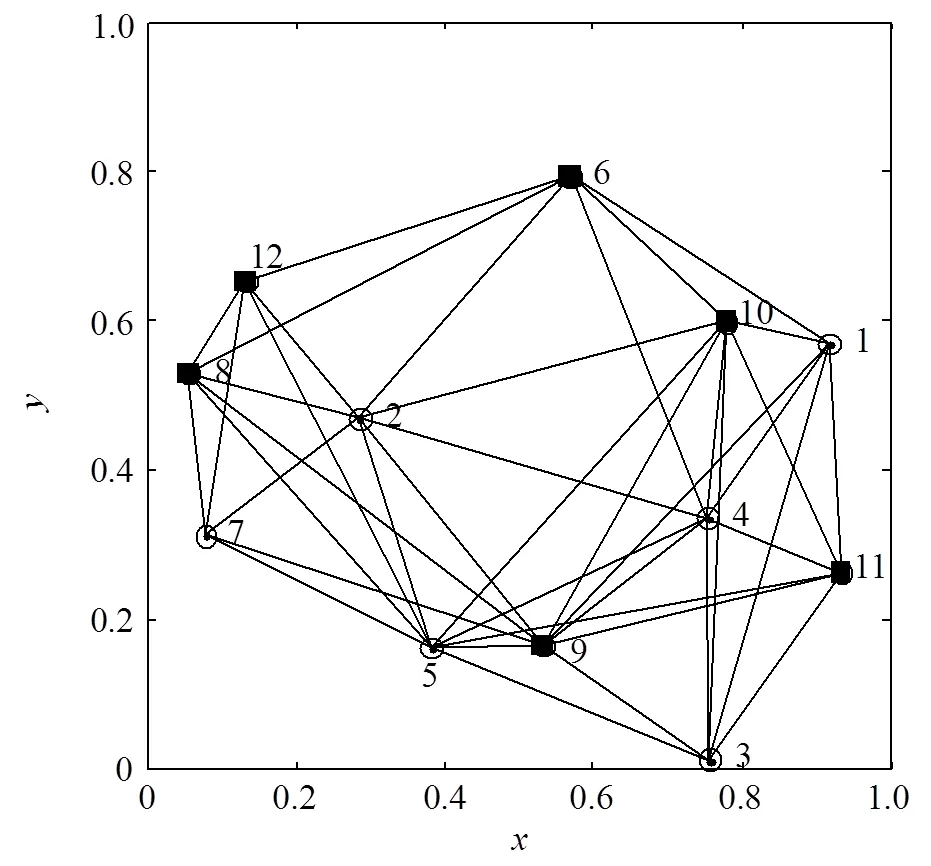
图2 网络拓扑图
连通支配集由连通的支配节点构成,网络所有节点要么在当前连通支配集中,要么是连通支配集的邻居节点[9]。如图2所示,12个节点随机分布于长宽各为1的正方形区域,节点间的边用连线表示,图中黑色方块是连通支配集节点{6,8,9,10,11,12}。连通支配集经过单步可以到达网络中的任意节点,故网络信息通过它可以高效传递。因此将文献[3]的方法与连通支配集相结合,可以借助网络拓扑结构,达到快速达成共识的效果。对于包含链路误差的随机网络模型,文献[9]提出了相应的更新和重算措施。
2.1 固定无向网络模型分布式共识频谱感知方法



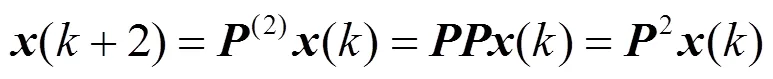
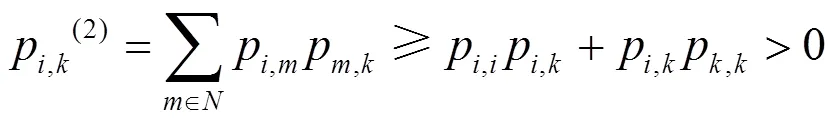
另:
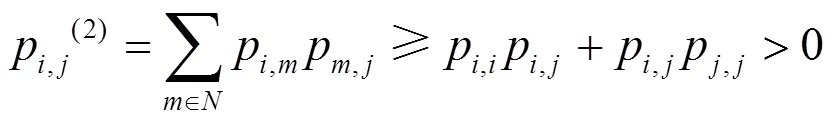



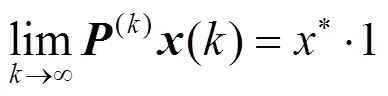
不同于文献[3]中的算法,这里各节点按照连通支配集分享的收敛值进行判决,进而有效地利用拓扑资源提升算法性能。连通支配集收敛值作为全网络的收敛值分享给周围非支配集的邻居节点,最后根据式(7)进行判决。
2.2 链路失败的无向随机网络分布式共识频谱感知

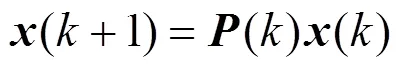

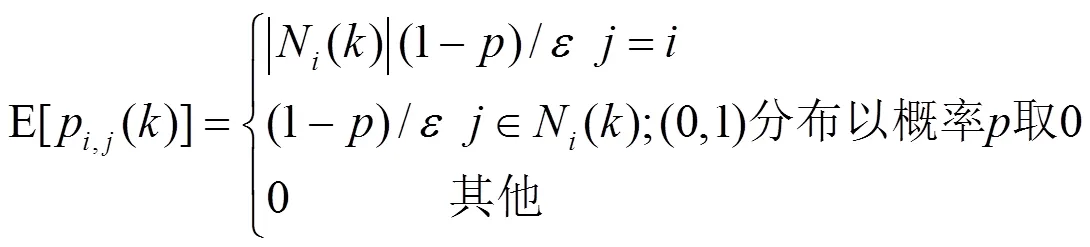
3 仿真分析
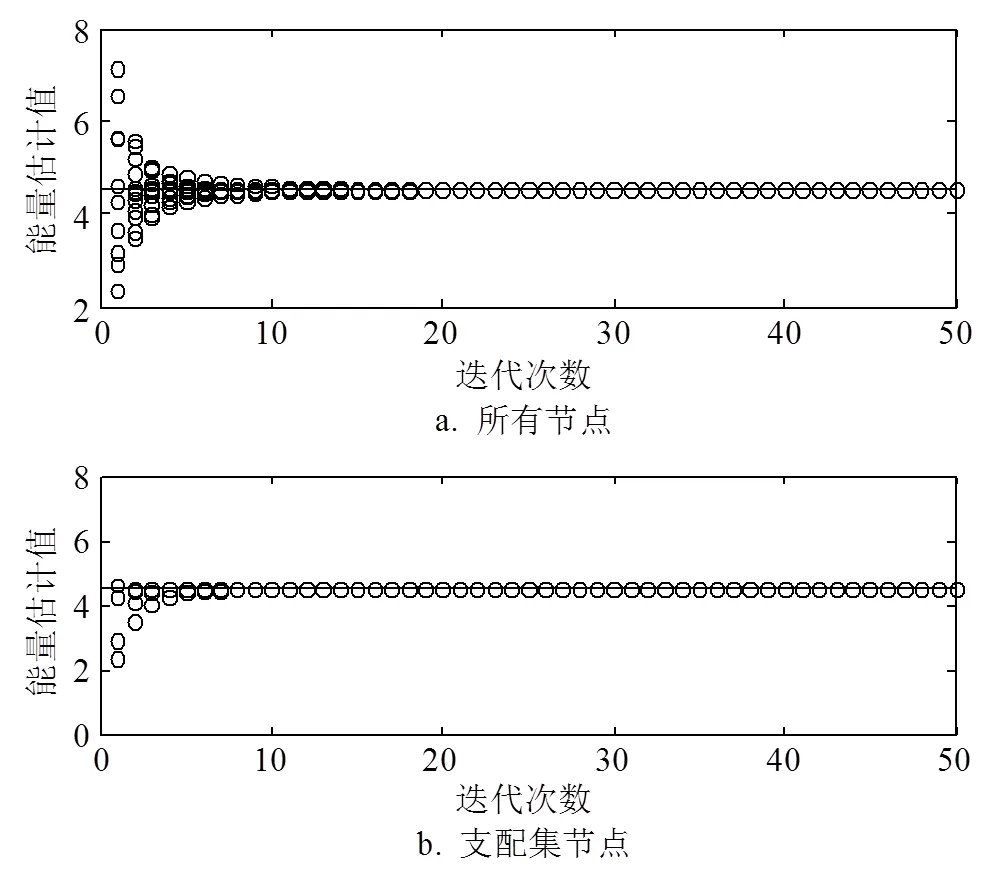
图3 12个节点固定网络

图4 20个节点随机网络

4 结束语
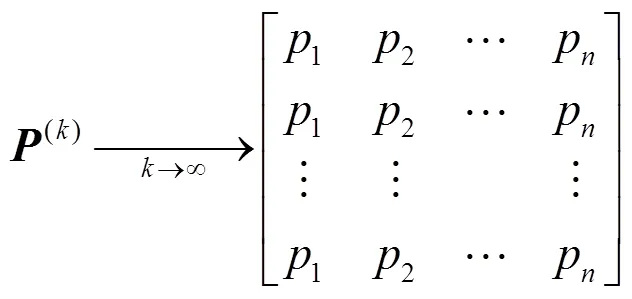
本文研究了无向网络中无中心分布式共识策略认知无线电频谱感知方法,对固定网络和随机网络中分布式感知收敛性进行了全新的推证,并将原有算法与支配集特性结合,利用支配集收敛结果能够更快获得收敛值,可将收敛分享给其他非支配集节点实现各个节点的判决。支配集与分布式算法结合使用体现了拓扑未知的分布式算法向拓扑可知分布式计算的过渡和迈进,这使得分布式算法与网络实际拓扑能够更好的匹配,算法性能得到更好的优化。当采用支配集与分布式结合的算法后,网络中其他节点通过支配集节点连接传输网络节点采集的信息,同时节点可以分享支配集的共识结果;另外因为支配集与其邻居节点覆盖了整个网络所有节点,所以可以避免信息的冗余传输、信道的资源浪费,同时可以节约能耗、提升信息的传递效率和分布式计算的收敛速度。
[1] CABRIC D, MISHRA S, BRODERSEN R. Implementation issues in spectrum sensing for cognitive radios[C]//The 38th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers. California: IEEE, 2004: 772-776.
[2] SUN C, ZHANG W, LETAIEF K B. Cluster-based cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio systems[C]//The 2007 IEEE International Conference on Communications. Glasgow, Scotland: IEEE, 2007: 2511-2515.
[3] LI Zhi-qiang, RICHARD Y U F, HUANG Min-yi. A distributed consensus-based cooperative spectrum-sensing scheme in cognitive radios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2010, 59(1): 383-392.
[4] LI B, SUN M, LI X, et al. Energy detection based spectrum sensing for cognitive radios over time-frequency doubly selective fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(2): 402-417.
[5] CHIWEWE T M, MBUYA C F, HANCKE G P. Using cognitive radio for interference-resistant industrial wireless sensor networks: an overview[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 11(6): 1466-1481.
[6] LUNDÉN J, MOTANI M, POOR H V. Distributed algorithms for sharing spectrum sensing information in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(8): 4667-4678.
[7] BERTRAND A, MOONEN M. Seeing the bigger picture: How nodes can learn their place within a complex ad hoc network topology[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2013, 30(3): 71-82.
[8] BERTRAND A, MOONEN M. Distributed computation of the fiedler vector with application to topology inference in ad hoc networks[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(5): 1106-1117.
[9] JIE W U, HAILAN L I. A dominating-set-based routing scheme in ad hoc wireless networks[J]. Telecommunication Systems, 2001, 18(1-3): 13-36.
[10] URKOWITZ H. Energy detection of unknown deterministic signals[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1967, 55(4): 523-531.
[11] KOSTYLEV V. Energy detection of a signal with random amplitude[C]//The 2002 IEEE International Conference on Communications. New York: IEEE, 2002: 1606-1610.
[12] HUANG M, MANTON J H. Coordination and consensus of networked agents with noisy measurements: Stochastic algorithms and asymptotic behavior[J]. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2009, 48(1): 134-161.
编 辑 叶 芳
Distributed Consensus Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Method Based on Connected-Dominating-Set
HUANG Qing-dong, SUN Qing, and YAN Qiao-qiao
(Informations and Communications Technology of National Experimental Teaching Center, School of Communication and Information Engineering, Xi’an University of Posts and Telecommunications Xi’an 710121)
Aiming at the problems of large amount of information exchange, slow convergence and unstable convergence result of the original whole-network distributed cooperative consensus method, a distributed consensus cooperative spectrum sensing method based on connected-dominating-set is proposed. In this paper, the connected-dominating-set method collects information of network spectrum sensing and does consensus calculation through the network connected dominating subset, which gets a stable consensus result. Then, the consensus results are shared to other non-dominated nodes in the network, so rapid convergence is achieved. There are two advantages of the proposed method compared with the original network distributed cooperative consensus method. One is that the amount of information exchanged among network nodes reduces, the other is that the network can quickly converge to a stable and accurate consensus result. The proof of convergence theorem of distribution consensus is given in this paper. Lastly, the simulation results show the excellent characteristics of this new algorithm.
cognitive radios; connected dominating set; cooperative spectrum sensing; consensus
TN911.23
A
10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2017.05.004
2016-04-12;
2017-06-02
国家重大专项(2017ZX03001012-005)
黄庆东(1976-),男,副教授,博士,主要从事分布式信号处理、阵列信号处理、低复杂度算法等方面研究.
