三峡库区马尾松细根分解及其养分释放
2017-02-23程瑞梅肖文发沈雅飞
王 娜,程瑞梅*,肖文发,沈雅飞
(1.中国林业科学研究院森林生态环境与保护研究所国家林业局森林生态环境重点实验室,北京 100091;2.南京林业大学南方现代林业协同创新中心,江苏 南京 210037)
三峡库区马尾松细根分解及其养分释放
王 娜1,2,程瑞梅1,2*,肖文发1,2,沈雅飞1,2
(1.中国林业科学研究院森林生态环境与保护研究所国家林业局森林生态环境重点实验室,北京 100091;2.南京林业大学南方现代林业协同创新中心,江苏 南京 210037)

三峡库区;马尾松;细根分解;养分释放


1 材料与方法
1.1 研究地概况


图1 土壤表层(010 cm)的平均温湿度Fig.1 Ttemperature and moisture at 010 cm soil layer
1.2 研究方法

1.2.2 化学成分分析 植物根样采用C-N元素分析仪测定马尾松细根C、N含量,HNO3-H2O2消解-ICP法测定细根P、K、Ca、Mg元素含量(相关实验均通过3次重复实验)。
1.2.3 数据分析
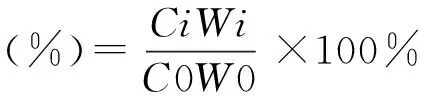
式中,W0为细根初始干重(g),Wi为细根分解t时间后的干重,C0为细根初始养分浓度,Ci为细根分解t时间后的养分浓度。

Person相关分析法分析土壤温度和湿度对细根分解的影响。数据的前期处理、统计分析及绘图分别在Excel2010、SPSS19.0和SigmaPlot11.0中完成。
2 结果与分析
2. 1 马尾松不同径级细根初始化学成分


表1 马尾松不同径级细根养分初始浓度Table 1 Nutrient concentration in different diameters fine roots of Pinus massoniana(mean±SE, n=3)
小写字母不同代表差异显著(p<0.05),相同代表差异不显著(p<0.05)。
2.2 马尾松不同径级细根分解速率


图2 马尾松不同径级细根残留物重量变化Fig.2 Dynamics in the remaining mass of Pinus massoniana fine root with different diameters
2.3 马尾松不同径级细根分解速率与土壤温湿度的相关性
表2 马尾松不同径级细根分解速率与土壤温湿度的
Person相关性
Table 2 Person correlations between soil tempera-
ture of moisture anddecomposition rate ofPinusmassonianafine root with different diameters

影响因子influencefactor<0.5mmrp0.51mmrp12mmrp土壤温度soiltemperature0.6170.0140.8170.0000.9670.000土壤湿度soilhumidity0.2060.4610.3560.1920.7320.002
2.4 马尾松不同径级细根分解过程中养分保持率变化

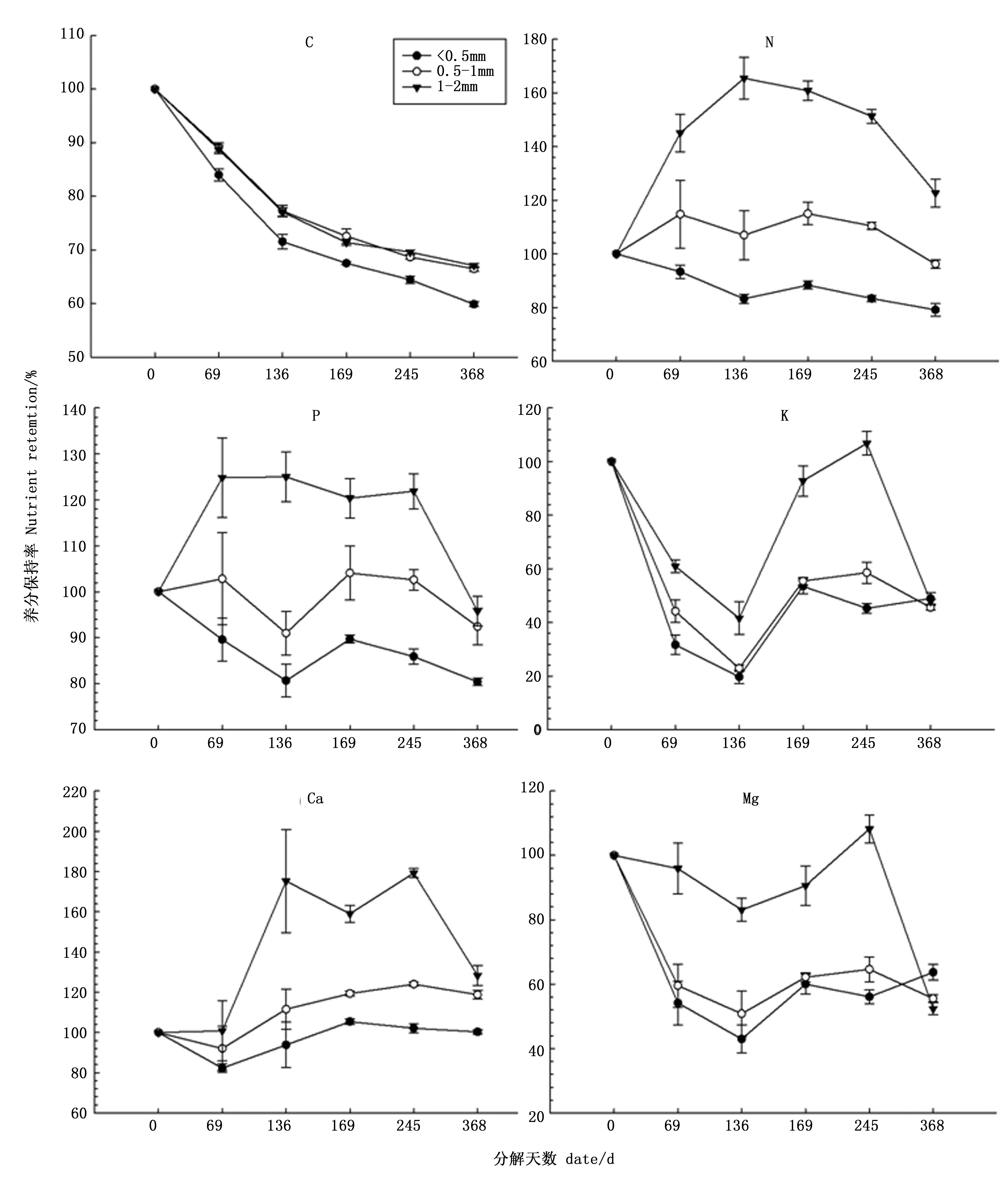
图3 马尾松细根分解过程中养分保持率Fig.3 Change in nutrient remaining rate of Pinus massoniana roots with different diameters during root decomposition
3 讨论
3.1 细根分解速率



3.2 细根养分释放



元素本身的特性和在根系中存在的形态也可能影响细根养分释放[7]。马尾松细根C、K、Mg元素表现为释放,Ca元素表现为富集,与李吉枚等[32]、翟明普等[35]、Yang等[36]的研究结果类似。元素C、K、Mg在植物组织中较为活跃,移动性较强,其中元素K还是非植物细根的结构性成分,不需要微生物活动的参与,最易受到外界环境条件如降水导致的淋溶过程等的影响,而Ca是植物组织内稳定性强的元素,移动性差,并且是植物组织的构建成分[37],因此表现出不同程度的释放或富集模式。
4 结论
本研究分析了不同径级马尾松细根分解速率以及细根分解过程中C、N、P、K、Ca、Mg养分释放动态变化,得出以下结论:
1) 细根分解速率与土壤温度和直径大小呈显著相关。其中细根分解速率随温度的升高而增大,随直径的增大而减小;

3) 在细根分解过程中,元素初始养分浓度、降水、土壤养分状况,以及元素本身的特性和在根系中存在的形态都影响细根养分释放。
[1] Yuan Z,Chen H.Fine root biomass,production, turnover rates,and nutrient contents in boreal forest ecosystems in relation to species,climate,fertility,and stand age:literature review and meta-analyses[J].Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences,2010,29 (4):204-221.
[2] 陈 曦,张乃莉,周晓梅,等.细根分解研究进展及存在问题[J].吉林师范大学学报:自然科学版,2012,(2):36-40.
[3] 林成芳,杨玉盛,陈光水,等.杉木人工林细根分解和养分释放及化学组成变化[J].亚热带资源与环境学报,2008,3(1):15-23.
[4] 王存国,韩士杰,周玉梅,等.长白山阔叶红松林群落的细根现存量及养分内循环[J].林业科学,2012,48(3):0148-0153.
[5] 王瑞丽,程瑞梅,肖文发,等.三峡库区马尾松人工林细根生产和周转[J].应用生态学报,2012,23(9):2346-2352.
[6] 肖文发,雷静品.三峡库区森林植被恢复与可持续经营研究[J].长江流域资源与环境,2004,13(2):138-144.
[7] 林成芳.中亚热带森林细根分解动态及影响因素[D].福建:福建师范大学,2008.
[8] 罗 达.南亚热带格木、马尾松幼龄纯林及其混交林碳氮特征研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2014.
[9] 王卫霞.南亚热带不同树种人工林生态系统碳氮特征研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2013.
[10] 葛晓改,肖文发,曾立雄,等.三峡库区不同林龄马尾松土壤养分与酶活性的关系[J].应用生态学报,2012,(02):445-451.
[11] Berg B,McClaugherty C.Plant Litter:Decomposition, Humus Formation,Carbon Sequestration[J].Berlin: Springer,2003.
[12] Lin C F, Yang Y S, Guo J F,etal.Fine root decomposition of evergreen broadleaved and coniferous tree species in mid-subtropical China: dynamics of dry mass, nutrient and organic fractions[J].Plant Soil,2010,338:311-327.
[13] 许玉庆,项文化,曾叶霖,等.中国森林生态系统细根分解格局及调控因子研究进展[J].广西林业科学,2015,44(2):149-155.
[14] 王新源,赵学勇,李玉霖,等.环境因素对干旱半干旱区凋落物分解的影响研究进展[J].应用生态学报,2013,11:3300-3310.
[15] Silver W L,Myia R K.Global patterns in root decomposition: comparisons of climate and litter quality effects[J].Oecologia,2001,129(3):407-419.
[16] Hishi T.Heterogeneity of individual roots within the fine root architecture: causal links between physiological and ecosystem functions[J].Journal of Forestry Research,2007,12(2):126-133.
[17] 勒贝贝,国庆喜.蒙古栎、白桦根系分解及养分动态[J].生态学报,2013,(8):2416-2424.
[18] Fan P P,Guo D L.Slow decomposition of lower order roots: a key mechanism of root carbon and nutrient retention in the soil[J].Oecologia,2010,163(2):509-515.
[19] 刘利芳,徐程杨.影响森林细根分解的机理研究进展[J].山东林业科技,2012,3:0097-0105.
[20] Sun T,Mao Z J,Han Y Y.Slow decomposition of very fine roots and some factors controlling the process: a 4-year experiment in for temperate tree species[J].Plant and Soil,2013,372(1):445-458.
[21] Chen H,Harmon M E,Grifiths R E.Decomposition and nitrogen relaese from decomposing woody roots in coniferous forests of the Pacific Northwest[J].Can J For Res,2001,31:246-260.
[22] Langley J A, Hungate B A.Mycorrhizal controls on below-ground litter quality[J].Ecology,2003,84:2302-2312.
[23] Langley J A,Chapman S K,Hungate B A.Ectomycorrhizal colonization slows root decomposition:the postmortem fungl legacy[J].Ecology Letters,2006,9:955-959.
[24] Koide R T,Malcolm G M.N concentration controls decomposition rates of different strains of ectomycorrhizal fungi[J].Fungal Ecology,2009,2:197-202.
[25] 王存国,陈正侠,马承恩,等.细根异速分解的3各可能影响途径[J].北京林业大学学报,2016,4(38):123-128.
[26] Wang W,Zhang X Y,Tao N,etal.Effects of litter types, microsite and root diameters on litter decomposition in Pinus silvestris plantations of north China[J].Plant and Soil,2014,374(1-2):677-688.
[27] Hobbie S E,Vitousek P M.Nutrient limitation of decomposition in Hawaiian forests[J].Ecology,2000,81:1867-1877.
[28] 王 瑾,黄建辉.暖温带地区主要树种叶片凋落物分解过程中主要元素释放的比较[J].植物生态学报,2001,25(3):375-380.
[29] Chen H,Harmon M E,Sexton J,etal.Fine-root decomposition and N dynamics in coniferous forests of the Pacific Northwest,USA[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,2002,32:320-331.
[30] Guo L B,Halliday M J,Gifford R M.Fine root decomposition under grass and pine seedlings in controlled environmental conditions[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2006,33(1):22-29.
[31] 张秀娟,吴 楚,梅 莉,等.水曲柳和落叶松人工林根系分解与养分释放[J].应用生态学报,2006,17(8):1370-1376.
[32] 李吉枚,张毓涛,李建贵,等.模拟氮沉降对天山云杉细根分解及其养分释放的影响[J].生态环境学报,2015,35(1):0182-0188.
[33] Ostertag R,Hobbie S E.Early stages of root and leaf decomposition in Hawaiian forest effect of nutrient availability[J].Oecologia,1999,121:564-573.
[34] Lambers H,Brundrett M C,Raven J A,etal.Plant mineral nutrition in ancient landscapes:high plant species diversityon infertile soils is linked to functional diversity for nutritional strategies[J].Plant and Soil,2011,348:7-27.
[35] 翟明普,蒋三乃,贾黎明.杨树刺槐混交林细根养分动态研究[J],林业科学,2004,40(4):0046-0051.
[36] Yang Y S,Chen G S,Guo J F,etal.Decomposition dynamic of fine roots in a mixed forest of Cunninggamia laceolate and Tsoongiodendron odorum in midsubtropics[J].Annals of Forest Science,2004,61:65-72.
[37] 陈灵芝,黄建辉,严昌荣.中国森林生态系统养分循环[M].北京:中国气象出版社,1997.
(责任编辑:崔 贝)
Fine Root Decomposition and Nutrient Release ofPinusMassonianain the Three Gorges Reservoir Area
WANGNa1,2,CHENGRui-mei1,2,XIAOWen-fa1,2,SHENYa-fei1,2
(1.Laboratory of Forest Ecology and Environment, Research Institute of Forest Ecology, Environment and Protection, Chinese Academy of Forestry,Beijing 100091, China; 2.Co-Innovation Center for Sustainable Forestry in Southern China, Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037, Jiangsu, China)

Three Gorges Reservoir Area;Pinusmassoniana; fine root decomposition; nutrient release
10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2017.01.003
2016-02-01
十三五国家重点研发计划(2016YFD0600204)、科技基础性工作专项(2014FY120700)、十二五科技支撑计划(2015BAD07B04)。
王 娜,女,在读硕士。主要研究方向:森林生态学。电话:18600607476。E-mail: 13121498454@163.com。通讯地址:北京市海淀区香山路东小府1号中国林科院森环森保所。
* 通讯作者:程瑞梅,研究员。主要研究方向:群落生物多样性和森林生态。E-mail: chengrm9533@sina.com
S791.248
A
1001-1498(2017)01-0018-07
