胰腺炎与脂肪肝的关系探讨
2017-02-09祁兴顺郭晓钟
高 帆, 祁兴顺, 侯 悦, 郭晓钟
(1 解放军第二〇二医院 医务处, 沈阳 110003; 2 沈阳军区总医院 消化内科, 沈阳 110840)
胰腺炎与脂肪肝的关系探讨
高 帆1, 祁兴顺2, 侯 悦2, 郭晓钟2
(1 解放军第二〇二医院 医务处, 沈阳 110003; 2 沈阳军区总医院 消化内科, 沈阳 110840)
胰腺炎系一种常见的、病死率高的消化系统疾病。临床医生常会遇到胰腺炎合并脂肪肝的患者。从脂肪肝在胰腺炎患者中的患病率、脂肪肝对胰腺炎预后的影响、妊娠急性脂肪肝诱发胰腺炎3个方面进行了阐述,以探讨胰腺炎与脂肪肝之间的关系。
胰腺炎; 脂肪肝; 预后
胰腺炎为常见的消化系统疾病[1-3],其中急性胰腺炎的年发病率为13/10万~45/10万[4-5],而慢性胰腺炎的年发病率为5/10万~12/10万[6-9]。在美国,急性胰腺炎居院内死亡原因的第5位[2];在英国,重症急性胰腺炎的院内死亡率可达15%~20%[10]。至今,国内外专家已针对胰腺炎管理方面制订了多部临床实践指南或共识[11-25]。胰腺炎的主要病因包括胆石症、高三酰甘油血症、酗酒等(表1)。目前,尚无指南或共识将脂肪肝列为胰腺炎的危险因素或病因。然而,在临床工作中,经常会遇到胰腺炎合并脂肪肝的患者[26](图1)。笔者通过PubMed及CNKI数据库以“pancreatitis”及“fatty liver”或“胰腺炎”及“脂肪肝”作为检索词鉴定相关文献,从脂肪肝在胰腺炎的患病率、脂肪肝对胰腺炎预后的影响、妊娠急性脂肪肝诱发胰腺炎3个主要方面进行阐述,以探讨胰腺炎与脂肪肝之间的关系。
1 脂肪肝在胰腺炎患者中的患病率
胰腺炎患者常伴有脂肪肝。有研究[27-34]报道了脂肪肝在不同类型胰腺炎患者中的患病率情况(表2)。根据急性胰腺炎的病因,高脂血症性急性胰腺炎患者比非高脂血症性急性胰腺炎患者有着更高的脂肪肝患病率[30-31,34]。相似地,急性胰腺炎伴有脂肪肝患者比无脂肪肝患者的甘油三酯水平更高[34]。这证明了在急性胰腺炎患者中血脂水平与脂肪肝之间的密切关系。此外,考虑到高脂血症系急性胰腺炎的确切病因,似乎可以合理地推测脂肪肝也可能是胰腺炎的诱因。然而,最近的证据提示,在重度高脂血症患者(甘油三酯≥1000 mg/dl)中,脂肪肝与急性胰腺炎的发生也许并无显著关系。Tada等[29]回顾性分析了215例重度高脂血症患者的临床特征,急性胰腺炎患者中脂肪肝患病率为50%(6/12),而无急性胰腺炎患者中脂肪肝患病率为55.7%(113/203),两组差异无统计学意义。然而,由于该研究仅包括12例急性胰腺炎患者,且两组间基线特征的均衡性不明,因此尚需进一步大样本研究来证实这一观点。但该研究却证实了血脂水平与急性胰腺炎风险呈正相关。急性胰腺炎患者较无急性胰腺炎患者有着更高的甘油三酯水平[(1872±1069)mg/dl vs (1440±625) mg/dl],两组差异有统计学意义(P=0.028)。Xiao等[32]通过分析50例急性胰腺炎患者的MR特征变化也发现,随着急性胰腺炎患者的甘油三酯水平下降,MR所示脂肪肝的程度也有所改善。因此,脂肪肝对急性胰腺炎发生的影响可能是依赖于甘油三酯水平改变。根据急性胰腺炎的严重程度,重症急性胰腺炎患者比非重症急性胰腺炎患者有着更高的脂肪肝患病率。Xiao等[32]发现,重症急性胰腺炎患者中脂肪肝患病率为100%,而轻度急性胰腺炎患者中脂肪肝患病率为59%。Xu等[34]研究发现,伴有脂肪肝的患者较无脂肪肝的患者更常发生中重度和重症急性胰腺炎(30.42% vs 17.89%;15.83% vs 6.66%);根据增强CT表现,伴有脂肪肝的患者也更常发生坏死型急性胰腺炎(38.33% vs 17.62%)。此外,脂肪肝的严重程度与急性胰腺炎的严重程度也密不可分。
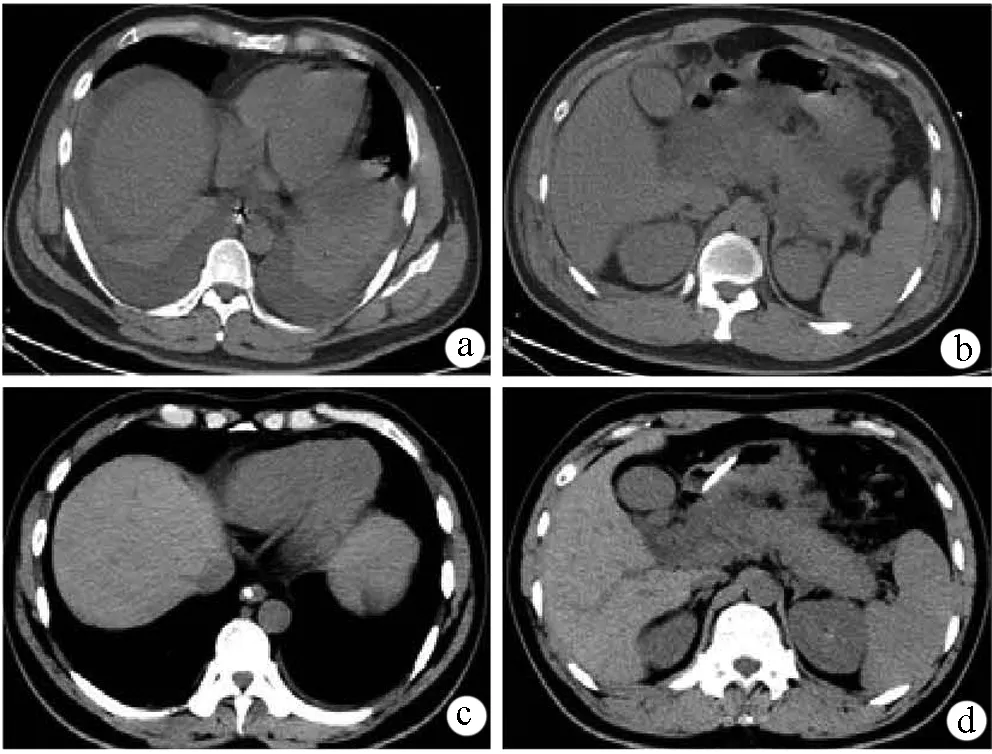
图1 急性胰腺炎合并脂肪肝的患者治疗前后的CT比较 a,b: 入院时CT平扫,胸腔积液,肝周积液,急性胰腺炎,胰周渗出,脂肪肝(肝/脾CT值<1);c,d:治疗后CT平扫,胸腔积液消失,肝周积液消失,空肠营养管置入,胰周渗液吸收,脂肪肝程度降低(肝/脾CT值>1)

表1 胰腺炎指南或共识中提及的病因
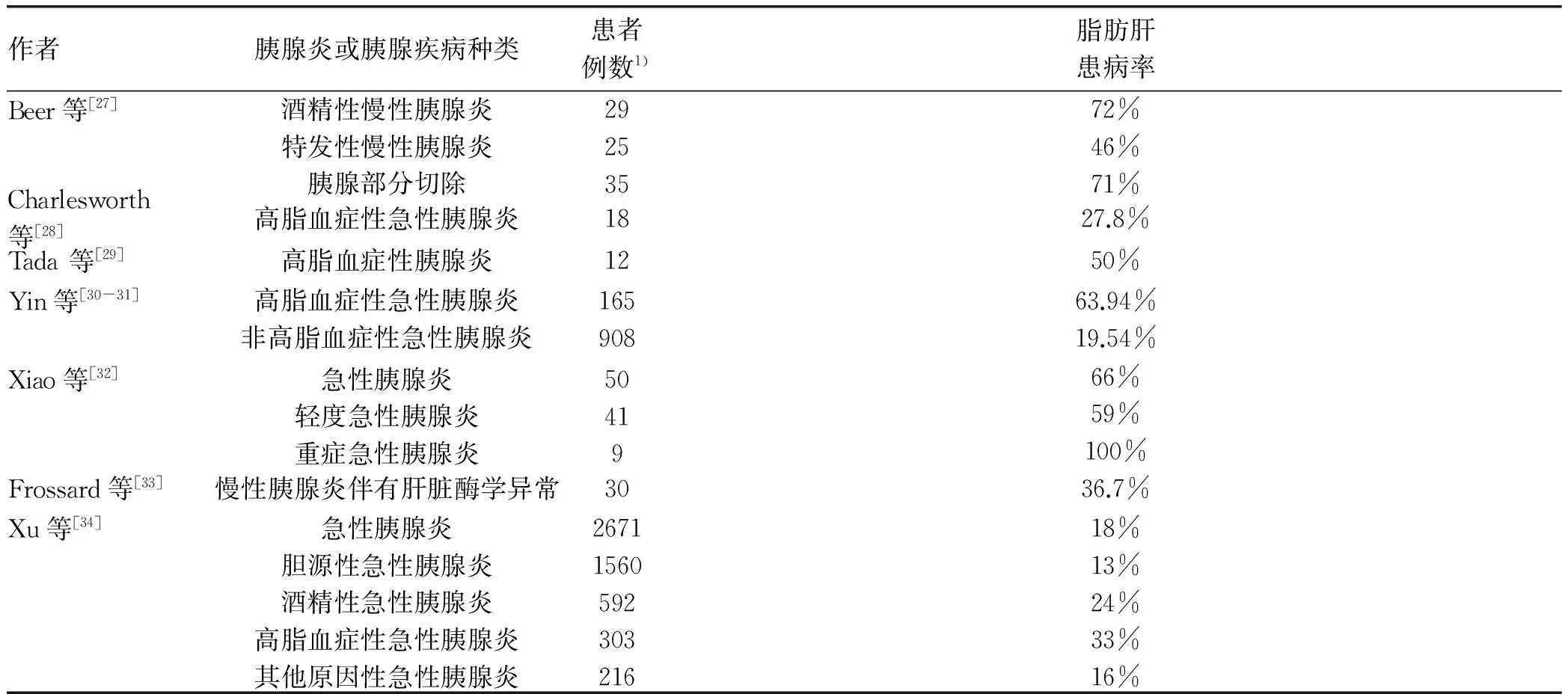
表2 脂肪肝在胰腺炎患者中的患病率
注:1)胰腺疾病患者
慢性胰腺炎可导致胰头部组织发生纤维化,进而造成胰管与胆总管共同开口处局部梗阻及胆汁淤积,最终发生肝纤维化,甚至继发性胆汁淤积性肝硬化。此外,酒精性慢性胰腺炎也可同时发生酒精性脂肪肝或肝硬化。脂肪肝在慢性胰腺炎患者中的患病率约为36.7%~72.0%。Beer等[27]通过应用瞬时弹性成像技术评估54例慢性胰腺炎患者发现,酒精性慢性胰腺炎患者比特发性慢性胰腺炎有着更高的脂肪肝患病率,但差异无统计学意义。
2 脂肪肝对胰腺炎预后的影响
脂肪肝与急性胰腺炎预后有着密切的关系。Xu等[34]回顾性分析了2671例急性胰腺炎患者的临床特征、并发症以及病死率。急性胰腺炎伴有脂肪肝的患者较无脂肪肝的患者更常发生局部并发症(22.08% vs 10.81%)、全身并发症(40.42% vs 16.07%)、呼吸衰竭(34.38% vs 13.37%)、肾衰竭(11.46% vs 4.43%)、全身炎症反应综合征(38.13% vs 17.89%)、感染(46.46% vs 37.7%),差异均有统计学意义。更为重要的是,研究者也发现,脂肪肝与死亡也密切相关(6.46% vs 1.69%)。基于这些研究结果,应在急性胰腺炎患者入院时鉴定是否存在脂肪肝及其严重程度,以初步评估预后。未来研究也有必要进一步探讨脂肪肝作为单一预后因素或联合传统预后评分(Ranson、BISAP、APACHE等)的价值。
3 妊娠期急性脂肪肝与胰腺炎
妊娠期并发急性胰腺炎已被广泛报道,其发病率为1/1000~1/3000,其主要诱因与非妊娠期急性胰腺炎相似。相比之下,妊娠期急性脂肪肝与急性胰腺炎的关系少有报道。
妊娠期急性脂肪肝常发生在妊娠晚期,发病率为1/7000~1/16 000,孕妇病死率为7%~18%,胎儿病死率为9%~23%[35-37]。长链-3-羟酰基辅酶A脱氢酶及其相关编码基因突变可导致胎儿线粒体脂肪酸β氧化缺陷,进而增加妊娠期急性脂肪肝发病风险。此病常在并发症出现时才得以诊断。主要的并发症包括肝性脑病、低血糖、肾衰竭、弥漫性血管内凝血、先兆子痫等。目前,也有学者[38-45]报道了妊娠期急性脂肪肝诱发急性胰腺炎的个案(表3)。其可能的发病机制包括:(1)妊娠期雌激素增加,继而导致高脂血症;(2)孕激素增加,继而导致脂肪酶及胰蛋白酶分泌增加,同时可导致Oddi氏括约肌痉挛和胰管压力过低;(3)免疫因素[42]。Moldenhauer等[46]对15例妊娠期急性脂肪肝诱发急性胰腺炎患者进行分析显示,平均孕妇年龄为26.3岁(21~37岁);以持续性恶心、呕吐为主要临床表现;11例患者伴有淀粉酶升高,另外1例患者伴有脂肪酶升高;8例行影像学检查的患者中,7例患者存在胰腺炎的影像学表现;主要合并疾病包括脑病、急性呼吸窘迫综合征、肾衰竭;孕妇病死率为17%(2/15)。
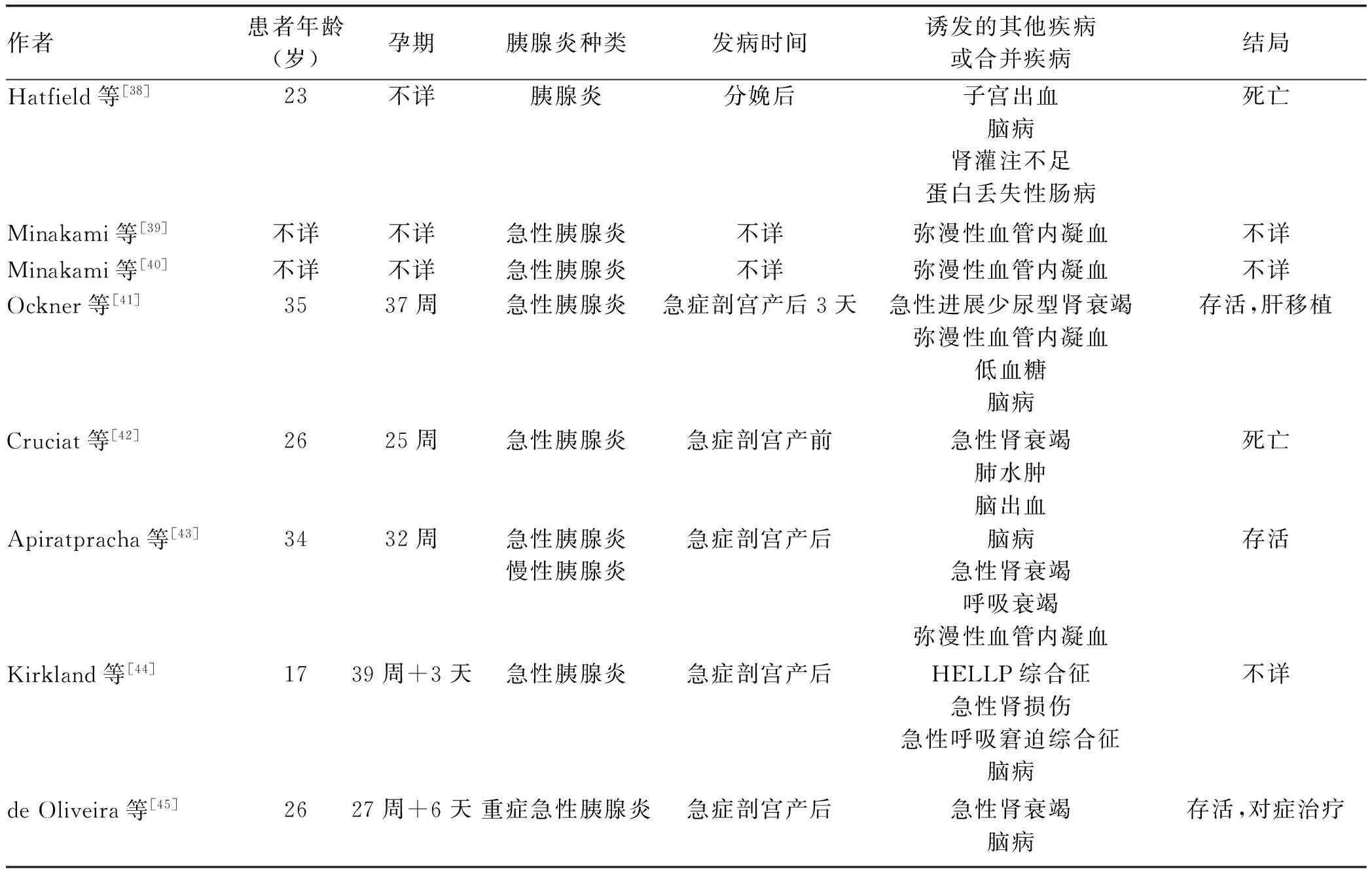
表3 妊娠期急性脂肪肝诱发胰腺炎的个案汇总
4 结语
脂肪肝在胰腺炎患者中较常见,且可增加胰腺炎相关并发症的发生风险及病死率。另外,虽然妊娠期急性脂肪肝诱发的胰腺炎罕见,但一旦发生,患者预后极差。因此,临床医生应加强对脂肪肝与胰腺炎之间关系的认识,积极防治脂肪肝也许有助于降低胰腺炎的发病风险并改善预后。
[1] FORSMARK CE, VEGE SS, WILCOX CM. Acute pancreatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2016, 375(20): 1972-1981.
[2] LANKISCH PG, APTE M, BANKS PA. Acute pancreatitis[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(9988): 85-96.
[3] MAJUMDER S, CHARI ST. Chronic pancreatitis[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10031): 1957-1966.
[4] SATOH K, SHIMOSEGAWA T, MASAMUNE A, et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of acute pancreatitis in Japan[J]. Pancreas, 2011, 40(4): 503-507.
[5] SHEN HN, LU CL, LI CY. Epidemiology of first-attack acute pancreatitis in Taiwan from 2000 through 2009: a nationwide population-based study[J]. Pancreas, 2012, 41(5): 696-702.
[6] HIROTA M, SHIMOSEGAWA T, MASAMUNE A, et al. The sixth nationwide epidemiological survey of chronic pancreatitis in Japan[J]. Pancreatology, 2012, 12(2): 79-84.
[7] ZHANG ZG, GEN XP. Interpretation of the 2013 International Association of Pancreatology/American Pancreas Association evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Ⅰ)[J]. J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2013, 21(5): 385-388. (in Chinese) 张志功, 耿小平. 2013年国际胰腺协会/美国胰腺协会循证医学基础上的急性胰腺炎处理指南解读(一)[J]. 肝胆外科杂志, 2013, 21(5): 385-388.
[8] ZHANG ZG, GEN XP. Interpretation of the 2013 International Association of Pancreatology/American Pancreas Association evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Ⅱ)[J]. J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2013, 21(6): 467-470. (in Chinese) 张志功, 耿小平. 2013年国际胰腺协会/美国胰腺协会循证医学基础上的急性胰腺炎处理指南解读(二)[J]. 肝胆外科杂志, 2013, 21(6): 467-470.
[9] ZHANG ZG, GEN XP. Interpretation of the 2013 International Association of Pancreatology/American Pancreas Association evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Ⅲ)[J]. J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2014, 22(1): 62-65. (in Chinese) 张志功, 耿小平. 2013年国际胰腺协会/美国胰腺协会循证医学基础上的急性胰腺炎处理指南解读(三)[J]. 肝胆外科杂志, 2014, 22(1): 62-65.
[10] JOHNSON CD, BESSELINK MG, CARTER R. Acute pancreatitis[J]. BMJ, 2014, 349: g4859.
[11] Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas (AISP), PEZZILLI R, ZERBI A, et al. Consensus guidelines on severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2015, 47(7): 532-543.
[12] HUANG GW, SHEN DC. Interpretation of consensus guidelines for severe acute pancreatitis (2015) in Italy[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2016, 25(3): 313-317. (in Chinese) 黄耿文, 申鼎成. 意大利重症急性胰腺炎共识指南(2015)解读[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2016, 25(3): 313-317.
[13] ISAJI S, TAKADA T, MAYUMI T, et al. Revised Japanese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis 2015: revised concepts and updated points[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2015, 22(6): 433-445.
[14] The Spleen and Stomach Disease Branch of China Association of Chinese Medicine. Consensus on acute pancreatitis management of Chinese medicine[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharma, 2013, 28(6): 1826-1831. (in Chinese) 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会. 急性胰腺炎中医诊疗专家共识意见[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2013, 28(6): 1826-1831.
[15] ITO T, ISHIGURO H, OHARA H, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for chronic pancreatitis 2015[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2016, 51(2): 85-92.
[16] LI XQ, QIAN JM. An excerpt of evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for chronic pancreatitis by Japanese Society of Gastroenterology in 2015[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(5): 857-859. (in Chinese) 李晓青, 钱家鸣. 《2015年日本胃肠病学会慢性胰腺炎循证临床实践指南》摘译[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(5): 857-859.
[17] SUN B, ZHAO ZJ. The interpretation of the evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for chronic pancreatitis by Japanese Society of Gastroenterology in 2015[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2016, 36(3): 305-308. (in Chinese) 孙备, 赵忠杰. 日本胃肠病学会《慢性胰腺炎循证临床实践指南(2015)》解读[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2016, 36(3): 305-308.
[18] Professional Committee of Pancreatic Disease, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese consensus on the multidisciplinary treatment (MDT) of acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(11): 1770-1775. (in Chinese) 中国医师协会胰腺病学专业委员会. 中国急性胰腺炎多学科诊治共识意见[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31(11): 1770-1775.
[19] Pancreatology Committee of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese consensus on acute pancreatitis by multiple discipline team (Draft)[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2015, 35(12): 1004-1010. (in Chinese) 中国医师协会胰腺病学专业委员会. 中国急性胰腺炎多学科诊治(MDT)共识意见(草案)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015, 35(12): 1004-1010.
[20] BANKS PA, BOLLEN TL, DERVENIS C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis-2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus[J]. Gut, 2013, 62(1): 102-111.
[21] LENG F, YANG L, CHANG ZG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis-2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2013, 29(4):Ⅰ-Ⅶ. (in Chinese) 冷芳, 杨力, 常志刚, 等. 急性胰腺炎分类——2012:亚特兰大分类和定义修订的国际共识[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2013, 29(4):Ⅰ-Ⅶ.
[22] Group of Pancreas Surgery, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the management of chronic pancreatitis(2014)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(3): 322-326. (in Chinese) 中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 慢性胰腺炎诊治指南(2014)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31(3): 322-326.
[23] Group of Pancreas Surgery, Chinese Society of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis(2014)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(1): 17-20. (in Chinese) 中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2014)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31(1): 17-20.
[24] Pancreas Study Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Pancreatology, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Digestion. Chinese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Shanghai, 2013)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2013, 29(9): 656-660. (in Chinese) 中华医学会消化病学分会胰腺疾病学组,《中华胰腺病杂志》编辑委员会,《中华消化杂志》编辑委员会. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2013年,上海)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2013, 29(9): 656-660.
[25] Pancreas Study Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (draft)[J]. Chin J Dig, 2004, 24(3): 62-64. (in Chinese) 中华医学会消化病学分会胰腺疾病学组. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(草案)[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2004, 24(3): 62-64.
[26] QI X, HOU Y, GUO X. Severe fatty liver disease and acute pancreatitis: is there a correlation between them?[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2016, 1(4): 127-130.
[27] BEER S, WIEGAND J, ROSENDAHL J, et al. High prevalence of fatty liver disease and fibrosis in patients with chronic pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 150(4): s908.
[28] CHARLESWORTH A, STEGER A, CROOK MA. Acute pancreatitis associated with severe hypertriglyceridaemia; A retrospective cohort study[J]. Int J Surg, 2015, 23(Pt A): 23-27.[29] TADA H, KAWASHIRI MA, NAKAHASHI T, et al. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia[J]. J Clin Lipidol, 2015, 9(4): 519-524.[30] YIN G, HU G, CANG X, et al. C-reactive protein: rethinking its role in evaluating the severity of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2014, 43(8): 1323-1328.
[31] YIN G, CANG X, YU G, et al. Different clinical presentations of hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis: a retrospective study[J]. Pancreas, 2015, 44(7): 1105-1110.
[32] XIAO B, ZHANG XM, JIANG ZQ, et al. Fatty liver in acute pancreatitis: characteristics in magnetic resonance imaging[J]. J Comput Assist Tomogr, 2012, 36(4): 400-405.
[33] FROSSARD JL, GIOSTRA E, RUBBIA-BRANDT L, et al. The role of transient elastography in the detection of liver disease in patients with chronic pancreatitis[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33(7): 1121-1127.
[34] XU C, QIAO Z, LU Y, et al. Influence of fatty liver on the severity and clinical outcome in acute pancreatitis[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0142278.
[35] LIU MM, JIA SN, ZHANG Q, et al. Advances in clinical research on liver disease during pregnancy[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(2): 386-389. (in Chinese) 刘苗苗, 贾胜男, 张倩, 等. 妊娠期肝病的临床研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(2): 386-389.
[36] ZHANG J, XU M, WANG XZ, et al. Liver disease during pregnancy[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2008, 24(5): 397-399. (in Chinese) 张健, 徐敏, 王心竹, 等. 妊娠期肝病[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2008, 24(5): 397-399.
[37] Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF), Italian Association for the Study of the Liver AISF. AISF position paper on liver disease and pregnancy[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2016, 48(2): 120-137.
[38] HATFIELD AK, STEIN JH, GREENBERGER NJ, et al. Idiopathic acute fatty liver of pregnancy. Death from extrahepatic manifestations[J]. Am J Dig Dis, 1972, 17(2): 167-178.
[39] MINAKAMI H, KIMURA K, KANAZAWA T, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy with hyperlipidemia, acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis and disseminated intravascular coagulation[J]. Asia Oceania J Obstet Gynaecol, 1985, 11(3): 371-376.
[40] MINAKAMI H, KIMURA K, TAMADA T, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy: report of a case complicating DIC and acute pancreatitis (author′s transl)[J]. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi, 1982, 34(5): 637-640.
[41] OCKNER SA, BRUNT EM, COHN SM, et al. Fulminant hepatic failure caused by acute fatty liver of pregnancy treated by orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. Hepatology, 1990, 11(1): 59-64.
[42] CRUCIAT G, STAMATIAN F, PUSCAS M, et al. Acute pancreatitis in a pregnant woman with acute fatty liver dystrophy. A case report[J]. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2007, 16(2): 193-196.
[43] APIRATPRACHA W, YOSHIDA EM, SCUDAMORE CH, et al. Chronic pancreatitis: a sequela of acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2008, 7(1): 101-104.
[44] KIRKLAND EB, SACHDEV R, KIM J, et al. Early pancreatic panniculitis associated with HELLP syndrome and acute fatty liver of pregnancy[J]. J Cutan Pathol, 2011, 38(10): 814-817.
[45] de OLIVEIRA CV, MOREIRA A, BAIMA JP, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy associated with severe acute pancreatitis: a case report[J]. World J Hepatol, 2014, 6(7): 527-531.
[46] MOLDENHAUER JS, O'BRIEN JM, BARTON JR, et al. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy associated with pancreatitis: a life-threatening complication[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2004, 190(2): 502-505. 引证本文:GAO F, QI XS, HOU Y, et al. Association between pancreatitis and fatty liver disease [J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(1): 40-45. (in Chinese) 高帆, 祁兴顺, 侯悦, 等. 胰腺炎与脂肪肝的关系探讨[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33(1): 40-45.
(本文编辑:葛 俊)
Association between pancreatitis and fatty liver disease
GAOFan,QIXingshun,HOUYue,etal.
(MedicalDepartment, 202HospitalofPLA,Shenyang110003,China)
Pancreatitis is a common digestive disease with a high mortality rate. Clinical physicians often encounter patients with pancreatitis and fatty liver disease. This article investigates the association between pancreatitis and fatty liver disease from the aspects of the prevalence of fatty liver disease in patients with pancreatitis, the influence of fatty liver disease on the prognosis of pancreatitis, and pancreatitis induced by acute fatty liver disease during pregnancy.
pancreatitis; fatty liver; prognosis
10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.01.008
2016-10-11;
2016-11-19。作者简介:高帆(1982-),女,主要从事内科诊疗研究。
祁兴顺,电子信箱:xingshunqi@126.com;郭晓钟,电子信箱:guoxiaozhong1962@126.com。
R576; R575.5
A
1001-5256(2017)01-0040-06
