冠心病患者经皮冠状动脉介入术后支架内再狭窄的危险因素分析
2017-11-03刘惠芬孙园园
邹 文,宋 嫣,赵 新,刘惠芬,孙园园
(南昌市第一医院超声科, 南昌 330008)
冠心病患者经皮冠状动脉介入术后支架内再狭窄的危险因素分析
邹 文,宋 嫣,赵 新,刘惠芬,孙园园
(南昌市第一医院超声科, 南昌 330008)
目的探讨冠心病(coronary atherosclerotic heart disease,CHD)患者经皮冠状动脉介入术(percutaneoues coronary intervention,PCI)后支架内再狭窄(in stent restenosis,ISR)的危险因素。方法收集2013年1—12月在南昌市第一医院成功接受PCI术130例CHD患者的临床资料,其中术后12个月行冠状动脉造影检查发生再狭窄49例(A组),无再狭窄81 例(B组)。对2组的相关临床资料行单因素分析与Logistic回归分析。结果A组左心房容积指数(LAVI)值、支架数量、高血压例数较B组显著增加(P<0.05 );LAVI值、高血压、支架数量是CHD患者PCI术后发生ISR的独立危险因素。结论CHD患者PCI术后发生ISR与LAVI值、高血压、支架数量相关。
冠心病; 经皮冠状动脉介入术; 支架内再狭窄; 危险因素
冠心病(coronary atherosclerotic heart disease,CHD)是威胁人类健康的常见疾病,现今治疗方法主要包括口服药物治疗、介入治疗、手术治疗等[1-2]。随着经皮冠状动脉介入术(percutaneoues coronary intervention,PCI)的临床广泛运用,如今已成为治疗冠心病最为常用的改善心肌血流灌注的方法之一。但PCI术后一般3~6个月支架内再狭窄(in stent restenosis,ISR)发生率高达10%~20%,如何有效地预防和控制ISR的发生率仍是目前医学研究的热点。相关诊断共识[3-4]表明,以体表面积计算的左心房容积指数(left atrial volume index,LAVI)≥32 mL·m-2是独立预测发生不良心血管事件的指标。本研究对2013年1—12月在南昌市第一医院成功接受PCI术130例CHD患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析,旨在探讨CHD患者PCI术后发生 ISR的危险因素。
1 资料与方法
1.1临床资料
130例CHD患者均为左冠状动脉前降支病变且为药物金属洗脱支架植入,经PCI术均成功,且无并发症发生。术后12个月行冠状动脉造影检查,再狭窄49例(A组),其中男30例,女19例,年龄50~76(60.61±10.89)岁;无再狭窄81 例(B组),其中男41例,女30例,年龄48~79(66.28±11.05)岁。
所有病例均于PCI术前记录下详细临床病史资料,包括高血压史、糖尿病史、血脂水平、身高、体质量等,且行超声心动图相关参数的测量,包括左心房前后径、左心房上下径、四腔心左房面积、两腔心左房面积等,术中记录植入支架数量、支架直径、病变长度及最大充气压力等相关数据。
所有病例均按标准方法进行PCI术,术后均接受阿司匹林100 mg,氯吡格雷75 mg服用6个月等药物规范治疗。
手术成功标准:残余狭窄≤30%,前向血流TIMIⅢ级,且无急性并发症。再狭窄的判断标准:诊断符合经冠状动脉造影证实支架植入段和包括支架近、远端各5 mm节段管腔直径狭窄≥50%。
1.2统计学方法
2 结果
2.1单因素分析
A组LAVI值、支架数量、高血压例数较B组显著增加(P<0.05 ),其余指标比较2组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1—2。

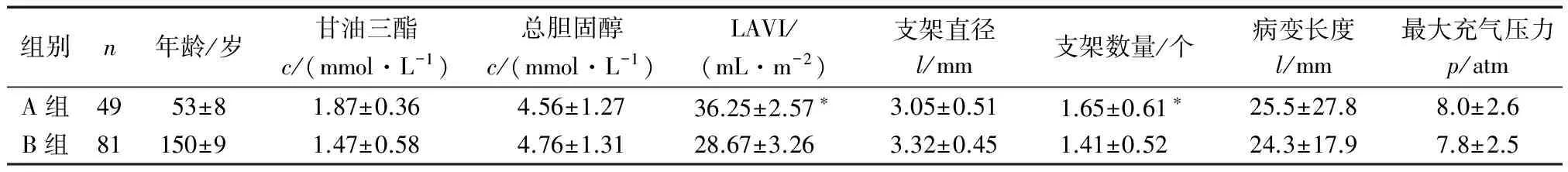
组别n年龄/岁甘油三酯c/(mmol·L-1)总胆固醇c/(mmol·L-1)LAVI/(mL·m-2)支架直径l/mm支架数量/个病变长度l/mm最大充气压力p/atmA组4953±81.87±0.364.56±1.2736.25±2.57∗3.05±0.511.65±0.61∗25.5±27.88.0±2.6B组81150±91.47±0.584.76±1.3128.67±3.263.32±0.451.41±0.5224.3±17.97.8±2.5
*P<0.05与B组比较;1 atm=101.325 kPa。

表2 2组计数资料比较 例
*P<0.05与B组比较。
2.2多因素Logistic回归分析
多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,LAVI值、支架数量、高血压是CHD患者PCI术后支架内再狭窄的独立危险因素,其中LAVI值与PCI术后发生再狭窄的OR值为1.624,95%CI为1.227~1.836(P<0.05);支架数量与PCI术后发生再狭窄的OR值为2.206,95%CI为1.589~3.316(P<0.05);高血压与PCI术后发生再狭窄的OR值为1.963,95%CI为1.165~2.786(P<0.05)。
3 讨论
PCI术是临床上常用于冠心病治疗的一种重要手段,但是进行介入治疗不可避免的会对血管内皮细胞造成损害,术后血管存在一定的再狭窄率。所以,ISR仍然是当今PCI术所面临的巨大挑战[5]。
目前认为CHD患者PCI术后ISR的发生机制主要是血管内皮细胞的完整性遭受损害后致使血管内膜过度增生,炎性因子活化、血管的重塑、微血栓的形成和血管的弹性回缩,血管重塑后期将导致血管壁的顺应性降低,并且一定程度上会发生血管壁的缩窄[6-9]。本研究结果显示,LAVI、支架数量、高血压均是PCI术后ISR的独立危险因素。
CHD合并高血压患者如果PCI术后血压控制不理想,将会加大血液对血管壁的剪切力和冲击力,增加血管内皮的二度损害,血管内皮的损伤将导致血管壁的重塑,最终致使CHD合并高血压患者更容易发生PCI术后ISR[10]。LAVI越大的CHD患者,冠状动脉粥样斑块的表面越是粗糙、边缘越容易形成隆起的偏心性狭窄或不规则狭窄,斑块容易破裂释放出栓子和致栓物质进人微循环,造成冠状动脉的二次微栓塞,反复的微栓塞可能并发心肌细胞的大量丢失,从而导致细胞外基质的数量发生改变,最终引发心肌重塑[11]。所以LAVI越大,此类CHD患者越容易发生PCI术后ISR。CHD患者植入支架数量越多,术中释放支架时承受的压力就越大,越容易破坏血管内皮的完整性,从而引起血小板的聚集,管腔内易形成微血栓,最终导致ISR[12]。本研究通过一定样本量测量CHD患者PCI术前LAVI,从而在一定程度上评估PCI术后ISR的发生率,为临床早期干预提供重要的参考价值。
[1] Dahlslett T,Karlsen S,Grenne B,et al.Early assessment of strain echoc,ardiography can aocurately exclude significant coronary artery stenosis in suspected non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome[J].J Am Soc Echocardiogr,2014,27:512-519.
[2] Koskinas K C,Windecker S,Raber L.Regrcssion of coronary athcrosclcrosis:current evidence and future perspectives[J].Trends Cardiovasc Med,2016,26:150-161.
[3] Di Biase L,Santangeli P,Anselmino M,et al.Does the left atrial appendagemorphology correlate with the risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation.Results from a multicenter study[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2012,60:531-538.
[4] Yamamoto M.Complex left atrial appendage morphology and left atrial appendage thrombus formation in patients with atrial fibrillation[J].Circ Cardiovasc Imaging,2014,7(2):337-343.
[5] Kaul U,Bangalore S,Seth A,et al.Paclitaxel-eluting versus everolimus-eluting coronary stents in diabetes[J].N Engl J Med,2015,373(18):1709-1719.
[6] 李方江,徐涛,工亚玲,等.冠状动脉介入治疗心肌梗死患者外周血内皮祖细胞与血管内皮生长因子的变化田[J].中华老年医学杂志,2012,31(7):555-557.
[7] Otsuka F,Vorpahl M,Nakano M,et al.Pathology of second-generation everolimus-eluting stems versus first-generation sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stems in humans[J].Circulation,2014,129(2):220-223.
[8] Cameo G,Tebaldi M,Vranckx P,et al.Short-versus long-term duration of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients treated for in-stmt restenosis:a PRODIGY trial substudy(Prolonging Dual Antiplatelet Treatment After Grading Stent-Induced Intimal Hyperplasia)[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2014,63(6):506-512.
[9] 刘永胜,江华,刘文卫,等.冠心病PCl术后再狭窄患者1L-18 ,IL-10和基质金属蛋自酶-9水平的研究[J].国际检验医学杂志,2014,35(11):1431-1432.
[10] Kurre W,Aguilar Prez M,Fischer S,et al.Solving the lssue of restenosis after stenting of lntracranial stenoses:Experience with two thin-strut drug-eluting stems(DES)-taxus element and resolute integrity?[J].Cardiovasc Ther Rad,2014,26:1-9.
[11] Leung D Y,Chi C,Allman C,et al.Prognostic implications of left atrial volume index in patients in sinus rhythm[J].Am J Cardiol,2010,105(11):1635-1639.
[12] Guerra E,Byrne R A,Kastrati A.Pharmacological inhibition of coronary restenosis:systemic and local approaches[J].Expert Opin Pharmacother,2014,15(15):2155-2171.
(责任编辑:况荣华)
RiskFactorsforIn-StentRestenosisFollowingPercutaneousCoronaryInterventioninPatientswithCoronaryHeartDisease
ZOUWen,SONGYan,ZHAOXin,LIUHui-fen,SUNYuan-yuan
(DepartmentofUltrasound,NanchangFirstHospital,Nanchang330008,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the risk factors for in-stent restenosis(ISR) following percutaneous coronary intervention(PCI) in patients with coronary heart disease(CHD).MethodsClinical data of 130 CHD patients who underwent PCI in Nanchang First Hospital between January and December 2013 were analyzed using univariate analysis and logistic regression analysis.Coronary angiography performed at 12 months postoperatively showed that 49 patients had restenosis(group A) and 81 patients had no restenosis(group B).ResultsCompared with group B,left atrial volume index(LAVI),number of stents and number of patient with hypertension significalty increased in group A(P<0.05).Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that LAVI,hypertension and number of stents were the independent risk factors for ISR following PCI in CHD patients.ConclusionThe LAVI,hypertension and number of stents are correlated with the occurrence of ISR following PCI in patients with CHD.
coronary atherosclerotic heart disease; percutaneous coronary intervention; in-stent restenosis; risk factors
R654.2
A
1009-8194(2017)08-0074-02
2017-02-20
邹文(1984—),男,硕士,主治医师,主要从事心脏超声的诊断研究。
10.13764/j.cnki.lcsy.2017.08.031
