迭代次数自适应的Grover算法
2017-01-10朱皖宁陈汉武
朱皖宁,陈汉武
(1.金陵科技学院软件工程学院,江苏南京 211199;2.东南大学计算机科学与工程学院,江苏南京210096;3.东南大学计算机网络和信息集成教育部重点实验室,江苏南京210096)
迭代次数自适应的Grover算法
朱皖宁1,2,陈汉武2,3
(1.金陵科技学院软件工程学院,江苏南京 211199;2.东南大学计算机科学与工程学院,江苏南京210096;3.东南大学计算机网络和信息集成教育部重点实验室,江苏南京210096)
本文提出了利用相位门自动控制Grover搜索算法迭代次数的算法.Grover搜索算法最终得到目标分量的概率非常依赖于酉算子迭代的次数.迭代次数的计算依赖于目标分量的数量.因此当目标分量数未知时,该方法无法以高概率测量到目标分量.在以往的解决方案中需要较高的Oracle查询复杂度才能以一定概率得到目标分量的数量.本文提出了一种通过判断叠加态相位正负性,可自动控制Grover搜索算法迭代次数的方法.只需要添加一个判断相位的门电路,仅增加一次Oracle查询次数就可以精确的在最优迭代次数时停止Grover搜索算法,在搜索空间较小时可比原算法有更大的概率得到目标分量.
Grover搜索算法;相位正负性;自动控制
1 引言
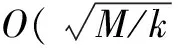
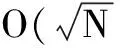
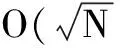
本文提出了一种基于判定X基下(|±〉={|0〉±|1〉}) 特定分量相位的正负性的新Grover算法.新算法只需要多一个可逆门和一次Oracle调用,就可以在目标分量未知时仍然可以以最高的概率测量出目标分量.
2 准备知识
Grover搜索算法是由一组酉算子的迭代运算组成.可以简单的由下图表示[9]:
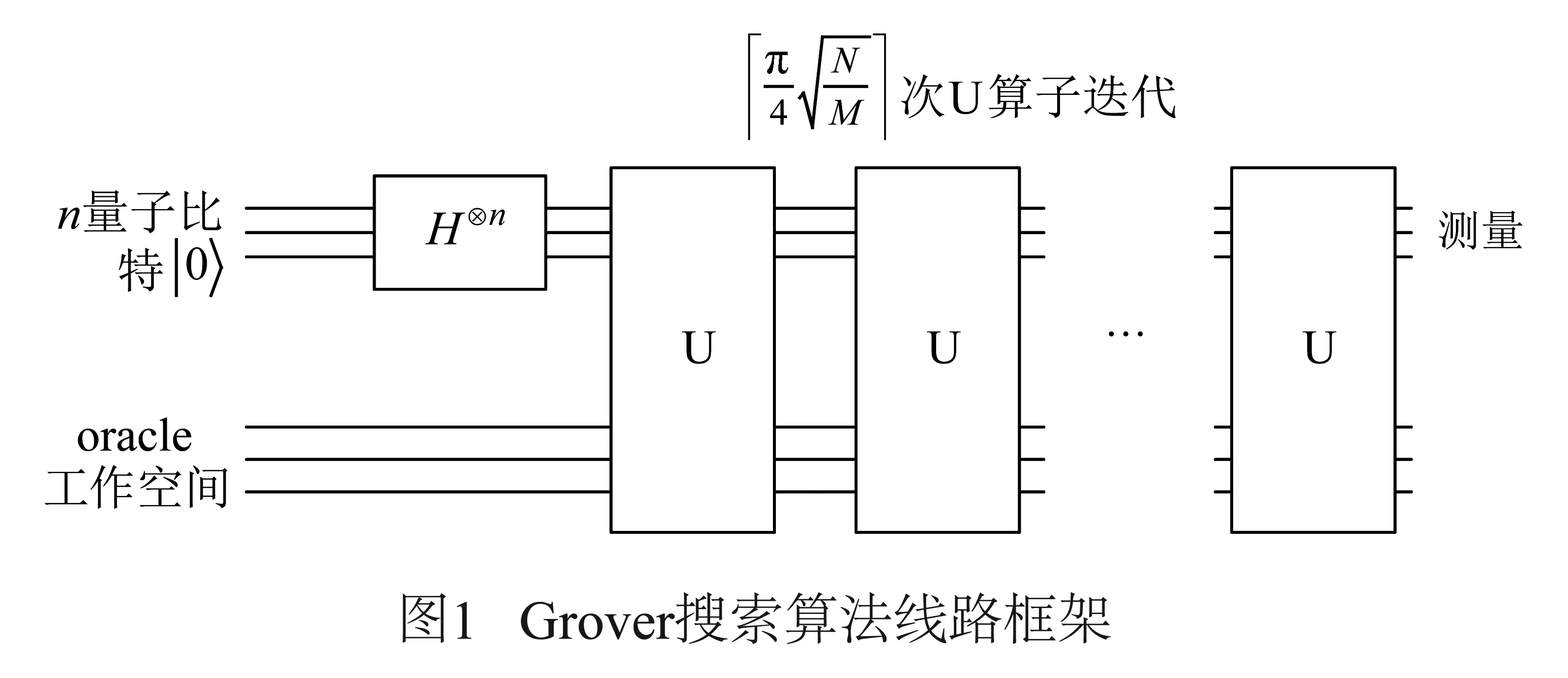
当n个量子比特初态|0〉⊗n经过门H⊗n后变成n量子均匀叠加态,具体变换过程由如下公式表示:
(1)
其中N=2n.令|s〉表示初态的均匀叠加态.U算子由一个Oracle决定解(即用一个函数可以表达出解)和一个Grover均值反演算子来增加解的概率.
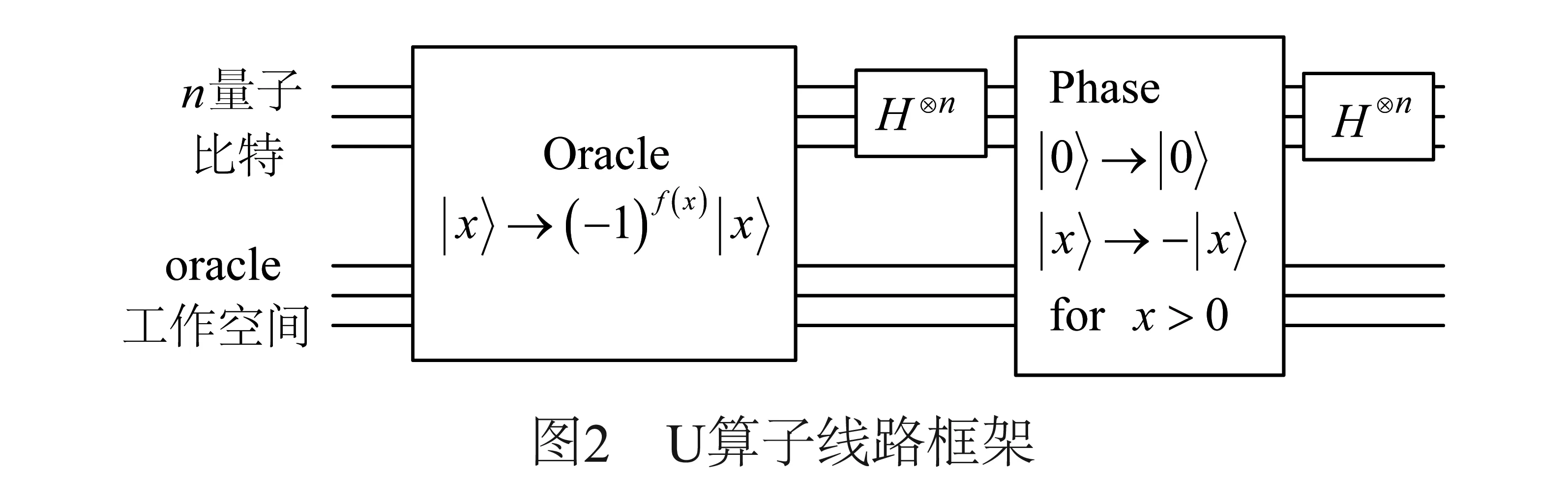
如图2所示的Oracle算子令所求目标分量相位翻转:Oracle=I-2|φ〉〈φ|;Grover均值反演算子通过简单计算可以得到如下表示:
(2)
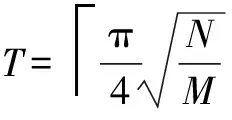
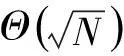
3 迭代次数自适应的Grover搜索算法
每次进行Grover算子迭代后,目标分量的幅度都会发生变化.且可以证明运行最佳迭代次数,目标分量的幅度都会增加,而目标分量的幅度直接影响最终测量出结果的概率.因此可以通过判断目标分量幅度是否已经最大化,控制Grover搜索算法的迭代次数.
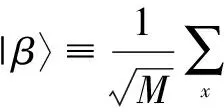
定理2(均值反演定理) 经过均值反演算子作用,叠加态所有分量的相位之和首次变为负值时目标分量的概率幅首次达到最大值.
(3)
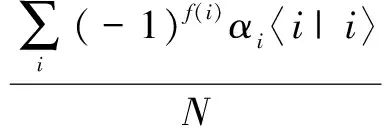

(4)
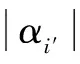
定理3(相位和定理) 叠加态分量Z基下相位和正负性由X基下的|++…+〉分量相位正负性所决定.
证明:这个结果可以很容易的通过变换基底获得.假设初始基底为Z基,即{|0〉,|1〉}基.那么一个n量子比特的叠加态总是可以表示为:
(α00|0〉+α01|1〉)(α10|0〉+α11|1〉)… (α(n-1)0|0〉+α(n-1)1|1〉)
(5)
现在将Z基转化为X基,即{|+〉,|-〉}基,某一量子比特的转换公式可如下表示:
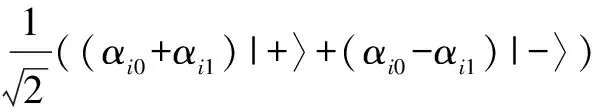
(6)

由于相位正负性可以估测[22,23],所以使用相位检测门Phase门,输入为需要进行相位判断的叠加态和一个辅助比特|ψ〉⊗|β〉.经过Phase门后,叠加态|ψ〉不产生变化.辅助位根据叠加态在X基下|+ + …+〉分量前相位φ|+ + …+ 〉正负性进行运算:当φ|+ + …+〉为正时不做任何操作,否则翻转控制端.显然此电路为可逆电路.Phase门可以由图3所示的线路所表示:
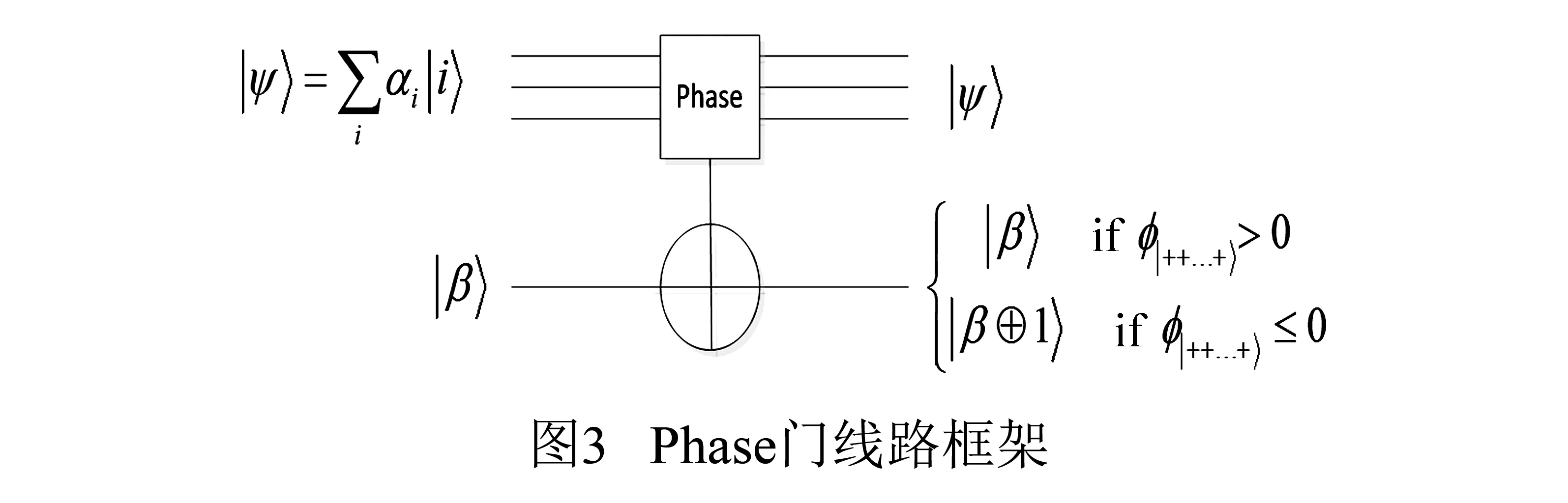
将这个电路加入到Grover算法电路的U算子中,令|ψ〉为经过Oracle算子的叠加态,令|β〉=|0〉.
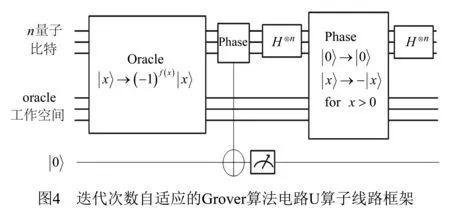
如图4所示,每迭代一次U算子时,都在运行Oracle算子后对辅助位进行一次测量再决定是否进行Grover均值反演算子的计算.当测量结果为|0〉时继续进行算法迭代,当测量结果为|1〉时结束算法.由此嵌入Phase门后的Grover搜索算法可以自适应的控制U算子迭代次数.

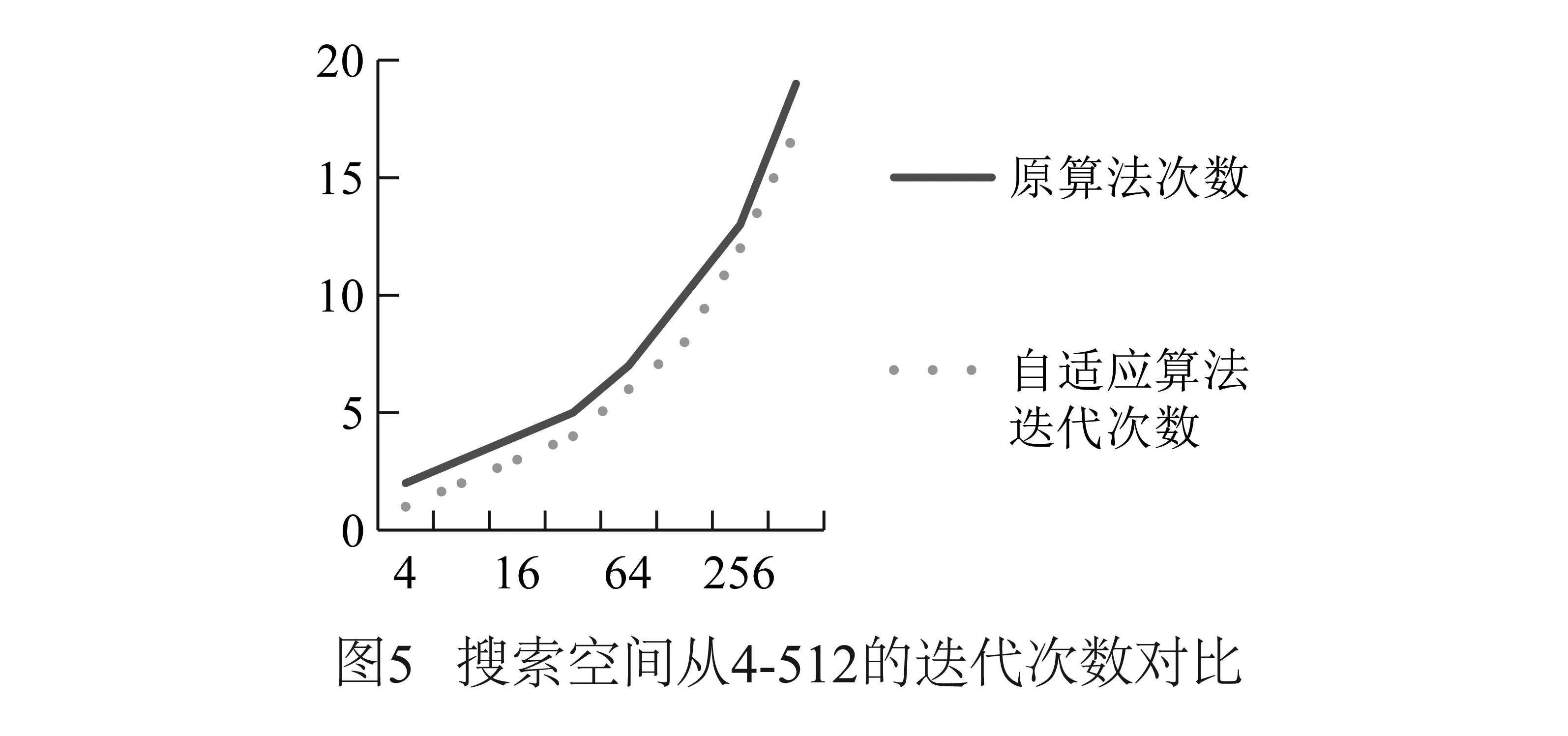
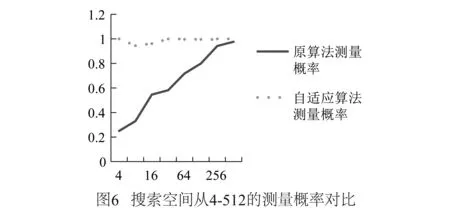

4 小结
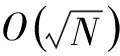
本文提出了一种在M未知时运行Grover算法的解决方案.利用判断经过Oracle后叠加态相位和的正负性,自动控制Grover算法酉算子的迭代次数,可以精确在目标分量概率达到最大值时停止算法,并且只加入了一个进行相位判断的门电路,只增加一次Oracle查询次数.不仅如此迭代次数自适应的Grover算法在搜索空间较小时会获得更高的概率测量到目标分量.在近几年来有许多学者对Grover算法进行了改进,增加测量出目标分量的概率并减少Oracle调用的次数.这些改进算法并没有改动均值反演算子这个核心,因此本文所述的方法均可以用于这些改进算法.
[1]Shor P W.Algorithms for quantum computation:discrete logarithms and factoring[A].Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on foundations of Computer Science[C].Santa Fe,NM:IEEE,1994.124-134.
[2]GroverL K.A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search[A].Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing[C].Philadelphia,USA:ACM,1996.212-219.
[3]Grover L K.Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack[J].Physical Review Letters,1997,79(2):325-328.
[4]Grover L K.Quantum computers can search rapidly by using almost any transformation[J].Physical Review Letters,1998,80(19):4329-4332.
[5]Long G L,Li Y S,Zhang W L,et al.Dominant gate imperfection in Grover’s quantum search algorithm[J].Physical Review A,2000,61(4):042305.
[6]Biron D,Biham O,Biham E,et al.Generalized Grover search algorithm for arbitrary initial amplitude distribution[A].Quantum Computing and Quantum Communications[C].Palm Springs,CA:Springer Berlin Heidelberg,1999.140-147.
[7]Chuang I L,Gershenfeld N,Kubinec M.Experimental implementation of fast quantum searching[J].Physical Review Letters,1998,80(15):3408-3411.
[8]Boyer M,Brassard G,Høyer P,et al.Tight bounds on quantum searching[OL].arXiv Preprint Quant-ph/9605034,1996.
[9]Michael A Nielsen,Isaac L Chuang.Quantum Computation and Quantum Information[M].British:Cambridge University Press,2000.240-243.
[10]Daniel Reitzner,Daniel Nagaj,Vladimir Buzek.Quantum walks[J].Acta Physica Slovaca,2011,61(6):603-725.
[11]金文梁,陈向东.相位不匹配的量子搜索算法[J].电子学报,2012,40(1):189-192. Jin Wenliang,Chen Xiangdong.Phase-unmatched quantum search algorithm[J].Acta Electronica Sinica,2012,40(1):189-192.( in Chinese)
[12]Zalka Christof.Using Grover’s quantum algorithm for searching actual databases[J].Physical Review A,2000,62(5):052305-052301.
[13]Yamashita S.How to utilize a Grover search in general paogramming[J].Laser Physics,2006,16(4):730-734.
[14]阮越,陈汉武,刘志昊,等.量子主成分分析算法[J].计算机学报,2014,37(3):666-676. Ruan Yue,Chen Hanwu,Liu Zhihao.Quantum principal component analysis algorithm[J].Chinese Journal of Computers,2014,37(3):666-676.(in Chinese)
[15]彭宏,荆晶.无线自组织量子通信网络的Grover路由算法研究[J].浙江工业大学学报,2014,42(6):612-615. Peng Hong,Jing Jing.Research on routing algorithm of Grover for wireless ad hoc quantum communication network[J].Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology,2014,42(6):612-615.(in Chinese)
[16]孙国栋,苏盛辉,徐茂智.求根问题的量子计算算法[J].北京工业大学学报,2015,41(3):366-371. Sun Guodong,Su Shenghui,Xu Maozhi.Quantum mechanical algorithms for solving root finding problem[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2015,41(3):366-371.( in Chinese)
[17]Shenvi N,Kempe J,Whaley R B.A quantum random walk search algorithm[J].Physical Review A,2003,67(5):052307.
[18]Aaronson S,Ambainis A.Quantum search of spatial regions[A].Proceedings of 44th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science[C].MA,USA:IEEE,2003.200-209.
[19]Ambainis A,Kempe J,Rivosh A.Coins make quantum walks faster[A].Proceedings of 16th ACM-SIAM SODA[C].British Columbia,Canada:ACM,2005.1099-1108.
[20]Ambainis A.Quantum walk algorithm for element distinctness[A].Proceedings of 45th Annual IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS’04)[C].Rome,Italy:IEEE,2004.22-31.
[21]Childs A M,Eisenberg J M.Quantum algorithms for subset finding[J].Quantum Information and Computation,2005,5(7):593-604.
[22]Dorner U,Demkowicz-Dobrzanski R,Smith B J,et al.Optimal quantum phase estimation[J].Physical Review Letters,2009,102(4):040403.
[23]Hradil Z.Phase measurement in quantum optics[J].Quantum Optics:Journal of the European Optical Society Part B,1992,4(2):93-110.

朱皖宁 男,1983年生,安徽淮南人,博士,主要研究领域为量子计算与量子可逆逻辑综合.
E-mail:granny025@163.com

陈汉武 男,1955年生,江苏南京人,博士,教授,主要研究领域为量子信息与量子计算技术.
E-mail:hanwu-chen@163.com
Grover Auto-Control Searching Algorithm
ZHU Wan-ning1,2,CHEN Han-wu2,3
(1.DepartmentofSoftwareEngineering,JinlingInstituteofTechnology,Nanjing,Jiangsu211199,China; 2.DepartmentofComputerScienceandEngineering,SoutheastUniversity,Nanjing,Jiangsu210096,China; 3.KeyLaboratoryofComputerNetworkandInformationIntegrationofMinistryofEducation,SoutheastUniversity,Nanjing,Jiangsu210096,China)
This paper presents an improved Grover searching algorithm which can automatically control the iterative processing when the number of target states is unknown.The probability of success of Grover searching algorithm depends on the number of iteration times and the number of the time of iterations relies on the number of target states.Therefore,it is hard to get the target state with high probability when the number of target states is unknown.To this question,the time complexity of conventional solution is high and the answer is non-deterministic.This paper shows an improved Grover searching algorithm,which is based on the sign for the phases of superposition state.Compared to existing research results,this algorithm can always stop the Grover iterations when the number of iteration times is optimal by the cost where just one more gate,and one more time Oracle call are needed to judge the sign of phase.
Grover searching algorithm;sign of phase;auto-control
2015-03-10;
2016-05-10;责任编辑:梅志强
国家自然科学基金(No.61170321,No. 61502101);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金(No.20110092110024);江苏省自然科学基金(No.BK20140651);金陵科技学院高层次人才科研启动基金(No.jit-b-201624)
TP387;TN911.73
A
0372-2112 (2016)12-2975-06
��学报URL:http://www.ejournal.org.cn
10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.12.023
