Research of tissue culture in Gynuradivaricate (L.) DC
2017-08-07LWINMoeMoeZHAOZeyiHANBoZHANGGuobin
LWIN Moe Moe, ZHAO Zeyi, HAN Bo, ZHANG Guobin
(1.School of Life Sciences, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079; 2.Department of Botany, Yeman Chaung Degree College, Myanmar; 3.Wuhan Foreign Languages School, Wuhan 430200; 4.School of Life Sciences, WuChang University of Technology, Wuhan 430223)
Research of tissue culture inGynuradivaricate(L.) DC
LWIN Moe Moe1,2, ZHAO Zeyi3, HAN Bo3, ZHANG Guobin4*
(1.School of Life Sciences, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079; 2.Department of Botany, Yeman Chaung Degree College, Myanmar; 3.Wuhan Foreign Languages School, Wuhan 430200; 4.School of Life Sciences, WuChang University of Technology, Wuhan 430223)
The tender leaves ofGynuradivaricata(L.)DC were used as the explants to research the regeneration system optimization of Eucommia. The results showed that callus inducement and callus proliferation grew well under the condition of MS+1.0 mg/L NAA+1.0 mg/L 6-BA+0.75% Agar+3% Sugar, with the induction rate of 100%. The growth cycle was 30 d at the process of callus proliferating. Growth curve appeared the shape of "S". The most suitable medium of buds inducement was MS+1.0 mg/L NAA+1.5 mg/L 6-BA. The induction rate was 100%. In a high concentration of 6-BA, the indefinite bud growth is weak. In the process of induced multiple shoots, adding suitable amount of IBA and GA is advantageous to the growth of multiple shoots, high concentration of NAA is conducive to root differentiation.
Gynuradivaricata(L.)DC; callus; induce; differentiation
Gynuradivaricata(L.) DC belongs to asteraceae family, chryantheumem, which called “Bai Bei San Qi” in China. it’s root, stem and leaf can be used as medicine[1]; and it is used as a healthy vegetable in daily life, which can improve metabolism level, build up strength of human body[2]. It is welcomed by many consumers. Recently study showed thatGynuradivaricata(L.) DC have very good effection on falling blood sugar[3]. It attached importsnce to people for its madcine value and edible value[4]. But the wild resources were damaged, the supply ofGynuradivaricata(L.) DC become less and less. BecauseGynuradivaricata(L.) DC produced few seeds, and cutting propagation is too slow. So tissue culture techniques can improve the breeding efficiency to meet the market demand.
1Materials and Methods
1.1Plant materials
tender leaves ofGynuradivaricataplants growing in soil.
1.2Plant sterilization
Young leaves ofGynuradivaricataplants growing healthy were rinsed with water for 1h , treated 30 s with 75% alcohol, rinsed twice with sterile water and then immersed into 0.1% HgCl2for 6 min. Wash away the remaining mercury, the sterilized leaves were rinsed 3~5 times with sterile water,and then put on sterile filter paper so as to remove the water on leaf surface .
1.3Tissue inoculation
The sterilized leaves were cut into small pieces about 0.4 cm×0.4 cm, put it on sterile filter paper. Then sterilized leaves were inoculated on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium (with 3% Sucrose and 0.75% Agar, pH 5.8~6.0) conical flasks supplemented with the indicated concentrations of 6-BA and NAA to induce callus. The flasks were cultured in light incubator, under condition of 16 h-light/8 h-dark photoperiod at 24℃ for cultivation. Twenty days later, the phenotype of the callus differentiation were recorded and analyzed.
1.4Callus proliferation and growth curve
For proliferation culture, the tissues grows a small amount of callus were placed to the proliferation medium. Each treatment for 6 bottles, each bottle inoculated with 7~8 explant as well. Callus on MS medium( MS+3.0% Sucrose+0.75% Agar, pH5.8~6.0) conical flasks were routinely grown under 24℃ with a 14 h-light/10 h-dark photoperiod. And 1 g weigh callus growing well was inoculated on the optimization culture medium (with the optimized proportion of callus inducement plant hormone), weighed the callus and calculated the growth rate of callus every two days to determination of growth curve.
1.5Adventitious Bud-induced Assays
Callus which growing well were placed to adventitious bud-induced medium. Each treatment for 6 bottles, each bottle have 4 explants, were Cultured on MS medium(MS+3.0% Sucrose+0.75% Agar, pH5.8~6.0) , grown under 24℃ with a 14 h-light/10 h-dark photoperiod. The callus growing well were induced to induce adventitious bud differentiation by adding different concentrations of plant growth substance and grown under 28℃ with a 16 h-light/8 h-dark photoperiod. Fifteen days later, recording the growth condition ofGynuradivaricataadventitious bud.
1.6Root-induced Assays
Gynuradivaricataplant bud growing well were cut and placed to the root-inducing medium, and were grown under 24℃ with a 16 h-light/8 h-dark photoperiod. Ten days later, the root growth status and root length was collected and recorded.
2Results
2.1Callus-induced Assays
Gynuradivaricataplant explants were inoculated into the callus-induced medium for one week later, the explants grown bigger than before and some were curled. A small amount of explants appeared white ice-like callus around the explants. After two weeks of tissue inducement, most of the explants were to be curled. And green transparent amorphous parenchyma cells came into being from leaf margin in some of the crimp explants. In addition, the explants were increasingly to be callus-like, and became bigger than before. After the explants were transferred to the callus-induced medium, almost all explants callusing. The fine condition differentiation of callus is shown in Tab.1.
Gynuradivaricataplant callus with different growth condition came into being from its explant growing on MS medium supplemented with the indicated concentrations of 6-BA and NAA, as shown in Tab.1.The explant growing on MS+1.0 mg/L NAA+1.5 mg/L 6-BA+0.75% Agar+3% Sucrose grown healthy and exuberant with yellowish green body that its around part is the pale yellow and relatively loose as well as the middle part is green and relatively close.

Tab.1 Effect of 6-BA and NAA on callus induce from explants

续表1
(—No callus;+Poor;++Nomal;+++Good;++++Extremely good)

Tab.2 Effect of MS+6-BA and NAA on callus multiplication
The results suggests that the optimized callus-induced culture medium forGynuradivaricataplant leaf is MS+1.5 mg/L NAA+1.0 mg/L 6-BA+0.75% Agar+3% Sucrose as shown in Tab.2. Moreover, these callus have pea yellow and relatively body with 100% callus-induced rate.

Fig.1 Growth cycle of Gynura divaricata callus
With the growth time goes, the quantity of cells and weight of callus was increasingly up. In the whole growth cycle, the callus growth expressed as a "S-type" curve, 0~6 d is at lag period, 7~15 d is at start phase, 16~21 d for the logarithmic growth phase, 21~30 d are stable phase.
2.2Adventitious bud-induced Assays
The results further suggests thatGynuradivaricataplant adventitious bud-induced rate is significantly high that may be relate to the species of plant materials and the optimized adventitious bud-induced culture medium is MS+0.7 mg/L NAA+1.0 mg/L 6-BA+0.75% Agar+3% Sucrose, bud-induced rate as shown in Tab.3. However, if the concentration of 6-BA exceed 1.0 mg/L, adventitious bud grow weakly, change to be yellow, not benefit for root-induced and transplanting .
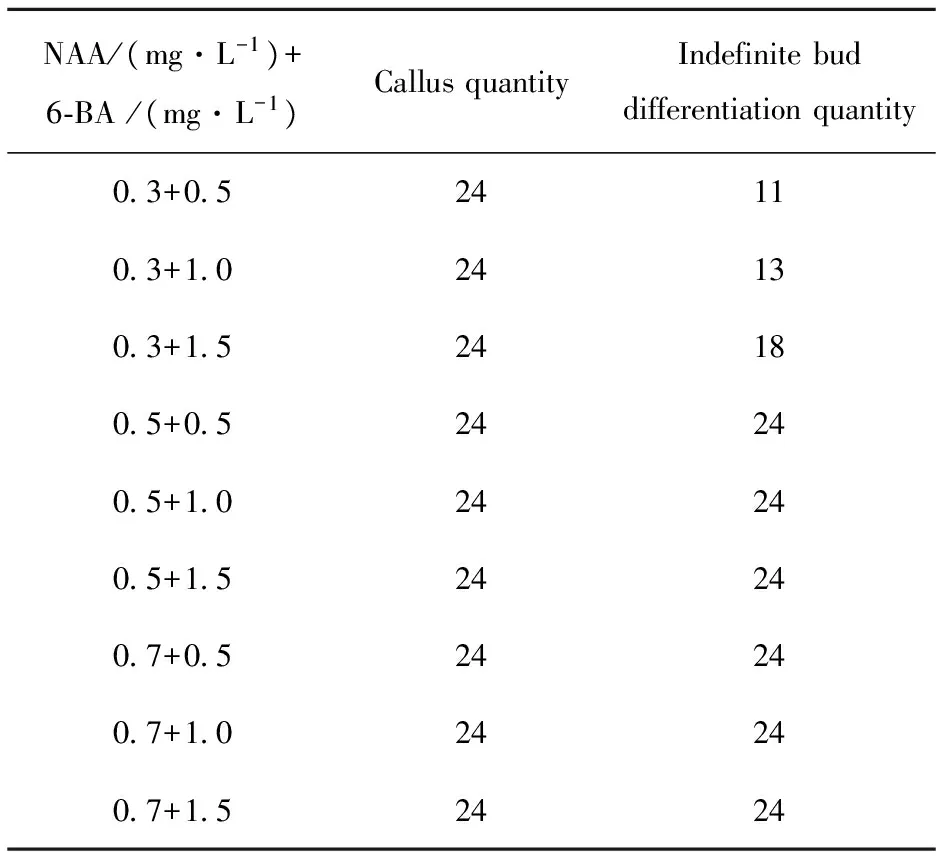
Tab.3 Effect of MS+6-BA and NAA on inducement of indefinite bud
2.3Multiple shoots differentiation inducement
Tab.4 and Tab.5 shows that only using IBA and NAA in inducing bud differentiation, and the adventitious buds is shorter and more slender. After adding 0.005 mg / L GA3 into the bud-induced medium, adventitious buds grown longer and thicker, however with the increasingly concentration of NAA, adventitious buds grown shorter. It suggests that the higher NAA concentration could inhibit the growth of adventitious buds. Therefore we can clearly know that low concentration of NAA is good forGynuradivaricataplant adventitious bud differentiation (Tab.4~5, Fig.2). 0.5 mg/L IBA+0.1 mg/L NAA is the best on multiple shoots differentiation, and the roots grew well.

Tab.4 Effect of MS+BA and NAA on multiple shoots differentiation
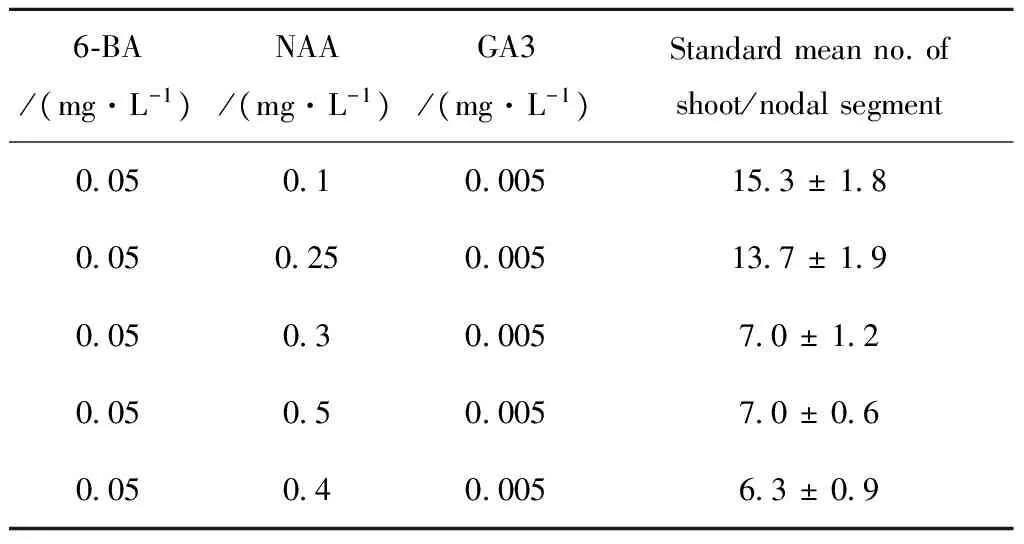
Tab.5 Effect of MA+6-BA , NAA, IBA and GA3 on multiple shoots differentiation
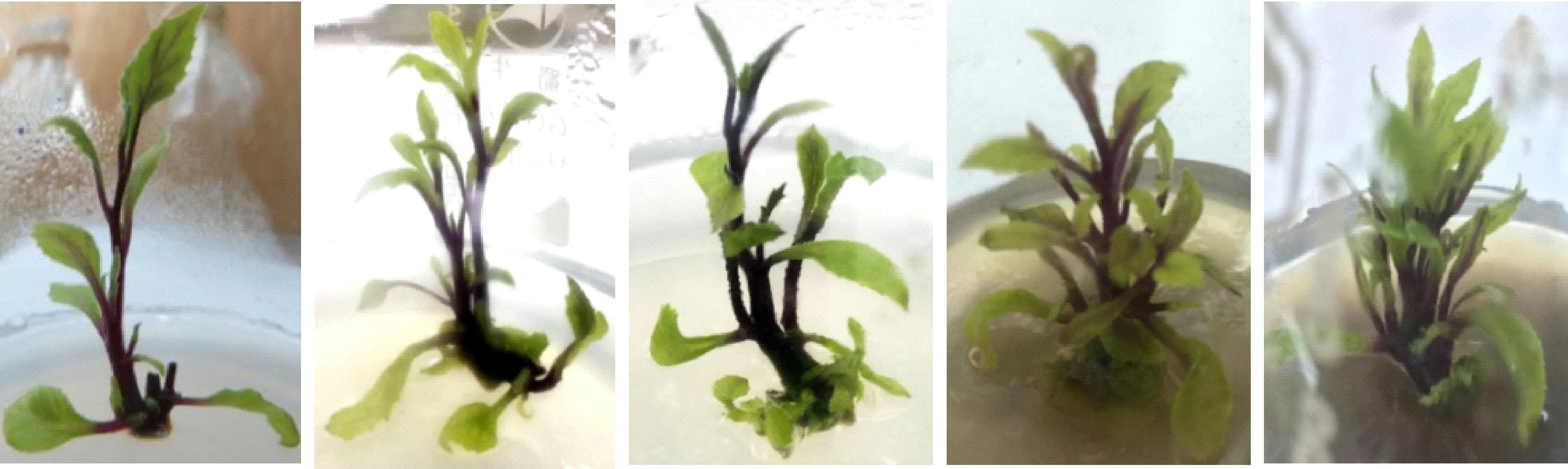

Fig.2 Axillary branching of buds from the nodal segments of Gynura procumbens of culture on MS medium supplemented with effect of BA (0.5~2 mg/L), NAA (0.1~0.5 mg/L), IBA (2.5 mg/L) and GA3 (0.005 mg/L).
2.4Root-induced Assays
Tab.6 showed that 0.1 mg/L NAA is optimal condition for root differentiation, and roots grow well and have long length. Hence, they were easier to place in soil. It clearly indicates that low concentrations of NAA promoteGynuradivaricataplant root differentiation, high concentrations of auxin inhibit it.
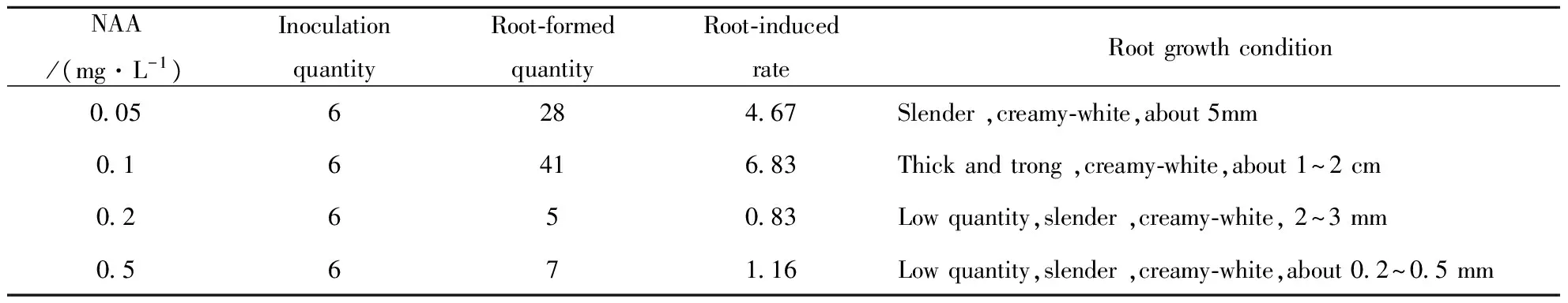
Tab.6 Effect of MS+NAA on root differentiation
2.5Transplanting
Gynuradivaricataplant multiple shoot clumps growing 3~5 long main roots were transplanted in soil. Carefully removing the seedlings from the culture flasks by tweezers (do not damage the roots), washing the medium adhered to roots, and then placing the seedlings into the pot with spraying appropriate water.
3Discussion
In the paper, the results showed that callus inducement and callus proliferation growed well under the condition of MS+1.0 mg/L NAA+1.0 mg/L 6-BA+0.75% Agar+3% Sugar, and inducement of buds of the most suitable medium was MS+1.0mg/L NAA+1.5mg/L 6-BA. Adding IBA and GA is advantageous to the growth of multiple shoots, high concentration of NAA is conducive to root differentiation.
Plant tissue culture technique is mainly one of the methods in rapid propagation of plants[5].ThoughGynuradivaricataplant is easy to cultivate, it is because that cutting propagation coefficient is low so as difficult to breed a large number of short-term[6]. In addition, micropropagation and callus-induced techniques applied for propagation did not totally use explants to induce sterile seedlings and its propagation rate is not high[7]. The high-frequency regeneration system was established using the young stem, young leaves as the explants[8]. In this study, 2,4-D also as a herbicide was applied for callus inducement[9]. It suggested that 2,4-D was easily to induceGynuradivaricataplant callus but not benefit to the callus inducement and differentiation and was easily lead to callus browning and low reproductive efficience[10]. Therefore, we built the most easily organ acquired sysem for tissue culture, obtained a well-gown sterile seedlings and transplanted for production.
[1] HUANG K Z, HAO Y J, ZENG C H, et al. Hypotensive effect of the aqueous extract fromGynuradivaricata(L.) DC. on spontaneous hypertensive rats[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2009(10): 1505-1508.
[2] ZHU B, PU S, XU D, et al. Advances in studies on chemical constituents and bioactivities of the genus Gynura Cass[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2012(04): 1-4.
[3] QI L F, SONG J H, XU G, et al. Research of cutting-seeding propagation techniques ofGynuradivaricata[J]. Chinese Horticulture Abstracts, 2015, 7(40): 217.
[4] SHI T L, ZHAO D D, YU B N, et al. In vitro rapid propagation system optimization for Gynura procubens[J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 33(2): 69-72.
[5] FAN S W, DONG L H, TU X W. Suspension culture of Gynura medica and effect on bio-synthesis of soluble polysaccharides by culture conditions[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2012, 31(7): 23-27.
[6] PAN L M, MA X J, MO C M, et al. Tissue culture technology forGynuradivaricata(L.) DC[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture. 2011, 42(12): 1458-1461.
[7] YAO J W, LI Y, XU W, et al. Tissue Culture and high-frequency regeneration ofGynuradivaricata(L.) DC[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2012, 48(11): 1091-1097.
[8] ZHANG H M, CAI B H, ZHANG L Z, et al. Cell suspension culture of Ephedrae sinica Stapf[J]. Biotechnology, 2011, 21(1): 82-84.
[9] GUO Z J, SHANG X C, JIANG Y, et al. Callus induction ofGynuradivaricate(L.) DC. and optimization of culture conditions[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2013, 35(1): 74-79.
[10] LILI H, YE A, FENG L, et al. Tissue culture and rapid propagation forGynuradivaricata(L.) DC.[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2010, 46(4): 377-378.
2017-05-02.
国家自然科学基金项目(31470365).
1000-1190(2017)04-0499-05
白背三七叶组织培养研究
LWIN Moe Moe1,2, 赵泽一3, 韩 博3, 张国彬4
(1.华中师范大学 生命科学学院, 武汉 430079; 2.Department of Botany, Yeman Chaung Degree College, Myanmar; 3.武汉外国语学校, 武汉 430200; 4.武昌理工学院 生命科学学院, 武汉 430223)
以白背三七幼叶和带芽茎段为外植体,探讨不同激素配比对白背三七离体繁殖的影响,建立白背三七种苗再生繁殖体系.结果表明:当NAA超过1.0 mg/L时,愈伤化都非常好,出愈率达到100%,但是当NAA浓度过高时,愈伤组织长势不好,不利于器官的诱导分化.继代培养中,1.0 mg/L NAA+1.0 mg/L 6-BA更有利于愈伤组织的进一步增长,达到完全愈伤化.愈伤组织的生长曲线基本上呈现迟滞期、对数增长期和稳定期.在不定芽诱导分化中,1.0 mg/L NAA+1.5 mg/L 6-BA最有利于芽的生长分化,过高浓度的6-BA时,不定芽生长较弱,不利于根分化及移栽.在带芽茎段诱导丛生芽的过程中,加入适量的IBA和赤霉素更有利于丛生芽的生长.根分化的过程中,高浓度的NAA抑制根的生长与分化.
白背三七; 愈伤组织; 诱导; 分化
O176.3
A
10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2017.04.014
*通讯联系人. E-mail: zhgbin_1973@qq.com.201702006980747.
