基于农田无线传感网络的分簇路由算法
2017-09-15唐大卫邬智俊韩光洁河海大学物联网工程学院常州30常州市传感网与环境感知重点实验室常州30
江 冰,毛 天,唐大卫,邬智俊,韩光洁(. 河海大学物联网工程学院,常州 30;. 常州市传感网与环境感知重点实验室,常州 30)
基于农田无线传感网络的分簇路由算法
江 冰1,毛 天1,唐大卫1,邬智俊1,韩光洁2
(1. 河海大学物联网工程学院,常州 213022;2. 常州市传感网与环境感知重点实验室,常州 213022)
由于无线传感网络节点的能量有限,如何有效地利用有限资源以及实现数据的有效传输,成为研究热点问题。针对农田区域广以及种植作物杂等环境特征,为延长农田无线传感器网络的生命周期,提高传感网的数据包投递率,构建了适用于农田信息采集的无线传感器网络架构,提出了一种混合式的分簇路由算法HCRA(hybrid clustering routing algorithm),研究了簇的形成、簇头竞选以及簇间路由过程,并对HCRA算法与低功耗自适应集簇分层型算法LEACH(low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy),以及使用固定簇半径的混合节能分簇算法HEED(hybrid energy-efficient distributed clustering)进行了仿真试验。结果表明:在1 000次迭代周期下,采用HCRA算法的网络生存时间要比LEACH算法长约28%,比HEED算法长约12%;采用HCRA算法的数据包投递率要比LEACH算法高约34个百分点,比HEED算法高约16个百分点。该研究可为农田环境信息采集自动化监测系统提供参考。
无线传感网络;数据传输;算法;分簇路由算法;网络生命周期;数据包投递率;HRCA算法
0 引 言
中国传统农业中,农户往往是通过实地考察农作物生长环境,凭借经验栽种农作物。这种传统的人工监测办法,容易造成判断错误,导致农户采取不当措施,造成农作物减产[1]。近些年来,农业领域出现了一些监测系统,然而大多为有线实时监测系统,其存在不足之处[2]:1)有线监测节点的布置需要大量地布线,在实际环境下操作不灵活;2)有线方式在实际的农业生产应用中,线缆容易损坏导致系统可靠性降低。而无线传感网技术可以有效地解决有线监测系统中存在的问题[3-5]。因此,需要有效地利用无线传感器网络技术来改造传统农业。
虽然无线传感器网络技术在农业上得到了一定的应用。如张波等[6]基于无线传感器网络的无人机农田信息监测系统;杜克明等[7]WebGIS在农业环境物联网监测系统中的设计与实现;高峰等[8]基于无线传感器网络的作物水分状况监测系统研究与设计。然而,无线传感器网络节点在使用过程中能量通常不能补给,因而如何高效利用能量以及延长网络生命周期,成为无线传感器网络的首要设计目标。研究表明,采用合理的无线传感器网络分簇路由算法可以有效地延长网络生命周期,提高网络数据包传递率[9-11]。
为延长网络生存周期,分簇是比较常用的一种办法。LEACH (low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy)是为WSN (wireless sensor networks)设计的低功耗自适应路由协议,其基本思想是网络周期性地随机选择簇头节点,其它的非簇头节点就近地加入相应的簇头,形成虚拟簇[12-14]。
PEGASIS(power efficient gathering in sensor information system)协议基本思想是从网络中离汇聚节点最远的节点开始,采用贪婪算法,将网络中的所有传感器节点形成一条链,使得节点只需要与离它距离最近的相邻节点进行通信即可[15-17]。HEED(hybrid energy-efficient distributed clustering)协议是由Ossama等提出的。簇头的选择主要依据主、次2个参数。主参数依赖于剩余能量,用于随机选取初始簇头集合。具有较多剩余能量的节点将有较大的概率暂时成为簇头,而最终该节点是否一定是簇头取决于剩余能量是否比周围节点多得多。考虑到分簇后簇内的通信开销,HEED以簇内平均可达能量(AMRP,average minimum reachability power)作为衡量簇内通信代价的标准[18-20]。
近些年,国内外相关学者对路由分簇算法也有一定的研究。陈炳才等[21]提出了一种基于LEACH协议改进的簇间多跳路由协议,刘伟强等[22]对无线传感器网络中的PEGASIS算法进行了研究与改进,姚新兵等[23]提出了一种基于HEED的簇首多跳融合路由算法, Amirthalingam[24]、Sapna Gambhir[25]、Bennani Mohamed Taj[26]等对LEACH 算法进行了研究与改进,Mishra[27]、Ghosh[28]等对PEGASIS算法进行了研究与改进,Taheri[29]、Jain[30]等对HEED协议进行了研究与改进。
LEACH算法中,所有簇头节点都直接与汇聚节点进行通信,这会使得离汇聚节点较远的簇头节点能量消耗严重;PEGASIS算法虽然减少了与汇聚节点直接通信的节点数,然而容易使网络形成较长的链路,从而缩短网络的寿命;HEED算法采用簇头直接与汇聚节点通信也要消耗很大的能量[31]。基于农田监测范围大,针对无线传感网的能量消耗问题,参考LEACH算法和HEED算法的原理,本文提出了一种适用于农田信息采集的混合式分簇路由算法HCRA(hybrid clustering routing algorithm)。
1 网络模型与能耗模型
1.1 网络模型
本文研究的被监测对象是农田土壤,传感器节点安置在农田里,为固定节点,研究所选的农田抽象成为圆形区域,节点信息可以在这片区域内按照一定的规则来传递。由于农田的监测范围大,节点之间进行通信所需的能量消耗较大。此外,随着农作物的生长,节点间传输消息所需的能耗也会越来越大,远离汇聚节点的节点信息可能无法有效地传输给汇聚节点,因此网络中需要多个汇聚节点。根据农田环境的特征,提出了具有以下特点的无线传感器网络模型:
1)传感网所监测的区域为圆形,半径为R(m);
2)传感网由N个普通节点组成,均能正常工作,且具有完全相同的功能和能量,节点部署完成后其位置固定不变,节点均匀分布在区域内;
3)节点能感知自身的剩余能量,当节点能量低于节点收发数据实际可用的最大能量时,节点不能进行收发工作;
4)每个节点都有唯一的ID,可以通过接收到的信号强度估算出发送节点与自身的距离,并可以根据通信距离的长短调整发射功率的大小。
1.2 能耗模型
无线传感器网络节点的能量消耗模型[32]如图1所示。
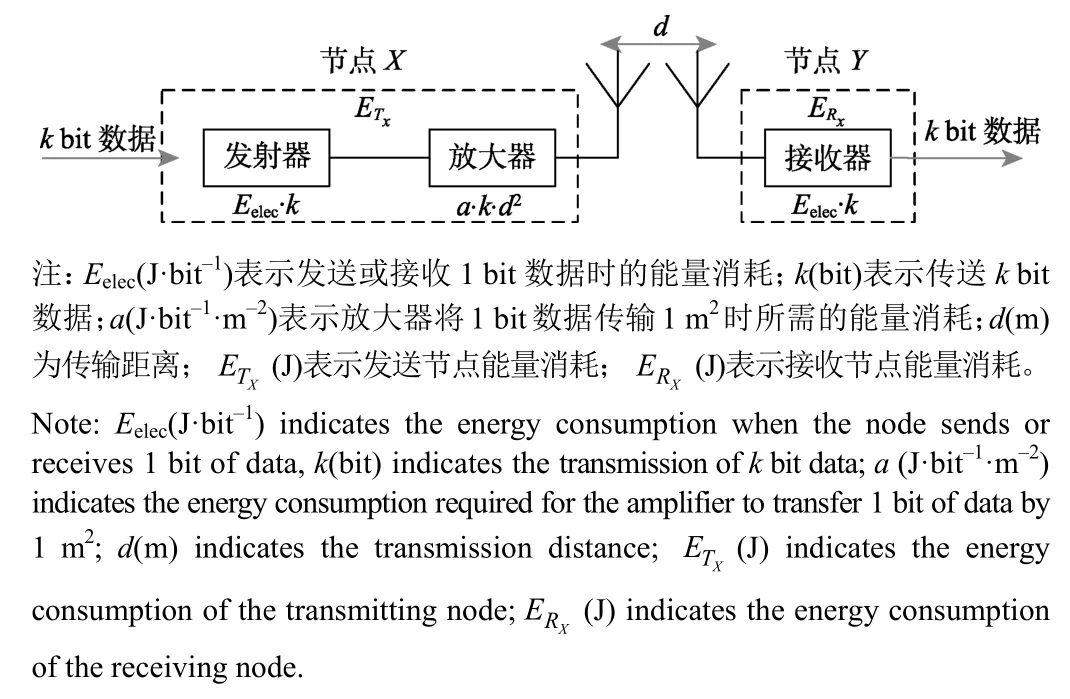
图1 无线传感网节点能量消耗模型Fig.1 Wireless sensor network node energy consumption model
根据此模型,假设节点X向与之距离为d的节点Y传输k比特数据,则发射节点和接收节点能量消耗分别如式(1)和式(2)所示。

式中a1和a2分别表示放大器在自由空间模型和多路径衰减模型中将1 bit数据传输1 m2时所需的能量消耗。d0=为临界距离。当传输距离d小于d0时,功率放大损耗采用自由空间模型;当传输距离d大于等于d0时,采用多路径衰减模型。此外,从式(1)可以看出,无线传感器网络节点发送数据的能量消耗随着其与接收节点之间的距离的增大而增大。
2 HCRA算法
基于农田无线传感器网络的分簇路由算法HCRA由簇的形成、簇头竞选、和簇间路由3个阶段组成。
2.1 簇的形成
基于节点能量的利用率考虑,HCRA算法将整片农田区域划分成若干小型区域。假定整个农田灌溉区域的基本形状是一个圆形区域,共部署了N个传感器节点。首先将中心节点sink置于圆心位置,然后从sink节点出发,以sink为圆心分别以r(m),2r,3r…为半径将整个圆形区域划分为m层,再将整个圆区域平均分为6部分(扇区)。每一个部分中的每个层分别再细分,例如,第一层分为1份,第二层分为2份…记Aijk,i(1~m)为节点所在层数编号,j(1~6)为扇区编号,k(1~m)为第i层第j个扇区中划分的区域编号(按顺时针进行编号),以此类推。每一层中的一小份区域即组成了无线传感器网络中的一个簇。算法中簇的形成如图2所示。
由于每一层各簇面积相等,进而使得同层中的簇处于一种同等的水平。层与层之间具有相等的面积差,因而不同层中的簇也处于同一水平。为保证簇头之间能够进行通信,即扇形的相邻环之间的簇能够进行通信,需满足条件2r〈d2(r(m)为层与层之间的距离,d2(m)为两节点在农田环境下的通信距离阈值)。在某一区域出现异常的情况下,基于编号的机制,一方面可以通过编号对节点进行定位,能及时发现问题区域;另一个方面,可以减小因为节点定位而产生的能耗。

图2 传感器网络分簇示意图Fig.2 Sensor network clustering diagram
HCRA算法中,簇形成后不再改变,与LEACH这种每轮循环都要重新构造簇的算法相比,大大减少了构造簇的能量消耗。同时,此算法中,簇头之间的通信仅局限于同一个扇形下的相邻层之间,因此通信的距离较之HEED算法也相应地减小了,一定程度上减小了簇头数据传输所需的能量消耗。
2.2 簇头竞选
在农田的无线传感器网络区域内,首先按照HEED算法选出每个簇的簇头节点。HEED算法具有健壮性,能够不依赖于网络规模的大小,通过O(1)次迭代过程实现分簇过程[33]。初始阶段,每个节点都需要确定同在一个簇范围内的所有相邻节点的集合,加以计算并进行广播。初始化阶段,节点之间竞争簇头,并发送竞争的消息,簇头的产生依据于各节点的初始化概率。初始化概率CHpmb的计算公式由式(3)确定。

式中Cpmb和Pmin是整个网络统一的参量,Eresident/Emax代表节点剩余能量与初始化能量的百分比。当簇头竞选成功后,其他非簇头节点依据在竞争阶段中收集来的信息有选择的加入簇。在每一次的迭代过程中,如果已有的临时节点已经被挑选出,则其他的节点则会将选择所有的临时节点中代价最小的一个作为它的临时簇头。如果没有临时簇头被挑选出,初始化概率将会加倍,继而能够以新的概率推荐自己成为临时簇头。如果成功,则将把自己已成为簇头节点的消息进行广播。
2.3 簇间路由
簇间路由是位于同一扇区不同层的簇头节点之间进行通信的路径,由此可以减小簇头之间的通信距离,减少能耗。第i层第j扇区的第l(1≤l≤I)个簇头节点需要将数据传给下一跳即第i-1层第j扇区的第n(1≤n≤l)个簇头节点,由簇形成的方式可知,下一跳有多个选择,必须综合考虑下一跳簇头节点的剩余能量以及通信代价。根据式(1)可以得出,两节点间的通信能耗与节点之间的距离平方成正比,因此两簇头之间的通信能耗同样与簇头之间的距离平方成正比。本文将簇头节点的剩余能量与单位数据通信代价的比值定义为簇头能耗比,并且选择能耗比大的簇头节点作为簇间路由的下一跳簇头,簇头能耗比的计算公式如式(4)所示。
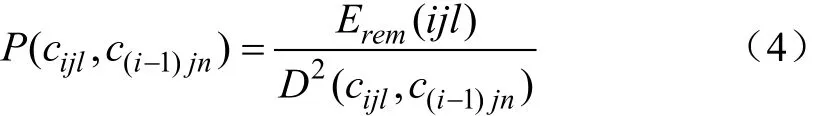
式中Erem(ijl)是第i层第j扇区的第l个簇头节点的剩余能量(J),D(cijl,c(i-1)jn)表示第i层第j扇区的第l个簇头节点到第i-1层第j扇区的第n个簇头节点的距离(m),由于节点间通信能耗与距离的平方成正比,所以D2(c,c)即代表通信代价。
ijl(i-1)jn
3 算法仿真试验
本文使用MATLAB作为平台,对提出的HCRA算法进行了仿真试验,并将其与LEACH、HEED 2种算法在无线传感网络生存时间和能量消耗方面进行了对比,网络仿真参数如表1所示。
3.1 网络生命周期
从网络生命周期上分析,仿真结果如图3a所示。LEACH算法,在0~150次的网络运行轮数中,节点死亡速率较快,100~700次,节点近乎全部死亡。HEED算法,在0~50次网络运行轮数时,没有节点死亡,在50~300次中,节点死亡速率较快,300~800次,节点死亡速率缓慢,近800次之后,节点几乎全部死亡。而HCRA算法经过1 000次的迭代,在0~75次的网络运行轮数中,几乎没有节点死亡,75~400次,节点死亡幅度较快,400~500次,节点死亡速率较75~400有所下降,500~900次,死亡幅度较慢,近900次之后,节点近乎全部死亡。据仿真结果分析可知,在迭代1 000次的情况下,采用HCRA算法的网络生存时间在相同的条件下要比LEACH算法长约28%,比HEED算法长约12%。
3.2 数据包传递率
从数据包传递率上分析,所有节点发送4 000 bit数据,对比3种算法下基站收到的数据包数目,仿真结果如图3b所示。基于LEACH算法时,在0~150次的网络运行轮数中,基站收到的数据包数目在不断增加,在200次时,投递率达到33.7%左右,并且随着节点全部死亡之后,基站收到的数据包数目不再增加。HEED算法在0~300次的网络运行轮数中,基站收到的数据包数目在不断增加,在500次时,投递率达到51.2%左右,500次之后数据包数目不再增加。而HCRA算法在0~500次的网络运行轮数中,基站收到的数据包数目在不断增加,在600次时,投递率达到67%左右,700次之后数据包数目不再增加。从仿真结果可以看出,在迭代1 000次的情况下,基于HCRA算法的数据包投递率在相同条件下要比LEACH算法高约34个百分点,比HEED算法高约16个百分点。
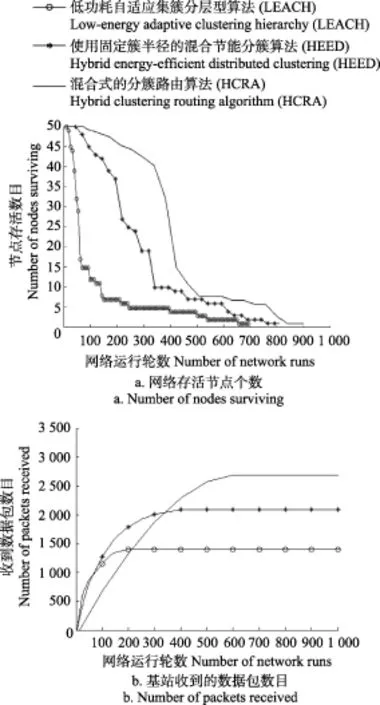
图3 网络运行轮数与各参数关系曲线Fig.3 Graph between number of running cycles of network and parameters
4 结 论
依据农田环境,构建了适用于农田信息采集的无线传感器网络架构,将农田划分为无数个小的扇区,便于节点的定位,采用层次型路由形式,实现了传感网簇头节点的均匀分布以及能量消耗的减少。基于HCRA(hybrid clustering routing algorithm)算法的分析,详细描述了传感网分簇过程、簇头的竞选过程以及簇头之间的路由,给出了仿真结果。根据仿真结果分析,在1 000次迭代周期下,采用HCRA算法的网络生存时间要比LEACH(low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy)算法长约28%,比HEED(hybrid clustering routing algorithm)算法长约12%;采用HCRA(hybrid clustering routing algorithm)算法的数据包投递率要比LEACH算法高约34个百分点,比HEED算法高约16个百分点。
[1] 王若冰. 水稻生长环境远程监控系统的研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2015. Wang Ruobing. Research on the Rice Growing Environment Remote Monitoring and Control System[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 李光云,胡钢,马国玉,等. 基于无线传感器网络的土壤墒情监测系统[J]. 微处理机,2014(2):89-93. Li Guangyun, Hu Gang, Ma Guoyu, et al. Design of farm detection system based on wireless sensor networks[J]. Microprocessors, 2014(2): 89-93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 廖建尚. 基于物联网的温室大棚环境监控系统设计方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(11):233-243. Liao Jianshang. Design of agricultural greenhouse environment monitoring system based on internet of things[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(11): 233-243. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 邹金秋,周清波,杨鹏,等. 无线传感网获取的农田数据管理系统集成与实例分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(2):142-147. Zou Jinqiu, Zhou Qingbo, Yang Peng, et al. Integration and example analysis for farmland data management system of wireless sensor networks[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(2): 142-147. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 邓然,朱勇,詹念,等. 基于ZigBee技术的温湿度数据采集系统设计[J]. 无线电通信技术,2017,43(3):81-84. Deng Ran, Zhu Yong, Zhan Nian, et al. Design of temperature and humidity data acquisition system based on zigbee technology[J]. Radio Communication Technology, 2017, 43(3): 81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张波,罗锡文,兰玉彬,等. 基于无线传感器网络的无人机农田信息监测系统[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(17):176-182. Zhang Bo, Luo Xiwen, Lan Yubin, et al. Agricultural environment monitor system based on UAV and wireless sensor networks[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(17): 176-182. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 杜克明,褚金翔,孙忠富,等. WebGIS在农业环境物联网监测系统中的设计与实现[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(4):171-178. Du Keming, Chu Jinxiang, Sun Zhongfu, et al. Design and implementation of monitoring system for agricultural environment based on WebGIS with internet of things[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(4): 171-178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 高峰,俞立,张文安,等. 基于无线传感器网络的作物水分状况监测系统研究与设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(2):107-112. Gao Feng, Yu Li, Zhang Wen'an, et al. Research and design of crop water status monitoring system based on wireless sensor networks[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(2): 107-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 吴迪,胡钢,倪刚. 无线传感器网络安全路由协议的研究[J]. 传感技术学报,2008,21(7):1195-1201.Wu Di, Hu Gang, Ni Gang. Research on secure routing protocols in wireless sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2008, 21(7): 1195-1201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] Yen L H, Tsai W T. The room shortage problem of tree-based zigbee/IEEE 802.15.4 wireless networks[J]. Computer Communication, 2010, 33(4): 454-462.
[11] Suparna Biswas, Jayita Saha, Tanumoy Nag, et al. A novel cluster head selection algorithm for energy-efficient routing in wireless sensor network[C]//Advanced Computing (IACC), 2016 IEEE 6th International Conference on. IEEE, 2016.
[12] Wendi Rabiner Heinzelman, Anantha Chandrakasan, Hari Balakrishnan. Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks[C]//In: Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii, USA, 2000: 3005-3014.
[13] Chauhan T, Nayyer M. Review on energy efficient protocol based on LEACH, PEGASIS and TEEN[C]//International Conference on Emerging Trends in Communication Technologies. IEEE, 2017.
[14] Liao C, Zhu K, Tang J, et al. Wireless sensor network performance research for Leach based on multi-agent simulation[C]// IEEE International Conference on Agents. IEEE, 2016: 98-99.
[15] Mohit A, Bharti. A comparative study between leach and pegasis: A review[C]//2016 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), 2016: 3271-3274.
[16] Fischer B, Buhmann J M. Bagging for path-based cluster[J]. IEEE Transaction on Pathern Annalysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(11): 1411-1415.
[17] Fischer B, Buhmann J M. Path-based clustering for grouping smooth curves and texture segmentation[J]. IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(4): 513-518.
[18] Youniso, Fahmy S. Heed: A hybrid energy-efficient distributed clustering approach for ad hoc sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2004, 3(4): 660-669.
[19] Hoda T, Peyman N. Improving on HEED protocol of wireless sensor networks using non probabilistic approach and fuzzy logic[C]//2015 5thInternational Symposium on Telecommunications, 2010: 193-198.
[20] Kour H, Sharma A K. Performance evaluation of HEED and H-HEED protocol for realistic models in WSN[C]// International Conference on Computer, Communication and Control. 2015: 1-5.
[21] 陈炳才,么华卓,杨明川,等. 一种基于LEACH协议改进的簇间多跳路由协议[J]. 传感技术学报,2014(3):373-377. Chen Bingcai, Yao Huazhuo, Yang Mingchuan, et al. A intercluster multi-hop routing protocol improved based on LEACH protocol[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2014(3): 373-377. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 刘伟强,蒋华,王鑫. 无线传感器网络中PEGASIS协议的研究与改进[J]. 传感技术学报,2013(12):1764-1769. Liu Weiqiang, Jiang Hua, Wang Xin. Research and improvement of PEGASIS protocol in wireless sensor network[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2013(12): 1764-1769. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 姚新兵,王向东. 一种基于HEED的簇首多跳融合路由算法[J]. 通信技术,2011,44(4):106-108. Yao Xinbing, Wang Xiangdong. A multi-hop fusion routing algorithms based on HEED[J]. Communications Technology, 2011, 44(4): 106-108. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] Amirthalingam K, Anurtaha V. Improved LEACH: A modified LEACH for wireless sensor network[C]//IEEE International Conference on Advances in Computer Applications Icaca. IEEE, 2016, 255-258.
[25] Sapna Gambhir, Parul. OE-LEACH: An optimized energy efficient LEACH algorithm for WSNs[C]//2016 Ninth International Conference on Contemporary Computing (IC3): 1-6.
[26] Bennani Mohamed Taj M, Ait Kbir M. ICH-LEACH: An enhanced LEACH protocol for wireless sensor network[C]// 2016 International Conference on Advanced Communication Systems and Information Security (ACOSIS): 1-5.
[27] Mishra A K, Rahman R U, Bharadwaj R, et al. An enhancement of PEGASIS protocol with improved network lifetime for wireless sensor networks[C]//Power, Communication and Information Technology Conference. IEEE, 2016: 142-147.
[28] Ghosh S, Mondal S, Biswas U. Enhanced PEGASIS using ant colony optimization for data gathering in WSN[C]// International Conference on Information Communication and Embedded Systems. IEEE, 2016: 1-6.
[29] Taheri H, Neamatollahi P, Naghibzadeh M, et al. Improving on HEED protocol of wireless sensor networks using non probabilistic approach and fuzzy logic (HEED-NPF)[C]// International Symposium on Telecommunications. IEEE, 2011: 193-198.
[30] Jain A K, Chargolra V, Prasad D. Reliable state-full hybrid energy efficient distributed clustering protocol for wireless sensor networks: RS-HEED[C]//IEEE, International Conference on Moocs, Innovation and Technology in Education. IEEE, 2016: 396-401.
[31] Divya P, Shivkumar S. Comparison of GSTEB, HEED and PEGASIS protocols[C]//2016 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), 2016: 1935-1939.
[32] Heinzelman W, Chandrakasan A, Balakrishnan H. An aplicationspecific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor Networks[J]. Wireless Communications, IEEE Transactions on 2002, 1(4): 660-670.
[33] Giri D, Roy U K. Address borrowing in wireless personal area network[C]//Patiala: 2009 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference, 2009: 181-186.
Clustering routing algorithm based on farmland wireless sensor network
Jiang Bing1, Mao Tian1, Tang Dawei1, Wu Zhijun1, Han Guangjie2
(1. Department of Internet of Things Engineering, Hohai University, Changzhou 213022, China; 2. Changzhou Key Laboratory of Sensing Network and Environmental Perception, Changzhou 213022, China)
As the wireless sensor network node's energy is limited, how to effectively use the limited resources and the effective transmission of data becomes a hot topic. In order to extend the life cycle of farmland wireless sensor network and improve the packet delivery rate of sensor network, a wireless sensor network suitable for farmland information collection was constructed, and a hybrid clustering routing algorithm (HCRA) was proposed in this paper. Two classical algorithms, LEACH (low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy) and HEED (hybrid energy-efficient distributed clustering), were evaluated for their merit to extend life cycle of wireless sensors. In the LEACH algorithm, all cluster head nodes communicate directly with the sink nodes, so that energy consumption of the cluster head node far from the sink node was serious, and cannot guarantee the cluster head evenly distributed, which could make some cluster head nodes’ energy consumption too large, affecting the network life cycle. The HEED algorithm, on the other hand, used the cluster head to communicate directly with the sink node, which consumed a lot of energy. Because the farmland information collection range was large, those two algorithms were not fully applicable to the wireless sensor network information gathering in farmland environment. Based on this evaluation and the principle of the HEED algorithm, we proposed a hybrid clustering routing algorithm (HCRA) for farmland information collection. In the proposed algorithm, the network model and the energy consumption models were described separately. In the network model, the monitoring area of the sensor network was abstracted as a circle area. Each node in the network had its own unique ID, and the location was not changed after the deployment was completed. All nodes were distributed evenly in the area. In the energy consumption model, the energy consumption of the wireless sensor network increased with the increase of the distance between the transmitting node and the receiving node, regardless of the power dissipation loss using the free space model or the multi-channel attenuation model. Besides, we also descried the HCRA algorithm in detail in this paper, including formation of cluster, cluster bidding and inter-cluster routing. The formation of the cluster was as follows: the center node sink was placed in the center position, and then from the sink node, taking r (the distance between layers and layers), 2r, 3r…as the radius, the entire circular area was divided into m flows. The entire area was divided into six parts, each of which was subdivided into small areas with equal area according to the number of layers. Each small area was a cluster in the wireless sensor network. The cluster head bidding process was as follows: the cluster head node was selected according to the heed algorithm, i.e., the cluster head was generated according to the initial probability of each node. When the cluster head was selected, other non-cluster head nodes joined the cluster selectively according to the collected information from the competition stage. The inter-cluster routing was the information transfer process between cluster heads, cluster head selected the next cluster head based on energy consumption. Finally, the proposed HCRA algorithm along with LEACH and HEED algorithm were simulated experimentally under the same conditions. The experimental results showed that the HCRA algorithm had 28% longer network lifetime than the LEACH algorithm, about 12% faster than the HEED algorithm, under the iteration period of 1000 times. The HCRA algorithm had a packet delivery rate, which was about 34 percentage points higher than the LEACH, and about 16 percentage points higher than HEED.
wireless sensor networks; data transfer; algorithms; clustered routing protocol; life cycle of network; packet delivery rate; HCRA(hybrid clustering routing algorithm) algorithm
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.024
TP393; S24
A
1002-6819(2017)-16-0182-06
江 冰,毛 天,唐大卫,邬智俊,韩光洁. 基于农田无线传感网络的分簇路由算法[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(16):182-187.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.024 http://www.tcsae.org
Jiang Bing, Mao Tian, Tang Dawei, Wu Zhijun, Han Guangjie. Clustering routing algorithm based on farmland wireless sensor network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(16): 182-187. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.16.024 http://www.tcsae.org
2017-03-12
2017-08-05
国家自然科学基金(61573128)
江 冰,女(汉族),江苏常州人,教授,研究方向:现代通信技术、智能信息处理。Email:jiangb@hhuc.edu.cn
