g-C3N4/NiO复合材料的制备及其对AP热分解的影响
2016-12-28谈玲华徐建华杭祖圣石丽丽
谈玲华,徐建华,寇 波,杭祖圣,石丽丽,王 钧
(1江苏省先进结构材料与应用技术重点实验室,南京 211167;2 南京工程学院 材料工程学院,南京 211167)
g-C3N4/NiO复合材料的制备及其对AP热分解的影响
谈玲华1,2,徐建华2,寇 波1,2,杭祖圣1,2,石丽丽2,王 钧2
(1江苏省先进结构材料与应用技术重点实验室,南京 211167;2 南京工程学院 材料工程学院,南京 211167)
通过混合煅烧法制备出g-C3N4/NiO复合材料,采用X射线衍射(XRD)、红外光谱(FT-IR)、场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)、X射线能谱(EDS)对其结构和形貌进行表征,利用差热分析(DTA)和热失重(TG)研究其对高氯酸铵(AP)热分解的影响。结果表明:纳米NiO均匀分散于g-C3N4的表面,g-C3N4/NiO使AP的高温和低温分解峰合并,高温分解温度降低62.5℃,表现出良好的催化作用。g-C3N4/NiO的复合催化效果优于单独使用g-C3N4或NiO,说明g-C3N4和NiO具有协同催化作用。
g-C3N4/NiO;高氯酸铵;催化性能;热分解;协同作用
g-C3N4是类石墨结构的氮化碳材料,以三嗪环(C3N3环)或3-s-三嗪环(C6N7环)为结构单元,C,N原子均发生sp2杂化,通过pz轨道上的孤对电子形成一个类似于苯环结构的大π键,组成高度离域的共轭体系,层与层之间存在大量自由移动的电子[1,2]。由于g-C3N4具有活性中心点多、化学稳定性好、耐高温、导电性能高、环境友好等特点[3,4],作为新型的无金属催化剂备受关注,在环境、能源和化工等领域都有较好的应用前景[5,6]。g-C3N4不仅可作为光催化剂用于光催化分解水制氢[7]、降解有机污染物[8]等方面,还可作为多相催化剂用于CO2活化反应[9]、Knoevenagel缩合反应[10]等方面[11]。与g-C3N4的光催化制氢及降解等方面的大量研究相比,在多相催化方面的研究报道相对较少。
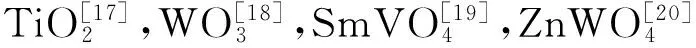
高氯酸铵(AP)是端羟基丁二烯(HTPB)复合固体推进剂中的高能组分,在推进剂中占60%~80%的比例,其热分解特性与推进剂的燃烧性能密切相关,通过研究催化剂对AP热分解的影响可推测推进剂的燃烧性能[21]。经前期研究,g-C3N4对AP的热分解表现出良好的催化作用,为了进一步提高g-C3N4的催化效果,将其与对AP有良好作用效果的NiO复合[22],探讨g-C3N4/NiO复合材料对AP热分解的催化效果,相关文献鲜见报道。
本工作拟采用混合煅烧法制备出g-C3N4/NiO复合材料,利用XRD,FT-IR,FESEM和EDS等对其进行表征,采用DTA和TG研究g-C3N4/NiO复合材料对AP热分解的影响,并探讨催化作用机理。
1 实验材料与方法
三聚氰胺,国药化学试剂有限公司,分析纯;无水乙醇,国药化学试剂有限公司,分析纯;纳米NiO,南京艾普瑞纳米科技有限公司,40nm。
采用半封闭一步热解法[2]制备g-C3N4。取一定量的三聚氰胺放入陶瓷坩埚中(盖上坩埚盖),在马弗炉中以50℃/min升温到500℃,焙烧1h;5min内快速升温到520℃,保温焙烧1h,冷却研磨得g-C3N4粉末。
采用混合煅烧法[19]制备g-C3N4/NiO。取0.05g纳米NiO在乙醇中超声分散10min,然后加入0.95g g-C3N4继续超声分散10min,完成后在研钵中研磨至物体呈糊状,放入50℃真空烘箱中4h后,取出放入管式炉中,在300℃下焙烧1h得到g-C3N4/NiO复合材料。
将AP分别与g-C3N4,NiO,g-C3N4/NiO按照质量比为97∶3的比例在一定量的乙醇溶液中混合、研磨,待乙醇挥发,干燥处理后得待测复合物(g-C3N4/NiO+AP)。
采用Ultima-IV型X射线衍射仪(XRD)分析样品的晶体结构,Kα辐射,波长为0.15406nm;采用NICOLET IS10型红外吸收光谱分析仪(FT-IR)进行红外分析,扫描范围400~4000cm-1;采用SU8010型场发射扫描电镜(FESEM)观察样品形貌,操作电压为30kV;采用GENESIS2000XMS60型X射线能谱仪(EDS)进行样品成分分析。
采用HTG-1型热分析仪(TGA)进行热失重分析,升温速率10℃/min,氮气流速20mL/min,试样量8mg左右,氧化铝样品池;采用404 PC型热分析仪(DTA)进行差热分析,升温速率10℃/min,氩气流速20mL/min,试样量10mg左右,氧化铝样品池。
2 结果与分析
2.1 物相分析
对所制备的g-C3N4和g-C3N4/NiO复合材料进行XRD分析,结果如图1所示。

图1 g-C3N4,NiO和g-C3N4/NiO的XRD曲线
由图1可知,所制备的g-C3N4在2θ为13.2°和27.4°处出现两个较强的特征衍射峰,结合JCPDS 87-1526[23],分别对应于g-C3N4的(100)和(002)面。其中13.2°是melon类物质的特征峰,对应的晶面间距为0.675nm;而27.4°是典型的层状结构堆积衍射峰,对应的晶面间距为0.326nm[2]。g-C3N4/NiO复合材料既出现了g-C3N4的特征衍射峰,还在37.5°,43.4°,63.4°,75.6°,79.7°出现纳米NiO的衍射峰 (JCPDS 47-1049)[24],说明所得的材料为g-C3N4/NiO复合材料。
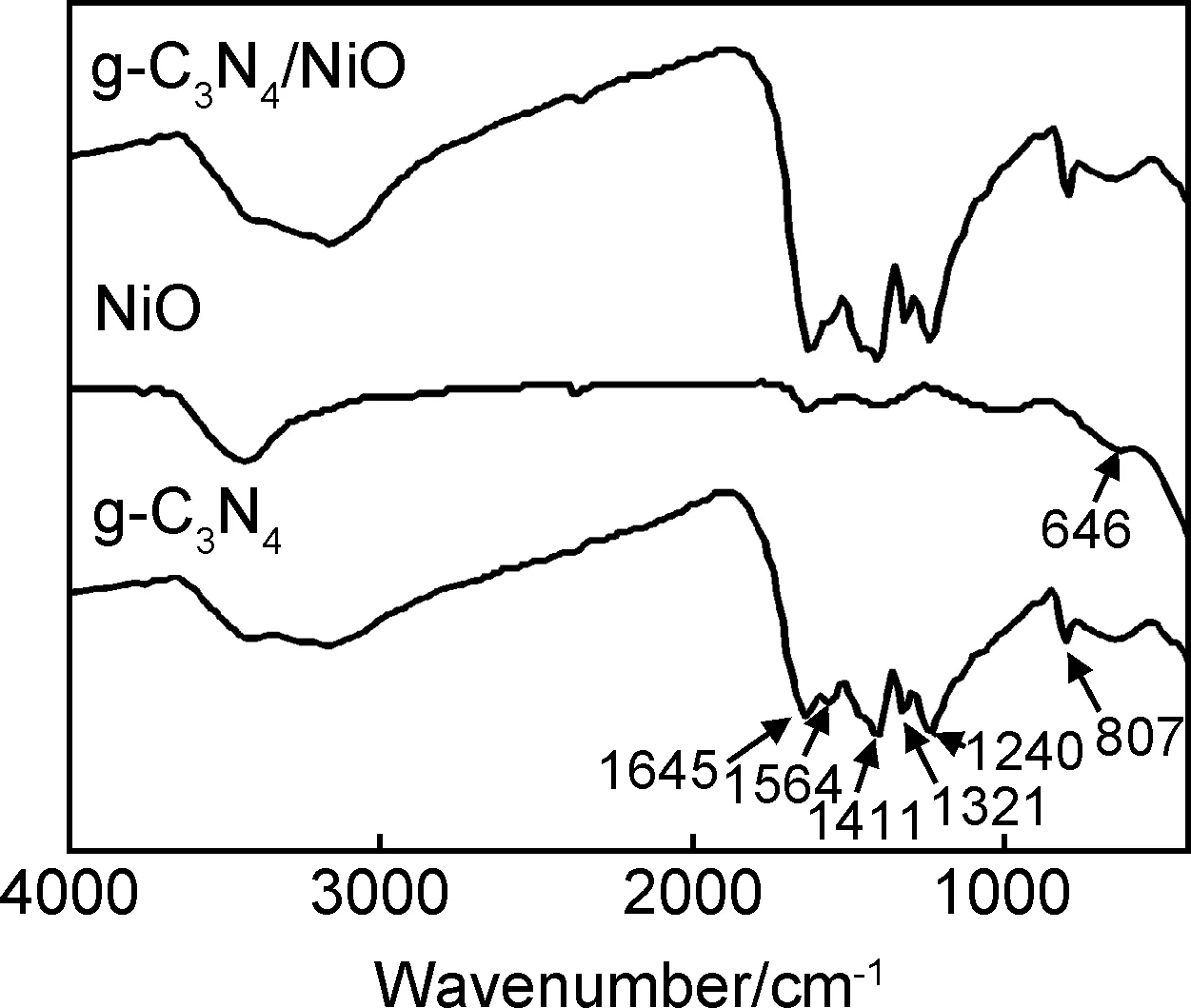
图2 g-C3N4,NiO,g-C3N4/NiO的FT-IR曲线
采用场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)进一步观察g-C3N4/NiO微观形貌及结构,结果如图3所示。
由图3可知,通过半封闭一步热解法制备得到的g-C3N4样品具有明显的层状结构,比较疏松[16]。图3(b)为g-C3N4/NiO的FESEM图片,其中亮点为纳米NiO,比较均匀地分散于g-C3N4的表面。对其进行EDS分析,结果如图3(c)所示,出现C,N,Ni,O的特征峰,由于g-C3N4/NiO中NiO的含量很少,所以Ni元素的特征峰比较低。FESEM和EDS结果说明NiO与g-C3N4复合,并均匀分布于g-C3N4的表面。
2.2 对AP热分解的催化性能研究
采用DTA和TG研究g-C3N4,NiO,g-C3N4/NiO对AP热分解的影响,结果如图4所示。
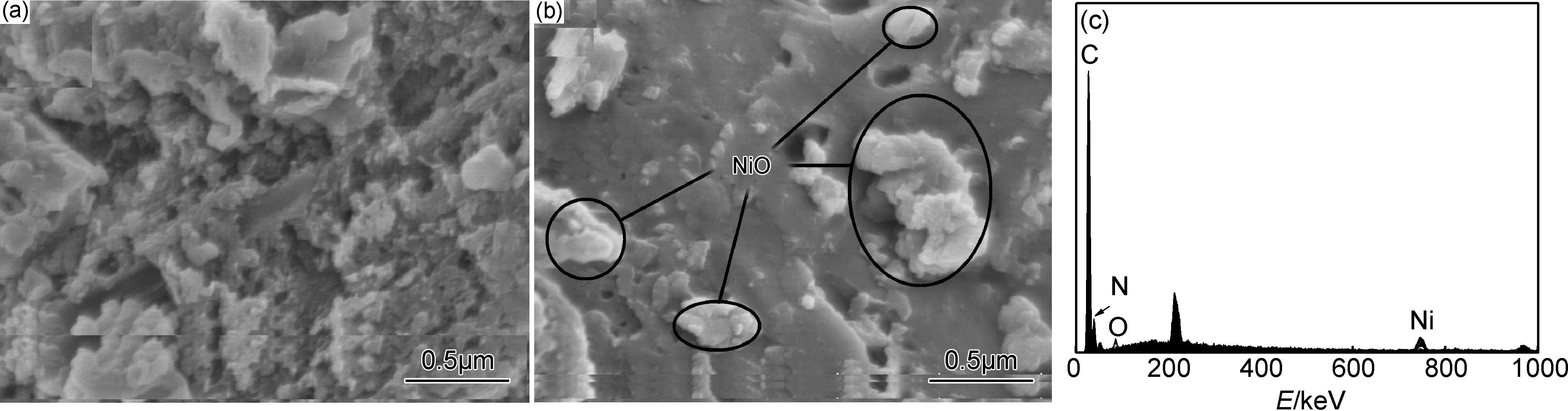

图3 g-C3N4(a),g-C3N4/NiO(b)的FESEM图像及EDS曲线(c)

图4 纯AP,g-C3N4+AP和g-C3N4/NiO+AP的DTA(a),TG(b),DTG(c)曲线
由图4可知,DTA曲线(如图4(a)所示)有1个吸热峰和2个放热峰,248.3℃的吸热峰为AP由斜方晶系转变为立方晶系,326.3℃和425.1℃分别对应于AP的低温分解阶段高温分解和高温分解阶段[28]。添加g-C3N4,NiO,g-C3N4/NiO对AP的晶型转变没有影响,但却均能使AP的高温分解温度降低,对AP的热分解有促进作用。单独添加g-C3N4和NiO时,高温分解温度分别降低30.9℃和42.0℃,而加入g-C3N4/NiO后,AP的高温分解峰和低温分解峰合并,在362.6℃急剧分解,分解温度比纯AP降低了62.5℃,说明g-C3N4/NiO复合材料对AP的热分解起到较强的催化作用[29]。g-C3N4/NiO催化效果均比g-C3N4或NiO单独使用时强,说明g-C3N4和NiO具有协同催化作用[30]。纯AP的TG曲线(如图4(b)所示)中出现两个失重平台,说明纯AP的热分解过程分两步进行。分别加入g-C3N4,NiO或g-C3N4/NiO后,AP的完全分解温度均有一定降低。根据图4(c)的DTG曲线可知,纯AP在332.6℃和447.1℃出现失重速率极值。单独添加g-C3N4和NiO后,失重仍然是两个阶段,第二阶段失重对应温度降低,说明单一的g-C3N4和NiO对AP的热分解也具有催化作用。加入g-C3N4/NiO仅出现一个较大的失重峰,说明在这一阶段内快速分解,分解温度比纯AP的第二分解阶段降低了87.7℃,显示出较强的催化效果,其效果优于单独使用g-C3N4或NiO,也说明g-C3N4和NiO具有协同催化作用[30]。

3 结论
(1)采用混合煅烧法制备出g-C3N4/NiO复合材料,NiO均匀分散于g-C3N4的表面。
(2)g-C3N4/NiO复合材料使AP的高低温分解峰合并,高温分解温度降低了62.5℃,对AP的热分解表现出良好催化作用。g-C3N4/NiO的催化效果优于单独使用g-C3N4或NiO,g-C3N4和NiO具有协同催化作用。
[1] ALGARA-SILLER G, SEVERIN N, CHONG S Y, et al. Triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride: a two-dimensional semiconductor[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2014, 126(29): 7580-7585.
[2] WANG X, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light[J]. Nature Materials, 2008, 8(1): 76-80.
[3] XU J, BRENNER T J, CHABANNE L, et al. Liquid-based growth of polymeric carbon nitride layers and their use in a mesostructured polymer solar cell with Vocexceeding 1 V[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(39): 13486-13489.
[4] LI X, WANG Y, KANG L, et al. A novel, non-metallic graphitic carbon nitride catalyst for acetylene hydrochlorination[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 311: 288-294.
[5] ZHANG J, ZHANG M, YANG C, et al. Nanospherical carbon nitride frameworks with sharp edges accelerating charge collection and separation at a soft photocatalytic interface[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(24): 4121-4126.
[6] ZHENG Y, LIN L, YE X, et al. Helical graphitic carbon nitrides with photocatalytic and optical activities[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(44): 11926-11930.
[7] SCHWINGHAMMER K, MESCH M B, DUPPEL V, et al. Crystalline carbon nitride nanosheets for improved visible-light hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(5): 1730-1733.
[8] YAN S C, LI Z S, ZOU Z G. Photodegradation performance of g-C3N4fabricated by directly heating melamine[J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(17): 10397-10401.
[9] HUANG Z, LI F, CHEN B, et al. Well-dispersed g-C3N4nanophases in mesoporous silica channels and their catalytic activity for carbon dioxide activation and conversion[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 136-137: 269-277.
[10] TALAPANENI S N, ANANDAN S, MANE G P, et al. Facile synthesis and basic catalytic application of 3D mesoporous carbon nitride with a controllable bimodal distribution[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(19): 9831-9840.
[11] WANG Y, WANG X, ANTONIETTI M. Polymeric graphitic carbon nitride as a heterogeneous organocatalyst: from photochemistry to multipurpose catalysis to sustainable chemistry[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(1): 68-89.
[12] SU F, MATHEW S C, LIPNER G, et al. mpg-C3N4-catalyzed selective oxidation of alcohols using O2and visible light[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(46): 16299-16301.
[13] MA T Y, DAI S, JARONIEC M, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet-carbon nanotube three-dimensional porous composites as high-performance oxygen evolution electrocatalysts[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53(28): 7281-7285.
[14] NIU P, YIN L, YANG Y, et al. Increasing the visible light absorption of graphitic carbon nitride (melon) photocatalysts by homogeneous self-modification with nitrogen vacancies[J]. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(47): 8046-8052.
[15] LIU G, NIU P, SUN C, et al. Unique electronic structure induced high photoreactivity of sulfur-doped graphitic C3N4[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(33): 11642-11648.
[16] LI X, CHEN J, WANG X, et al. Metal-free activation of dioxygen by graphene/g-C3N4nanocomposites: functional dyads for selective oxidation of saturated hydrocarbons[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(21): 8074-8077.
[17] HUANG Z A, SUN Q, LV K, et al. Effect of contact interface between TiO2and g-C3N4on the photoreactivity of g-C3N4/TiO2photocatalyst: (001) vs (101) facets of TiO2[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 164: 420-427.
[18] CHEN S, HU Y, MENG S, et al. Study on the separation mechanisms of photogenerated electrons and holes for composite photocatalysts g-C3N4-WO3[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2014, 150-151: 564-573.
[19] LI T, ZHAO L, HE Y, et al. Synthesis of g-C3N4/SmVO4composite photocatalyst with improved visible light photocatalytic activities in RhB degradation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 129: 255-263.
[20] SUN L, ZHAO X, JIA C, et al. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4-ZnWO4by fabricating a heterojunction: investigation based on experimental and theoretical studies[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(44): 23428-23438.
[21] LIU L L, LI F S, TAN L H, et al. Effects of nanometer Ni, Cu, Al and NiCu powders on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2004, 29(1): 34-38.
[22] 谈玲华,李勤华,杭祖圣,等. 负载型纳米 NiO 催化高氯酸铵热分解的 DSC/TG-MS 研究[J]. 功能材料, 2011, 42(3): 564-567.
TAN L H, LI Q H, HANG Z S, et al. Catalytic effect of supported nanometer NiO on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate by DSC/TG-MS[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2011, 42(3): 564-567.
[23] SHI H, CHEN G, ZHANG C, et al. Polymeric g-C3N4coupled with NaNbO3nanowires toward enhanced photocatalytic reduction of CO2into renewable fuel[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2014, 4(10): 3637-3643.
[24] KIM H, JEONG H, KIM T, et al. Enhanced ethanol sensing characteristics of In2O3-decorated NiO hollow nanostructures via modulation of hole accumulation layers[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(20): 18197-18204.
[25] ZHANG J, CHEN X, TAKANABE K, et al. Synthesis of a carbon nitride structure for visible-light catalysis by copolymerization[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(2): 441-444.
[26] VIJAYAKUMAR S, NAGAMUTHU S, MURALIDHARAN G. Supercapacitor studies on NiO nanoflakes synthesized through a microwave route[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(6): 2188-2196.
[27] HUANG L, XU H, LI Y, et al. Visible-light-induced WO3/g-C3N4composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2013, 42(24): 8606-8616.
[28] BOLDYREV V V. Thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2006, 443(1): 1-36.
[29] ZHANG W, LI P, XU H, et al. Thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate in the presence of Al(OH)3·Cr(OH)3nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 268: 273-280.
[30] SUN J, YUAN Y, QIU L, et al. Fabrication of composite photocatalyst g-C3N4-ZnO and enhancement of photocatalytic activity under visible light[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41(22): 6756-6763.
[31] THOMAS A, FISCHER A, GOETTMANN F, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride materials: variation of structure and morphology and their use as metal-free catalysts[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2008, 40(9):4893-4908.
[32] 谈玲华,李勤华,杭祖圣,等. 纳米NiO/MgO的制备及其对AP热分解催化性能影响[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2011, 34(2): 214-219.
TAN L H, LI Q H, HANG Z S, et al. Preparation of nanometer NiO/MgO and its catalytic performance for thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2011, 34(2): 214-219.
[33] GAO Y, WANG L, LI Z, et al. Preparation of MXene-Cu2O nanocomposite and effect on thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate[J]. Solid State Sciences, 2014, 35: 62-65.
--------------------●
Preparation of g-C3N4/NiO Composites and Its Effect onThermal Decomposition of Ammonium Perchlorate
TAN Ling-hua1,2,XU Jian-hua2,KOU Bo1,2,HANG Zu-sheng1,2,SHI Li-li2,WANG Jun2
(1 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials and Application Technology,Nanjing 211167,China;2 School of Materials Science and Engineering,Nanjing Institute of Technology,Nanjing 211167,China)
g-C3N4/NiO composites were prepared by a simple mixing-calcination method . The structure and morphology of g-C3N4/NiO were characterized by X-ray Diffraction(XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer(FT-IR), Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy(FESEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy(EDS). The catalytic effect of g-C3N4/NiO on thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate(AP) was investigated by Differential Thermal Analysis(DTA) and Thermo Gravimetric Analysis (TG). The results show that nanometer NiO is uniformly dispersed on the surface of g-C3N4, g-C3N4/NiO composites make the two decomposition peaks of AP combine and the high-temperature decomposition peak value of AP decrease by 62.5℃, which exhibits good catalytic performance. The catalytic activity of g-C3N4/NiO is much higher than that of single-phase g-C3N4and NiO, clearly demonstrating a synergistic effect between g-C3N4and NiO.
g-C3N4/NiO;ammonium perchlorate;catalysis;thermal decomposition;synergistic effect
10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.11.016
TB321
A
1001-4381(2016)11-0096-05
江苏省自然科学基金(BK20130747);江苏省高校自然科学研究课题(14KJD430002);江苏省先进结构材料与应用技术重点实验室开放基金(ASMA201408);南京工程学院校级科研基金项目(ZKJ201402)
2015-01-19;
2016-03-13
谈玲华(1978-),女,副教授,博士,从事纳米材料制备及性能研究,联系地址:南京市江宁科学园弘景大道1号南京工程学院材料工程学院(211167),E-mail:tanlinghua@njit.edu.cn
