Effect of surfactant on zeta potential and rheology behavior of methylene bis(thiocyanate)suspension concentrate☆
2017-05-28JianfengHuYanCaiShanLuJiezhenXuZhongrunYunJianhengHuangYuliangWenJinqingQu
Jianfeng Hu *,Yan CaiShan Lu Jiezhen Xu Zhongrun Yun ,Jianheng Huang Yuliang Wen ,Jinqing Qu
1 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,China
2 School of Materials Science and Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,China
3 Guangzhou Goaland Energy Conservation Tech Co.,Ltd,of Luogang District,Guangzhou 510663,China
1.Introduction
Suspension concentrate(SC)is a kind of slurry which is composed of disperse phase,like solid or liquid which cannot be dissolved in water[1].It is wildly used in drinks,medicines and pesticides because of its simple preparation process,environmentally friendly nature,and excellent performance suspension state performance.Methylene bis(thiocyanate)(MBT)is pale yellow freeflowing powder or crystals,and its melting point is about 101°C.As a broad-spectrum antibiotic,MBT can sanitize anaerobic bacteria,aerobic bacteria,fungus,algae and other bacteria well.But its sterilization capability is limited in solid state because it can be dissolved in hot water but not in cold water[2].Powder or crystal can be smashed into smaller size as dispersed phase to increase its contacted area with deionized water.So transforming MBT powder or crystal state into suspension concentration is very important to raise MBT's performance and reduce the potential damage to the environment in the producing,storing and applying.
The particles suspended in SC can be easily gathered and deposited because a particle with small size has big superficial area and high interfacial energy[3,4].So surfactant is supposed to add in SC to increase its stability.The main reason of dispersed phase steady suspension in continuous phase is that surfactant molecular can be gathered around particles that form a hydrated layer or electric double layer.The formation of the layer depends on the types of surfactant.And then the exclusion effect and steric effect were induced to reduce the interfacial energy[5–7].Meanwhile,surfactant molecular embedded on the surface of solid particles,modifying the surface characters of particles.Thus changed the viscosity,surface tension,acting force between disperse phase particles,and rheology behaviors of SC were changed.Tanet al.studied the influence of poly-electrolyte on rheology behaviors of zirconia slurry.It was found that rheology behavior of zirconia slurry can be improved with high solid content and low viscosity by adding 0.8 wt%–1.2 wt%surfactants[8].Meiet al.investigated regular solid content cordierite glass-ceramics slurry with different content surfactants and found that low content surfactant slurry showed Bingham model fluid behavior,middle content surfactant slurry showed Newton fluid behavior,while high content surfactant slurry showed Casson model fluid behavior[9].With the wild usage of SC in industrial and civil field,the study on Zeta potential and rheology behavior on SC affected by combined surfactants is still not enough.
Zeta potential of MBT SC was studied in this paper,and the effect of some surfactants,such as Morwet D425,Morwet EFW with different ratio,was investigated to find out the effect of surfactants on the rheology behaviors of 10%MBT SC.The shear viscosity under different shear rates was measured and effect principles of surfactants on rheology behavior of MBT SC were studied.
2.Experimental
2.1.Materials
MBT(≥98%)was purchased from Guangdong Xingning Fine Chemistry Co.,Ltd.Morwet D425 and Morwet EFW were purchased from Akzo Nobel Co.,Ltd.Xanthan gum(XG)was obtained from Zibo Hailan Chemical Engineering Co.,Ltd.Magnesium aluminum silicate was received from Guangzhou New Rare-earth Metallurgy Chemical Engineering Co.,Ltd.Foamex 805 was purchased from Foshan Meihan trading company.Glacial acetic acid was provided from Chengdu City United Chemical Engineering Reagent Institute.All reagents were used without further purified.
2.2.Preparation of SC
SC was prepared with wet-grinding technology.Firstly,XG and magnesium aluminum silicate were dissolved in deionized water with stirring.And then MBT,surfactant(D425,EFW)and Foamex 805 were added in the mixture.Finally,acetic acid was used to adjustthe solution pHvalue to 6.This mixture was transferred to a dispersion machine and pre-dispersed at 400 r·min−1speed for 1 h.It was then switched into a sand mill(SFJ-400,Shandong Feicheng Jiabeir Apparatus Co.,Ltd.)grinded for 3 h using 1–1.5 mm zirconium silicate bead,and then purified by filtration[10].Fig.1 shows the preparation process of MBT SC.
Fig.1.Scheme illustration of preparation of MBT SC.
2.3.Characterization of MBT SC
pH value of MBT SC was measured with pH meter(PHB-3,Shanghai San Xin Instrument and Meters Factory).Zeta potential of MBT SC was measured with Zeta Potential Analyzer(Zetasizer 2000 Instrument,Malvern)under0.01 mg·L−1.Basic groups of materials were characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer(Perkin-Elmer spectrum-2000,KBr,4000–400 cm−1).Rheology properties of MBT SC were investigated by Rheometer(AR550,TA instruments)with parallel plates system(D=40 mm)and the shear viscosity η and shear stress τ were tested under the scanning frequency between 0.1–400 s−1in room temperature(25±0.5)°C.
3.Results and Discussions
3.1.FTIR analysis of main materials
Groups of surfactants are the key factor that affects the stability of SC.D425 and EFW are condensation polymers of sodium alkyl naphthalene sulfonate.Fig.2 shows the FTIR spectra of D425,EFW and XG.In the curve of D425,a peak at 3434 cm−1represents the strong absorption of–OH,the peaks at 1625 cm−1,1504 cm−1and 1445 cm−1are corresponding to naphthalene group,and the peaks at 1383 cm−1and 1187 cm−1present the absorptions of S=O.The FTIR spectrum of EFW is quite similar with that of D425 except that EFW presents a peak at 1728 cm−1,which is corresponding to the association of carboxylate.For the spectrum of XG,it presents another two peaks at 3430 cm−1and 1645 cm−1,respectively.The former is caused by–OH,and the latter can be attributed to carbonyl group,implying that XG is a polysaccharide.
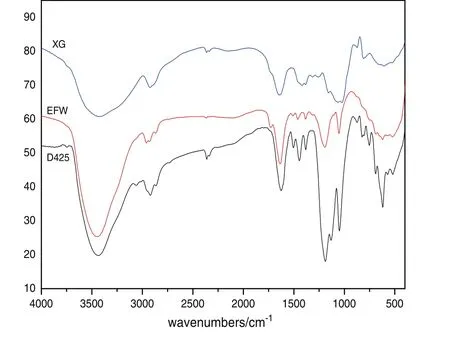
Fig.2.FTIR spectrum of D425,EFW and XG.

Fig.3.Model of stern electric double layer[11].
3.2.Zeta potential
Fig.3 is the model of stern electric double layer.As shown in Fig.3,Zeta potential ζ is the potential difference between the stern layer and shear layer when the relative movement happened between solid phase and liquid phase[9].The positive and negative values of Zeta potential represents plus and minus of charges.It can accurately reflect the electric behavior of solid particles for that a tiny change of electric charge in stern layer can cause the fluctuating of electric potential.In theory,for particles,bigger potential absolute value means stronger repulsion force between them[12,13].In Fig.4,as the ionic surfactant with same electric property added,electricity in stern layer and potential absolute value increase.Fig.5 shows the change of Zeta potential in stern layer during 10 times SC dilution at pH=4.5.The electrical potential is negative because surfactant is anionic surfactant.As shown in the image,the electrical potential absolute value initially increases with the content of D425.After then,as the content of D425 increases to 2%–4%,electrical potential absolute value climbs to a platform on the curve,after 4%,it increases rapidly again.The maximum ζa(absolute value)at 5%is 31.93 mV,and the minimum ζaat 1%is 22.77 mV.In acidic environment,electricity in stern layer increases with the accumulation of D425 in stern layer.
By contrast,in acidic environment,when only EFW dissolved in SC,electrical potential ζadecreases with the increase of EFW.The relationship between content of EFW andζais almostlinear.The maximumζaat 1%is 33.01 mV,and the minimum ζaat 5%is 20.69 mV.
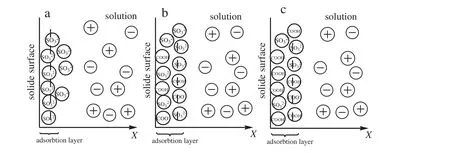
Fig.4.Adsorption of surfactant in stern layer.
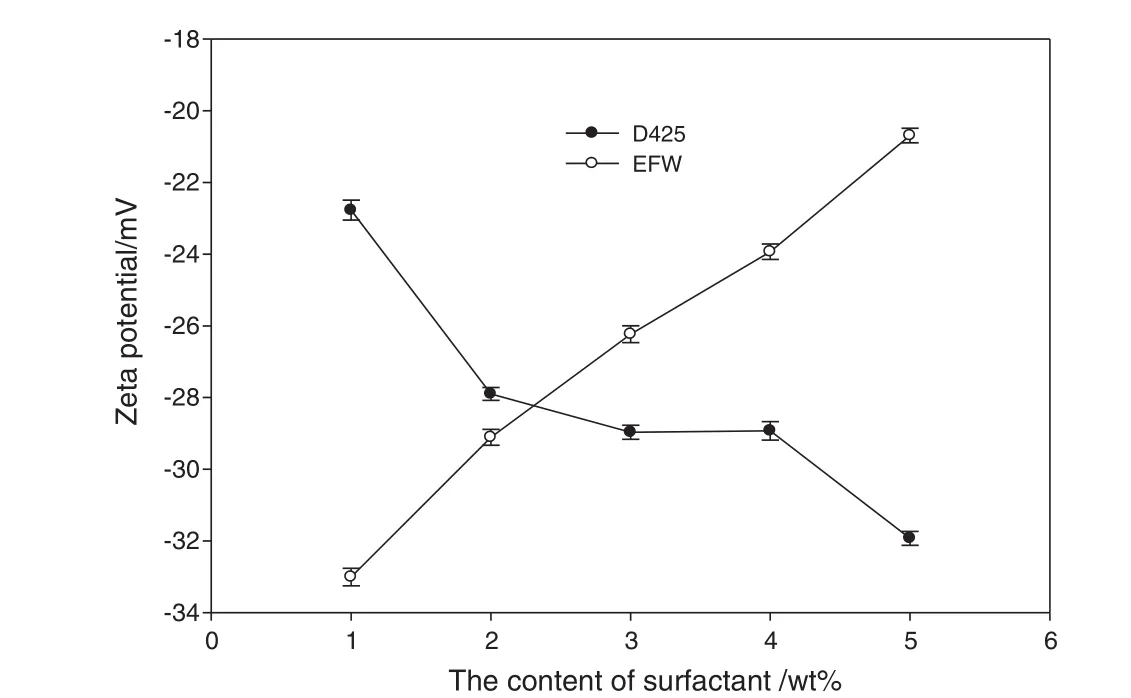
Fig.5.Zeta potential of EFW and D425.Values are means±SD(standard deviation)(n=3).
In contrast with D425,there are other groups in EFW,like–COO−,et al.When the content of EFW increases,−COO−would therefore increase.In acidic environment,protonation of–COO−is in a high level and hydrophobicity of–COOH is higher than –COO−and –SO32−that reduced the contentof–SO32−.Normally,the stability decreases whenζaincreases,but here,the stability is steady because of steric hindrance of EFW on the surface of particles.
Fig.6 shows the effect ofD425 content in D425 and EFW complex on ζ of SC(EFW wt%+D425 wt%=3%).ζainitially increases with D425g,and after D425 wt% > 2%,it turns to drop.The maximum of ζais 29.79 mV at the point of D425 wt%=2.When D425 is the only surfactant in SC,particles'surface was covered with–SO32−(Fig.4a).And the absorbing tends to be monolayer adsorption because of the repulsive force induced by the same electric property.After the content of EFW increased,−COOHis gathering on the particles'surface(Fig.4b).Meanwhile,−SO32−was absorbed on the surface too.That is why ζaincreased.But when D425 wt% > 2,−COOH starts to replace the–SO32−,then it directly affects the tendency ofζato drop as it is shown in Figs.6 and 4c.

Fig.6.Effect of EFW and D425 complex on Zeta potential of SC.Values are means±SD(n=3).
3.3.In fluence of D425 on shear viscosity of MBT SC
Fig.7(a)shows the changes of MBT SC's shear viscosity in different contents of D425.Under low shear rate,SC-D shows shear thinning behavior.That is because XG is polysaccharide which has a lot of–OH and–COOH that can form hydrogen bond with H2O in SC.So the force between molecules was enhanced[14].H2O and MBT particles were locked in the network built by hydrogen bond and XG molecular and the viscosity was increased in static state.Shear rate changed between 4–30 s−1,shear force destroyed the hydrogen bond,so viscosity descended rapidly.And when shear rate is greater than 30 s−1,there is a platform on the curve of viscosity,that means the viscosity is stable after 30 s−1.
Fig.7(b)shows the changes of shear stress in SC caused by D425.At the same shearrate,when D425 increases,shear stress reduces first and then increases.The peak is at 3%.MBT particles were surrounded by D425,so the effect on viscosity is produced by the electrostatic repulsion between particles caused by –SO32−,and hydrogen bonds of D425 and XG.In the case of the increasing of D425(< 3wt%),–SO32−on the surface of MBT particles is gathering too,so that electrostatic repulsion adds.The result is that electrostatic repulsion is stronger than hydrogen bonds of D425 and XG,and shear stress reduces as well.On the contrary,with the increasing of D425(<3wt%),hydrogen bonds in SC increases rapidly.And the particles were surrounded by–COOH.All the particles were locked in network system built by hydrogen bonds.That causes the shear stress increase[15].
As showed in Fig.7(a),(b),rheology behavior curve of MBT SC with D425 is according to Herschel–Bukley model[16].Fig.7a shows the relationship between shear rate and viscosity.According to Eq.(1):

where η,and η0are viscosities(Pa·s),kis a constant,and γ is shear rate(s−1).
Fitting data and variance are showed in Table 1.
Fig.7b shows the relationship between shear rate and shear force.According to Eq.(2):

where τ is shear force,Pa;τ0is yield stress,Pa;Kis viscosity coefficient N·sn·m−2;γ is shear rate;andnis a special constant of fluid.

Fig.7.Relationship of shear rate-viscosity(a)and the relationship of shear rate–shear stress(b)of SC-D(D425 in SC).
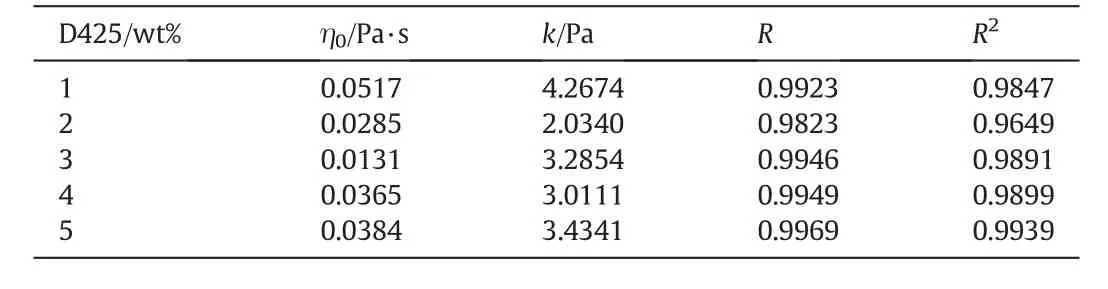
Table 1The fitting data of SC-D about the property of shear rate-viscosity

Table 2The fitting data of SC-D about the property of shear rate–shear stress
As shown in Tables 1 and 2,the curve fits Herschel–Bulkley model well.According to the above analysis,viscosity of yield stress decreases first and then increases with the increase of D425.In Eq.(2),npresents fluid type,n<1,viscosity reduced when fluid was sheared,so SC-D is yield pseudo-plastic fluid.
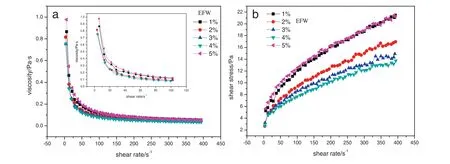
Fig.8.Relationship of shear rate-viscosity(a)and shear rate–shear stress(b)about SC-E.
3.4.In fluence of EFW on shear viscosity of MBT SC
Fig.8(a)shows the effect of EFW on shear viscosity.Similar to D425,shear viscosity of SC-E(EFW in SC)extremely reduces when the shear rate increases,and it is very close to a constant.Fig.8(b)presents the relationship between shear rate and shear stress in different contents of EFW.Compared with D425,at the same shear rate,when EFW increases,shear stress reduces before 4%,and increases after 4%.While the changing point of shear stress of SC-D when D425 is 3%.Because of–COO−in EFW,in acidity environment,−COOH is produced and absorbed on solid particles.Electrical groups are excluded from the surface of solid particles.So that the repulsion between particles increases slowly,and viscosity at same shear rate increases until the content of EFW reaches 4%.When EFW is after 4%,the hydrogen bond between molecules arestronger than electrostatic repulsion between particles,and shear stress increases rapidly.According to Herschel–Bulkley model,Fig.8(a)shows the relationship of shear rate with viscosity and shear stress of SC-E.

Table 3Fitting data of SC-E about the property of shear rate-viscosity
Tables 3 and 4 show,the curve of SC-E fluid fits Herschel–Bulkley model well.And it appears nonlinear shear thinning behavior.Andn<1,so SC-E is Yield Pseudoplastic Fluid.
3.5.Influence of combination of EFW and D425 on shear viscosity of MBT SC
Fig.9(a)shows the combination of EFW and D425 has the same rheology behavior as single EFW or D425,they all belong to Yield Pseudoplastic Fluid.At the same shear rate,whenm(the rate of EFW:D425)increases,viscosity of SC decreases first and then increases.Whenm=2,viscosity is minimum at the same shear rate.Fig.4(a)and(b)shows Zeta potential between particles increases and steric repulsion increases too.Viscosity of SC reduces because steric repulsion is stronger than hydrogen bond whenm<2.And Fig.4(c)shows Zeta potential between particles increases and steric repulsion increases too.Viscosity of SC increases because steric repulsion is weaker than hydrogen bond whenm>2.
Fig.9 shows that the combination surfactant SC has the similar rheology curve as the single surfactant SC,and fits Herschel–Bulkley model well,as was shown in Tables 5 and 6.
The results of Tables 5 and 6 show that this fluid is Yield Pseudoplastic Fluid according to the results of Fig.9.
4.Conclusions
1)In 10 times diluted SC-D,with the increasing of D425,surfactant was absorbed on the particles and electrical groups increased too.Respectively,Zeta potential ζaincreased.While,in SC-E,Zeta potential ζadecreased with EFW increased and in SC-E-D,Zeta potential ζadecreased first and then increased with the combination increased.
2)Combination of EFW and D425 shows SC's viscosity was affected by the cooperation of steric repulsion and hydrogen bond force.Steric repulsion is stronger than attraction of hydrogen bond,viscosity of SC decreased,while viscosity increased when steric repulsion is weaker than attraction of hydrogen bond.
3)SC-E,SC-D,and SC-E-D fits Herschel–Bulkley model well.At the same shear rate,the shear stress decreased first and then increased when the content of surfactant increased in SC-E,SC-D,and SC-E-D.MBT SC can be used to exterminate the main germs in circulating water, fishpond,and cooling wateretc.,These conclusions can help to optimize the parameters of MBT SC in manufacture,storage and application,and understand the performance of combined surfactants.
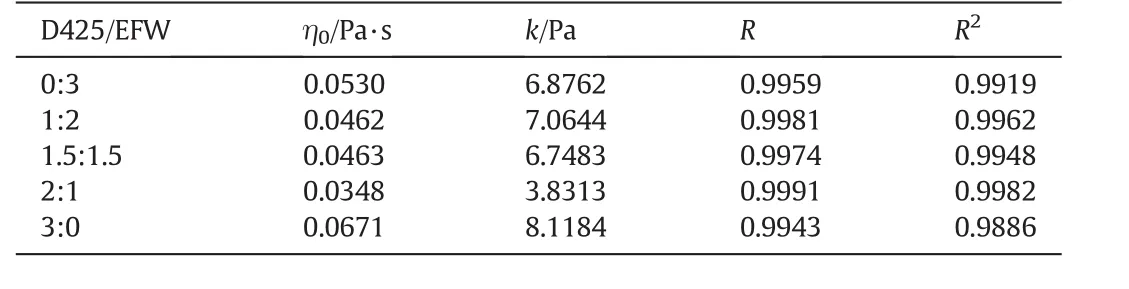
Table 5Fitting data of SC-E-D(EFW and D425 in SC)about the property of shear rate-viscosity
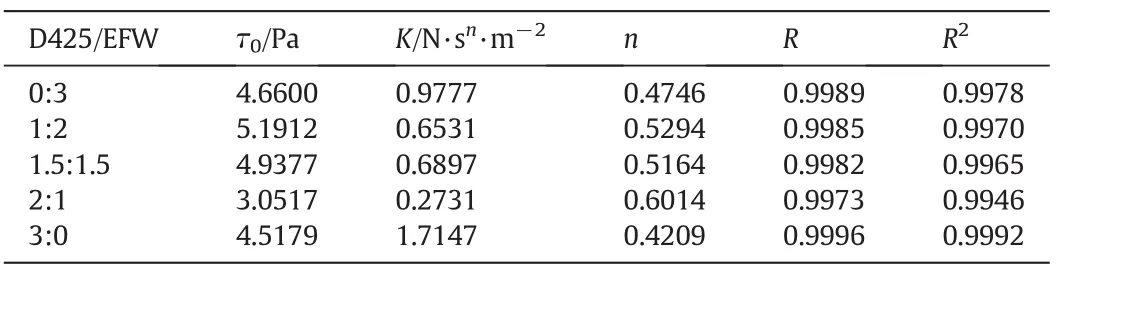
Table 6Fitting data of SC-E-D about the property of shear rate–shear stress
Nomenclature
Kviscosity coefficient,N·sn·m−2
kconstant,Pa
mthe rate of EFW:D425
na special constant of fluid
γ shear rate,s−1
ζ Zeta potential,mV
η viscosity,Pa·s
τ shear force,Pa
τ0yield stress,Pa
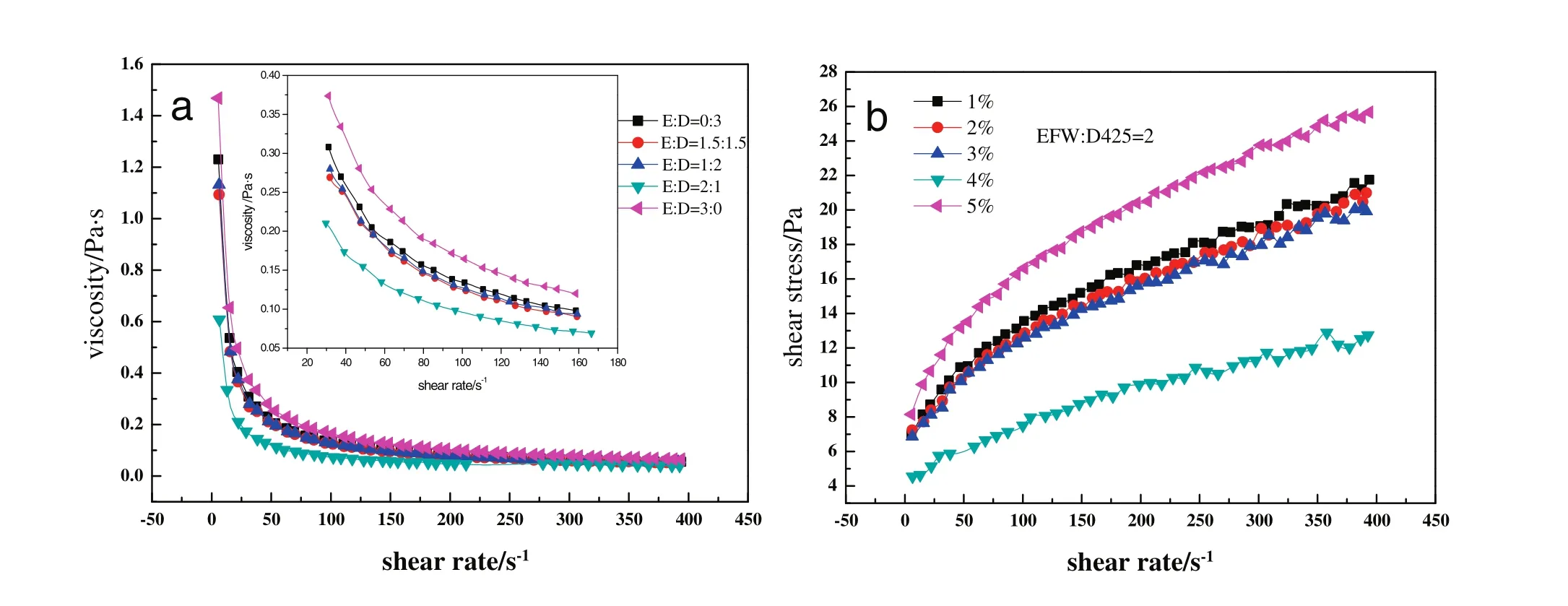
Fig.9.Relationship of shear rate-viscosity(a)and the relationship of shear rate–shear stress(b)under the proportion of EFW and D425.
[1]W.Guo,Liquid Preparation,Chemical Industry Press,Beijing,2003 1–10.
[2]T.Singh,Migration of methylene bis tiocyanate in wood and its effect on a wood degrading fungus,For.Res.3(2008)195–202.
[3]B.Li,Study on 25%difenoconazole suspension concentrates,Mod.Agrochemicals1(2009)30–33.
[4]Z.Wang,Physics and Chemistry,High Education Press,Beijing,2001 310–313.
[5]J.Sun,L.Gao,Dispersing SiC powder and improving its rheological behavior,J.Eur.Ceram.Soc.13(2001)2447–2451.
[6]J.Yang,J.Zhao,Y.Fang,etal.,Calorimetric studies of the interaction between sodium alginate and sodium dodecyl sulfate in dilute solutions at different pH values,Carbohydr.Res.4(2008)719–725.
[7]L.Zhou,Y.Huang,Z.Xie,Gelcasting of concentrated aqueous silicon carbide suspension,J.Eur.Ceram.Soc.1(2000)85–90.
[8]Q.Tan,Z.Zhang,Z.Tang,et al.,Rheological properties of nanometer tetragonal polycrystal zirconia slurries for aqueous gel tape casting process,Mater.Lett.16-17(2003)2375–2381.
[9]S.Mei,J.Yang,J.M.F.Ferreira,Effect of dispersant concentration on slip casting of cordierite-based glass ceramics,J.Colloid Interface Sci.5(2001)417–421.
[10]J.Hu,J.Huang,H.Shen,Preparation of methylene bis thiocyanate suspension concentrate,Plant Prot.3(2012)82–85.
[11]Z.Shen,Colloid and Surface Chemistry,Chemical Industry Press,Beijing,1997 64–67.
[12]W.Li,M.Gu,Y.Jin,Effect of dispersant concentration on rheological behavior of SiC aqueous suspension,J.Chin.Ceram.Soc.11(2004)1356–1360.
[13]F.Guillemet,L.Piculell,Interactions in aqueous mixtures of hydrophobically modified polyelectrolyte and oppositely charged surfactant.Mixed micelle formation and associative phase separation,J.Phys.Chem.22(1995)9201–9209.
[14]J.Yang,S.Chen,Y.Fang,Effect of surfactants on the shear viscosity of dilute aqueous solutions of sodium alginate,Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.25(2009)752–756.
[15]Z.Yi,Y.Huang,Z.Xie,J.Ma,Dispersion and rheological property of the concentrated SiC suspension,J.Chin.Ceram.Soc.4(2002)517–520.
[16]T.Shi,D.Wu,Foundation of Macromolecule Rheology,Chemical Industry Press,Beijing,2009 31–32.
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering的其它文章
- Influence of Na+,K+,Mg2+,Ca2+,and Fe3+on filterability and settleability of drilling sludge☆
- An optimal filter based MPC for systems with arbitrary disturbances☆
- Measurement and calculation of solubility of quinine in supercritical carbon dioxide☆
- Solubility and metastable zone width measurement of 3,4-bis(3-nitrofurazan-4-yl)furoxan(DNTF)in ethanol+water
- Partition coefficient prediction of Baker's yeast invertase in aqueous two phase systems using hybrid group method data handling neural network
- The effect of transition metal ions(M2+=Mn2+,Ni2+,Co2+,Cu2+)on the chemical synthesis polyaniline as counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells☆
