Solubility and metastable zone width measurement of 3,4-bis(3-nitrofurazan-4-yl)furoxan(DNTF)in ethanol+water
2017-05-28LizhenChenLiangSongGuanchaoLanJianlongWang
Lizhen Chen,Liang Song,Guanchao Lan,Jianlong Wang*
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering,North University of China,Taiyuan 030051,China
1.Introduction
Generally speaking,it is essential to purify the energetic material after it synthesized,in that the purity plays a significant role in the application of energetic material.Crystallization is a key unit operation especially in fine chemical,agrochemical,and pharmaceutical industries to produce high quality crystals and purify solids[9].The solubility data and MSZW are important for the study of crystallization.Ethanol is the most widely used organic solvent because it is inexpensive,non-toxic and environment-friendly.Moreover,the solubility of DNTF is moderate and changing obviously with the changing of temperature and concentration in ethanol+water.Besides,the product was obtained from ethanol+water of high density,regular morphology and low sensitive.Thus,it is necessary to study the solubility and MSZW of DNTF in ethanol+water for the purpose of preparing better DNTF crystal.
In this work,the solubilities of DNTF in four different concentration ethanol+water solvents are measured.The standard dissolution enthalpy,standard dissolution entropy and standard Gibbs energy are calculated according to the experimental data.The influence of the cooling rate,stirring rate,temperature and the concentration of ethanol+water on the MSZW is studied,and the apparent nucleation order is calculated according to the relationship between the cooling rate and MSZW.
2.Experimental Procedure
2.1.Materials and apparatus
DNTF sample,provided by Xi'an Modern Chemistry Research Institute,was purified by recrystallization in alcohol whose mass fraction purity was greater than 0.995.Ethanol of analytical reagent grade was purchased from local reagent factory without further purification whose mass fraction purity was no less than 0.995.Deionized water was obtained by a Millipore Milli-Q Plus water system.The experiment setup for measuring solubility and supersolubility of DNTF was shown schematically in Fig.1.
2.2.Determination of solubility
The solubilities of DNTF both in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system were determined by using the laser monitor system[10,11].Firstly,turn on the laser monitor system to preheat 30 min.Next,certain amounts of ethanol,water and DNTF were weighed and placed in the inner chamber of 100 ml triple necked crystallizer with an internal diameter of 60 mm.Then the suspension was agitated at the rate of300 r·min−1with a cylinder stirring bar whose length and diameter are 38 mm and 6 mm respectively,and was heated at the rate of 0.05 K·min−1with the control of a programmable thermostatic bath.At the beginning,lots of DNTF particles which could reflect and scatter the laser beam,result in the display of the photoelectric switch was low.With the increase of the temperature the DNTF particles gradually dissolved and the reading of photoelectric switch was increased.When the DNTF particles completely dissolved,the reading of photoelectric switch reached the maximum.The corresponding temperature of dissolution was the saturation temperatureTsat.The same solubility experiments were carried out three times,the average value of those three data is considered to be the solubility data,and the relative uncertainty between the experimental solubility values and the average value was less than 0.03.
The solubility of DNTF in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system expressed by mole fraction was calculated by Eq.(1),the initial mole fraction composition of the binary solvent mixtures is de fined by Eq.(2):


Fig.1.Flow diagrams of experiment 1—laser generator,2—crystallizer,3—condenser pipe,4—digital display,5—photoelectric switch,6—thermostatic bath,7—magnetic stirrer,8—burette,9—mercury thermometer.
wherex1was the solubility(solid–liquid equilibria)of DNTF in mole fraction,x2represents the solute-free mole fraction of ethanol in the binary liquid solvents,m1,m2,andm3represented the mass of DNTF,ethanol,water,respectively,andM1,M2,andM3were the molecular mass of DNTF,ethanol,water,respectively.
(2)合理选址,灵活收购。在实际运营中,由于燃料收集半径过大,导致发电成本增加,秸秆收集经济半径不应超过25km,锅炉容量应根据半径内燃料实际可利用燃料量的40%来确定。在燃料收购方面,建议选择“小经纪人”模式,有效避免燃料供应受制于单一经纪人的现象,降低燃料对单一大经纪人的依赖度。
2.3.Determination of supersolubility
The supersolubility curve is a cluster of curves which are influenced by the operating conditions[12,13].In this study,the influence of temperature,cooling rate,stirring rate and the concentration of ethanol+water on the supersolubility was studied.The supersolubility of DNTF is measured right after the measurement of the solubility by cooling the saturation system.The solubility of DNTF is decreased with the decreasing temperature,when the temperature decreasing to an appropriate value,DNTF would be nucleated from the solution.With the appearance of the DNTF particles,the intensity of the laser beam passed through the suspension is weakened,which results in the decay of the digital display.The corresponding temperature of the appearance of the DNTF nucleus was the supersolubility temperatureTnuc.The difference between the saturation temperature and the temperature at the point of nucleation is considered as the metastable zone width ΔTmax,which can be given as:
The supersolubility of DNTF both in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system was measured under the cooling rate of 0.2 K·min−1and stirring rate of 300 r·min−1to study the influence of the concentration of ethanol+water on the MSZW.Measure the supersolubility of DNTF in pure ethanol at stirring rate of 300 r·min−1under cooling rate of 0.1 K·min−1,0.15 K·min−1,0.2 K·min−1,and 0.25 K·min−1respectively for the purpose of researching the influence of cooling rate on the MSZW.In order to obtain the relationship between the stirring rate and the MSZW,the supersolubility of DNTF in pure ethanol was measured at cooling rate of 0.2 K·min−1under the stirring rate of 200 r·min−1,300 r·min−1,and 400 r·min−1respectively.The same supersolubility experiments were carried out three times,the average value of those three data is considered to be the supersolubility data,and the relative uncertainty between the experimental supersolubility values and the average value was less than 0.1 K.
3.Results and Discussions
3.1.Measured solubility
The solubility of DNTF in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system at various temperatures was determined.The obtained experimental solubility data are shown in Table 1 and demonstrated graphically in Fig.2.It is found that the solubility of DNTF increases with increasing temperature and decreasing concentration of water.

Table 1Experimental mole fraction solubility values x1 of DNTF in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system at saturation temperature T sat and pressure p=0.1 MPa①
The solubility data of DNTF in pure ethanol of this study have significant inconsistencies with that of Cui[14],which is graphically illustrated in Fig.3.We retested many times and found that the data of Cui is inaccurate,besides,our data have been checked many times when we studied the crystallization process.We consider that the main reason which caused the discrepancy is the difference of the methods between us.Compared with laser monitor system,there are many operation factors that can affect the accuracy of the final data by using the method of reference[14]such as the calibration curve and the loss of sampling.

Fig.2.Mole solubility values and fitting curves of DNTF in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary solvent mixture:■,x2=1;●,x2=0.85;▲,x2=0.74;▼,x2=0.64,◄,x2=0.55;►,x2=0.48.The points represent the experimental data.Curves are calculated according to Eq.(4)using the Modified Apelblat equation.
Since(solid+liquid)equilibrium is usually not available,correlation and prediction schemes are frequently utilized.Apelblat equation[15,16],deduced from the Clausius–Clapeyron equation,was used to correlate the experimental solubility values of DNTF.The equation can be expressed as:

wherexstands for the mole fraction of DNTF in ethanol+water binary system,Tis the absolute temperature of experiment,andA,BandCare the model parameters.The model parameter values ofA,B,Cand correlation coefficient(R2)are shown in Table 2.The fitting solubility curves of DNTF are shown in Fig.2.From the correlation results we can deduce that the Apelblat equation is a perfect model to correlate the relationship between experimental mole fraction solubility data and the absolute temperature of DNTF both in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system.
3.2.Apparent thermodynamic properties for DNTF dissolution
The apparent thermodynamic properties such as the dissolution enthalpy(ΔdisH),dissolution entropy(ΔdisS)and the Gibbs energy(ΔdisG)are closely related to the solubility data and,hence,when the solubility of DNTF is measured,the ΔdisH, ΔdisS,and ΔdisGcan be calculated.According to van't Hoff analysis,the apparent enthalpy change of solution could be related to the temperature and the solubility as following the equation[17]:


Fig.3.The comparison between experimental data and the data from reference 14:■,experimental ethanol data;□,literature ethanol data.
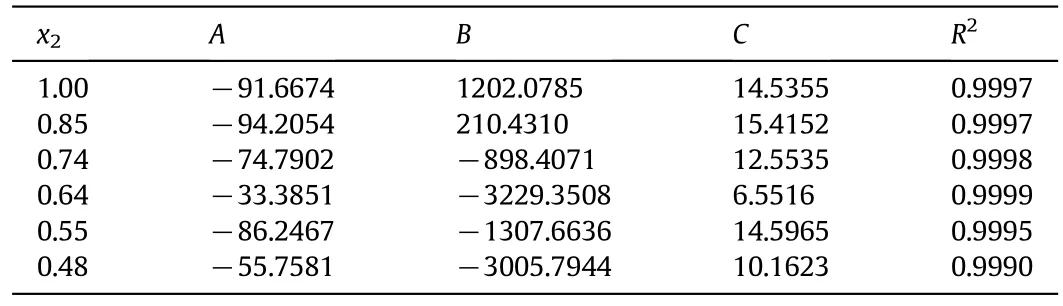
Table 2Model parameters and R2 of modified Apelblat equation
Overa limited temperature interval the heat capacity change of solution may be assumed to be constant.Thus,combined with the Apelblat model the ΔdisH,ΔdisS,and ΔdisGcan be calculated by the following equation,respectively[18].
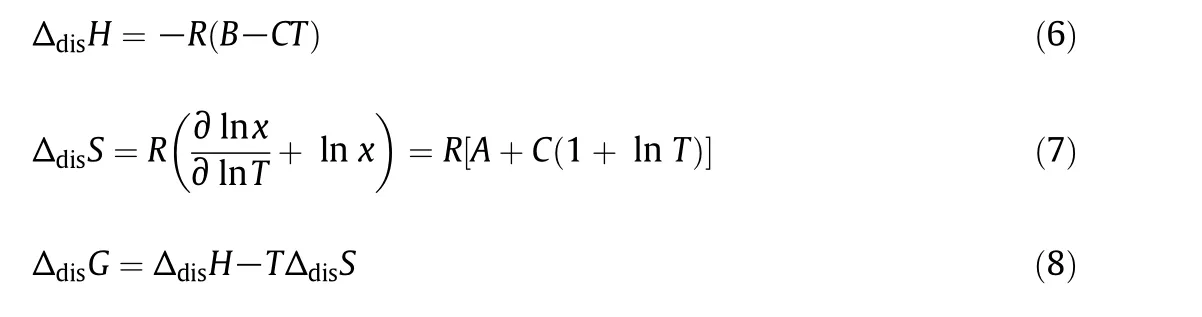
The ξHand ξS,which represent the comparison of the relative contribution to the standard Gibbs energy by enthalpy and entropy in the solution process respectively,are de fined by the following two equations[18]:

The calculated dissolution enthalpy,entropy,and Gibbs energy together with ξHand ξScalculated at 318.15 K are shown in Table 3.
From Table 3,it can be concluded that the course of DNTF dissolving both in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system is endothermic,in that the ΔdisH> 0,which can explain the result of the solubility of DNTF in solvent increases with increasing temperature.The dissolution process is endothermic because the interactions between DNTF molecules and solvent molecules are more powerful than those between the solvent molecules.The positive ΔdisHand ΔdisSreveal that DNTF being dissolved in binary solvent of ethanol and water was an entropy-driving process,and the positive ΔdisGillustrates that the dissolution of DNTF in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system is a non-spontaneous process.Moreover,the main contributor to thestandard molar Gibbs energy of dissolution is the enthalpy instead of entropy,in that the ξHis greater than ξS.
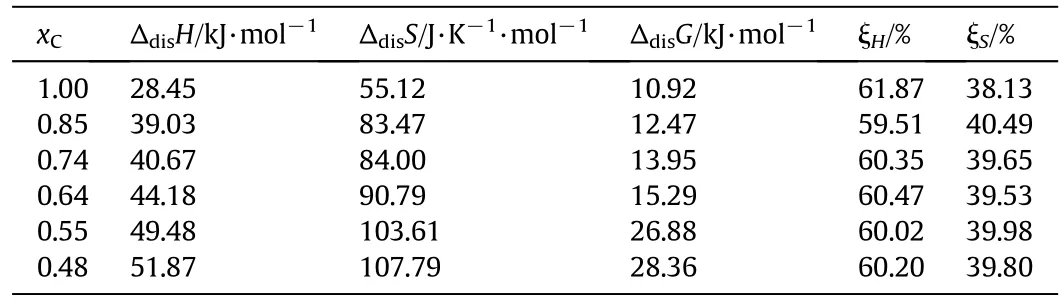
Table 3Standard dissolution enthalpy(Δdis H),entropy(Δdis S),and Gibbs energy at T=318.15 K(Δdis G)together with the ξH,ξS
3.3.Metastable zone width
The MSZW is a region between the solubility curve and supersolubility curve,which is important for the crystallization process,which usually influenced by temperature,initial concentration,solution history,cooling rate,stirring,impurities,etc.[19].In order to obtain the excellent DNTF crystal,the operation curve of DNTF crystallization should be located in the metastable zone,and the MSZW is important for the crystallization kinetics.So it is necessary to determine the MSZW under different operation condition.In this study,the factors of initial concentration,cooling rate,stirring rate and concentration of solvent were considered in the MSZW measurement.
3.3.1.Effect of ethanol concentration and temperature on MSZW
The MSZWs of DNTF in different concentration ethanol+water at different temperature under cooling rate of 0.2 K·min−1are exhibited in Fig.4 which clearly illustrates that the MSZWs tend to narrow with the increase of temperature.As the solubility of DNTF changes more remarkably at high temperature,under the same MSZW the supersaturation is higher at high temperature and,thus,it is easier to nucleate.What's more,the viscosity of the solution is lower at higher temperature,which can increase the movement of molecule,molecule collision frequency,and mass transportation,thus enhancing the probability of nucleation.In addition,the higher is the temperature,the lower is the surface tension,which makes the formation of the nucleus easier.Fig.4 also reveals that when the concentration of DNTF is the same,the MSZW broadens with increasing ethanol ratio,in that,the solubility of DNTF increases with the increasing ethanol ratio,and thus,under the same concentration of DNTF,the temperature of the ethanol+water solution of low concentration is higher than the ethanol of high concentration.Besides,since the solubility of DNTF in ethanol is much larger than in water,the intermolecular force between DNTF and ethanol is larger than that of DNTF and water.Hence,when the ratio of the water decreased,the binding force of solution to the DNTF molecule decreased,and the nucleation is easier.
3.3.2.Effect of cooling rate on MSZW
The MSZWs ofDNTF under different cooling rate at different temperature in pure ethanol and constant stirring rate of 300 r·min−1are depicted in Fig.5.From Fig.5 we can obtain that the MSZW of DNTF in pure ethanol is broaden with the increasing cooling rate,and the influence of cooling rate on MSZW is more obvious under the lower temperature.When the solution was in supersaturation,it still needs an induction period to undergo nucleation[20],and if the supersaturation of the system was created by the cooling,the higher is the cooling rate,the longer is the induction period.When the temperature is high the influence of the temperature which is the dominant resultin the impact of the cooling rate is low.While under low temperature the influence of the cooling rate on the MSZW is enlarged,in that,the effective collision between the DNTF molecules is decreased at low temperature and the nucleation is reduced.Hence,under high cooling rate the nucleation of DNTF molecules will delay.
3.3.3.Effect of stirring rate on MSZW

Fig.4.MSZW of DNTF in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system under cooling rate of 0.2 K·min−1 and stirring rate of 300 r·min−1.Solubility:■,x2=1;●,x2=0.85;▲,x2=0.74;▼,x2=0.64;supersolubility□,x2=1;○,x2=0.85;△,x2=0.74;▽,x2=0.64.
The MSZWs of DNTF under different stirring rate at different temperature in pure ethanol under constant cooling rate of 0.2 K·min−1are displayed in Fig.6.From Fig.6 we can deduce that the MSZW is broaden with the decreasing stirring rate.The collision of molecule is more frequent,and turbulivity of the solution can be enhanced,and the mass and energy transform are enhanced by the stirring,thus enhancing nucleation.However,compared with the temperature the influence of stirring rate on the MSZW is much lower,because,when the temperature is changed the movement state and energy of every molecule change obviously,while the stirring can only change the movement state of molecule,and the longer is the distance between the molecules and the stirring bar,the lower is the influence of stirring.

Fig.5.MSZWofDNTF in ethanolwith differentcooling rates.Solubility:■;supersolubility□,0.2 K·min−1;○,0.2 K·min−1;△,0.2 K·min−1;▽,0.2 K·min−1.

Fig.6.MSZWofDNTF in ethanolwith differentstirring rates.Solubility:■;supersolubility□,400 r·min−1;○,300 r·min−1;△,200 r·min−1.
3.4.Calculation of apparent nucleation order m
According to the classical theory of nucleation,the nucleation rate relationship between cooling rates and MSZW can be expressed by[12,21]:

where β stands for the cooling rate,knrepresents a constant related to the nucleation rate,andmis the apparent nucleation order.ΔTmaxexpresses the MSZW.The equation of DNTF about lgΔTmaxto lgβ is summarized in Table 4 and plotted in Fig.7.
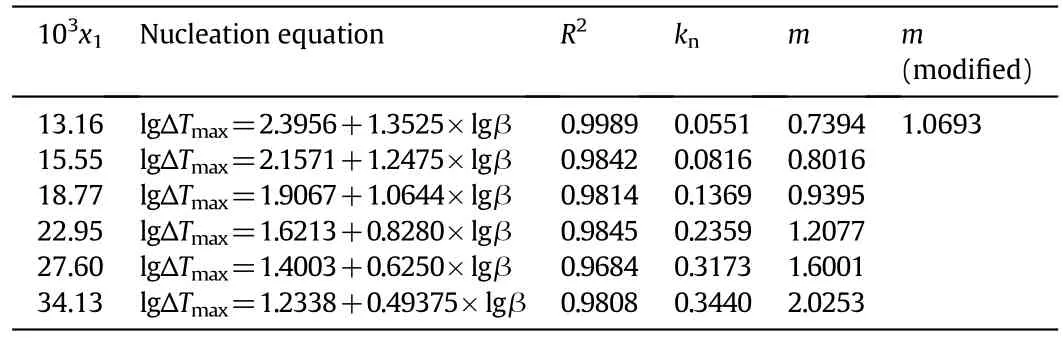
Table 4Calculation of apparent order m and nucleation rate constant k n of DNTF in pure ethanol
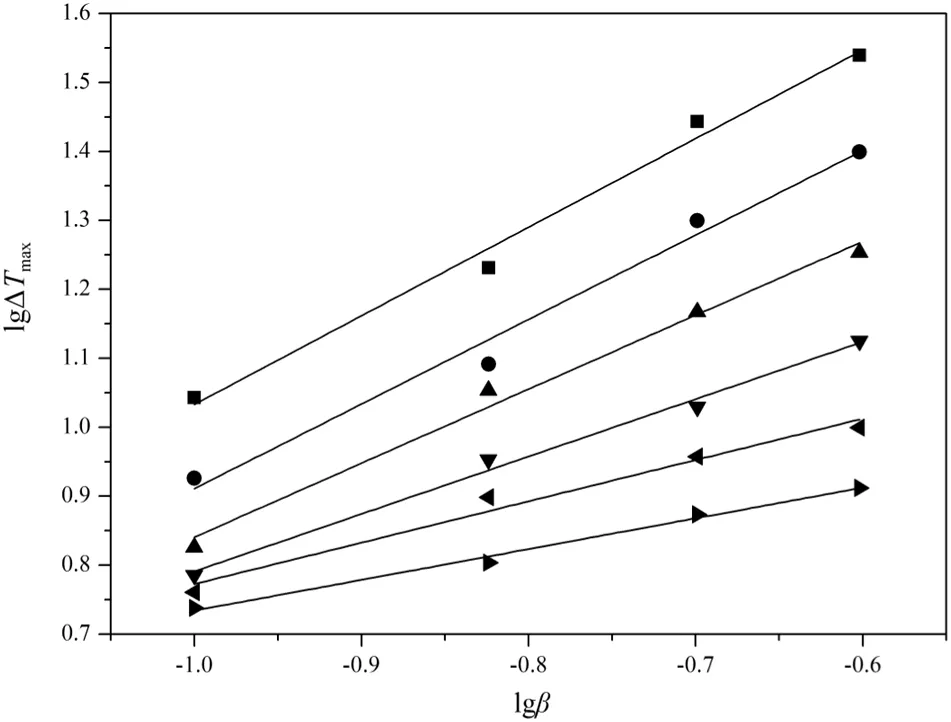
Fig.7.Relationship between the lg(β)and lg(ΔT max):■,13.16×10−3;●,15.55×10−3;▲,18.77×10−3;▼,22.95×10−3;◄,27.60×10−3;►,34.13×10−3.
Since there are some deviations because of the measurement errors,the apparentordersmiof DNTF with different saturation concentrations are not exactly identical.A modified linear regression method has been used to correct the apparent orders by the following formula.
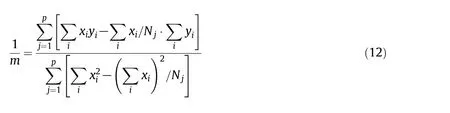
wherexi=lg(β),yi=lg(ΔTmax),pis the total number of straight lines,andNjis the number of measurements carried out for each line.From Table 4 we can see that the nucleation order of DNTF in pure ethanol increases with the increasing concentration of DNTF.
4.Conclusions
The solubility and supersolubility of DNTF in pure ethanol and ethanol+water binary system have been studied.The solubility values of DNTF increase with the increasing temperature and the concentration of ethanol.The Apelblat equation is a perfect function to correlate the relationship between mole fraction solubility values of DNTF and temperature.The standard dissolution enthalpy,standard dissolution entropy and standard Gibbs energy have been calculated,and we found that the dissolution of DNTF is an endothermic and nonspontaneous process.The influence of temperature,cooling rate,stirring rate and ethanol concentration on the MSZW was studied,and the apparent nucleation order has been calculated.
[1]H.X.Hu,G.M.Qin,Z.Z.Zhang,3,4-Dinitrofurazanfuroxan explosive,CN Pat.,02101092,2002.
[2]Y.S.Zhou,B.Z.Wang,J.K.Li,C.Zhou,L.Hu,Z.Q.Chen,Z.Z.Zhang,Study on synthesis,characterization and properties of 3,4-bis(4′-nitrofurazano-3′-yl)furoxan,Acta Chim.Sin.69(2011)1673–1680.
[3]J.Wang,H.S.Dong,Y.G.Huang,J.S.Li,Snythesis of 3,4-diaminofurazanfuroxan,Chin.J.Energy Mater.(Supplement)(2004)91–93.
[4]Y.S.Zhou,Z.Z.Zhang,J.K.Li,X.R.Guan,X.P.Huang,C.Zhou,Crystal structure of 3,4-dinitrofurazanofuroxan,Chin.J.Explos.Propellants28(2005)43–46.
[5]V.P.Sinditskii,A.V.Burzhava,A.B.Sheremetev,N.S.Aleksandrova,Thermal and combustion properties of 3,4-bis(3-nitrofurazan-4-yl)furoxan(DNTF),Propellants Explos.Pyrotech.37(2012)575–580.
[6]F.Q.Zhao,P.Chen,R.Z.Hu,etal.,Thermochemical properties and non-isothermal decomposition reaction kinetics of 3,4-dinitrofurazanfuroxan(DNTF),J.Hazard.Mater.113(2004)67–71.
[7]H.X.Hu,Z.Z.Zhang,F.Q.Zhao,C.Xiao,Q.H.Wang,B.H.Yuan,A study on the properties and application of high energy density material DNTF,Acta Armamentarii25(2004)155–158.
[8]W.Zheng,J.N.Wang,Review on 3,4-bisnitrofurazanfuroxan(DNTF),Chin.J.Energy Mater.14(2006)463–466.
[9]M.Lenka,D.Sarkar,Determination of metastable zone width,induction period and primary nucleation kinetics for cooling crystallization of L-asparaginenohydrate,J.Cryst.Growth408(2014)85–90.
[10]X.H.Shi,C.R.Zhou,Y.G.Gao,X.Z.Chen,Measurement and correlation for solubility of(S)-(+)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane carbox amide in different solvents,Chin.J.Chem.Eng.14(2006)547–550.
[11]L.Z.Chen,T.B.Zhang,M.Li,J.Li,D.L.Cao,Solubility of 2,2′,4,4′,6,6′-hexanitrostilbene in binary solvent of N,N-dimethylformamide and acetonitrile,J.Chem.Thermodyn.95(2016)99–104.
[12]J.Y.Peng,Y.P.Dong,Z.Nie,F.Z.Kong,Q.F.Meng,W.Li,Solubility and metastable zone width measurement of borax decahydrate in potassium chloride solution,J.Chem.Eng.Data57(2012)890–895.
[13]F.X.Zou,W.Zhuang,J.L.Wu,J.W.Zhou,P.P.Yang,Q.Y.Liu,Y.Chen,H.J.Ying,Determination of metastable zone widths and the primary nucleation and growth mechanisms for the crystallization of disodium guanosine 5′-monophosphate from a water–ethanol system,Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.54(2015)137–145.
[14]K.J.Cui,Z.B.Xu,L.R.Chen,M.Xue,Z.H.Meng,G.G.Xu,R.Wang,W.J.Liu,Z.H.Lin,Solubility of 3,4-bis(3-nitrofurazan-4-yl)furoxan in common solvents at temperatures between 293.15 K and 313.15 K,J.Chem.Eng.Data58(2013)2677–2680.
[15]A.Apelblat,E.Manzurola,Solubilities of manganese,cadmium,mercury and lead acetates in water fromT=278.15 K toT=340.15 K,J.Chem.Thermodyn.33(2001)147–153.
[16]L.Zhou,P.P.Zhang,G.D.Yang,R.Lin,W.R.Wang,T.T.Liu,L.Q.Zhang,J.Y.Zhang,Solubility of chrysin in ethanol and water mixtures,J.Chem.Eng.Data59(2014)2215–2220.
[17]J.Yu,T.L.Ma,A.Li,X.C.Chen,Y.Chen,J.J.Xie,J.L.Wu,H.J.Ying,Solubility of disodium cytidine 5′-monophosphate in different binary mixtures from 288.15 K to 313.15 K,Thermochim.Acta565(2013)1–7.
[18]Y.H.Hu,X.Liu,W.G.Yang,J.J.Yin,Y.Liu,M.M.Liang,Measurement and correlation of the solubility of 4-methylbenzoic acid in(methanol+acetic acid)binary solvent mixtures,J.Mol.Liq.193(2014)213–219.
[19]L.P.Wang,H.T.Feng,J.Y.Peng,N.J.Dong,W.Li,Y.P.Dong,Solubility,metastable zone width,and nucleation kinetics of sodium dichromate dehydrate,J.Chem.Eng.Data60(2015)185–191.
[20]Y.Y.Qian,G.M.Lu,Y.Z.Sun,X.F.Song,J.G.Yu,Metastable zone width of SrCl2·6H2O during cooling crystallization,Cryst.Res.Technol.49(2014)78–83.
[21]J.Y.Peng,Z.Nie,L.L.Li,L.P.Wang,Y.P.Dong,W.Li,Solubility and metastable zone width of sodium tetraborate decahydrate in a solution containing lithium chloride,J.Chem.Eng.Data58(2013)1288–1293.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Application of response surface methodology for optimization of purge gas recycling to an industrial reactor for conversion of CO2 to methanol
- The effect of transition metal ions(M2+=Mn2+,Ni2+,Co2+,Cu2+)on the chemical synthesis polyaniline as counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells☆
- Catalytic ozonation of thymol in reverse osmosis concentrate with core/shell Fe3O4@SiO2@Yb2O3 catalyst:Parameter optimization and degradation pathway☆
- Influence of Na+,K+,Mg2+,Ca2+,and Fe3+on filterability and settleability of drilling sludge☆
- Partition coefficient prediction of Baker's yeast invertase in aqueous two phase systems using hybrid group method data handling neural network
- Measurement and calculation of solubility of quinine in supercritical carbon dioxide☆
