Stokes方程拟应力—速度形式的稳定化有限元法
2017-05-18张现强
张现强
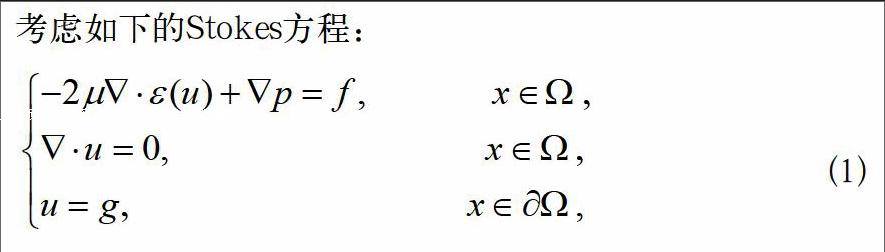


摘 要:隨着非牛顿流问题在工程领域的广泛应用,基于拟应力-速度形式的数值格式成为了计算流体力学和计算数学领域的研究热点。该文针对Stokes方程提出了一种基于拟应力-速度形式的稳定化有限元法。拟应力和速度分别采用非协调矩形元和分片常数元来逼近。该方法通过在通常的混合 Galerkin 形式中添加基于拟应力的梯度跳跃的稳定项强化格式的稳定性。我们证明该方法是稳定的,并具有拟最优阶精度。
关键词:Stokes方程 拟应力-速度形式 混合有限元 稳定化方法 非协调元
中图分类号:O241.82 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-3791(2017)03(c)-0213-04
A stabilized Finite Element Method for Stokes Equations Based on Pseudostress-velocity Formulation
Zhang Xianqiang
(School of Mathematics and Statistics, Ningxia University, Yinchuan Ningxia, 750021, China)
Abstract: In this paper, we develop and analyze a stabilized nonconforming rectangular finite element method for the stationary Stokes equations based on the pseudostress-velocity formulation. The pseudostress is approximated by nonforming rectangular elements and the velocity by piecewise constants. It is shown that the method is stable and yields quasi-optimal accuracy. Finally, numerical results verifying the theoretical predictions are presented.
Key Words:Stokes equations; Pseudostress-velocity formulation; Mixed finite element; Stabilized methods; Noncomforming element
Stokes方程是流体力学中的一个重要方程,关于其混合有限元法的研究已有很多工作,其中绝大多数是基于其原始变量形式[1-3]。近年来,随着非牛顿流问题在工程领域的广泛应用,基于应力-速度-压力形式的数值格式成为了计算流体力学和计算数学领域的研究热点。 然而,这类方法都有一个共同问题,即混合有限元空间要满足所谓的LBB条件。应力张量的对称性约束使得其有限元空间的构造过于复杂,不利于实际应用[4-5]。
为了解决上述矛盾,一种有效的途径是引入非对称的拟应力张量取代原始的应力张量,文献[6-9]相继提出并分析了 Stokes 方程和Navier-Stokes方程拟应力-速度和拟应力-速度-压力形式的混合有限元法。值得注意的是,为了保证这类有限元格式的稳定性,我们必须控制拟应力的-范数。 因此,构造这类问题稳定收敛的有限元方法并不是一件容易的事。文献[10-11]针对奇异摄动Darcy-Stokes问题和Darcy-Stokes-Brinkman模型构造了一种新型的非协调矩形元,该有限元的法向分量和切向分量具有一定意义下的弱连续性。 该文针对拟应力-速度形式的Stokes方程提出了一种稳定化非协调有限元方法,对拟应力和速度分别采用新型矩形元和分片常数元来逼近,并且通过引入一个基于拟应力在单元边界上跳跃的稳定项来满足格式的稳定性。 通过具体考察非协调矩形元的特殊性质,我们讨论了该文所提格式的稳定性和收敛性,给出了误差估计。
1 模型及初步知识
2 有限元格式
设为区域的拟一致正则矩形剖分,对任意的剖分单元,记为单元的直径,网格尺寸,用表示单元的边,并记。对任意的分片连续函数,定义其在边上的跳跃值为
3 误差分析
4 结语
Stokes方程是描述流体介质运动的基本方程,在科学与工程等领域有广泛而重要的应用。尽管应力张量具有重要的物理意义,对称性约束使得其有限元空间的构造过于复杂,不利于计算分析。该文在Stokes方程的拟应力-速度形式的基础上,采用稳定化非协调混合有限元的方法对其求解,证明了有限元解的存在唯一性,以及有限元逼近在某种意义下是最优的。
参考文献
[1] Girault V,Raviart P.Finite element methods for Navier-Stokes equations:theory and algorithms[M].Berlin: Springer-Verlag,1986.
[2] Gunzburger M.Finite Element Methods for Viscous Incompressible Flows [M]. New York: Academic, 1989.
[3] Pironneau O. Finite Element Methods for Fluids [M]. New York: Wiley,1989.
[4] Arnold D, Winther R. Mixed finite element for elasticity [J]. Numer Math,2002(92):401-419.
[5] Brezzi F, Fortin M. Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods [M]. New York: Springer-Verlag,1991.
[6] Cai Z, Tong C, Vassilevski P et al. Mixed finite element methods for incompressible flow: stationary Stokes equations[J].Numer Methods PDE,2010,26(4): 957-978.
[7] Cai Z, Wang C,Zhang S.Mixed finite element methods for incompressible flow: Stationary Navier-Stokes equations[J].SIAM J Numer Anal,2010,48(1):79-94.
[8] Cai Z, Zhang S.Mixed methods for stationary Navier-Stokes equations based on pseudostress-pressure-velocity formulation[J].Math Comp,2012,81(280):1903-1927.
[9] Gatica G, Máquez A, Sáchez M.Analysis of a velocity-pressure-pseudostress formulation for the stationary Stokes equations[J].Comput Meth Appl Mech Engrg, 2010,199(17):1064-1079.
[10] Zhang S, Xie X, Chen Y. Low order nonconforming rectangular finite element methods for Dary-Stokes problem[J].J Comput Math,2009,27:400-424.
[11] Qi R, Yang X.A nonconforming rectangular finite element pair for the Darcy-Stokes-Brinkman model[J]. Numer Methods PDE,2013,29(2):510-530.
[12] Thomée V.Galerkin finite element methods for parabolic problems[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag,1997.
