类风湿性关节炎患者外周血白细胞介素-37及可溶性PD-1分子的检测价值分析
2017-09-15马万明岳飞利白珊珊周自城杨名宇
马万明,岳飞利,白珊珊,周自城,杨名宇
四川省雅安市人民医院 检验科(雅安625000)
·论著·
类风湿性关节炎患者外周血白细胞介素-37及可溶性PD-1分子的检测价值分析
马万明,岳飞利,白珊珊,周自城,杨名宇
四川省雅安市人民医院 检验科(雅安625000)
目的研究类风湿性关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)患者外周血抗炎性因子及可溶性PD-1(soluble PD-1,SPD-1)分子的检测价值。方法选择2015年1月至2016年12月四川省雅安市人民医院收治的RA患者68例纳入病例组,选择同期健康人68例纳入对照组,以酶联免疫吸附试验检测两组外周血白细胞介素-37(IL-37)、白细胞介素-1(IL-1)、干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)、肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)及SPD-1等细胞因子水平,评价病例组患者RA诊断得分,并判断病例组IL-37、SPD-1与RA诊断得分、IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α水平的相关性。结果病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1、IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α水平均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1和RA诊断得分呈正相关性(P<0.05);病例组外周血IL-37与IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α均呈正相关性(P<0.05);病例组外周血SPD-1与IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α均呈正相关性(P<0.05)。结论RA患者外周血IL-37、SPD-1与RA的严重程度及其他多种炎性因子密切相关,在RA的临床检测中具有较高应用价值。
类风湿性关节炎;抗炎性因子;可溶性PD-1分子;炎性因子;检测价值
类风湿性关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)是以关节炎性反应为主要特点的自身免疫性疾病,早期表现为关节热痛红肿及功能障碍,继续发展可逐渐出现关节不同程度的畸形变化,并累及关节外多个系统[1]。资料[2]显示,RA发病机制较为复杂,但最终均导致关节腔炎性反应,炎性反应常引发关节腔内纤维及肉芽组织增生,严重影响关节腔正常血供,并最终导致关节腔局部坏死,累及关节。有研究[3]显示,免疫功能紊乱是引发RA的关键机制,在RA发病及进展过程中,干扰素、趋化因子、白细胞介素、协同刺激分子等细胞因子起到了重要作用。为探究RA发病机制,四川省雅安市人民医院于2015年1月至2016年12月检测RA患者外周血白细胞介素-37(interleukin-37,IL-37)与可溶性PD-1(soluble PD-1,SPD-1)分子,以探究IL-37、SPD-1与RA的关系,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1临床资料
选择2015年1月至2016年12月我院收治的RA患者共68例,其中,男38例(55.88%),女30例(44.12%),年龄20~69(46.52±4.63)岁。纳入标准:1)符合美国风湿病学院与欧洲风湿病防治联合会2010年制定的RA诊断标准患者;2)30 d内未行免疫抑制剂治疗患者;3)无其他感染性疾病患者;4)知情同意患者。排除标准:1)系统性红斑狼疮患者;2)急慢性疾病史患者;3)肝肾功能异常患者;4)恶性肿瘤患者;5)其他风湿性疾病患者;6)糖尿病患者。将上述68例RA患者纳入病例组。选择同期健康人68例纳入对照组,其中,男35例(51.47%),女33例(48.53%),年龄21~70(46.36±4.61)岁。两组性别、年龄和体质量指数(BMI)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性(表1)。
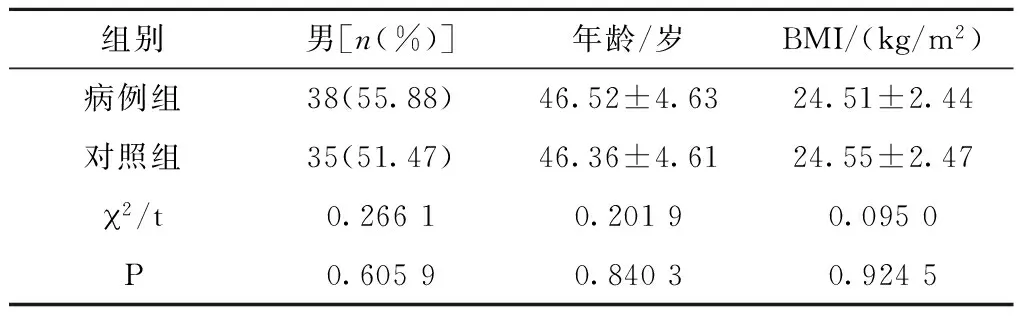
表1 两组一般资料比较(n=68)
1.2方法
以酶联免疫吸附试验检测两组外周血IL-37、白细胞介素-1(interleukin 1,IL-1)、干扰素-γ(interferon-γ,IFN-γ)、肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)及SPD-1等细胞因子水平。两组均于清晨采集3 mL空腹静脉血,3 000 r/min,离心半径10 cm,离心15 min,血浆分离后于-80 ℃温度下保存待测,检测严格按照试剂盒说明书进行。为避免误差,每个外周血重复检测3次。检测仪器为酶标分析仪(南京普朗医疗设备有限公司,型号:DNM-9606);IL-37、IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α、SPD-1检测试剂盒(Uscn Life Science, Inc)。
1.3RA诊断评分标准
受累关节:0分:中~大关节1个;1分:中~大关节2~10个;2分:小关节1~3个;3分:小关节4~10个;5分:小关节>10个。外周血:0分:抗环胱氨酸肽抗体与类风湿因子均为阴性;1分:抗环胱氨酸肽抗体或类风湿因子为低滴度阳性;2分:>低滴度阳性,但≤正常值上限的3倍;3分:抗环胱氨酸肽抗体或类风湿因子为高滴度阳性。滑膜炎:0分:持续时间<6周;1分:持续时间≥6周。急性期反应物:0分:红细胞沉降率与C反应蛋白均正常;1分:红细胞沉降率或C反应蛋白异常[4]。
1.4统计学方法
2 结果
2.1两组外周血IL-37、SPD-1水平比较
病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1水平均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表2)。
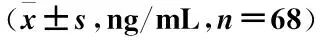
表2 两组外周血IL-37、SPD-1水平比较
2.2两组外周血IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α水平比较
病例组外周血IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α水平均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表3)。
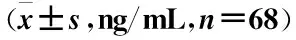
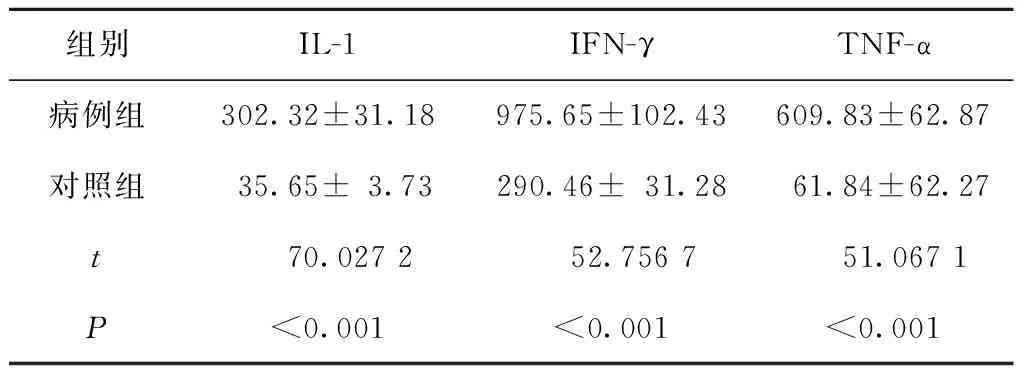
组别IL-1IFN-γTNF-α病例组302.32±31.18975.65±102.43609.83±62.87对照组35.65±3.73290.46±31.2861.84±62.27t 70.0272 52.7567 51.0671P<0.001<0.001<0.001
2.3病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1与RA诊断得分的相关性
病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1和RA诊断得分存在明显正相关性(P<0.05)(表4)。
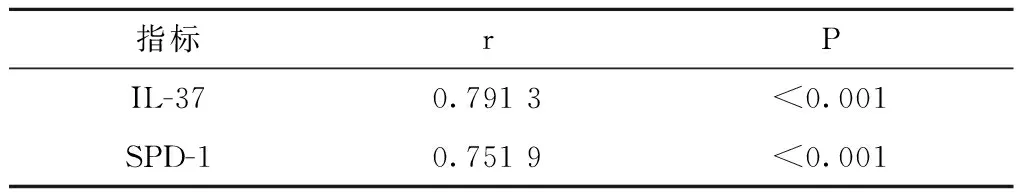
表4 病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1和RA诊断得分的相关性
2.4病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1与IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α的相关性
病例组外周血IL-37与IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α均存在明显正相关性(P<0.05);病例组外周血SPD-1与IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α均存在明显正相关性(P<0.05)(表5)。
表5病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1与IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α的相关性
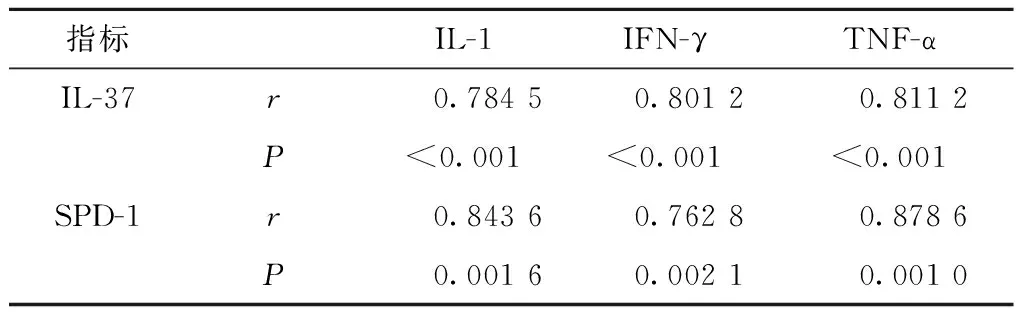
指标IL-1IFN-γTNF-αIL-37r 0.7845 0.8012 0.8112P<0.001<0.001<0.001SPD-1r 0.8436 0.7628 0.8786P 0.0016 0.0021 0.0010
3 讨论
研究[5]发现,炎性细胞因子与抗炎性细胞因子失去平衡是引发关节炎性反应的重要机制,而自身免疫性疾病与上述失衡关系密切。有研究[6]证明,IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α在RA发病进程中具有重要作用。IL-1可参与炎性反应,刺激滑膜及软骨细胞生成基质金属蛋白酶等,抑制表达基质金属蛋白酶-3抑制剂,降解软骨基质[7];IL-1还可抑制关节软骨细胞增殖及诱导其凋亡[8]。IFN-γ可提高巨噬细胞活性,促进释放氧自由基、蛋白酶及NO的释放,导致滑膜及软骨损伤[9];IFN-γ还可激活NK细胞,促进炎性介质分泌,参与滑膜组织细胞与免疫细胞间的作用,促进RA发展[10]。TNF-α能够诱导黏附分子表达,促进白细胞的黏附渗透,引发局部炎性反应[11];TNF-α可刺激软骨细胞、滑膜成纤维细胞生成胶原酶及前列腺素E2,抑制合成骨胶原,促进成纤维细胞增生,促进骨质的破坏与吸收[12]。
IL-37为抗炎性细胞因子,属于IL-1家族,在自身免疫性疾病中可抑制机体炎性反应[13]。研究[14-16]证明,IL-37可抑制STATsl-4磷酸化,影响促炎性因子信号传导通道以减轻炎性反应;IL-37可结合Smad3,经抑制STAT1、STAT3拮抗炎性反应;IL-37可抑制促炎性转录因子中的c-Jun,而促炎性转录因子可经IL-1诱导;IL-37能够降低p38MAPK的磷酸化水平,抑制促炎性反应信号传导通道;IL-37还可促进CSK3α/β激酶磷酸化,降低其活性,发挥抑制炎性反应的作用。此外,IL-37可通过结合Smad3蛋白,提高TGF-β活性,抑制固有免疫反应与适应性免疫反应,纠正自身免疫性失衡状态,促进关节软骨与骨的修复[17]。SPD-1分子为协同刺激分子,可参与血液循环,调节免疫应答,纠正免疫失衡[18]。研究[19-20]证明,SPD-1可抑制自身免疫性疾病患者促炎性反应T细胞的过度反应,保护组织细胞;SPD-1还可抑制B细胞,减少分泌IFN-γ、IL-10等细胞因子,起到免疫调节的作用。在本研究中,病例组外周血IL-37、IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α、SPD-1水平均高于对照组(P<0.05),提示在RA患者机体存在着一定的炎性反应。此外,本研究结果表明,病例组外周血IL-37、SPD-1与IL-1、IFN-γ、TNF-α、RA诊断得分均呈正相关性(P<0.05),说明IL-37、SPD-1与部分炎性因子及病情进展关系密切,在RA病理发展进程中具有重要作用。
综上所述,IL-37、SPD-1与RA患者外周血多种炎性因子及RA严重程度密切相关,在RA的临床检测中具有较高应用价值,可应用于RA诊断。
[1]Gauri L A, Fatima Q, Diggi S,etal. Study of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and its Co-relation with Severity of the Disease[J]. J Assoc Physicians India, 2017, 65(4): 26-30.
[2]Penatti A, Facciotti F, De Matteis R,etal. Differences in serum and synovial CD4+ T cells and cytokine profiles to stratify patients with inflammatory osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2017, 19(1): 103.
[3]肖雪野. 抗 CCP 抗体、补体及免疫球蛋白在类风湿性关节炎病理过程中的变化及临床意义[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2017, 23(4): 514-517.
[4]杨超, 刘荣臻, 张晓延, 等. 类风湿性关节炎患者血清中IL-37水平变化的探索研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2014, 12(7): 1035-1037.
[5]Nakachi S, Sumitomo S, Tsuchida Y,etal. Interleukin-10-producing LAG3+ regulatory T cells are associated with disease activity and abatacept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2017, 19(1):91.
[6]朱阳春, 刘丹冰, 林琳, 等. 补肾通督胶囊对类风湿性关节炎患者TH1/TH2细胞平衡的影响[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2014, 41(7): 1451-1453.
[7]Atabaki M, Hashemi M, Daneshvar H,etal. Association between interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 1 rs3027898 A/C gene polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Biomedical Reports, 2017, 6(3): 335-338.
[8]Hahn M, Frey S, Hueber A J. The novel interleukin-1 cytokine family members in inflammatory diseases[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2017, 29(2): 208-213.
[9]孟明, 陈丹, 许鸣华, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者 iNKT 细胞频率与 IFN-γ/IL-4的相关性研究[J]. 中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2015, 35(3): 213-218.
[10] 申健, 王瑞琳, 徐瑾, 等. 类风湿性关节炎滑膜组织中IFN-γ和IL-4的表达及意义[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2014, 30(5): 519-522.
[11] Vanier A, Mariette X, Tubach F,etal. Cost-Effectiveness of TNF-Blocker Injection Spacing for Patients with Established Rheumatoid Arthritis in Remission: An Economic Evaluation from the Spacing of TNF-Blocker Injections in Rheumatoid Arthritis Trial[J]. Value Health, 2017, 20(4): 577-585.
[12] Fehlman J A, Burkemper N M, Missall T A. Ulcerative necrobiosis lipoidica in the setting of anti-tumor necrosis factor-α and hydroxychloroquine treatment for rheumatoid arthritis[J]. JAAD Case Reports, 2017, 3(2): 127-130.
[13] Yang L, Zhang J, Tao J,etal. Elevated serum levels of Interleukin-37 are associated with inflammatory cytokines and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Apmis, 2015, 123(12): 1025-1031.
[14] Cavalli G, Koenders M, Kalabokis V,etal. Treating experimental arthritis with the innate immune inhibitor interleukin-37 reduces joint and systemic inflammation[J]. Rheumatology (Oxford), 2016, 55(12): 2220-2229.
[15] Xia L, Shen H, Lu J. Elevated serum and synovial fluid levels of interleukin-37 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Attenuated the production of inflammatory cytokines[J]. Cytokine, 2015, 76(2): 553-557.
[16] 陈栖栖, 田娟, 张晶, 等. 类风湿关节炎患者血清IL-37和可溶性PD-1分子的表达水平及临床意义[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2017, 33(3): 422-425.
[17] Yang T, Lin Q, Zhao M,etal. IL-37 Is a Novel Proangiogenic Factor of Developmental and Pathological Angiogenesis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2015, 35(12): 2638-2646.
[18] Bommarito D, Hall C, Taams L S,etal. Inflammatory cytokines compromise programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)-mediated T cell suppression in inflammatory arthritis through up-regulation of soluble PD-1[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2017,188(3): 455-466.
[19] Greisen S R, Rasmussen T K, Stengaard-Pedersen K,etal. Increased soluble programmed death-1 (sPD-1) is associated with disease activity and radiographic progression in early rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2014, 43(2): 101-108.
[20] Li S, Liao W, Chen M,etal. Expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1) on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Inflammation, 2014, 37(1): 116-121.
TheValueofDetectingHumanInterleukin-37andSolublePD-1inthePeripheralBloodofPatientswithRheumatoidArthritis
MaWanming,YueFeili,BaiShanshan,ZhouZicheng,YangMingyu.
DepartmentofClinicalLaboratory,YaanPeople'sHospitalofSichuan,Yaan625000,China
ObjectiveTo explore the value of detecting human Interleukin-37(IL-37) and soluble PD-1(SPD-1) in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).Methods68RA cases treated in Yaan People's Hospital of Sichuan from January of2015to December of2016were selected into the case group, while the other68healthy cases over the corresponding period were selected into the control group. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) was used to detect the levels of cytokines including IL-37, Interleukin-1(IL-1), Interferon-γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and SPD-1in the peripheral blood of the two groups. The diagnosis of those RA patients were evaluated and scored. Then the analysis was made to explore whether the levels of IL-37and SPD-1were correlated with the RA diagnostic score and the levels of IL-1, IFN-γ and TNF-α respectively.ResultsThe levels of IL-37, SPD-1, IL-1, IFN-γ and TNF-α in the case group were significantly higher than those in the control group respectively (P<0.05). The levels of IL-37and SPD-1were positively correlated with the RA diagnostic score respectively in the case group (P<0.05). The levels of IL-37and SPD-1were positively correlated with the levels of IL-1, IFN-γ and TNF-α respectively in the case group (P<0.05).ConclusionThe levels of IL-37and SPD-1in the peripheral blood of patients with RA are correlated with the severity of RA and the other inflammatory factors, so the detection of IL-37and SPD-1has high application value in the clinical examination of RA.
Rheumatoid arthritis; Anti-inflammatory factor; Soluble PD-1; Inflammatory factor; Detective value
http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1705.R.20170829.1023.002.html
10.3969/j.issn.1674-2257.2017.04.027
R446.62
A