乳腺癌手术中保留胸前神经和肋间臂神经的临床效果观察
2017-05-22王西跃张蓉邓丁梅
王西跃+张蓉+邓丁梅
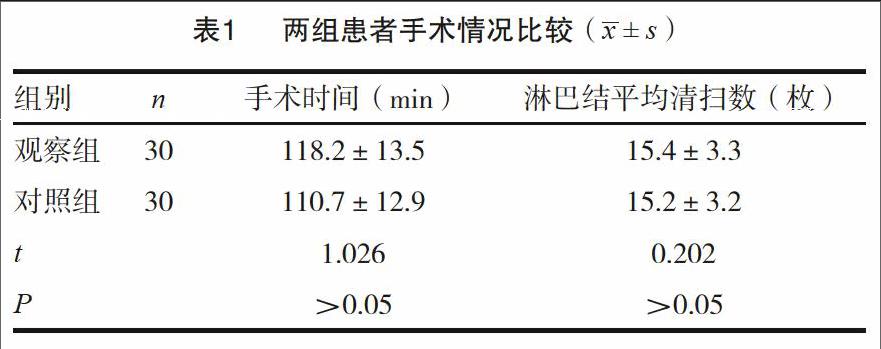
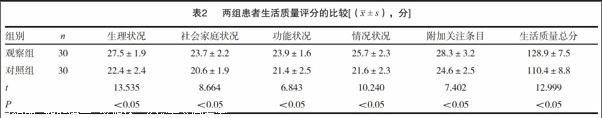
[摘要] 目的 分析保留胸前神经和肋间臂神经的乳腺癌手术临床效果。 方法 选取我院2013年1月~2014年1月收治入院的择期手术的乳腺癌患者60例作为研究对象,并按不同的治疗方式分为两组,对照组30例患者采用传统乳腺癌手术治疗,观察组30例患者采用保留肋间臂神经和胸前神经的乳腺癌手术,对患者的不良反应、并发症、肿瘤复发及转移率进行观察及比较。 结果 观察组平均手术时间及清除淋巴结数目比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);观察组生活质量情况要显著比对照组好,各项基本评分以及总分都要明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组患者复发、并发症的发生率显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 保留肋间臂神经和胸前神经的乳腺癌手术能够显著减少患者胸肌萎缩,腋窝疼痛、上臂麻木感、皮肤感觉疼痛或障碍等不良反应,并且可显著降低术后转移率和复发率,对提高患者的生活质量意义重大,值得临床推广。
[关键词] 胸前神经;肋间臂神经;乳腺癌
[中图分类号] R737.9 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 2095-0616(2017)06-132-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the clinical effect of breast cancer with thoracic nerve and intercostal nerve. Methods 60 patients with breast cancer underwent elective surgery in our hospital from January 2013 to January 2014 were selected as the subjects. According to the different treatment methods,they were divided into two groups.30 patients in the control group were treated with traditional breast cancer treatment,30 patients in observation group were treated with intercostal nerve and thoracic nerve retention of breast cancer surgery.The patients adverse reactions and complications,tumor recurrence and metastasis rate were observed and compared. Results There was no significant difference in the average operative time and the number of lymph nodes removed in the observation group(P>0.05).The quality of life in the observation group was significantly better than that in the control group.The basic scores and total scores were significantly higher than those in the control group(P<0.05).The incidence of recurrence and complication in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group(P<0.05). Conclusion Retention of intercostal nerve and thoracic nerve in breast cancer surgery can significantly reduce adverse events such as chest muscle atrophy,axillary pain,upper arm numbness,skin sensory pain or disorder,and significantly reduce postoperative metastasis and recurrence rates.It has great significance in improving the quality of life of patients.It is worthy of clinical promotion.
[Key words] Chest nerve;Intercostal nerve;Breast cancer
乳腺癌是一种较为常见的恶性肿瘤疾病,其发病率居高不下,且越来越趋于年轻化。据有关部门的统计发现,乳腺癌在女性新发恶性肿瘤中的比例达到了30%[1]。因此,研究乳腺癌的最佳治疗方式是非常有必要的。目前,乳腺癌的主要治疗方式是通过手术治疗,正确选择手术方式可以最大程度改善患者的预后[2]。传统的手术方法将患者胸前神经以及肋间臂神经进行切除,导致患者出现了胸肌萎缩、腋窝疼痛及上臂麻木等症状[3]。本研究通过对我院收治的乳腺癌手术中保留胸前神经和肋间臂神经的乳腺癌患者30例进行效果分析,旨在探讨出最有效的治疗方法,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取我院2013年1月~2014年1月收治入院的择期手术的乳腺癌患者60例作为研究对象,全部为女性。按治療方式的不同分为两组,对照组30例患者采用传统乳腺癌手术治疗,观察组30例患者采用保留肋间臂神经和胸前神经的乳腺癌手术,观察组患者中年龄25.4~67.9岁,平均(41.4±4.6)岁;肿瘤部位:左侧为17例,右侧为13例;根据国癌症联合委员会(AJCC)癌症分期手册(第7版)的乳腺癌分期标准:8例为I期,10例为II期,8例为III期,4例为IV期。按病理类型可分为侵润性小叶癌患者5例,侵润性导管癌患者19例,黏液腺癌患者6例;对照组患者中年龄25~63岁,平均(40.12±5.83)岁,肿瘤部位:左侧为18例,右侧为12例;根据国癌症联合委员会(AJCC)癌症分期手册(第7版)的乳腺癌分期标准:7例为I期,11例为II期,7例为III期,5例为IV期。按病理类型可分为侵润性小叶癌患者4例,侵润性导管癌患者21例,黏液腺癌患者5例;两组患者年龄、临床分期、病理类型、病变部位等内容比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。
