板桥党参对激活GSK-3β诱导的AD模型大鼠认知功能障碍的保护作用及其机制
2017-07-25罗洪斌刘翔宇牟南樵樊莎莎谢文执杨晨宇谢枫枫
罗洪斌,刘翔宇,牟南樵,陈 玮,樊莎莎,谢文执,商 楠,杨晨宇,谢枫枫,谌 勤,魏 征
(生物资源保护与利用湖北省重点实验室,湖北民族学院医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,湖北民族学院神经精神共患病研究所,湖北 恩施 445000)
◇论 著◇
板桥党参对激活GSK-3β诱导的AD模型大鼠认知功能障碍的保护作用及其机制
罗洪斌,刘翔宇,牟南樵,陈 玮,樊莎莎,谢文执,商 楠,杨晨宇,谢枫枫,谌 勤,魏 征
(生物资源保护与利用湖北省重点实验室,湖北民族学院医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,湖北民族学院神经精神共患病研究所,湖北 恩施 445000)
目的 探索板桥党参(BCP)水煎液对激活糖原合成酶激酶-3β(GSK-3β)诱导的阿尔兹海默病(AD)模型大鼠认知功能障碍的保护作用及其可能机制。方法 将50只4月龄♂SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、AD模型组、低剂量板桥党参组、中剂量板桥党参组、高剂量板桥党参组。前2组饮用水灌胃14 d,后3组灌服板桥党参水煎液14 d。灌胃同时进行自主行为测试,d 8开始进行水迷宫训练。训练5 d后,选择能在15 s内找到隐藏平台的治疗组和模型组大鼠进行侧脑室注射渥曼青霉素(Wortmannin,PI3K特异性抑制剂)和GF-109203X(GFX,PKC特异性抑制剂)(浓度均为100 μmol·L-1)各5 μL;假手术组注射2% DMSO 10 μL。24 h后进行水迷宫测试。观察各组大鼠侧脑室注射前、后空间学习记忆力是否改变。Western blot和免疫组化检测大鼠脑海马组织Tau磷酸化水平及其相关蛋白激酶GSK-3β表达情况及活性变化。尼氏染色观察神经元尼氏小体变化情况。结果 自主行为活动检测结果发现板桥党参能明显减少大鼠活动次数;水迷宫检测结果发现板桥党参能明显改善模型大鼠认知功能障碍;Western blot和免疫组化结果显示模型组海马组织GSK-3β活性升高,并导致Tau蛋白多个位点发生过度磷酸化,而用药后GSK-3β活性降低,Tau蛋白多个位点磷酸化水平下调;尼氏染色结果提示模型组海马神经元内尼氏小体数量减少,而治疗后尼氏小体增多,且呈剂量依赖性。结论 板桥党参可有效改善GSK-3β活性升高所诱导的大鼠认知功能障碍,其可能机制与下调GSK-3β活性,进而抑制Tau蛋白过度磷酸化、促进神经元发育有关。
阿尔兹海默病;板桥党参;GSK-3β;Tau磷酸化;学习记忆能力;水迷宫
阿尔兹海默病(Alzheimer′s disease, AD)是一种多发于老年人的神经退行性疾病,是老年痴呆最常见类型,主要临床特征为逆行性遗忘,对患者及其家庭造成严重影响[1]。该疾病主要病理特征为神经元外的老年斑(amyloid-β protein, SP)[2]和神经元内的神经纤维缠结(neurofibrillary tangles, NFTs)[3]。老年斑主要由β淀粉样蛋白组成[2],NFTs主要由过度磷酸化的Tau蛋白组成[3-4]。Tau蛋白是一种微管相关蛋白(MAPs),与微管组装及微管稳定性有关[3-4],还参与细胞信号转导及物质交换[5]。Tau蛋白异常过度磷酸化将导致自身聚集且拮抗泛素-蛋白酶系统降解,从而形成NFT[5];还可破坏微管稳定性、损伤神经元并引起物质运输障碍,最后导致AD发生[6];同时,Tau蛋白过度磷酸化也是AD早期病理变化,所形成的NFT数量与患者痴呆程度呈正相关[6-7]。因此,抑制Tau蛋白过度磷酸化是治疗AD关键。糖原合成酶激酶-3β(GSK-3β)在导致AD样Tau蛋白异常过度磷酸化中起着重要作用。细胞水平研究证实,GSK-3β可催化Tau蛋白多个位点发生过度磷酸化[7-8]。在整体水平,利用磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase, PI3K)的特异性阻断剂Wortmannin和蛋白激酶C(PKC)特异性抑制剂(GF-109203X, GFX)进行侧脑室注射,可激活GSK-3β,引起Tau蛋白异常过度磷酸化,同时可导致实验动物学习记忆障碍[9]。因此,寻找针对GSK-3β进行靶向治疗AD的有效药物是治疗AD的有效途径,但到目前为止尚无特效药物。
板桥党参(BanqiaoCodonopisisPilosula, BCP)在治疗AD方面具有一定疗效[10]。板桥党参属川党(CodonopsistangshenOijv. )中小条党参,位列四大党参之首,为恩施州道地药材,具有补气、补血、生津之功效[11]。现代药理研究证明板桥党参具有活血、镇静安神、增强免疫功能、抗氧自由基损伤、延缓衰老、抗缺氧等药理作用[11]。已有研究证实,板桥党参提取物对注射氟哌啶醇建立的AD模型大鼠具有改善学习记忆能力及抗氧化作用[10]。本研究拟通过建立GSK-3β过度激活导致Tau过度磷酸化的AD大鼠模型,初步探讨不同剂量板桥党参提取物能否通过抑制GSK-3β活性达到防治AD的目的及可能机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 药物与试剂 板桥党参购自湖北恩施板桥党参加工厂,并经文德鉴副教授鉴定。根据临床用药量按人(60 kg)为标准,板桥党参给药低、中、高剂量分别为15、30、60 g·kg-1·d-1,换算成大鼠(250 g为标准)的低、中、高剂量分别为0.54、1.08、2.16 g·kg-1·d-1。换算方法根据《药理实验中动物间和动物和人体间的等效剂量换算》计算获得。水煎液制备方法:称量108 g板桥党参,加适量水煎煮1 h,煎煮2次,合并药液,纱布过滤,再浓缩定量至0.54 kg·L-1备用。Wortmannin、GF-109203X、DMSO、三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)、丙烯酰胺(Arc)、亚甲基双丙烯酰(Bis)、甘氨酸(glycine)、十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)、TEMED等:美国Sigma公司;硝酸纤维素膜:英国Hybond公司;多聚甲醛、MSF等:天津市福晨化学试剂厂;BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒:北京康为世纪生物科技有限公司;PV-9001超敏二步法免疫组化检测试剂盒:北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司;Tau-5抗体:美国Abcam公司;GSK-3β抗体:美国Cell Signaling Technology公司;pT231、pS262、pS396、pS404抗体:美国SAB公司;β-actin抗体:美国Proteintech公司。
1.2 仪器 YLS-1B大鼠自主行为测试仪 (山东省医学科学院),DMS-2型Morris水迷宫系统(中国医学科学院药物研究所),099C K5424匀浆机(美国Glas-Col公司),1658001电泳仪、1703930转膜仪、1645050基础电泳仪电源(美国Bio-Rad公司),Odyssey双色红外激光成像系统(美国基因公司),VT1200S振荡切片机(德国Leica公司),三目数字摄影显微镜(日本Nikon公司)。
1.3 实验动物与分组 ♂ SD大鼠,购自湖北省实验动物研究中心,许可证号SCK(鄂)2015-0018,合格证号42000600003985,体质量(250±30)g,50只(另有50只备用)。自由进食饮水1周后,随机分为5组:假手术组,AD模型组,高、中、低3个治疗组,每组10只。
1.4 AD模型建立及给药、自主行为测试和水迷宫训练 给药组按每只大鼠体质量给予足量板桥党参水煎液灌胃14 d,AD模型组和假手术组饮用水灌胃14 d。每组d 1灌胃后立即放入小动物自主活动检测仪,测定30 min内大鼠自主活动,每5 min记录1次。在灌胃d 8进行水迷宫训练。训练5 d后,选择能在15 s内找到隐藏平台大鼠(其搜索轨迹笔直简单)用于后续实验[12]。训练d 6行侧脑室注射,模型组和治疗组均注射WT+GFX各5 μL(浓度均为100 μmol·L-1),假手术组注射2% DMSO 10 μL。24 h后进行水迷宫测试。水迷宫训练和测试方法参照文献[13]并做适当修改。记录大鼠寻找平台的潜伏期及游泳轨迹等。
1.5 海马匀浆蛋白Western blot分析 水迷宫测试完后断头取脑,冰上快速分离海马,匀浆后进行Western blot,实验方法按本课题组前期建立方法进行[5,13]。一抗抗体分别为p-Tau(pT231、pS262、pS396、pS404)(1 ∶1 000)。相应荧光二抗孵育1 h后TBST洗涤3次,每次10 min。Odyssey扫描成像显色分析,Odyssey软件分析灰度值。
1.6 脑片免疫组织化学法染色 多聚甲醛内固定:大鼠水迷宫测试完后7%水合氯醛麻醉,固定四肢、头部,并按参考文献方法[5,13]进行多聚甲醛灌流内固定。灌流完毕后取脑,4%多聚甲醛继续后固定。振荡切片机切脑片,并保存在含0.02%叠氮钠PBS溶液中备用。取海马完整清晰脑片进行免疫组化染色,具体方法详见文献[5,13]。一抗抗体为p-Tau(pS404)(1 ∶100)。实验结束后中性树胶封片,显微镜下观察拍照。
1.7 脑片尼氏染色 取脑片置于16孔板中。PBS洗3次,每次5 min。加入1%甲苯胺蓝水溶液染色,37℃孵育20 min,蒸馏水洗净,酒精脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片,显微镜下观察尼氏小体变化。
2 结果
2.1 BCP单次给药对SD大鼠自主行为的影响 SD大鼠给药后未发生震颤等不适现象。与未给药组相比,给药组自主活动次数减少,低、中剂量组在5、10 min时间点处差异具有统计学意义(低、中剂量组P<0.05,5 min时中剂量组P<0.01),但抑制作用持续时间短,30 min时间点处BCP虽使自主活动有降低趋势,但各给药组间自主活动差异无统计学意义(Fig 1A)。统计各组30 min内总自主活动次数发现,0.54、1.08、2.16 g· kg-1明显抑制SD大鼠自主活动,且差异具有显著性(P<0.01),说明该药能作用于大脑发挥作用(Fig 1B)。
2.2 BCP对AD模型大鼠空间认知功能的影响 水迷宫实验结果发现,随训练天数延长,逃避潜伏期逐渐缩短,说明大鼠空间记忆力训练有效。测试结果显示,注射WT+GFX激活GSK-3β活性造模后,大鼠寻找平台的潜伏期无论是与注射前比较,还是与对照组比较,均明显延长(P<0.01),见Fig 2A,且游泳轨迹杂乱无章(Fig 2B),明显引起大鼠空间学习记忆障碍。预先给予低、中、高剂量BCP可明显改善大鼠空间学习记忆障碍(P<0.05),逃避潜伏期明显缩短,且呈剂量依赖性,见Fig 2A。与模型组相比,各剂量BCP还能明显改善大鼠搜寻策略,游泳运行轨迹接近正常的直线型(Fig 2B)。上述结果发现,低、中、高剂量BCP能有效改善WT+GFX激活GSK-3β活性引起的大鼠空间学习记忆障碍。
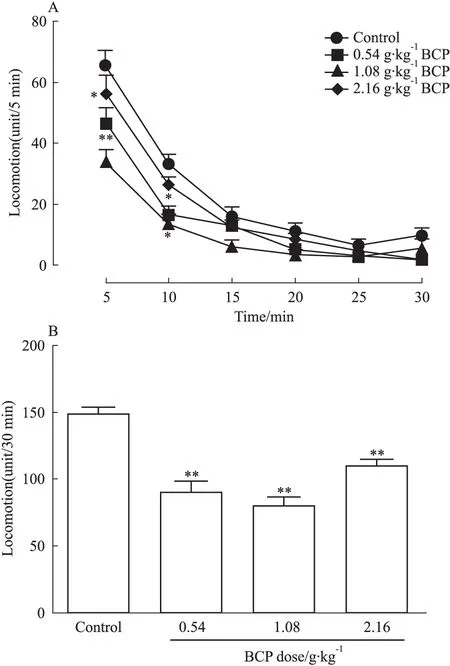
Fig 1 BCP inhibits independent behavior activities of SD rats(±s,n=10)
A:After intragastric administration of BCP, the rat autonomous behavior activities in each group all showed a declining trend and the differences in low-dose and middle-dose groups had statistical significance compared with blank group in 30 minutes; B: BCP significantly inhibited the total number of rat autonomic behavior activities in 30 minutes.*P<0.05,**P<0.01vscontrol
2.3 BCP对AD模型大鼠脑海马GSK-3β活性的影响 与对照组相比,AD模型大鼠脑海马总GSK-3β表达量升高,同时表现非活性GSK-3β的S9-GSK-3β(即GSK-3β第9位丝氨酸被磷酸化)表达量与总GSK-3β表达量之间的比值下降,且差异有显著性(P<0.05),表现其活性的T216-GSK-3β(即GSK-3β第216位苏氨酸被磷酸化)表达量与总GSK-3β表达量之间的比值上调,差异也具有显著性(P<0.05),表明造模成功。而与模型组相比,BCP低、中、高治疗组其S9-GSK-3β表达量比值升高,差异有显著性(P<0.05),而T216-GSK-3β表达量比值下调,差异有显著性(P<0.05),二者均呈剂量依赖性(Fig 3A、3B)。结果表明,低、中、高不同剂量BCP均能下调GSK-3β活性并具剂量依赖性。

Fig 2 BCP prevents rats from WT+GFX induced spatial memory retention dysfunction(±s,n=8)
A:BCP shortened the escape latency of WT+GFX injected rats and the therapeutic effect of BCP was dose-dependent; B: BCP improved the swimming pathway which was recorded 24 h after the injection of WT+GFX (after). The results showed that WT+GFX injected rats lost their directional bearings and thus employed random search strategy rather than straight search strategy. Control rats did not change much in their pathway to find the hidden platform. BCP significantly inhibited WT+GFX induced impairment of spatial memory retention.**P<0.01vscontrol;##P<0.01vsbefore WT+GFX injection;ΔP<0.05vsafter WT+GFX injection

Fig 3 Effects of BCP on WT+GFX induced overactivation of GSK-3β(±s, n=6)
A: Western blot results showed the activity of GSK-3β in AD model group was up-regulated compared with the blank group and BCP inhibited the high activity of GSK-3β induced by WT+GFX; B: BCP decreased the level of T216 GSK-3β phosphorylation and increased the level of S9 GSK-3β phosphorylation and the results had statistical significance.*P<0.05vscontrol (DMSO);#P<0.05vsWT+GFX injection
2.4 BCP对AD模型大鼠脑海马Tau蛋白磷酸化的影响 运用Western blot检测模型大鼠脑海马组织Tau蛋白磷酸化水平并进行分析。结果发现,Tau蛋白pT231、pS262、pS396、pS404等4个位点磷酸化水平在AD模型大鼠脑海马中明显高于对照组,且差异具有显著性(P<0.05),而BCP低、中、高治疗组Tau蛋白4个位点的磷酸化水平低于模型组(P<0.05),且呈剂量依赖性,见Fig 4A、4B。同时应用免疫组化实验检测脑海马CA3区Tau蛋白磷酸化水平,发现AD模型大鼠CA3区Tau蛋白磷酸化水平明显高于对照组,差异有显著性(P<0.05)。给予BCP低、中、高剂量后,其CA3区磷酸化水平均明显低于模型组,差异具有显著性(P<0.05),且呈剂量依赖性(Fig 4C、4D)。
2.5 尼氏染色结果 对照组可见脑海马CA1、CA3区神经元排列整齐密集,胞体饱满,着色较深,核大而圆,可见较多尼氏小体。而模型大鼠脑海马CA1、CA3区神经元数量稀少,着色浅,胞体萎缩呈空泡状,尼氏小体少见。而BCP低、中、高剂量组脑海马CA1、CA3区神经元恢复较好,数量多,胞体较为饱满,着色较深,核较大而圆,可见较多尼氏小体,特别是高剂量BCP更能明显恢复尼氏小体(Fig 5A、5B)。
3 讨论
AD是世界各国最为常见老年痴呆症,对社会及家庭危害极大,目前尚无根治办法[1]。较多文献[14]证明GSK-3β活性升高是导致SP和NFT产生的重要因素,因此,下调GSK-3β活性成为治疗AD的关键所在[15]。
研究发现,包括BCP在内的很多中药具有防治AD的作用[16-17]。因此,我们先用过度激活GSK-3β活性模拟AD大鼠模型,然后尝试运用BCP来治疗该类型AD。首先,我们检测了BCP对大鼠自主活动的影响,结果表明BCP可能透过血脑屏障作用于中枢神经而起到抑制中枢神经作用,但由于党参主要成分为多糖,代谢较快,因此认为该抑制作用较短暂,不会影响后续行为学实验。应用BCP时,同步进行水迷宫实验以检测大鼠空间学习记忆能力,结果显示模型大鼠空间认知功能下降,记忆力减退。注射WT+GFX的大鼠运用低、中、高剂量BCP后可明显改善这种空间认知功能障碍,并呈剂量依赖性。行为学实验结果说明BCP可透过血脑屏障作用于大脑,可在一定程度上改善AD认知功能障碍。文献报道海马与短期记忆能力密切相关,而海马CA1、CA3区是其关键部位,对学习记忆信息储存尤为关键,其GSK-3β活性升高所导致Tau蛋白过度磷酸化水平又与痴呆程度密切相关[16,18-20]。因此,我们首先应用Western blot技术检测了模型大鼠脑海马组织内GSK-3β表达情况,同时还检测了GSK-3β特异位点磷酸化情况,结果发现GSK-3β活性升高,表明造模成功。同样的方法又检测了灌服BCP的模型大鼠脑海马组织内GSK-3β活性情况,结果发现该激酶活性明显下降,这一结果表明,BCP具有降低GSK-3β活性的作用。

A: Western blot results showed the level of multiple phosphorylation sites of Tau in AD model group rat hippocampus was increased than that in the blank group. Compared with AD model group, BCP decreased the level of multiple phosphorylation sites of Tau; B: Western blot results of multiple phosphorylation sites of Tau had statistical significance; C: Immunohistochemistry results showed the level of Tau S404 phosphorylation in AD model group was increased than that in blank group in the area of CA3. Compared with AD model group, BCP decreased the level of Tau phosphorylation; D: The immunohistochemistry results of Tau S404 phosphorylation had statistical significance.*P<0.05vscontrol;#P<0.05vsWT+GFX injection
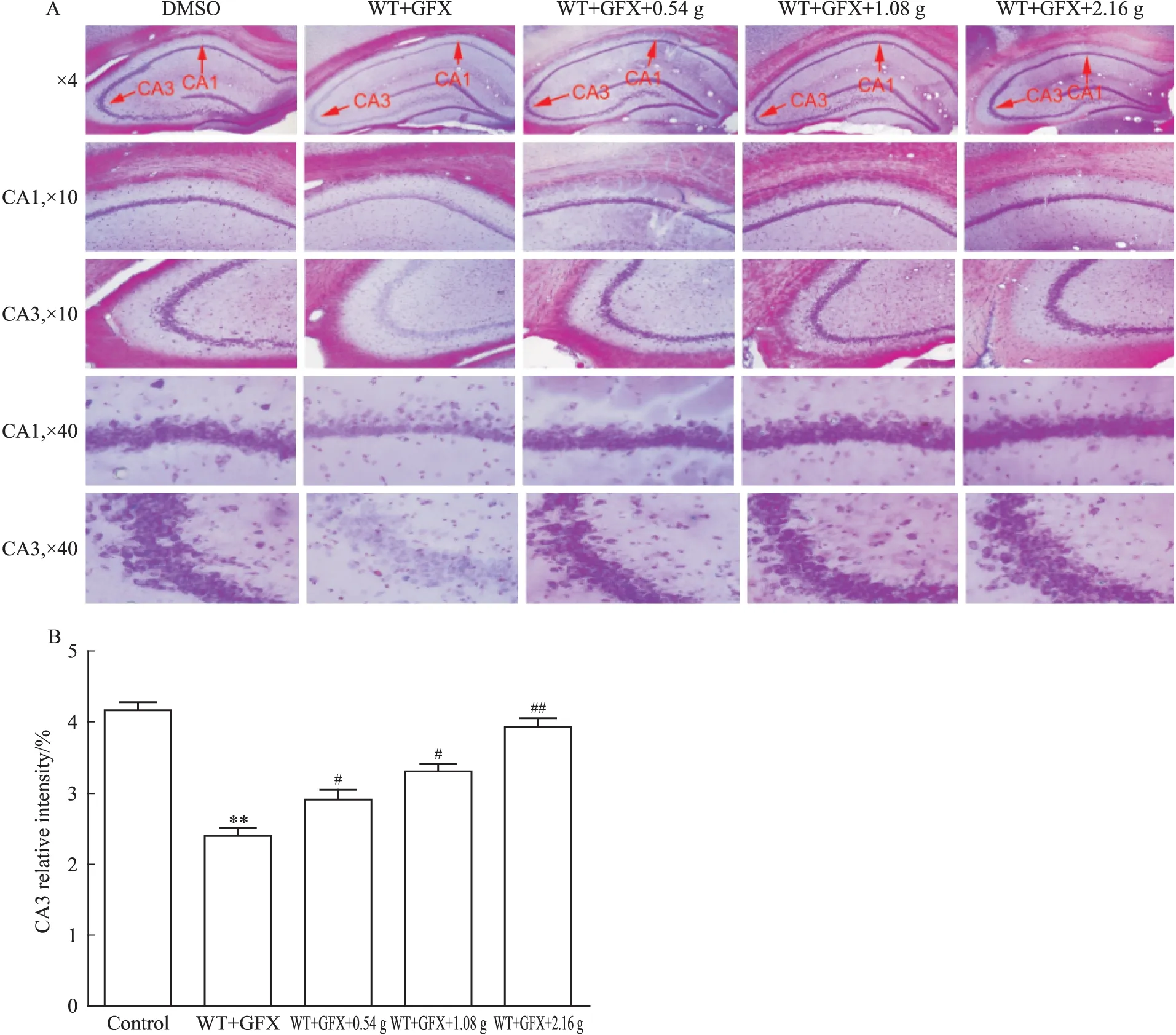
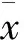
A: Nissl′s staining results showed the number of Nissl′s bodies in neuron cells of hippocampus in hippocampal CA3 was obviously less than that in blank group, and BCP markedly increased the number of Nissl′s bodies in neuron cells; B: Nissl′s staining results of the number of Nissl′s bodies had statistical significance.**P<0.01vscontrol;#P<0.05,##P<0.01vsWT+GFX injection
由于GSK-3β是导致Tau蛋白过度磷酸化的关键激酶之一,因此有必要检测Tau蛋白磷酸化水平以验证BCP是否对AD大鼠具有防治作用。Western blot结果发现,BCP低、中、高剂量组大鼠脑海马区Tau蛋白pS262、pS356、pS396、pS404等4个位点的磷酸化水平明显低于模型组,表明BCP确能通过降低GSK-3β进而下调Tau蛋白多个位点的磷酸化水平。该结果与其它中药作用结果类似[21]。近年来,对Tau蛋白磷酸化位点的研究发现,Tau蛋白第Ser404位点是GSK-3β活化后诱导的AD中一个特异性修饰位点,其磷酸化(pS404)具有使Tau变成毒性分子,从而拮抗微管相关蛋白正常生理功能并导致AD发生[3,8,22]。因此,我们应用了免疫组化实验来检测各组大鼠脑海马CA1和CA3区Tau蛋白pS404位点磷酸化水平,结果表明BCP仍然可降低AD模型大鼠CA1、CA3区Tau蛋白pS404位点磷酸化水平,特别是CA3区尤为明显(P<0.05)且呈剂量依赖性。该结果与Western blot结果一致。因此,我们有理由相信BCP确能降低Tau蛋白磷酸化水平,进而改善AD模型大鼠认知功能障碍。而尼氏染色结果表明,BCP具有促进AD模型大鼠脑海马神经元内已溶解的尼氏小体重现,进而恢复其合成蛋白质的功能,达到保护海马神经元、促进神经发育的作用。
上述实验结果表明,BCP可改善AD大鼠的空间认知功能障碍,其机制可能是通过下调GSK-3β活性,进而降低海马神经元内Tau的过度磷酸化,同时促进海马神经元的发育和保护作用。查阅文献,尚未发现BCP对GSK-3β的活性具有调节功能并通过这种调节功能达到预防性治疗AD的目的,此为本实验新发现。该发现表明,具有“补中益气补血”功效之中药BCP对AD具有一定防治或延缓作用,值得临床推广应用。但由于其成分较为复杂,有赖于在后续研究中进一步明确其防治AD的有效成分。
(致谢: 本文实验在湖北民族学院医学院神经精神共患病研究所实验室和生物资源保护与利用湖北省重点实验室完成,在此,对两个实验室的各位老师及同学表示衷心感谢!)
[1] Querfurth H W, LaFerla F M. Alzheimer′s disease[J].NEnglJMed, 2010, 362(4): 329-44.
[2] Sagare A P, Bell R D, Zlokovic B V. Neurovascular defects and faulty amyloid-β vascular clearance in Alzheimer′s disease[J].JAlzheimersDis, 2013, 33(Suppl 1): S87-100.
[3] Wang J Z, Liu F. Microtubule-associated protein tau in development, degeneration and protection of neurons[J].ProgNeurobiol, 2008, 85(2): 148-75.
[4] Mandelkow E M, Mandelkow E. Biochemistry and cell biology of tau protein in neurofibrillary degeneration[J].ColdSpringHarbPerspectMed, 2012, 2(7): a006247.
[5] Luo H B, Xia Y Y, Shu X J, et al. SUMOylation at K340 inhibits tau degradation through deregulating its phosphorylation and ubiquitination[J].ProcNatlAcadSciUSA, 2014, 111(46): 16586-91.
[6] Bukar M M, Al-Hilaly Y K, Serpell L C. Nuclear tau and its potential role in Alzheimer′s disease[J].Biomolecules, 2016,6(1): 9.
[7] Khan S S, Bloom G S. Tau: the center of a signaling nexus in Alzheimer′s disease[J].FrontNeurosci, 2016, 10(1): 31.
[8] Wang J, Wang X, Liu R, et al.Invitroanalysis of tau phosphorylation sites and its biological activity[J].ChinMedSciJ, 2002, 17(1):13-6.
[9] Liu S J, Zhang A H, Li H L, et al. Overactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by inhibition of phosphoinositol-3 kinase and protein kinase C leads to hyperphosphorylation of tau and impairment of spatial memory[J].JNeurochem, 2003, 87(6): 1333-44.
[10]黄丽亚, 叶嗣颖. 党参注射液上调抗氧化酶表达作用的实验研究[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2006,26(1):70-1.
[10]Huang L Y, Ye S Y. Study on the effect of Codonopsis pilosula injection increase the expression of antioxidant enzymes[J].ChinJGerontol, 2006, 26(1): 70-1.
[11]朱永红, 吕 盼, 欧晓群. 板桥党参的研究现状[J]. 亚太传统医药,2012,8(3):189-90.
[11]Zhu Y H, Lyu P, Ou X Q. Research status of BanqiaoCodonopisisPilosula[J].Asia-PacTraditMed, 2012, 8(3):189-90.
[12]姜 霞. L-肉毒碱在Alzheimer样Tau蛋白过度磷酸化和空间记忆障碍中的保护作用[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2008.
[12]Jiang X. Effect of L-Carnitine on Alzheimer-like tau hyperphosphorylation and spatial memory retention deficits[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2008.
[13]姜 霞. 空间学习对AD模型鼠海马突触可塑性及神经发生的影响[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2012.
[13]Jiang X. Roles of spatial learning in synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis in Alzheimer′s disease models[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2012.
[14]Maqbool M, Mobashir M, Hoda N. Pivotal role of glycogen synthase kinase-3: a therapeutic target for Alzheimer′s disease[J].EurJMedChem, 2016, 107(7): 63-81.
[15]Shim S S, Stutzmann G E.Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3: an emerging target in the treatment of traumatic brain injury[J].JNeurotrauma, 2016, 33(23): 2065-76.
[16]陈地灵,陈 鹏,林 励,等. 巴戟天低聚糖对Aβ25-35致拟痴呆模型大鼠学习记忆障碍的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报,2013,29(2):271-6.
[16]Chen D L, Chen P, Lin L, et al. Effect of oligosaccharides fromMorindaOfficinalison β-amyloid-induced learning and memory dysfunction in rats[J].ChinPharmacolBull, 2013, 29(2): 271-6.
[17]李 林,张 兰. 中药治疗阿尔茨海默病的作用特点[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展,2012,39(8):816-28.
[17]Li L, Zhang L. Action characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of Alzheimer′s disease[J].ProgBiochemBiophys, 2012, 39(8): 816-28.
[18]Medina M, Avila J. New insights into the role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in Alzheimer′s disease[J].ExpertOpinTherTargets, 2014, 18(1): 69-77.
[19]Ma T. GSK3 in Alzheimer′s disease: mind the isoforms[J].JAlzheimersDis, 2014, 39(4): 707-10.
[20]King M K, Pardo M, Cheng Y, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors: rescuers of cognitive impairments[J].PharmacolTher, 2014, 141(1): 1-12.
[21]张 雄,李 昱. 姜黄素通过抑制GSK-3β的活性防治AD的体外研究[J]. 中国药理学通报,2009,25(11):1507-12.
[21]Zhang X, Li Y. Curcum in inhibits the activity of GSK-3β to prevent ADinvitro[J].ChinPharmacolBull, 2009, 25(11): 1507-12.
[22]Alonso Adel C, Mederlyova A, Novak M, et al. Promotion of hyperphosphorylation by frontotemporal dementia Tau mutation[J].JBiolChem, 2004, 279(33): 34878-81.
BanqiaoCodonopisisPilosulaimproves cognitive dysfunction induced by high GSK-3β activity and its possible mechanism
LUO Hong-bin, LIU Xiang-yu, MOU Nan-qiao, CHEN Wei, FAN Sha-sha, XIE Wen-zhi, SHANG Nan, YANG Chen-yu, XIE Feng-feng, CHEN Qin, WEI Zheng
(KeyLabofBiologicResourcesProtectionandUtilizationofHubeiProvince;DeptofBiochemistryandMolecularBiology,MedicalCollege;InstituteofNeurologicalandPsychiatricComorbidity,HubeiUniversityforNationalities,EnshiHubei445000,China)
Aim To assess the effects of BanqiaoCodonopisisPilosula(BCP) decoction on learning and memory dysfunction in AD model rats induced by high activity GSK-3β and its possible mechanism.Methods The SD rats(4 months old, ♂) were divided into five groups, namely, sham-operated group(blank group), AD model group, BCP high-dose(2.16 g·kg-1·d-1) group, BCP medium-dose(1.08 g·kg-1·d-1) group, and BCP lower-dose(0.54 g·kg-1·d-1) group. Treatment group
BCP decoction by gavage once a day for 14 days, while other groups were offered drinking water by gavage once a day for 14 days. The autonomous behavior activities of all rats were observed and recorded after gavage. In the last seven days by gavage, Morris water maze test was used to test the spatial learning and memory ability of the five groups. After five days training, treatment groups and AD model group were injected wortmannin(WT, PI3K specific inhibitor) and GF-109203X(GFX, PKC specific inhibitor)(100 μmol·L-1of each, total volume of 10 μL) into the right lateral ventricle of the rats. The blank group was only injected 2% DMSO. The spatial memory retention was detected by water maze 24 hours after lateral ventricle injection. Then, changes in the spatial learning memory of rats were observed. The level of Tau phosphorylation in SD rat hippocampus and the expression and activity changes of related protein kinase GSK-3β were detected by Western blot and immunohistochemistry. The changes of Nissl bodies in SD rat hippocampus were observed by Nissl′s staining.Results After intragastric administration of BCP, the rat autonomous behavior activities in each group all showed a declining trend, and the differences in low-dose and middle-dose groups had statistical significance compared with blank group. The Morris water maze tests showed that the latency navigation of model group was significantly longer than that of blank group(P<0.01), while that of the BCP three doses groups was shorter than that of model group(P<0.05).Compared with the same group, the latency navigation of the three groups after gavage BCP low, middle and high dose was significant shorter than that without gavage(P<0.05). Western blot results showed that the activity of GSK-3β in AD model group was up-regulated compared with the blank group. However, BCP inhibited activity of GSK-3β. Western blot and immunohistochemistry results showed the level of Tau phosphorylation in AD model group was increased compared with the blank group in the area of CA3(P<0.05). Compared with AD model group, the level of Tau phosphorylation was decreased in treatment group. Nissl′s staining results showed that dendritic spines in AD model group was significantly attenuated compared with the blank group(P<0.05). Far more dendritic spines were observed in treatment group than in AD model group. The number of Nissl′s bodies in neuron cells of hippocampus in hippocampal CA3 was obviously larger in treatment groups than in AD model group. These effect of BCP was dose-dependent.Conclusions BCP can prevent the learning and memory dysfunction in AD model rats induced by high activity of GSK-3β. The mechanism may be related to inhibiting GSK-3β activity and then reducing the level of phosphorylation of Tau and improving neural development.
Alzheimer′s disease; BanqiaoCodonopisisPilosula(BCP); GSK-3β; Tau phosphorylation; learning and memory ability; water maze test
2017-05-18,
2017-06-20
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No 81260172,81660223);湖北民族学院科技创新团队项目(No MY2011T005);湖北民族学院博士基金启动项目(No MY2012B015);生物资源保护与利用湖北省重点实验室开放基金项目(No PKLHB1318)
罗洪斌(1968-),男,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,研究方向:神经退行性疾病的发病分子机制,通讯作者,E-mail:luohongbin6809@126.com; 刘翔宇(1990-),男,硕士生,研究方向:中医药对神经退行性疾病的防治,并列第一作者,E-mail:1013972335@qq.com
时间:2017-7-7 11:04 网络出版地址:http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1086.R.20170707.1104.012.html
10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2017.08.006
A
1001-1978(2017)08-1060-08
R-332;R282.71;R322.81;R338.64; R745.702.2;R977.3