渤海湾盆地青东凹陷古近系原油地球化学特征及油源分析
2017-05-23葛海霞张枝焕
葛海霞,张枝焕,闵 伟
(1.中国石油大学 地球科学学院,油气资源与探测国家重点实验室,北京 102249;2.中国石化 胜利油田石油开发中心,山东 东营 257015)
渤海湾盆地青东凹陷古近系原油地球化学特征及油源分析
葛海霞1,张枝焕1,闵 伟2
(1.中国石油大学 地球科学学院,油气资源与探测国家重点实验室,北京 102249;2.中国石化 胜利油田石油开发中心,山东 东营 257015)

生物降解油;生物标志物;油源对比;青东凹陷;济阳坳陷;渤海湾盆地
1 区域地质概况及样品分布
青东凹陷为位于济阳坳陷东部、郯庐断裂带西侧的新生代陆相断陷湖盆,在太古界结晶变质岩之上发育了古生界、中生界、新生界及第四系等沉积岩系,目前已钻至中生界,古近系孔店组、沙河街组,新近系馆陶组、明化镇组及第四系平原组。沙三下和沙四上亚段为烃源岩和油气分布主要层位。凹陷存在常规原油和稠油,常规原油分布在深洼地带,埋深大于2 000 m;稠油分布在凹陷边缘,埋深小于2 000 m。原油在不同深度和部位遭受生物降解程度不同,过渡带(青东4井)达到8级,西部斜坡带(青东17井)为6级,青东5井区为2级[6](图1)。
2 原油地球化学特征及成因类型划分

2.1 Ⅰ类原油

图1 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷青东凹陷区域构造位置及样品分布据詹润等[17],2012,有修改。
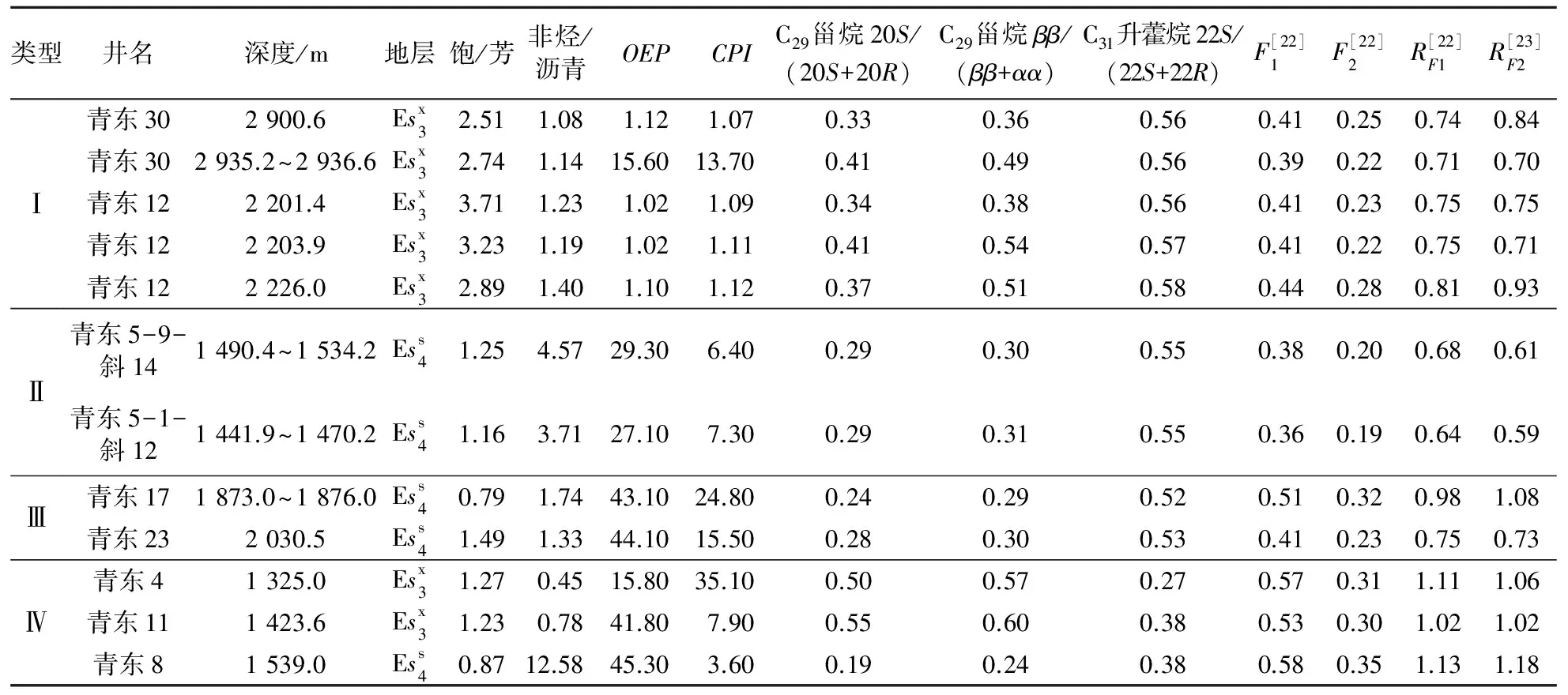
表1 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷青东凹陷古近系典型原油族组分、饱和烃及芳烃参数指示成熟度特征
注:F1= (3-MP+2-MP)/(1-MP+2-MP+3-MP+9-MP);F2=2-MP/(1-MP+2-MP+3-MP+9-MP);RF1=2.242F1-0.166;RF2=3.73F2-0.112。
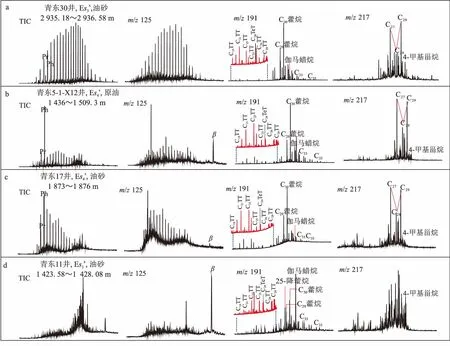
图2 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷青东凹陷古近系各类原油部分生物标志化合物质量色谱TT表示三环萜烷; TeT表示四环萜烷

2.2 Ⅱ类原油

2.3 Ⅲ 类原油

2.4 Ⅳ类原油

3 烃源岩地球化学特征及类型划分
3.1 有机地球化学参数特征
青东凹陷主力烃源岩为沙三下亚段和沙四上亚段,均在凹陷中北部深洼达到最大厚度。沙四上亚段为半干旱条件下的滨浅湖和半深湖沉积,为暗色泥岩夹油页岩、白云岩;沙三中下亚段暗色泥岩为稳定的深湖—半深湖相沉积,沉积厚度和分布范围变小。烃源岩处于低熟—成熟阶段,成熟门限约为2 250 m;有机质类型以Ⅰ-Ⅱ型为主,有机质丰度均达到好的烃源岩标准(表2)。
3.2 生物标志物组成特征及类型划分

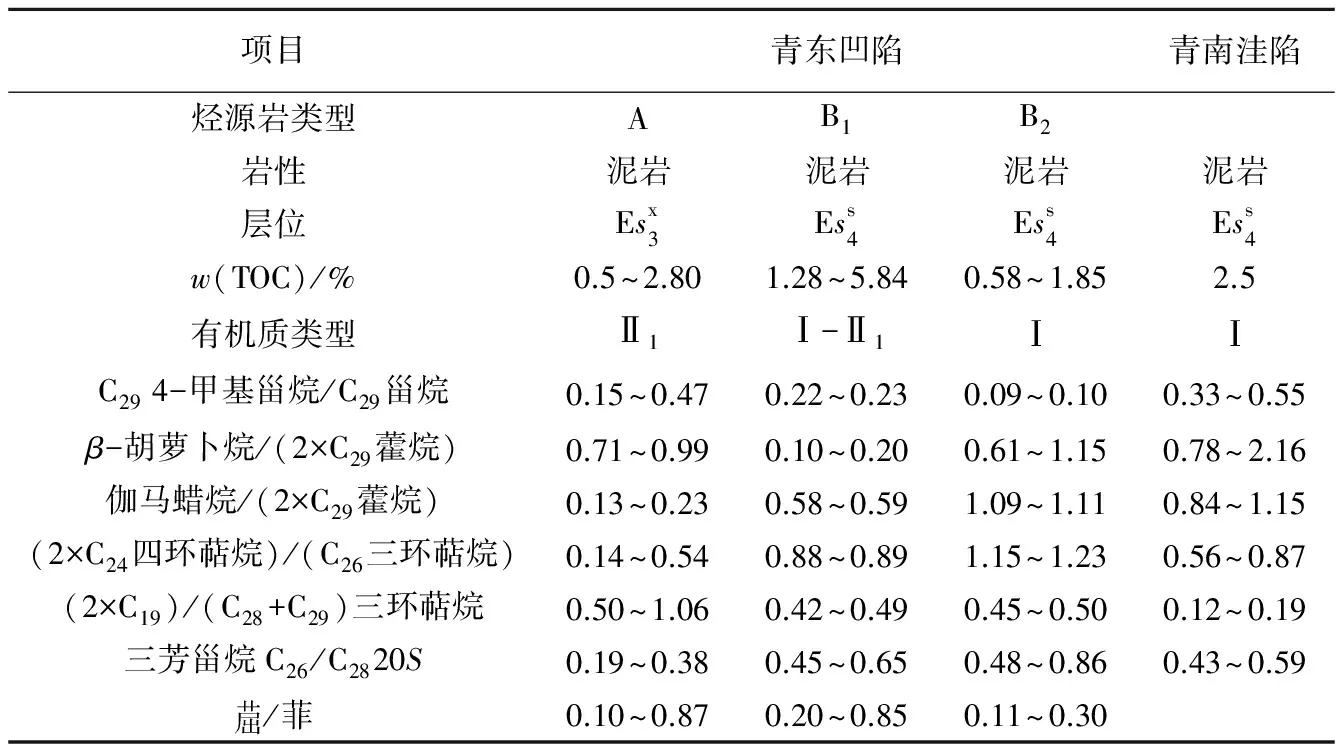
表2 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷青东凹陷与青南洼陷沙河街组烃源岩主要地球化学特征
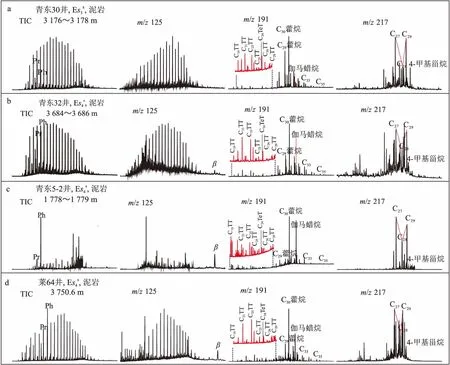
图3 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷青东凹陷烃源岩部分生物标志化合物谱图TT表示三环萜烷; TeT表示四环萜烷
4 油源分析
4.1 Ⅰ类原油来源分析
Ⅰ类原油与A类烃源岩均具有姥鲛烷优势,β-胡萝卜烷、伽马蜡烷、C24四环萜烷及升藿烷相对含量低(图4)。饱和烃和芳烃成熟度参数计算结果吻合,皆显示原油为成熟油(表1),推测Ⅰ类原油来源于凹陷沙三下亚段成熟烃源岩。
4.2 Ⅱ类原油来源分析

4.3 Ⅲ 类原油来源分析

4.4 Ⅳ类原油来源分析

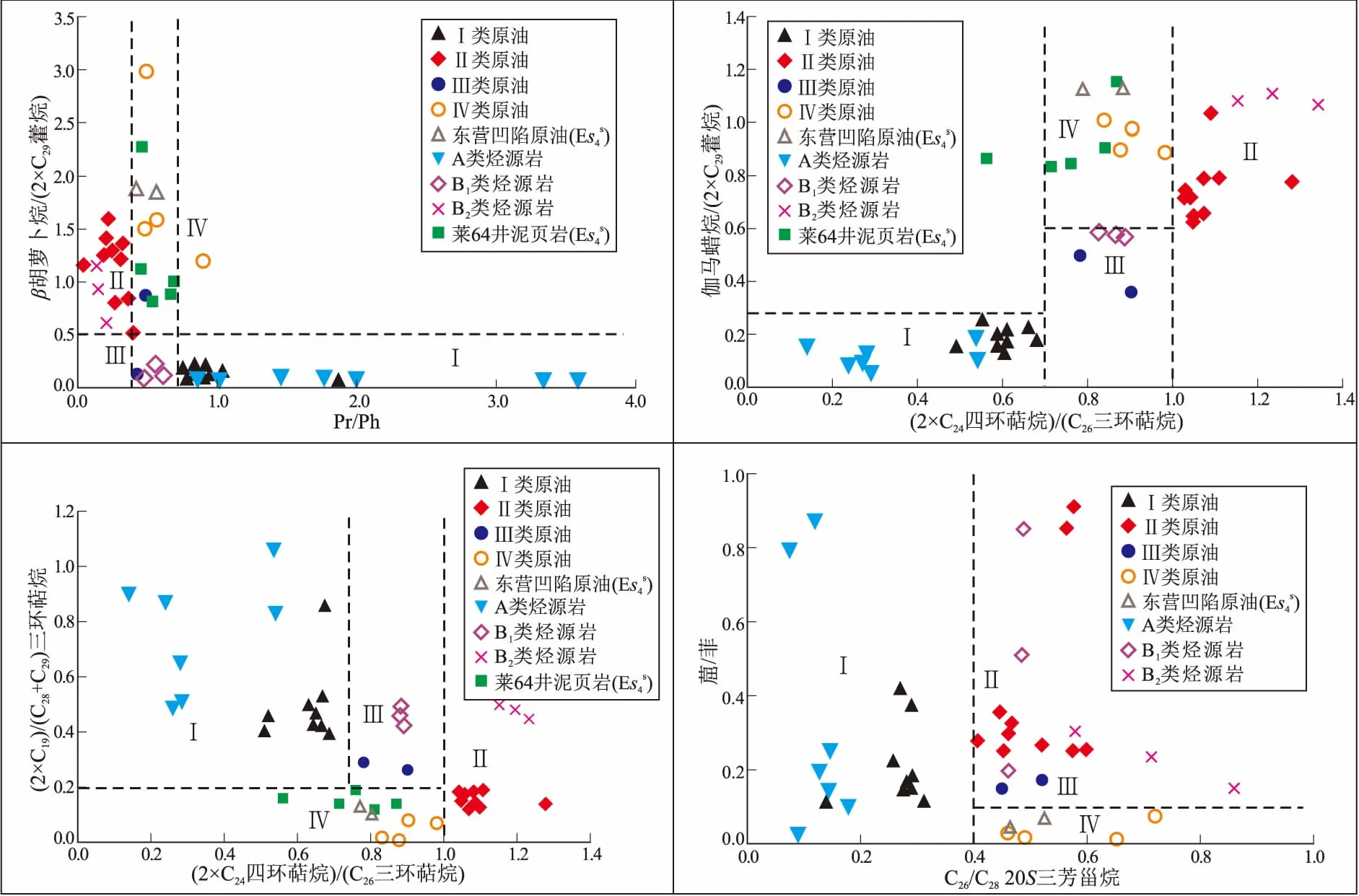
图4 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷青东凹陷原油与烃源岩部分生物标志化合物参数特征
5 结论
(1)青东凹陷分布有4类原油(Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ和Ⅳ),Ⅰ类原油主要分布在凹陷中北部沙三下亚段储层中(青东30井、青东12井),Ⅱ类原油主要分布在凹陷西南部斜坡带的沙四上亚段储层中(5-2-斜11井),Ⅲ类原油主要分布在凹陷西北部斜坡带的沙四上亚段储层中(青东17井、青东23井),Ⅳ类原油分布在青东—青南过渡带的沙三下亚段及沙四上亚段储层中(青东11井、青东4井)。
(2)研究区烃源岩包括2大类3小类(A、B1和B2)。油源分析表明,Ⅰ类原油来自凹陷中北部深洼的沙三下亚段成熟烃源岩(A类);Ⅱ类原油来自凹陷南部沙四上亚段烃源岩(B2类);Ⅲ类原油来源于凹陷中北部洼陷沙四上亚段烃源岩(B1类);Ⅳ类原油来源于东营凹陷青南洼陷沙四上亚段烃源岩,其中青东8井原油应有青东凹陷南部沙四上亚段烃源岩的贡献。
[1] 张水昌,梁狄刚,黎茂稳,等.分子化石与塔里木盆地油源对比[J].科学通报,2002,47(S1):16-23.
Zhang Shuichang,Liang Digang,Li Maowen,et al.Molecular fossils and oil-source rock correlations in Tarim Basin,NW China[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2002,47(S1):20-27.
[2] 王传刚,王铁冠,张卫彪,等.塔里木盆地北部塔河油田原油分子地球化学特征及成因类型划分[J].沉积学报, 2006,24(6):901-909.
Wang Chuangang,Wang Tieguan,Zhang Weibiao,et al.Molecular geochemistry and classifications of genetic types of petroleum from Tahe oilfield of the northern Tarim Basin[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2006,24(6):901-909.
[3] Jiang Zhusheng,Fowler M G,Lewis C A,et al.Polycyclic alkanes in a biodegraded oil from the Kelamayi oilfield,northwestern China[J].Organic Geochemistry,1990,15(1):35-46.
[4] Seifert W K,Moldowan J M,Demaison G J.Source correlation of biodegraded oils[J].Organic Geochemistry,1984,6:633-643.
[5] Fazeelat T,Asif M,Jalees M I,et al.Source correlation between biodegraded oil seeps and a commercial crude oil from the Pun-jab Basin,Pakistan[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2011,77(1):1-9.
[6] Peters K E,Moldowan J M.The biomarker guide:Interpreting mole-cular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments[M].Englewood Cliffs:Prentice Hall,1993:100-170.
[7] 马安来,张水昌,张大江,等.生物降解原油地球化学研究新进展[J].地球科学进展,2005,20(4):449-454.
Ma Anlai,Zhang Shuichang,Zhang Dajiang,et al.The advances in the geochemistry of the biodegraded oil[J].Advance in Earth Science,2005,20(4):449-454.
[8] 国朋飞,何生,朱书奎,等.利用三环萜烷对比泌阳凹陷生物降解油油源[J].石油实验地质,2015,37(1):80-87.
Guo Pengfei,He Sheng,Zhu Shukui,et al.Application of tricyclic terpanes in biodegraded oil-source correlation in Biyang Sag[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2015,37(1):80-87.
[9] 李水福,胡守志,何生,等.泌阳凹陷北部斜坡带生物降解油的油源对比[J].石油学报,2010, 31(6):946-951.
Li Shuifu,Hu Shouzhi,He Sheng,et al.Oil-source correlation for biodegraded oils in the north slope of the Biyang Depression[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica,2010,31(6):946-951.
[10] Moore R J,Thorpe R E,Mohaney C L.Isolation of methylchrysene from petroleum[J].Journal of the American Chemistry Society,1953,75(9):2259.
[11] Laflamme R E,Hites R A.The global distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in recent sediments[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1978,42(3):289-303.
[12] Laflamme R E,Hites R A.Tetra- and pentacyclic,naturally-occurring,aromatic hydrocarbons in recent sediments[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1979,43(10):1687-1691.
[13] Grice K,Nabbefeld B,Maslen E.Source and significance of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments (Hovea-3 well,Perth Basin,Western Australia) spanning the Permian-Triassic boundary[J].Organic Geochemistry,2007,38(11):1795-1803.
[14] 王岩.近海沉积物中几种多环芳烃的生物降解研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2011.
Wang Yan.A study on biodegradation of several PHAs in estuary sediment[D]. Qingdao:Chinese Marine University,2011.
[15] Garrigues P,De Sury R,Angelin M L,et al.Relation of the methylated aromatic hydrocarbon distribution pattern to the maturity of organic matter in ancient sediments from the Mahakam delta[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1988,52(2):375-384.
[16] Kruge M A.Determination of thermal maturity and organic matter type by principal components analysis of the distributions of polycyclic aromatic compounds[J].International Journal of Coal Geology,2000,43(1/4):27-51.
[17] 詹润,朱光有.济阳坳陷青东凹陷基底断裂复活规律和方式[J].地质论评,2012,58(5):816-828.
Zhan Run,Zhu Guangyou.Reactivity features and patterns of basement faults in the Qingdong Sag,Jiyang Depression[J].Geological Review,2012,58(5):816-828.
[18] Philp R P.Correlation of crude oils from the San Jorges Basin,Argentina[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1983,47(2):267-275.
[19] 米敬奎,张水昌,陈建平,等.塔北地区原油碳同位素组成特征及影响因素[J].石油勘探与开发,2010,37(1):21-25.
Mi Jingkui,Zhang Shuichang,Chen Jianping,et al.Carbon isotopic compositions and its effect factors of oil from northern Tarim Basin[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2010,37(1):21-25.
[20] 王大锐,董爱正,蔡笛.吐哈盆地侏罗系原油单体烃系列碳同位素研究[J].石油勘探与开发,1997,24(2):19-21.
Wang Dayue,Dong Aizheng,Cai Di.A stable carbon isotope research on the hydrocarbon manomer series molecules in crude oils and extracts of the Jurassic in Turpan-Hami Basin[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,1997,24(2):19-21.
[21] 赵孟军,黄第藩.不同沉积环境生成的原油单体烃碳同位素分布特征[J].石油实验地质,1995,17(2):171-179.
Zhao Mengjun,Huang Difan.Carbon Isotopic distributive characteristics of crude oil monomers produced in different sedimentary environments[J].Experiment Petroleum Geology,1995,17(2):171-179.
[22] Kvalheim O M,Christy A A,Telns N,et al.Maturity determination of organic matter in coals using the methylphenanthrene distribution[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1987,51(7):1883-1888.
[23] 霍秋立,李振广,付丽,等.烷基二苯并噻吩的分布与有机质成熟度关系的探讨[J].大庆石油地质与开发,2008,27(2):32-35.
Huo Qiuli,Li Zhenguang,Fu Li,et al.Study on the correlation of methyldibenzothiophenes distribution and organic maturity[J].Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2008,27(2):32-35.
[24] 王铁冠,钟宁宁,侯读杰,等.低熟油气形成机理与分布[M].北京:石油工业出版社,1995.
Wang Tieguan,Zhong Ningning,Hou Dujie,et al.Genetic mechanism and occurrence of immature hydrocarbon[M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Publishing House,1995.
[25] 徐永昌,沈平,刘文汇,等.未熟—低熟油的同位素组成特征及判识标志[J].科学通报,2001,46(10):867-872.
Xu Yongchang,Shen Ping,Liu Wenhui,et al.Isotopic composition characteristics and identification of immature and lowmature oils[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2001,46(22):1923-1929.
[26] 曾凡刚,妥进才,李原,等.百色盆地低熟油的地球化学特征及成因机制[J].沉积学报,1998,16(1):92-97.
Zeng Fangang,Tuo Jincai,Li Yuan,et al.Geochemical characteristics and genetic mechanism of immature oils from Baize Basin[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1998,16(1):92-97.
(编辑 黄 娟)
Geochemical characteristics and oil-source correlation of Paleogene oils in Qingdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
Ge Haixia1, Zhang Zhihuan1, Min Wei2
(1.StateKeyLaboratoryofPetroleumResourceandProspecting,SchoolofGeosciences,ChinaUniversityofPetroleum,Beijing102249,China; 2.PetroleumDevelopmentInstituteofSINOPECShengliOilfieldCompany,Dongying,Shandong257015,China)
Biodegraded oils have been discovered in the Qingdong Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. On the basis of the geochemical characteristics of source rocks and crude oils, the less affected C29hopane, is chosen to calculate biomarker parameters, includingβ-carotane/(2×C29hopanes), gammacerane/(2×C29hopanes). The tricyclic terpane parameters (2×C24tetracyclic terpane)/(C26tricyclic terpanes), (2×C19)/(C28+C29) tricyclic terpanes and chrysene/phenanthrene, combined with 4-methylsteranes and carbon isotopes. Crude oils in the Qingdong Sag were divided into 4 types (Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅳ), while source rocks were divided into 3 types (A, B1, B2). Crude oils of type I derived from mature source rocks (type A) in the lower part of the third member of Shahejie Formation in the northern part of the sag. Crude oils of type Ⅱ were sourced from rocks (type B2) in the upper part of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in the southern part of the sag. Crude oils of type Ⅲ were derived from type B1source rocks in the upper part of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in the central and northern parts of the sag. Crude oils of type Ⅳ were sourced from rocks in the upper part of the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in the Qingnan Sag. Oils in well QD-8 partially originated from source rocks in the southern part of the Qingdong Sag.
biodegraded oils; biomarker; oil-source correlation; Qingdong Sag; Jiyang Depression; Bohai Bay Basin
1001-6112(2017)03-0383-07
10.11781/sysydz201703383
2016-12-21;
2017-04-05。
葛海霞 (1987—),女,在读博士,主要研究方向为油气地球化学。E-mail:lily6059.com@163.com。
国家科技重大专项项目(2016ZX05049-006-08HZ)资助。
TE122.114
A
