热活化过硫酸盐氧化修复柴油污染土壤
2017-11-10李永涛
李永涛 罗 进 岳 东
(西南石油大学化学化工学院,四川 成都 610500)
热活化过硫酸盐氧化修复柴油污染土壤
李永涛 罗 进 岳 东
(西南石油大学化学化工学院,四川 成都 610500)
采用热活化过硫酸盐法,考察了过硫酸盐浓度、温度、水土比和初始pH对柴油污染土壤氧化修复的影响,并分析了其动力学和热力学参数。结果表明,当Na2S2O8摩尔浓度为0.8mmol/g、温度为70 ℃、水土比为2.0mL/g、初始pH为11.00时,反应72h后的柴油降解率最高,达到77.85%。动力学和热力学分析表明,热活化过硫酸盐氧化降解柴油过程为自发、吸热、熵增的过程,表观活化能为-80.73kJ/mol。
硫酸根自由基 柴油 热活化 过硫酸盐
随着石油工业的迅速发展,大量的石油污染物进入地表水、包气带土层,甚至迁移至地下水,严重影响了生态环境和农业生产。因此,石油污染土壤亟待修复。石油污染物主要包括原油及其炼制品(汽油、煤油、柴油等)。物理修复虽然是石油污染土壤最重要的修复方法,但污染物并不能完全去除;生物修复的修复周期较长且对污染物具有选择性;相比而言,化学修复的优势是对污染物具有普适性、修复周期短且能彻底去除污染物[1-3]。

1 材料与方法
1.1 材料和仪器
0#柴油,密度为0.84 g/cm3,购自成都市新都区某加油站;过硫酸钠(Na2S2O8)、四氯化碳(CCl4)等,均为分析纯试剂;实验用水为去离子水。
FA2004型电子天平;GKC型数显智能恒温水浴锅;PHS-3E型pH计;OIL-460型红外分光测油仪。
1.2 供试土壤
供试土壤,取自西南石油大学周边(含油量低于检出限)0~20 cm的表层土壤,去除砾石、动植物残体后,于室内阴凉处自然风干,过60目(0.25 mm)筛备用,风干后土壤的含水率为1.12%,总有机质为3.25 g/kg,pH为8.52。
1.3 实验设计
按10.0 mL/kg的油土比把柴油与风干土壤混合均匀,置于阴凉干燥通风处1周[15],测得含油量为3 120.09 mg/kg。对过硫酸盐浓度、温度、水土比和初始pH进行单因素影响实验,反应时间为72 h。
1.3.1 过硫酸盐浓度的影响实验
控制柴油污染土壤10 g、水土比2.0 mL/g、温度50 ℃、初始pH 6.58,考察Na2S2O8摩尔浓度(0.4~1.0 mmol/g)对柴油的降解率影响。
1.3.2 温度的影响实验
控制柴油污染土壤10 g、水土比2.0 mL/g、初始pH 6.58、Na2S2O8摩尔浓度0.8 mmol/g,考察温度(30~80 ℃)对柴油的降解率影响。
1.3.3 水土比的影响实验
控制柴油污染土壤10 g、Na2S2O8摩尔浓度0.8 mmol/g、初始pH 6.58、温度70 ℃,考察水土比(0.5、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0 mL/g)对柴油的降解率影响。
1.3.4 初始pH的影响实验
控制柴油污染土壤10 g、水土比2.0 mL/g、Na2S2O8摩尔浓度0.8 mmol/g、温度70 ℃,考察初始pH(3.00、5.00、7.00、9.00、11.00)对柴油的降解率影响,并考察了初始pH为3.00、7.00、11.00时的后续pH变化。
1.4 含油量测定
根据《城市污水处理厂污泥检测方法》(CJ/T 221—2005)中的《城市污泥 矿物油的测定 红外分光光度法》测定含油量,用CCl4作萃取剂, 红外分光测油仪测定,检出限为0.10 mg/kg。
1.5 热力学和动力学参数计算
在Na2S2O8摩尔浓度为0.8 mmol/g、水土比为2.0 mL/g、初始pH为6.00的条件下,考察温度为40、50、60、70 ℃时的柴油降解动力学过程,采用准一级动力学方程进行拟合[16-18],得到表观反应速率常数(k,s-1)。
热力学参数标准吉布斯自由能变(ΔGθ,J/mol)、标准焓变(ΔHθ,J/mol)和标准熵变(ΔSθ,J/(mol·K))根据式(1)和式(2)计算。
ΔGθ=-RTlnk
(1)

(2)
式中:R为理想气体常数,J/(mol·K),R=8.314 J/(mol·K);T为热力学温度,K。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 过硫酸盐浓度对柴油降解率的影响


图1 Na2S2O8摩尔浓度对柴油降解率的影响Fig.1 Effect of Na2S2O8 molar concentration on the degradation efficiency of diesel oil
2.2 温度对柴油降解率的影响


图2 温度对柴油降解率的影响Fig.2 Effect of temperature on the degradation efficiency of diesel oil
2.3 水土比对柴油降解率的影响


图3 水土比对柴油降解率的影响Fig.3 Effect of water-soil ratio on the degradation efficiency of diesel oil
2.4 初始pH对柴油降解率的影响
由图4可见,在偏碱性条件和偏酸性条件都有较高的柴油降解率得到,但初始pH为11.00时柴油降解率相对最高,为77.85%。进一步考察初始pH分别为3.00、7.00、11.00条件下的后续pH变化,结果如图5所示。在3种初始pH条件下进行反应,72 h后pH均降至1.50左右,可能初始pH对柴油降解率的影响并不是很大。
2.5 动力学和热力学分析
动力学和热力学参数计算结果如表1所示。由表1可知,热活化过硫酸盐氧化降解柴油过程的标准吉布斯自由能变均为负值,表明该过程可自发进行。标准焓变为正值,表明该降解过程为吸热反应,温度升高有利于降解进行,与2.2节的分析结果吻合。标准熵变为正值,表明热活化后,过硫酸盐及柴油相界面的混乱度有增加的趋势,接触几率增加,有助于反应进行。根据表观反应速率常数计算得到,热活化过硫酸盐降解柴油污染土壤的表观活化能为-80.73 kJ/mol。

图4 初始pH对柴油降解率的影响Fig.4 Effect of initial pH on the degradation efficiency of diesel oil

图5 降解过程中pH的变化Fig.5 The varation of pH during the reaction process
3 结 论
(1) 当Na2S2O8摩尔浓度为0.8 mmol/g、温度为70 ℃、水土比为2.0 mg/L、初始pH为11.00时,柴油降解率最高,为77.85%。
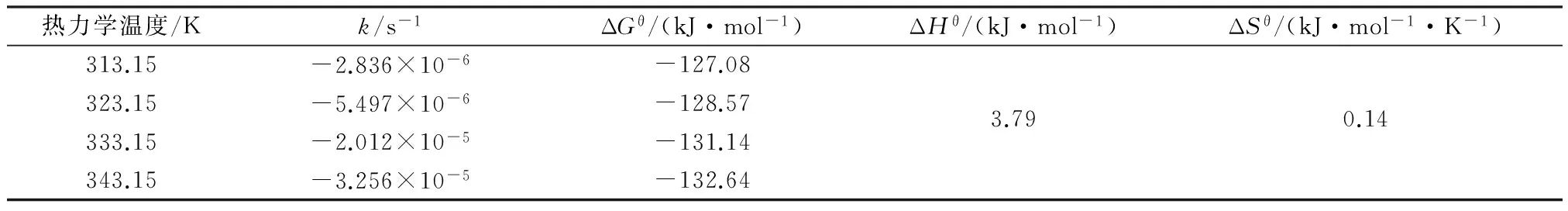
表1 动力学和热力学参数
(2) 热活化过硫酸盐氧化降解柴油过程为自发、吸热、熵增的过程,表观活化能为-80.73 kJ/mol。
[1] 冯俊生,张俏晨.土壤原位修复技术研究与应用进展[J].生态环境学报,2014,23(11):1861-1867.
[2] 王威,苏小四,张玉玲,等.石油类污染场地的自然衰减作用[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2011,41(增刊1):310-314,327.
[3] 吴昊,孙丽娜,王辉,等.活化过硫酸钠原位修复石油类污染土壤研究进展[J].环境化学,2015,34(11):2085-2095.
[4] 纪录,张晖.原位化学氧化法在土壤和地下水修复中的研究进展[J].环境污染治理技术与设备,2003,4(6):37-42.
[5] 孙艳英,刘菲,陈鸿汉,等.H2O2氧化修复柴油污染土壤[J].应用化学,2007,24(6):680-683.
[6] YEN C H,CHEN K F,KAO C M,et al.Application of persulfate to remediate petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil:feasibility and comparison with common oxidants[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,186(2/3):2097-2102.
[7] CAO J S,ZHANG W X,BROWN D G,et al.Oxidation of lindane with Fe(Ⅱ)-activated sodium persulfate[J].Environmental Engineering Science,2008,25(2):221-228.
[8] ZHOU L,ZHENG W,YUE F,et al.Ferrous-activated persulfate oxidation of arsenic(Ⅲ) and diuron in aquatic system[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013,263:422-430.
[9] DENG D Y,LIN X T,OU J M,et al.Efficient chemical oxidation of high levels of soil-sorbed phenanthrene by ultrasound induced,thermally activated persulfate[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,265:176-183.
[10] LI H X,WAN J Q,MA Y W,et al.Influence of particle size of zero-valent iron and dissolved silica on the reactivity of activated persulfate for degradation of acid orange 7[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2014,237:487-496.
[11] LIANG C J,GUO Y Y.Remediation of diesel-contaminated soils using persulfate under alkaline condition[J].Water,Air,& Soil Pollution,2012,223(7):4605-4614.
[12] HORI H,YAMAMOTO A,KOIKE K.Persulfate-iduced photochemical decomposition of a fluorotelomer unsaturated carboxylic acid in water[J].Water Research,2007,41(13):2962-2968.
[13] PENG H J,ZHANG W,LIU L,et al.Degradation performance and mechanism of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE209) by ferrous-activated persulfate in spiked soil[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,307:750-755.
[14] CHEN X Q,MURUGANANTHAN M,ZHANG Y R.Degradation of p-Nitrophenol by thermally activated persulfate in soil system[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2016,283:1357-1365.
[15] ZHAN D,LIAO X Y,YAN X L,et al.Effect and mechanism of persulfate activated by different methods for PAHs removal in soil[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013,254/255:228-235.
[16] WALDENER R H,TRATNYEK P G,JOHNSON R L,et al.Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by heat-activated persulfate:kinetics and products[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(3):1010-1015.
[17] MORA V C,ROSSO J A,MARTIRE D O,et al.Phenol depletion by thermally activated peroxydisulfate at 70 ℃[J].Chemosphere,2011,84(9):1270-1275.
[18] WAN L K,PENG J,LIN M Z,et al.Hydroxyl radical,sulfate radical and nitrate radical reactivity towards crown ethers in aqueous solutions[J].Radiation Physics & Chemistry,2012,81(5):524-530.
[19] HORI H,NAGAOKA Y,MURAYAMA M,et al.Efficient decomposition of perfluorocarboxylic acids and alternative fluorochemical surfactants in hot water[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2008,42(19):7438-7443.
Thermoactivatedpersulfateoxidationforremediationofdieseloilcontaminatedsoil
LIYongtao,LUOJin,YUEDong.
(SchoolofChemistryandChemicalEngineering,SouthwestPetroleumUniversity,ChengduSichuan610500)
Thermo activated persulfate oxidation was selected to repair diesel oil contaminated soil. The effects of concentration of persulfate,temperature,water-soil ratio,and initial pH on the degradation efficiency of diesel oil were investigated,and kinetic and thermodynamic parameters were analyzed. Results showed that the degradation efficiency of diesel oil reached peak (77.85%) when Na2S2O8molar concentration was 0.8 mmol/g,temperature was 70 ℃,water-soil ratio was 2.0 mL/g,and initial pH was 11.00 after 72 h. According to the kinetic and thermodynamic analysis,it was showed that the remediation process could occur spontaneously. The oxidation process was a endothermic and entropy-increasing reaction with an apparent activation energy of -80.73 kJ/mol.
10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2017.10.021
李永涛,男,1977年生,博士,副教授,主要从事油气田环境污染防治与地下水环境保护研究。
2016-11-07)
