Development of a topical ointment of betamethasone dipropionate loaded nanostructured lipid carrier
2017-01-19
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,103 Wenhua Road,Shenyang 110016,China
Development of a topical ointment of betamethasone dipropionate loaded nanostructured lipid carrier
Xin Kong,Yuan Zhao,Peng Quan,Liang Fang*
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,103 Wenhua Road,Shenyang 110016,China
A R T I C L EI N F O
Article history:
Received 7 May 2015
Received in revised form 3 July 2015
Accepted 9 July 2015
Available online 28 August 2015
Nanostructured lipid carrier(NLC) Betamethasone dipropionate(BD) Topical ointment
The purpose of this study was to design an innovative topical ointment containing betamethasone dipropionate loaded nanostructured lipid carrier(BD-NLC)for the treatment of atopic dermatitis(AD).BD-loaded NLC was produced with precirol ATO 5 and oleic oil(OA)by melt emulsifcation method.Effects of surfactant concentration,amount of solid lipid and liquid lipid on skin retention and skin penetration were investigated byin vitropercutaneous permeation experiment.The optimized BD-NLC showed a homogeneous particle size of 169.1 nm(with PI=0.195),negatively charged surface(−23.4 mV)and high encapsulation effciency(85%).Particle morphology assessed by TEM revealed a spherical shape.In vitroskin permeation study was carried out to investigate the percutaneous behaviors ofW/O ointment with BD-NLC and Carbopol emulgel ointment with BD-NLC.W/O ointment with BDNLC showed high skin retention(35.43 μg/g)and low penetration(0.87 μg/ml).In vitrodrug release studies were carried out to demonstrate the drug releasing properties of the two ointments.W/O ointment with BD-NLC showed an advantage for skin retention as it was better for drug release.The tissue distribution test suggested that BD distribution was skin>muscle>blood.Self-made topical ointment in mice showed no skin irritation.The animal experiments indicated that BD-loaded NLC ointment was effective and safe for topical use.
©2016 The Authors.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Phar maceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license
(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
1.Introduction
The nature of skin,especially the bulk of stratum corneum(SC) is the main physical barrier of transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS)[1].The approaches to enhance drug permeation include chemical techniques based on chemical penetration enhancers(CPEs)[2],and physical techniques such as ultrasound[3], iontophoresis[4],and microneedles[5,6].CPEs can enhance skin permeability of drugs.Though CPEs are commonly used in enhancing drug penetration,they are limited by safety concerns, such as skin irritation[7].The overall effectiveness ofphysical strategies is as strong as that of CPEs,but their inconvenient use and high cost limit their use.Recently,lipid nanoparticles have been introduced into topical application to improve skin drug delivery.Many researches have been conducted on this novel strategy,indicating remarkable results [8–10].
Nanostructured lipid carrier(NLC)is new generation of lipid nanoparticles,which is an aqueous colloidal dispersion composed of blended solid lipids and liquid lipids(oils)[11].It was recognized as a promising drug carrier system for topical application because of its improving skin penetration properties [12].The applications of NLC in the treatments of skin diseasessuchasskindermatitis,psoriasisandinfammationswere reported in the literature[12,13].For TDDS,molecular properties of active compound are crucial for transdermal potential. For example,when the molecular weight is>500 Da,it is considered that the drug cannot go through skin.So far,the mechanism of the improved skin penetration of NLC is not yet clear.Compared with other vehicles such as creams,tinctures,and emulsions,NLCs possess such advantages as controlled drug release,protection of active compounds and negligibleskinirritation.Moreover,thesmallparticlesizesensure that the nanoparticles are in close contact with the stratum corneum(SC),thus promoting the amount of active compound which penetrates into the skin[11].Lipid nanoparticles used as a carrier system for topical delivery of several drugs including clotrimazole,prednicarbate,betamethasone 17-valerate and podophyllotoxin were investigated and they were reported to have a skin targeting potential[14,15].
Atopic dermatitis(AD)is a kind of skin dermatitis.Topical glucocorticoids are recommended for acute exacerbations of atopic dermatitis[16].Betamethasone Dipropionate(BD),a kind of glucocorticoid,is mainly used for the treatment of AD[17,18]. As we know,glucocorticoids can bring many side effects.Normally,short-term treatment,and reducing the amount of drug are recommended in the clinic[17].Hence,it is necessary to improve the drug skin retention and reduce the penetrating amount into systemic circulation in topical application,which will decrease the risk of a systemic side effect.
In the present study,NLC was investigated as a drug delivery system for BD.Particle size,zeta potential,morphology and the entrapment effciency of NLC dispersions were characterized.It would be convenient for topical use when NLC dispersions are combined with ointment.Therefore,W/O ointment and Carbopol emulgel ointment were prepared as topical ointment matrix,respectively.Meanwhile,in vitrodrug release studies were carried out to demonstrate drug release properties of the two ointments.Tissue distribution experiment in mice was conducted fnally to evaluate the skin retention effect for reducing the penetration amount into systemic circulation.Skin irritation test was carried out to demonstrate whether NLC could reduce the risk of skin irritation.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Chemistry and materials
Betamethasone Dipropionate(BD)(purity>99%)was provided byWuhan Dahua Pharmaccutical Co.,Ltd.(Wuhan,China). Oleic oil(OA),Tween 80,Span 80,liquid paraffn and stearyl alcohol were obtained byTianjin Bodi Chemical Co.,Ltd.(Tianjin, China).Carbopol 971 was from Lubrizol Co.Ltd.(Ohio,USA). White vaseline,iso-propyl alcohol and isopropyl palmitate(IPP) were provided by Shandong Damao Chemical Reagent Factory (Shandong,China),ShandongYuwang Industrial Co.,Ltd.(Shandong,China),and International Specialty Products Inc.(New Jersey,USA),respectively.Transparent cellophane membrane and sephadex G-50 were from Shangyu cellophane Co.,Ltd. (Zhejiang,China)and Pharmacia&Upjohn Company(New Jersey,United States),respectively.Precirol ATO 5 was a generous gift from Gattefossé(Lyon,France).All other chemicals used were of analytical grade and commercially available.
2.2.Animals
Rabbits(male,1.5–2.0 kg)and KM mice(male,20±2.0 g)used in the experiments were purchased from the Experimental Animal Center of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University (Shenyang,China).The experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines for animal use published by the Life Science Research Center of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
2.3.Preparation and characterization of BD loaded NLC
2.3.1.Preparation of BD loaded NLC
BD-loaded NLC was produced using melt emulsifcation combined with ultra-sonication technique as reported previously [19].In brief,Precirol ATO 5 and OA(3%in total,w/v)were blended under gentle stirring in water bath at 85°C to form the lipid phase.Successively,BD(0.05%,w/v)was added in the lipid phase until completely dissolved.Meanwhile,Tween 80 was dissolved into distilled water corresponding to 10 ml at 85°C and added dropwise to the lipid phase,with moderate magnetic stirring for 7 minutes.The coarse emulsion was further subjected to an ultrasonication procedure through a probe-type sonicator(Scientz-II D,NingBoXinZhi,Ningbo,China) for 72 s under 400 W ultrasonic output power to reduce the particle sizes of emulsions to nano range.The obtained nanoemulsions were cooled down in an ice-water bath to form the NLC rapidly.The total volume of BD-NLC suspensions were supplemented by adding distilled water to 10 ml.
2.3.2.Characterization of the NLC dispersion
Mean particle size(Z-average),dispersity index(PI)and zeta potential of BD-NLC suspensions were determined by photon correlation spectroscopy(PCS)(Malvern Nanosizer ZS90,Worcestershire,UK)for characterizing the width of distribution and the stability of the product under 25°C.For particle size and PI detection,the PCS was performed at a detection angle 90°C. Before the detection,each sample was diluted 100 folds with distilled water.Each value was measured in triplicate.
The shape and surface morphology of BD loaded NLC was observed by transmission electron microscopy(TEM,JEM-1200EX,Tokyo,Japan).A drop of NLC suspensions diluted 5 folds was dispersed on a 200-mesh copper grid.After the excessive water was removed with flter paper,the sample was negatively stained with 2.5%phosphotungstic acid for 4 min for observing.

Table 1–Formulation of Carbopol emulgel ointment matrix.
2.3.3.Determination of NLC entrapment effciency(EE)
Non-encapsulated BD was separated from nanoparticles by size exclusion chromatography(SEC)using the mini-column centrifugation method.Briefy,5.0 ml disposable syringe barrels were plugged with cotton flters and flled with Sephadex G-50 Medium.After spinning the column at 2000 rpm to remove the liquid,BD-NLC suspensions(0.5 ml)were added onto the top of the gel bed.The columns were centrifuged again at 2000 rpm for 3 min to expel the void volume containing the nanoparticles and the eluates were kept for assaying.The eluent(distilled water,1.0 ml)was loaded onto the micro column and centrifuged for 1.0 min(2000 r/min).This step was repeated forth until all nanoparticles had come off the column.The eluent was collected together and diluted to 10 ml.BD in the diluted sample (1.0 ml)was dissolved by methanol and diluted to 5.0 ml.The sample was fltered through a 0.45 μm syringe flter.Finally,the drug concentration in the eluates was determined by UV-2800 spectrophotometer(Unico Instrument Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai, China).The concentration of BD was marked with C1.
BD-loaded NLC dispersions(0.5 ml)were diluted by distilled water to 10 ml.The diluted sample(1.0 ml)was dissolved by methanol and diluted to 5.0 ml.The sample was fltered sucessfully through a 0.45 μm syringe flter.The concentration of BD was detected by the same method and marked with C2.EE of the sample was calculated by Eq.1:

2.4.Preparation of NLC ointment
Generally,BD-loaded NLC dispersions can be incorporated into ointment for topical use.Carbopol emulgel ointment and W/O ointment were investigated as matrix of the topical NLC ointment here.
The formulation of Carbopol emulgel ointment was labeled in Table 1.Carbopol 971 was dispersed into distilled water 24 h before the test.The pH of the sample was adjusted to 7.0 by triethanolamine.Finally,the mixture of Span 80 and IPP was dropped to Carbopol dispersion under agitation.
The formulation of W/O ointment was labeled in Table 2. The oil phase of W/O matrix contained stearyl alcohol,liquid paraffn,white vaseline,and Span 80.The oil phase and distilled water were both heated in 80°C water bath.Then the oil phase was dropped into distilled water under magnetic stirring.Finally,the matrix was cooled down to room temperature.
BD-loaded NLC dispersions(10 ml)were incorporated into the two topical vehicles under homogeneous stirring, respectively.
2.5.In vitro skin permeation experiment
2.5.1.Preparation of rabbit skin
The process of the preparation and storage of the rabbit abdominal skin were based on an ordinary method published in a transdermal report[20,21].The details were described here. The rabbits should be anesthetized with urethane(20%,w/v, i.v.).The electric clipper and razor were used to remove the abdominal hair.The skin without hair(full thickness skin here including epidermis with SC and dermis)was then excised from the shaved abdomen.The subcutaneous fat was removed carefully from the obtained skin with a surgical scissor.Finally,the skin was washed immediately with phosphate-buffered saline and stored at−70°C.The skin samples were used within 1 month,which is about the time when the normal activity of the stratum corneum(SC)layer is still preserved.
2.5.2.In vitro skin permeation
Franz vertical diffusion cells were used in thein vitroskin permeation experiment of BD-loaded NLC dispersion.The effective diffusion area of the diffusion cell was 1.77 cm2.The rabbit abdominal skin was situated between the donor chamber and the receiver chamber.The mixture of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS,pH 7.4)and iso-propyl alcohol(7:3,v/v)was used as a receiver liquid.The volume of the receiver liquid was 7.0 ml.The media was stirred at about 600 rpm,and the temperature of receiver chamber was maintained at 32°C by a circulatingwater jacket during the whole experiment.NLC sample(2.0 ml) was applied into the donor chamber.The permeation experiment lasted for 24 h.
After 24 h skin permeation,the receiver medium was collected and centrifuged at 16,000 rpm for 5 min.The concentration of BD was determined by HPLC.
The skin sample was taken off from the Franz cell and wiped off with cotton swabs to remove the excessive drug on the surface.The sample was weighed precisely and cut into small pieces.Ethyl acetate(1.0 ml)was added into skin sample and sonicated for 20 min to extract BD from skin.The concentration of BD in ethyl acetate was determined by HPLC.The drug retention in the skin was expressed as microgram of BD per gram of skin weight(μg/g).

Table 2–Formulation of W/O ointment matrix.
2.6.In vitro drug release
In vitrodrug release behaviors of Carbopol emulgel ointment with BD-NLC and W/O ointment with BD-NLC were investigated with Franz vertical cells.The receiver liquid was the same as thein vitroskin permeation experiment in Section 2.5.2. Transparent cellophane membrane was used as permeation barrier,and the ointment(2.0 g)was applied into each donor chamber.The sampling time points were designed as 0,4,6,8,10,12 and 24 h.At each time point,samples(5 ml)were withdrawn from the receptor for detection and an equal amount of the fresh receptor medium was added to keep a constant volume.
2.7.Tissue distribution experiment
2.7.1.Experiment design
Skin,muscle and blood drug distribution in KM mice at different times was investigated in this experiment.The abdomen hair of the mice was cut off carefully before the test.The abdomen skin was cleaned with distilled water,and 100 mg of the W/O ointment with BD-NLC was daubed on the surface of skin.The area of skin applied ointment was 2.0×2.0 cm.Administration duration of the self-made ointment was 2,4,6, 8,12 and 24 h,respectively.The ointment was cleaned at each time point using a cotton swab,except for the 24 h administration sample,which was cleaned at 12 h.Finally,the ointment on skin was cleaned up and the skin and muscle samples were cut off after the mice were sacrifced.Four mice were used for each time point in this test.
2.7.2.Sample extraction process
Skin and muscle cut from mice were weighed precisely and divided into small pieces.1.0 ml of methanol was added into skin and muscle samples,respectively.The samples were under sonicate procedure for 30 min and centrifuged at 16,000 rpm for 5 min.
For the skin sample,100 μl of the supernatant was mixed with 100 μl of internal standard.The mixture was injected into the HPLC system for analysis.
For the muscle sample,the supernatant was withdrawn and evaporated to dryness under nitrogen at 40°C.The residue was reconstituted by 200 μl of methanol and vortex-mixed for 3 min. The sample was centrifuged at 16,000 rpm for 5 min successfully.After that,100 μl of internal standard was added into equal volume of supernatant.Finally,the mixture was injected into the HPLC system for analysis.
2.8.HPLC analysis
The concentration of BD was analyzed by HPLC.The HPLC system consisted of a Hitachi L-2130 pump,a Hitachi L-2200 automatic injector and a Hitachi L-2400 ultraviolet detector.The separation was performed on a Diamonsil C18column (200×4.6 mm,5 μm,Dikma,China)with the fow rate of 1.0 ml/ min,and the detection wavelength was 239 nm.The mobile phase was the mixture of methanol and water(80:20,v/v).
For the determination of BD in the receptor liquid,200 μl of the sample was mixed with equal volume of the internal standard(itraconazole solution,10 μg/ml).The volume of the mixture for HPLC analysis was 20 μl.
For the determination of BD in skin and muscle,100 μl of the sample was mixed with equal volume of the internal standard(itraconazole solution,5 μg/ml).20 μl of the mixture was injected into HPLC for analysis.
2.9.Skin irritation experiment
For topical ointment,skin irritation should be avoided.Rabbits were used to detect the irritation of the self-made preparation.The skin irritation test was evaluated by the Draize method [22].The hair of two sides of the rabbits’body was shaved 24 h before test.Four groups of formulations were designed in this experiment:SDS(sodium dodecyl sulfate,10%,w/v);W/O ointment with BD-NLC;W/O ointment with no-drug-NLC(blank bases)and the mixture of BD and W/O ointment.SDS(0.5 ml) and other groups(0.5 g)were smeared on the hairless skin of the rabbits and removed 4 hours later.Finally,the reactions of skin were inspected in the next 1,24,48 and 72 h.The degree of erythema and edema were both recorded by the score of dermal reactions.The score of 0 represented no erythema or edema,the score of 1 represented very slight erythema or edema,the score of 2 represented well-defned erythema or edema,the score of 3 represented moderate to severe erythema or edema,and the score of 4 represented severe erythema or edema.The average score of every rabbit in every day was calculated by Eq.2.The category of irritation was scored on the basis of the mean primary irritation index as follows:

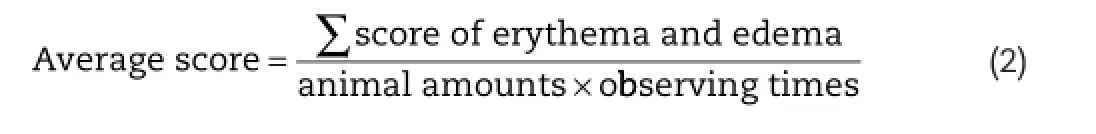
3.Results and discussion
3.1.Preparation of BD loaded NLC
PrecirolATO 5 and OA were usually used as solid lipid and liquid lipid in many researches of topically used NLC.Tween 80 was chosen as the emulsifer in this experiment.The concentration ofTween 80 and different ratios of Precirol ATO 5:OA were investigated in thein vitroskin penetration experiment.The results are shown in Table 3.For topical preparations,high skinretention and low penetration amount were expected.Therefore,formulation 3 was chosen for the preparation of topical ointment.The skin retention and skin permeation of BD was 312.83 μg/g and 1.71 μg/ml,respectively.

Table 3–In vitroskin penetration of BD-loaded NLC under different preparation conditions(n=3,mean±SD).
The results suggested that the formulations with 2.0%of Tween 80 obtained higher skin retention of BD than formulations with 1.5%of Tween 80.Obviously,the surfactant had an effect in improving skin penetration properties.Tween 80 was no longer added to optimize the formulation in case of any skin irritation phenomenon.Therefore 2.0%ofTween 80 was chosen for the further study.Subsequently,it could be seen that the skin retention of the drug was improved with the increase of OA loading.The liquid lipid in the lipid core of NLC was conducive to the dissolution of drug from the carrier,whose possible explanation could be that the addition of OA could have created a less ordered skin penetration properties in solid lipid matrix,resulting in the increase of drug loading in the particles[23,24].Furthermore,the lower melting point of OA may be another reason for increasing drug retention.
3.2.Characterization of drug loaded NLC
The particle size,zeta potential,and EE of formulation 3 were investigated.The results showed that the particle size and zeta potential of BD loaded NLC were 169.1 nm(SD=0.5)(PI=0.195, SD=0.013)and−23.4 mv,respectively.In general,smaller particles(less than 200 nm)display more skin retention[25,26]. Zeta potential is a useful sign in controlling the stability of BDNLC,and an unstable system is usually accompanied by a decrease in the value of zeta potential accelerating the approach of particles and formation of a particle aggregation[27]. An accepted arbitrary value for an incipient stable system that separates low-charged surfaces from highly-charged surfaces is 20–25 mv[28].The micrograph of TEM in Fig.1 represented that the drug loaded NLC was in spherical shape. The entrapment effciency(EE%)of formulation 3 reached 85%, which suggested that most of BD had been better entrapped into the lipid matrix of NLC.

Fig.1–Transmission electron micrograph of BD-loaded NLC.

Table 4–In vitroskin penetration of Carbopol emulgel ointment with BD-NLC and W/O ointment with BD-NLC (n=3,mean±SD).
3.3.In vitro skin permeation of topical ointment
Carbopol emulgel ointment matrix and W/O ointment matrix were selected as the NLC ointments for the preparation of the fnal product.The results ofin vitroskin permeation of the two NLC ointments are represented in Table 4.The skin retention of Carbopol emulgel ointment with BD-NLC and W/O ointment with BD-NLC were 19.24 μg/g and 35.43 μg/g,respectively, while skin penetration of the two preparations were 2.10 μg/ ml and 0.87 μg/ml,respectively.W/O ointment with BD-NLC obtained higher skin retention and lower skin penetration amount.Apparently,the W/O matrix was more appropriate for the topical use of BD-loaded NLC.
3.4.In vitro drug release of NLC ointment
In vitrodrug release experiment was designed to explain the different transdermal results between the two topical ointments.The results are presented in Fig.2.The accumulated release amount of BD in W/O ointment with BD-NLC in 24 h was 10.04%,while the Carbopol ointment with BD-NLC was 7.60%.Obviously,the lipophilicW/O ointment matrix had better release property than Carbopol NLC ointment(P<0.05).When the W/O ointment with BD-NLC was applied onto skin,both W/O matrix and lipophilic drug could penetrate into SC.Since the SC layer was lipophilic,the W/O matrix,BD and SC had good affnity to each other.This further induced larger drugretention and lower penetration.Compared to W/O ointment with BD-NLC,there was less BD released from Carbopol ointment with BD-NLC.When the lipophilic drug was released from the vehicle,the hydrophilic environment showed little affnity to the drug.BD in the SC layer showed more tendencies to pass through skin.As a result,Carbopol ointment with BDNLC showed much more skin penetration than W/O ointment with BD-NLC.

Fig.2–In vitrodrug release of W/O ointment with BD-NLC and Carbopol emulgel ointment with BD-NLC(n=3, mean±SD).

Fig.3–The concentration of BD in skin and muscle of micein vivo.
3.5.Tissue distribution experiment
W/O ointment with BD-NLC was applied to the living mice in the tissue distribution experiment.The results are presented in Fig.3.The amount of BD in skin tissue was much higher than that in muscle.In 2 h and 4 h,a small amount of drug could be detected in the muscle tissue.The active compound retention in the skin increased with administration duration, which suggested that self-made ointment had a good tendency to be retained in the skin.Since the amount of drug retained in the skin at 12 h and 24 h were 3.65 μg/g and 4.04 μg/ g,respectively,there was no signifcant difference between them.On the other hand,a small amount of drug was detected in the blood of mice in this experiment.
3.6.Skin irritation experiment
Skin irritation is an important side effect which should be considered for ointment for topical use.The results of rabbit skin irritation test are shown in Fig.4.The erythema and edema could be observed apparently in rabbit skin of the positive control group.The mean score of dermal observation of positive control was 5.25,which indicated moderate irritation.It implied that the rabbit skin could refect the actual condition of the skin when the irritation occurred.There was no erythema and edema of skin in the NLC ointment group within 72 h.The mixture of BD and ointment matrix induced slight erythema with the score of 0.5625.Obviously,the results suggested that when drug loaded into NLC,the skin irritation could be decreased.From this perspective,NLC was a safe carrier in dermal and transdermal drug delivery system.

Fig.4–Skin irritation observation of rabbits of positive control and different formulations.
4.Conclusion
The BD-loaded NLC was prepared by the melt emulsifcation method for topical delivery of BD.Thein vitropermeation study showed that 2.0%of Tween 80 increased the skin retention of BD.Meanwhile,when the proportion of Precirol ATO 5 and OA was 1:2,the BD-NLC showed highest skin retention.W/O ointment with BD-NLC exhibited higher skin retention(35.43 μg/ g)and lower skin penetration(0.87 μg/ml)than Carbopol ointment with BD-NLC,respectively.In vitrodrug release test indicated that the W/O ointment with BD-NLC which could increase skin retention was better for drug release.The selfmade topical ointment also showed desirable drug retention in skin tissue of living mice and no skin irritation of rabbits. In conclusion,this study will facilitate the development of BDNLC,which may improve skin retention,reduce the adverse effects induced by systemic absorption and reduce skin irritation.
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Benson HAE.Skin structure,function and permeation.New York:John Wiley&Sons;2012.p.26–42.
[2]Ibrahim SA,Li SK.Effects of chemical enhancers on human epidermal membrane:structure-enhancement relationship based on maximum enhancement(E(max)).J Pharm Sci 2009;98:926–944.
[3]Smith NB.Perspectives on transdermal ultrasound mediated drug delivery.Int J Nanomedicine 2007;2(4):585–594.
[4]Frederic B,Malika LS,Madeleine B,et al.Effect of iontophoresis and penetration enhancers on transdermal absorption of metopimazine.J Dermatol Sci 2008;52:170–171.
[5]Mikszta JA,Alarcon JB,Brittingham JM,et al.Improved genetic immunization via micromechanical disruption of skin-barrier function and targeted epidermal delivery.Nat Med 2002;8(4):415–419.
[6]Verbaan FJ,Bal SM,Van den Berg DJ,et al.Improved piercing of microneedle arrays in dermatomed human skin by an impact insertion method.J Control Release 2008;128(1):80–88.
[7]Karande P,Jain A,Mitragotri S.Insights into synergistic interactions in binary mixtures of chemical permeation enhancers for transdermal drug delivery.J Control Release 2006;115:85–93.
[8]Cevc G,Vierl U.Nanotechnology and the transdermal route: a state of the art review and critical appraisal.J Control Release 2010;141:277–299.
[9]Singh R,Lillard JJW.Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery.Exp Mol Pathol 2009;86:215–223.
[10]Neubert RHH.Potentials of new nanocarriers for dermal and transdermal drug delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2011;77:1–2.
[11]Fang JY,Fang CL,Liu CH,et al.Lipid nanoparticles as vehicles for topical psoralen delivery:solid lipid nanoparticles(SLN)versus nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC).Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2008;70:633–640.
[12]Schafer-Korting M,Mehnert W,Korting HC.Lipid nanoparticles for improved topical application of drugs for skin diseases.Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2007;59:427–443.
[13]Lapteva M,Mondon K,Möller M,et al.Polymeric micelle nanocarriers for the cutaneous delivery of tacrolimus:a targeted approach for the treatment of psoriasis.Mol Pharm 2014;11:2989–3001.
[14]Patzelt A,Richter H,Knorr F,et al.Selective follicular targeting by modifcation of the particle sizes.J Control Release 2011;150:45–48.
[15]Chen H,Chang X,Du D,et al.Podophyllotoxin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for epidermal targeting.J Control Release 2006;110:296–306.
[16]Wozniak KD.Use of glucocorticoids in dermatitis.Z Arztl Fortbild(Jena)1987;81(15):789–791.
[17]Nicol NH.Effcacy and safety considerations in topical treatments for atopic dermatitis.Pediatr Nurs 2011;37(6):295–301.
[18]Voigtländer V.A clinical comparison of betamethasone 17, 21-dipropionate and clobetasol propionate creams in dermatology.J Int Med Res 1977;5(2):128–131.
[19]Luo Q,Zhao J,Zhang X,et al.Nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC)coated with chitosan oligosaccharides and its potential use in ocular drug delivery system.Int J Pharm 2011;403:185–191.
[20]Xi H,Cun D,Xiang R,et al.Intra-articular drug delivery from an optimized topical patch containing terifunomide and lornoxicam for rheumatoid arthritis treatment:does the topical patch really enhance a local treatment?J Control Release 2013;169:73–81.
[21]Zhang Y,Cun D,Kong X,et al.Design and evaluation of a novel transdermal patch containing diclofenac and terifunomide for rheumatoid arthritis therapy.J Pharm Sci 2014;9:251–259.
[22]Draize JH,Woodard G,Calvery HO.Methods for the study of irritation and toxicity of substances applied topically to the skin and mucous membranes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1944;82:377–390.
[23]Jana P,Aiman H,Rainer HM.Lipid nanoparticles(SLN,NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products.Int J Pharm 2009;366:170–184.
[24]Vitorino C,Almeida J,Gonçalves LM,et al.Co-encapsulating nanostructured lipid carriers for transdermal application: from experimental design to the molecular detail.J Control Release 2013;167:301–314.
[25]Labouta HI,El-Khordagui LK,Kraus T,et al.Mechanism and determinants of nanoparticle penetration through human skin.Nanoscale 2011;3:4989–4999.
[26]Lademann J,Richter H,Meinke MC,et al.Drug delivery with topically applied nanoparticles:science fction or reality. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 2013;26:227–233.
[27]Freitas C,Müller RH.Effect of light and temperature on zeta potential and physical stability in solid lipid nanoparticle (SLNTM)dispersions.Int J Pharm 1998;168:221–229.
[28]Greenwood R,Kendall K.Selection of suitable dispersants for aqueous suspensions of zirconia and titania powders using acoustophoresis.J Eur Ceram Soc 1999;19:479–488.
*< class="emphasis_italic">Corresponding author.
.Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,No.103 Wenhua Road,Shenyang 110016,China.Tel.:+86 24 23986330;fax: +86 24 23986330.
E-mail address:fangliang2003@yahoo.com(L.Fang).
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.07.005
1818-0876/©2016 The Authors.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Atopic dermatitis(AD)
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Preparation and characterization of solidifed oleanolic acid–phospholipid complex aiming to improve the dissolution of oleanolic acid
- Supersaturation induced by Itraconazole/Soluplus®micelles provided high GI absorption in vivo
- Quality assessment of Chrysanthemum indicum Flower by simultaneous quantifcation of six major ingredients using a single reference standard combined with HPLC fngerprint analysis
- Rapid and sensitive analysis of melatonin by LC-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetic study in dogs
- Effect of process parameters on the recrystallization and size control of puerarin using the supercritical fuid antisolvent process
- The 1st Euro-Mediterranean Workshop:Natural Products in Health and Diseases:Cairo,Egypt, March 2,2015
