西藏亚东地区铁杉树轮样本稳定氧同位素的气候响应
2017-03-15TakeshiNakatsuka宋慧明王丽丽他维媛
李 强,刘 禹,,Takeshi Nakatsuka,宋慧明,王丽丽,他维媛
1.中国科学院地球环境研究所 黄土与第四纪地质国家重点实验室,西安 710061
2.全球变化研究协同创新中心,北京 100875
3.西安交通大学 人居环境与建筑工程学院,西安 710049
4.Research Institute for Humanity and Nature,Kyoto 603-8047,Japan
5.中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所,北京 100101
西藏亚东地区铁杉树轮样本稳定氧同位素的气候响应
李 强1,2,刘 禹1,2,3,Takeshi Nakatsuka4,宋慧明1,2,王丽丽5,他维媛1
1.中国科学院地球环境研究所 黄土与第四纪地质国家重点实验室,西安 710061
2.全球变化研究协同创新中心,北京 100875
3.西安交通大学 人居环境与建筑工程学院,西安 710049
4.Research Institute for Humanity and Nature,Kyoto 603-8047,Japan
5.中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所,北京 100101
为调查树轮稳定氧同位素在西藏南部的气候应用潜力,选择了西藏亚东县三个铁杉(Tsuga chinesis Pritz.)样本进行分析。其中两个样本表现出长期的稳定氧同位素下降趋势,而另一个表现出增高趋势,且三者相关性很低。当对三条稳定氧同位素序列进行一阶差处理之后,它们的相关关系有了非常显著的提高,表现出很好的一致性(p< 0.0001)。无论是原始还是一阶差树轮稳定氧同位素序列,它们都与夏季相对湿度和降水反相关,而与温度正相关,然而方差解释量未能达到古气候重建的最低要求。周期分析发现亚东树轮稳定氧同位素序列仅存在4.657年的显著周期,可能与ENSO活动有关,进一步研究显示1978年之前上年冬天到当年夏天的赤道中东太平洋海表温度对亚东树轮稳定氧同位素有显著影响(p< 0.01),而在1978年之后则无任何影响,20世纪70年代末期的全球气候突变改变了ENSO对该地树轮稳定氧同位素的影响。
西藏亚东;铁杉;树轮稳定氧同位素;气候响应;海表温度
树木年轮气候学历经近百年的发展,无论是理论思想还是技术路线都有了较大的突破,我国的树轮气候学研究也获得了一些成就(刘禹,2010;刘禹等 ,2010,2012a,2012b;Lu et al,2012;王亚峰和梁尔源,2012;喻树龙等,2012;张慧等,2012;包光等,2013;张艳华等,2013)。近些年,更多的新技术应用到树木年轮气候学中,由传统单一的轮宽指标演变为同位素、密度等指标(郑紫薇等,2014)。其中,树轮稳定氧同位素由于生理机制较为明了,树龄效应较低,复本性好等优点,在近几年来得到长足发展。
为了验证树轮稳定氧同位素在西藏南部地区进行气候变化研究的前景,使用采自西藏亚东县的铁杉(Tsuga chinesis Pritz.)样本,进行稳定氧同位素分析,用来测试不同树轮样本间的个体差异特点,以及对当地气候的响应程度。如果它们的稳定氧同位素序列间存在较好关系,且对气候反应较为敏感,那么,今后在该地区根据经典树轮气候学标准采样,可获得更为可靠的古气候重建数据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样本信息及当地气候
亚东县位于西藏自治区南部、喜马拉雅山脉中段南麓,西接印度、东连不丹,是西藏地区的边境县之一。全县海拔2800 — 3400 m,县域内大部分地区为天然森林。树木年轮样本于2004年5月采自亚东县的亚东林场(27°24′N,88°56′E)(图1)。使用5 mm生长锥在每棵树上采集样芯3个,其中,A、B两芯由合作单位进行分析,C芯由中国科学院地球环境研究所树木年轮实验室进行稳定同位素分析。所采树种为铁杉(Tsuga chinesis Pritz.),采样海拔高度2840 m,坡度40°,坡向东偏北30°。由于C芯样本混合放置,且大部分样本都断裂,选择有树皮的样本,然而,由于这些断裂样本的起始生长年仍然未知,这就有可能导致有些样本处于幼龄期间,而有些样本处于成熟稳定期。最终选择3个生长轮较为清晰的样本(11C、13C和20C)进行更进一步的实验以测量它们的稳定氧同位素变化,研究时段取最近50年,以便与气象资料进行对比。
气象资料取自亚东县帕里气象站,气象测量数据始于1956年。降雨量、温度和相对湿度都在夏季达到最大(图2)。从1956年到2003年,年总降水量426 mm,年平均温度0.1℃,年平均相对湿度68%。
1.2 纤维素样本测量
每年样本在显微镜下用刀片切成薄片,将样本放置在U型带滤芯的玻璃管中进行化学反应。根据Sohn and Reiff(1942)描述的纤维素提取方法,通过NaOH和NaClO的一系列化学反应,得到纤维素样本。为了使样本混合均匀,用超声波细胞粉碎机对每个纤维素样本进行均质化。最后,经过冷冻干燥的样本就成为最终提取到的纤维素。需要说明的是,其中几年由于样本较窄,提取出的纤维素样本不够质谱测量的量,因此存在几个缺年值。

图1 采样点位置(黑色三角形)Fig.1 The location of sampling site (black triangle)

图2 帕里气象站平均月降水、温度和相对湿度(1956 — 2003)Fig.2 Mean annual precipitation,temperature and relative humidity during 1956 — 2003 at Pali meteorological station
将130—180 μg的纤维素样本放入银囊中,压制成立方体后在TC/EA-Delta V Advantage稳定同位素质谱仪中进行测量,纤维素在高温下裂解成CO气体,后者被送入同位素质谱仪中测量稳定氧同位素(δ18O)比率,测量精度通过重复测量标准物质得到,即小于0.2‰。
2 稳定氧同位素结果
在研究时段(1954 — 2003年)内,样本11C、13C和20C序列的δ18O值范围分别为(29.00 ± 1.82)‰,(26.71 ± 1.33)‰和(23.66 ± 1.60)‰。然而,三个序列呈现出不同的长期趋势(图3a),例如,11C和13C的δ18O有一个长期下降的趋势,而20C表现出一个轻微上升的趋势。它们的原始序列相关很低,相关系数范围0.230 — 0.467,仅11C和13C的相关系数达到显著(p= 0.001)。由于缺乏足够的信息,判断11C和13C或许处于幼龄阶段,表现出明显的δ18O幼龄效应。
然而,这三个样本具有明显一致的高频特征,例如,1958年和1966年都为高δ18O年份,而1989 年和2000年都为低δ18O年份。为了调查序列间的高频变化是否有共同特征,对每个序列都进行了一阶差计算,如图3b,三个δ18O序列展现出了极高的一致性,相关系数范围也增加至0.585 — 0.708,相关全部达到显著水平(p<0.0001)。三个随机树轮样本δ18O的原始序列虽然存在较大差异,但是经过一阶差计算之后,发现它们重合度很高,具有一致的变化。

图3 三个树轮样本氧同位素的原始序列(a)和一阶差序列(b)变化以及样本间相关系数Fig.3 Three tree-ring stable oxygen isotope series (a) and their year-to-year difference series (b); tables show the correlations among them
3 气候响应分析
为了与一阶差的气象响应关系进行对比,也调查了三个原始δ18O序列对当地气候的响应关系,选择附近的帕里气象站温度、降水和相对湿度数据进行逐月相关分析,分析时段从上年4月至当年10月,结果如图4所示。另外,也分析了三个δ18O序列的算数平均序列与气象资料的关系(图4d)。
单月或月份组合的最高相关系数为上年7月到当年6月降水与13C,其相关系数为− 0.51(n= 49,p< 0.001)。总体上看,三个序列均与当年夏季降水和相对湿度负相关,而与夏季温度正相关,相关模式与大部分树轮氧同位素研究相同。
再来看δ18O序列的一阶差变化与气象资料一阶差的响应关系(图5),虽然三个δ18O序列经过一阶差处理后表现出较高的相关性,但是它们与当地气候资料的关系并未见提高。最高相关出现在2月相对湿度与20C(r= 0.54,n= 49,p< 0.001)。其余整体相关与原始序列相似,即与夏季降水和相对湿度负相关,与夏季温度正相关。

图4 帕里观测降水(P)、相对湿度(RH)和温度(T)与11C(a),13C(b),20C(c)和三芯平均(d)氧同位素序列的相关系数Fig.4 Correlations between observed precipitation (P),relative humidity (RH) and temperature (T ) and measured tree-ring δ18O of 11C (a),13C (b),20C (c) and mean of them (d) at Pali
从以上结果可以发现,不管是原始序列还是一阶差序列,它们与当地的气象记录虽有相关,但是相关较低,均未能达到方差解释量超过40%这一气候重建的要求。以下几方面可能导致较低的气候响应。其一,采样点与气象站距离较远,两地的环境不同,海拔高度不同。例如,若气象站建立在高山之上,而样本采集自河边,其相关关系自然会减弱。再次,原始δ18O数据存在与生长相关的趋势,而这些趋势与气候变化本身无关,当一阶差之后,气象数据和δ18O数据均缺少低频信号,一些气候的长期变化信号被抹去。最后,树轮δ18O序列有较为明显的缺失值。
4 对海表温度的响应
为了调查亚东树轮稳定氧同位素受哪些大尺度气候因素影响,利用周期分析探讨平均原始序列的显著周期。结果显示,在95%置信水平上,仅存在4.657年的周期(图6)。虽然样本总长度只有50年,发现这样的短周期也是可靠的。
本研究发现的4.657年周期很有可能是ENSO周期,因为ENSO的显著周期是2 — 7年。为此,用整序列(及其一阶差序列)与印度洋-太平洋海表温度(SST)进行空间相关,结果显示树轮δ18O与SST并无明显关系(未在本文展示相关图)。更进一步分析,发现三个树轮δ18O序列的一阶差虽然相关很高,但在1980年以后它们的振幅相差很大,而在1980年之前三者的振幅基本重合(图3b)。无论在陆地还是海洋,20世纪70年代末期是一个气候上公认的突变点(Gong and Ho, 2002;Wu et al,2005)。将树轮δ18O平均序列分为两个时段,即1978年以前和以后,与印度洋-太平洋海表温度(SST)进行空间相关分析。原始树轮δ18O序列中并未发现与SST有非常显著的相关关系,但是却在一阶差数据中发现了非常好的关系(图7),其原因可能是本研究的树轮δ18O和ENSO均具有显著的高频周期。如图7a所示,在ENSO盛期(上年冬天,12 — 2月)赤道中-东太平洋SST对1955 — 1978年的亚东树轮δ18O有最显著的影响,接下来的月份具有持续影响(图7b — d),直到当年夏天(图7e)。结果表明在20世纪70年代末期气候突变前,ENSO对亚东树轮δ18O有显著影响(p< 0.01),而在突变点之后,则不受ENSO影响(图7f — j)。
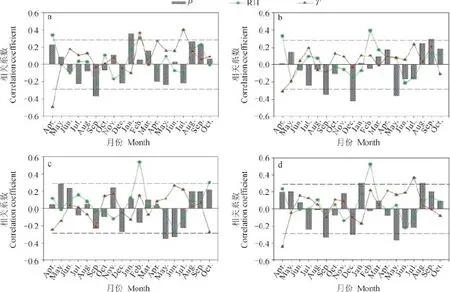
图5 帕里观测降水(P),相对湿度(RH)和温度(T)与11C(a),13C(b),20C(c)和三芯平均 (d) 氧同位素一阶差序列的相关系数Fig.5 Correlations between observed precipitation (P),relative humidity (RH) and temperature (T ) and measured tree-ring δ18O of 11C (a),13C (b),20C (c) and mean of them (d); all data are processed by year-to-year difference

图6 平均原始树轮δ18O序列的周期分析(蓝线为95%显著性水平)Fig.6 Spectrum analysis of mean tree-ring δ18O series (Blue line indicated 95% con fi dence level)

图7 三芯平均氧同位素一阶差序列与海表温度(SST)的相关系数Fig.7 Spatial correlation patterns between mean year-to-year difference δ18O series and gridded SST datasets
5 结论
本研究使用来自西藏亚东县的铁杉树轮样本,调查它们的δ18O变化序列。结果显示测量的三条δ18O序列存在趋势不一致、序列间相关较差的现象。然而,经过一阶差去除低频信号之后,三条δ18O序列的显著性有非常明显的提高(p< 0.0001),其变化趋势也一致,说明原始序列或许存在幼龄效应。原始和一阶差δ18O序列均与夏季相对湿度和降水正相关,而与夏季温度负相关,虽然相关系数显著,但仍然未达到气候重建的要求。周期分析发现平均树轮δ18O序列仅存在4.657年的显著周期,可能与ENSO活动有关。通过与太平洋-印度洋SST格点数据空间相关,发现ENSO在20世纪70年代末期的气候突变之前对亚东树轮δ18O影响非常明显(p< 0.01),影响时段从上年冬天开始,到当年夏天结束,而在气候突变之后,则没有影响,这也可能是三条树轮δ18O序列在1980年之后振幅出现大幅不一致的原因。
致谢:野外采样得到王雷等人的支持,在此一并感谢!
包 光,刘 禹,刘 娜,等.2013.蒙古高原东部和南部气候要素变化特征及其生态环境影响分析[J].地球环境学报,4(5):1444 – 1449.[Bao G,Liu Y,Liu N,et al.2013.Characteristics of climate changes during the instrumental period in the easternand southern Mongolian Plateau and their ecological-environmental effects [J].Journal of Earth Environment,4(5):1444 – 1449.]
刘 禹.2010.树轮与冰心反映的南北半球高海拔地区温度变化之遥相关[J].地球环境学报,1(2):100 – 104.[Liu Y.2010.Temperaturetele-connections reflected in tree rings and ice core from high-latitude regions between North and South hemispheres [J].Journal of Earth Environment,1(2):100 – 104.
刘 禹,雷 莺,宋慧明,等.2010.以白皮松树轮宽度重建公元1616年以来山东于林年平均最低气温[J].地球环境学报,1(1):28 – 35.[Liu Y,Lei Y,Song H M,et al.2010.The annual mean lowest temperature reconstruction based onPinus bungeanas(Zucc.) ring width in the Yulin region,Shandong,China since AD 1616 [J].Journal of Earth Environment,1(1):28 – 35.
刘 禹,相 楠,宋慧明.2012.内蒙古阿尔山过去187年温度变化的树轮记录[J].地球环境学报,3(3):862 – 867.[Liu Y,Xiang N,Song H M.2012.Tree-ring temperature records in Arxan,Inner Mongolia for the past 187 years [J].Journal of Earth Environment,3(3):862 – 867.]
刘 禹,解 利,李 强,等.2012.公元1820年以来甘肃东大山地区树轮宽度对3 — 9月平均最低温度的响应分析[J].地球环境学报,3(3):900 – 907.[Liu Y,Xie L,Li Q,et al.2012.Growth-climate response analysis between tree-ring width and March—September mean minimum temperature in Dongda Mountain,Gansu,China since 1820 AD [J].Journal of Earth Environment,3(3):900 – 907.]
王亚锋,梁尔源.2012.树线波动与气候变化研究进展[J].地球环境学报,3(3):855 – 861.[Wang Y F,Liang E Y.2012.A review on progresses in treeline dynamics and climate change [J].Journal of Earth Environment,3(3):855 – 861.]
喻树龙,袁玉江,秦 莉,等.2012.新疆沙湾夏季最低气温的重建和分析[J].地球环境学报,3(3):868 – 873.[Yü S L,Yuan Y J,Qin L,et al.2012.Reconstruction and analysis of the minimum temperature in summer for the Shawan in the Tianshan Mountains [J].Journal of Earth Environment,3(3):868 – 873.]
张 慧,邵雪梅,张 永.2012.不同海拔高度树木径向生长对气候要素响应的研究进展[J].地球环境学报,3(3):845 – 854.[Zhang H,Shao X M,Zhang Y.2012.Research progress on the response of radial growth to climatic factors at different altitudes [J].Journal of Earth Environment,3(3):845 – 854.]
张艳华,刘 禹,宋慧明,等.2013.河南神农山过去162年树轮季节降水重建[J].地球环境学报,4(5):1450 – 1460.[Zhang Y H,Liu Y,Song H M,et al.2013.Tree-ring-based seasonal precipitation reconstruction in Mt.Shennong for the last 162 years [J].Journal of Earth Environment,4(5):1450 – 1460.]
郑紫薇,赵兴云,商志远,等.2014.利用黑松树轮δ13C 重建山东塔山地区近七十年来冬春季节的平均气温[J].地球环境学报,5(1):10 – 15.[Zheng Z W,Zhao X Y,Shang Z Y,et al.2014.The winter and spring average temperature reconstruction based on tree ringδ13C in recent 70 years in Tashan,Shandong Province [J].Journal of Earth Environment,5(1):10 – 15.]
Gong D Y,Ho C H.2002.Shift in the summer rainfall over the Yangtze River valley in the late 1970s [J].Geophysical Research Letters,29(10).DOI:10.1029/2001GL014523.
Lu R J,Jia F F,Shang Y,et al.2012.Responses ofPinus tabulaeformistree rings to climatic metrics in Hasi Mountain [J].Journal of Earth Environment,3(6):1149 – 1155.
Sohn A W,Reif F.1942.Natriumchlorit als aufschluβmittel [J].Der Papierfabrikant,1(2):5 – 7.
Wu L,Lee D E,Liu Z.2005.The 1976/77 North Paci fi c climate regime shift:the role of subtropical ocean adjustment and coupled ocean-atmosphere feedbacks [J].Journal of Climate,18(23):5125 – 5140.
Climate responses of tree-ring stable oxygen isotopes from Yadong County,Tibetan Plateau
LI Qiang1,2,LIU Yu1,2,3,Takeshi Nakatsuka4,SONG Huiming1,2,WANG Lili5,TA Weiyuan1
1.State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology,Institute of Earth Environment,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Xi’an 710061,China
2.Joint Center for Global Change Studies (JCGCS),Beijing 100875,China
3.School of Human Settlements and Civil Engineering,Xi’an Jiaotong University,Xi’an 710049,China
4.Research Institute for Humanity and Nature,Kita-ku,Kyoto 603-8047,Japan
5.Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
Background,aim,and scopeDendroclimatology is one of the important approaches in paleoclimate studies because of tree-ring’s high temporal resolution and accuracy of dating.Traditional dendrcoalimatology employed tree-ring width to investigate climate variations.To obtain more climate signals,other tree-ring parameters such as density,stable isotope ratios are employed during recently years.Tree-ring stable oxygenisotope ratios have the advantage that the physiological controls are well understood and relatively simple in comparison to many factors controlling tree-ring width.The tree-ring stable oxygen isotope ratios may keep the memory of past changes in the stable oxygen isotope ratio of precipitation because tree roots absorb soil water that are from precipitation.In addition,relative humidity is known as the other factor impacting the tree-ring stable oxygen isotope ratios by affecting the enrichment of stable oxygen isotope ratios in leaf water.Generally,it is a necessary step to remove age-related trend in tree-ring widths studies.However,time series of tree-ring stable oxygen isotope are not necessary to carry out the detrending process because of rarely juvenile effect,consequently tree-ring stable oxygen isotope series could preserve more low-frequency climate signals.In Europe and North America,tree-ring stable oxygen isotope study has developed over the past half century.Comparing with tree-ring widths studies,tree-ring stable oxygen isotope studies are very rare in China,especially in some ecologically fragile regions such as Tibetan Plateau,where climate variations are very important to global climate change.To investigate the climate potential of tree-ring stable oxygen isotope in southern Tibetan Plateau,we employed three tree-ring samples of growing Tsuga chinesis Pritz from Yadong County,Tibetan Plateau to carry out the analysis of climate responses in this study.Materials and methodsThere are missing rings or false rings in most trees in Tibetan Plateau because of critical hydrological conditions.In order to obtain the exact calendar year of the samples,we performed cross dating using the Skeleton Plot method.Annual tree-ring width was measured using a LINTAB system that has a precision of 0.01 mm.Quality control was carried out using the COFECHA program.Tree-ring cores,11C,13C and 20C,were selected to carry out cellulose stable oxygen isotope analysis in this study.The pith year of the samples are unclear because all samples may be fractured during store.Annual wood material of the three cores without any missing rings,were separated from each tree-ring core.Most of the rings is very narrow,and there is indistinct boundary between earlywood and latewood.To avoid separation errors,we used whole annual rings to do the isotopic analyses.We usesd a razor blade to separate annual sample carefully under a binocular microscope.The wood material of the annual ring was put to a labeled small bottle.Then the cellulose of annual ring was extracted from annual wood material by organic solvent and sodium hydroxide.About 0.13 — 0.17 mg of homogeneous cellulose was loaded into a silver capsule,(in duplicate for each sample) and then determined the cellulose stable oxygen isotope ratio with a continuous fl ow system with a pyrolysis-type elemental analyzer (Finnigan TC/EA) and an isotope ratio mass spectrometer (Thermo Delta V Advantage) in Research Institute for Humanity and Nature,Japan.We calculated cellulose stable oxygen isotope ratio by a comparison with an isotope ratio that was predetermined using commercial cellulose (Merck KGaA,Darmstadt,Germany) which was inserted frequently during the measuring process.The oxygen isotope ratios were expressed asδ18O,which represents the per mil deviation relative to the Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water (VSMOW).The analytical accuracy for repeated measurements of the commercial cellulose was 0.2‰ (1σ).ResultsThe cellulose value of 11C,13C and 20C were (29.00 ± 1.82)‰,(26.71 ± 1.33)‰ and (23.66 ± 1.60)‰,respectively. The results revealed that two of three trees presented a decreasing trend in stable oxygen isotope ratios.The other one showed a slight increasing trend in stable oxygen isotope ratios.The correlations among three tree-ring stable oxygen isotope series were from 0.230 to 0.467.DiscussionAlthough the correlations among three orignial tree-ring stable oxygen isotope series are low.We found there may exist similarity in high-frequency signals of three orignial tree-ring stable oxygen isotope series.To emphasize high-frequency signals,we used year-to-year data to investigate the correlations.Their yearto-year difference data represented a strong common variance (p< 0.0001).The correlations improved to 0.585 — 0.787.Both stable oxygen isotope series and their year-to-year difference series were negatively correlated with local summer relative humidity/precipitation,positively correlated with summer temperature.However,the results did not meet the requirement of quantitatively climate reconstruction because lowerexplained variance of observed climate records (< 40%).Spectrum analysis suggested that there was a significant cycle at 4.657 year,which probably related to ENSO variations.ConslusionsThree tree-ring stable oxygen isotopes series from Yadong Country,Tibetan Plateau represented common high-frequency signals,but did not show similar variations in their original time series.All year-to-year times series were negatively correlated with summer relative humidity and precipitation,positively correlated with summer temperature.Spatial correlation between gridded Sea Surface Temperature (SST) and mean tree-ring stable oxygen isotope demonstrated that central-eastern tropical SST of previous winter to current summer impacted on tree-ring stable oxygen isotope before late 1970s,on the contrary there were any significant correlation after late 1970s.Recommendations and perspectivesThe tree-ring stable oxygen isotope in southern Tibetan Plateau is signi fi cant in climate study,which not only could present past climate variations,but also could supply the evidence of ENSO’s in fl uence.More such studies in southern Tibetan Plateau are needed.
SKLLQG; Western doctor of CAS; Youth Innovation Promotion Association,CAS (2017451)
LIU Yu,E-mail:liuyu@loess.llqg.ac.cn
Yadong County;Tsuga chinesis Pritz.; tree-ring stable oxygen isotope; climatic response; sea surface temperature
2016-11-30;录用日期2016-12-28
Received Date:2016-11-30;Accepted Date2016-12-28
黄土与第四纪地质国家重点实验室开放基金;中国科学院西部博士;中国科学院青年创新促进会(2017451)
刘 禹,E-mail:liuyu@loess.llqg.ac.cn
李 强,刘 禹,Takeshi Nakatsuka,等.2017.西藏亚东地区铁杉树轮样本稳定氧同位素的气候响应[J].地球环 境学报,8(1):6 – 14.
: Li Q,Liu Y,Takeshi Nakatsuka,et al.2017.Climate responses of tree-ring stable oxygen isotopes from Yadong County,Tibetan Plateau [J].Journal of Earth Environment,8(1):6 – 14.
10.7515/JEE201701002
