RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料的合成及光催化性能
2016-12-22王辉虎董一帆马新国董仕节
芦 佳,王辉虎,2,董一帆,常 鹰,马新国,董仕节,2
(1 湖北工业大学 机械工程学院,武汉 430068;2 湖北工业大学绿色轻工材料湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430068;3 湖北工业大学材料学院,武汉 430068;4 湖北工业大学 理学院,武汉 430068)
RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料的合成及光催化性能
芦 佳1,王辉虎1,2,董一帆1,常 鹰3,马新国4,董仕节1,2
(1 湖北工业大学 机械工程学院,武汉 430068;2 湖北工业大学绿色轻工材料湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430068;3 湖北工业大学材料学院,武汉 430068;4 湖北工业大学 理学院,武汉 430068)
采用水热合成法制备ZnO纳米棒及RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料。研究不同含量的RGO对RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料光催化活性的影响。采用X射线衍射仪(XRD)、场发射电子显微镜(FESEM)、光电子能谱仪(XPS)及漫反射紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis)检测手段对RGO/ZnO进行表征。结果显示:RGO与ZnO纳米棒成功复合。加入GO的含量不同,获得的RGO/ZnO样品在可见光区域的吸光度值不同。以甲基橙作为模拟污染物的光催化结果表明,RGO/ZnO复合材料具有高的紫外-可见光光降解效率,加入GO与ZnO的质量比为3%时,样品紫外-可见光光催化性能最佳,120min内甲基橙基本可以完全降解;且在波长大于400nm可见光照射下,RGO/ZnO具有一定的可见光活性,180min内其降解甲基橙效率最大可达26.2%。同时,RGO/ZnO具有较好的光稳定性。
还原石墨烯;ZnO;光催化;甲基橙
近年来,利用纳米半导体对有机污染物进行净化已引起广泛关注。ZnO具有价格低廉、无毒、生产工艺简单及性能稳定等优点[1,2],但是,ZnO作为光催化剂在实际应用中还存在一些问题。一方面,光生载流子的快速复合导致ZnO具有较低的量子效率和较差的光催化效率[3,4];另一方面,ZnO在室温下禁带宽度为3.37eV[5,6],较大的禁带宽度限制其只能在紫外光作用下被激发。因此,人们采用了不同的方法来提高ZnO光催化活性及其吸收光波长,如贵金属修饰[7,8]、金属化合物沉积[9,10]等。但这些改性方法工艺复杂、制备条件苛刻、成本高。此后碳纳米管、石墨烯等碳系材料相继出现,由于它们的特殊性能被逐渐引入到光催化体系中并受到了广泛重视。石墨烯是由sp2-键片层碳原子组成的二维晶格材料,具有较高导电性、高载流子迁移率(2×105cm2·V-1·s-1)、大比表面积(2600m2·g-1)[11,12]。目前,石墨烯表面沉积金属或与金属氧化物复合所获得的复合材料被证明具有优异的光催化性能[13,14]。但是石墨烯的不溶性与难加工性使得其实际使用受到极大限制。
还原石墨烯(Reduced Graphene Oxide,RGO)是先氧化石墨烯得到氧化石墨烯(Graphene Oxide,GO),之后还原去除GO表面含氧官能团获得的产物,其层间距远大于石墨烯。通常采用的还原方法有化学法[15]、电化学法[16]和热还原法[17]等。RGO与石墨烯特性相似,将其引入到光催化体系中形成的还原石墨烯基复合材料同样具有优异的光催化特性。Liu等[6]在非水介质中采用微波辅助将分散的纳米ZnO颗粒沉积在RGO片上,发现RGO的复合不但能增加ZnO的比表面积,而且能促进光生电子的传输转移。Liu等[18]采用紫外线辅助催化法合成RGO/ZnO粉末。研究发现,RGO/ZnO紫外光降解Cr(VI)效率比纯ZnO高30%。Zhang等[19]通过机械混合RGO粉末与ZnO纳米颗粒,发现混合物在紫外光照射下降解亚甲基蓝的效果显著。Pant等[4]采用花状ZnO和Ag纳米颗粒复合RGO片,同样发现获得的复合材料表现出优良的紫外光光催化性能。Dong等[20]将氧化锌纳米团簇嵌入RGO纳米片,发现复合后的RGO/ZnO具有可见光活性,且降解甲硝哒唑效率比纯ZnO高32.4%。
与传统的ZnO粉末相比,ZnO纳米棒具有较高的光捕获率、较大的比表面积及较快的光生电子转移速率[21]。但很少有人采用ZnO纳米棒复合RGO片来制备RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料,并研究其光催化性能[5]。本工作在水热法制备ZnO纳米棒的基础上,通过同时加入GO粉末,利用水热过程中GO粉末的还原,一步合成RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料。利用X射线衍射仪、场发射电子显微镜、光电子能谱仪及漫反射紫外-可见吸收光谱等研究了RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料的微观特性,并将甲基橙(Methyl Orange,MO)作为模拟污染物,研究了RGO含量对RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料的光催化性能及光稳定性的影响规律,分析了其光催化机制。
1 实验材料与方法
实验中所用原料均为分析纯。GO采用Hummer法[22]制得。在反应器中倒入一定量的浓硫酸,加入2g石墨粉、1g硝酸钠和6g高锰酸钾搅拌,控制反应温度低于20℃。反应一段时间后升温至35℃,继续搅拌2h。然后缓慢加入少量的去离子水,98℃搅拌15min后,加入适量双氧水还原残留的氧化剂使溶液变为亮黄色,趁热过滤,采用5~8mL的盐酸溶液及去离子水洗涤,直到滤液中无硫酸根被检测到为止。最后将样品置于真空干燥箱中充分干燥得到GO粉末。
RGO/ZnO采用一步水热法制备。将0.58g乙酸锌和0.53g氢氧化钠与一定量的GO混合,加入80mL无水乙醇,25℃下搅拌30min。将获得的混合溶液转移至反应釜内,密封加热到160℃,保温24h后自然冷却至室温,取出进行抽滤、洗涤。重复上述步骤3~5次后于60℃干燥12h,研磨得到RGO/ZnO样品。根据加入的GO量不同,将GO与ZnO质量比为1%,3%,5%,7%的样品分别记为1%RGO/ZnO,3%RGO/ZnO,5%RGO/ZnO,7%RGO/ZnO。
配置20mg/L的甲基橙(MO)溶液,加入50mg的RGO/ZnO粉末,振荡、搅拌获得均匀混合溶液。以300W氙灯为光源,对其光照120min。可见光光催化活性测试时,采用400nm滤光片滤去紫外光。反应过程中每15min取一次试样,离心取上层MO清液,采用紫外分光光度计测试,在464nm处取得吸光度值,计算其浓度。
光稳定性研究选用3%RGO/ZnO样品进行测试,采用上述方法,经过紫外-可见光照射120min,之后将反应产物洗涤抽滤,然后放入干燥箱内干燥。循环5次后,根据MO降解效率的变化分析RGO/ZnO光稳定特性。
采用X射线粉末衍射仪(X’pert Pro MPD)分析样品晶相组成,扫描范围为10°~80°,扫描速率为2(°)/min;通过扫描电子显微镜(Quanta 450)观察分析样品表面形貌,加速电压为10kV;采用X射线光电子能谱仪(VG Multilab 2000)分析样品表面组成,XPS谱线峰位均以吸附的碳氢化合物的Cls(Eb= 284.6eV)谱为参照;通过紫外可见分光光度计(U-3900)对样品进行紫外漫反射光谱分析,以BaSO4作参照,扫描范围为200~700nm。
2 结果与分析
2.1 XRD分析
图1为RGO,ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品的XRD谱图。由图1可知,RGO样品XRD谱的衍射峰位于23.6°和42.6°,表明水热反应过程中GO在高温高压下成功还原成RGO,这与其他文献结果一致[23,24]。在ZnO及RGO/ZnO样品的XRD谱中,位于31.8°, 34.4°, 36.3°, 47.5°, 56.6°, 66.4°, 68.0°和69.9°的衍射峰对应于纤锌矿结构ZnO[25,26]。RGO/ZnO样品的衍射峰与纯ZnO一致,未出现明显的RGO衍射峰,这可能是因为RGO/ZnO粉末中的RGO含量极少,不易被检测出的缘故。

图1 RGO,ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品的XRD谱图Fig.1 XRD patterns of RGO,ZnO and RGO/ZnO samples
2.2 FESEM分析
图2为1%RGO/ZnO, 3%RGO/ZnO, 5%RGO/ZnO, 7%RGO/ZnO的FESEM照片。可以看出, 产物中RGO以分散的片状形式存在。经过水热反应后, 在片状RGO表面均可形成ZnO纳米棒且分布均匀,这可能是由于RGO片层表面具有多种极性含氧官能团,极性含氧基团使得Zn2+离子以氢键和静电吸附的方式结合在这些活性点上进一步水解,同时生成的ZnO能够有效阻止RGO片层间的相互作用[27]。GO加入量的增加,一方面,使RGO片层数量增加,片层表面生成的ZnO纳米棒也更加分散;另一方面,使负载ZnO的活性位点增多,RGO片层表面吸附的ZnO纳米棒也随之增多,促使RGO/ZnO复合材料片层尺寸有所增大。

图2 RGO/ZnO样品的FESEM图 (a)1%RGO/ZnO;(b)3%RGO/ZnO;(c)5%RGO/ZnO;(d)7%RGO/ZnOFig.2 FESEM images of RGO/ZnO samples (a)1%RGO/ZnO;(b)3%RGO/ZnO;(c)5%RGO/ZnO;(d)7%RGO/ZnO
2.3 XPS分析
通过XPS检测可以进一步分析RGO/ZnO样品的表面元素组成。图3为3%RGO/ZnO的C1s,O1s和Zn2p的XPS谱图。由图3(a)可以看出,C1s谱具有3个峰,分别位于284.6,286.3eV与288.5eV,对应C-C,C-O,C=O键[28,29]。图3(b)中O1s谱的两个峰分别位于531.2,532.9eV,前者为ZnO中的晶格氧,后者为RGO/ZnO中C-OH/C-O-C键的氧[26]。图3(c)中Zn2p的峰位于1021.8eV,表明Zn以Zn+的形式存在[28,30]。

图3 3%RGO/ZnO样品的C1s(a),O1s(b)和Zn2p(c) XPS谱图Fig.3 C1s(a),O1s(b) and Zn2p(c) XPS spectra of 3%RGO/ZnO sample
2.4 UV-Vis检测
图4为RGO,ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品的漫反射紫外-可见吸收光谱图,吸光曲线边缘在紫外光区域。由图4显示,纯RGO样品吸收光谱在260nm处有最大吸收峰。纯ZnO样品呈白色,加入RGO后颜色发生改变。随着RGO含量的不断增加,RGO/ZnO颜色从白色逐渐变成黑色,由于物质的颜色越深,吸光度值越大,因此RGO/ZnO样品在可见光区域内的吸光度值随GO含量的增加而增加,此结果与其他文献一致[1,31]。

图4 RGO,ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品的UV-Vis谱图Fig.4 UV-Vis spectra of RGO,ZnO and RGO/ZnO samples
2.5 光催化性能
图5为ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品在紫外-可见光照射下降解MO效率曲线。由图5可知, RGO/ZnO都具有优异的光催化活性。相比与纯ZnO,RGO/ZnO降解MO效率明显提高。同时,GO的加入量对RGO/ZnO纳米棒复合材料的光催化活性具有很大影响。3%RGO/ZnO样品的MO降解效率最高,在120min内达到97.5%。但随着GO加入量的继续增加,MO降解率开始下降。这可能是因为RGO自身能吸收紫外光,随着加入的GO量不断增多并超过3%时,ZnO与RGO之间存在着光捕获竞争关系,减少了ZnO纳米棒的光吸收。除此之外,过量的RGO可能会充当光生电荷的复合载体,抑制光生电子与空穴的分离,最终降低RGO/ZnO的光催化活性[18,32]。
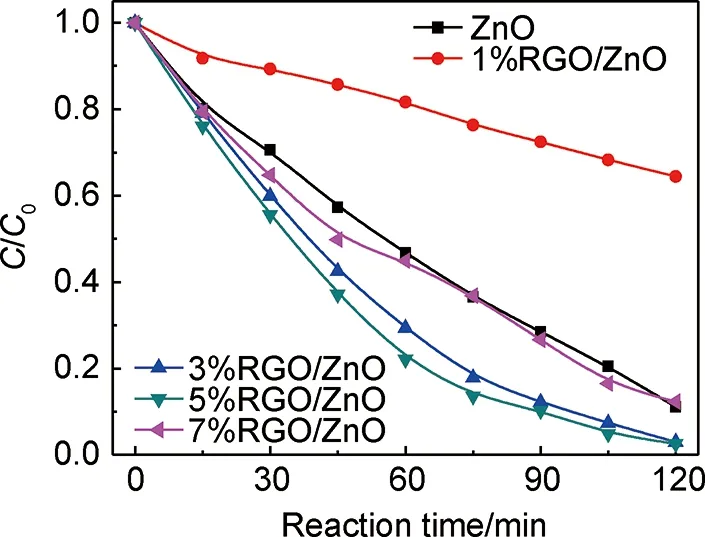
图5 ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品紫外-可见光降解MO曲线Fig.5 Degradation curves of MO for ZnO and RGO/ZnO samples under UV-Vis
图6为ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品在可见光照射下降解MO曲线。可以看出,纯ZnO没有可见光催化活性,但复合了RGO后,可见光下对MO具有降解效果。根据加入的GO量不同,RGO/ZnO光催化降解MO效率为:3%RGO/ZnO >5%RGO/ZnO > 1%RGO/ZnO > 7%RGO/ZnO。3%RGO/ZnO样品的可见光光催化性能最佳,180min内甲基橙降解效率达26.2%。

图6 ZnO和RGO/ZnO样品可见光降解MO曲线Fig.6 Degradation curves of MO for ZnO and RGO/ZnO samples under visible irradiation
图7为3%RGO/ZnO紫外-可见光照射下循环降解MO的柱状图。可知经过5次循环使用后,3%RGO/ZnO降解MO效率基本保持不变。实验结果表明RGO/ZnO复合材料光稳定性较好。
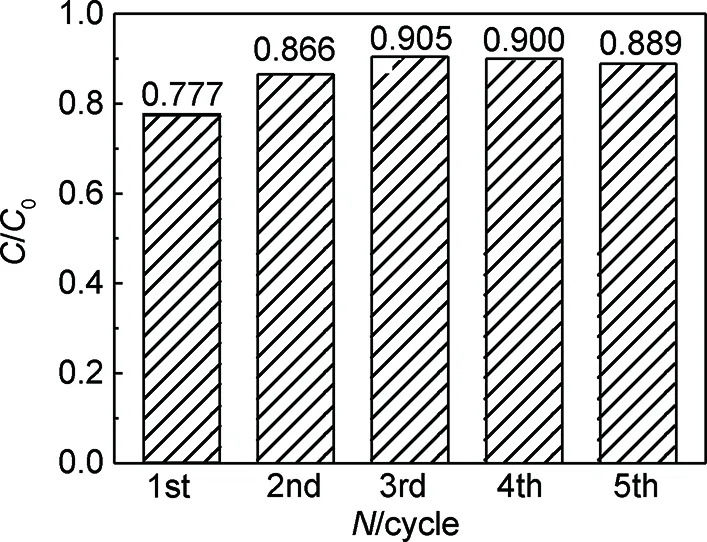
图7 3%RGO/ZnO样品5次循环降解MO图Fig.7 Degradation of MO for 3%RGO/ZnO sample for five cycles
3 结论
(1)采用一步水热法,以ZnO纳米棒为载体成功制备了RGO/ZnO纳米复合材料。随着复合材料中RGO含量的增加,RGO/ZnO纳米复合材料中层片状物质尺寸增大,同时其在可见光区域的吸光度值增加。
(2)光催化降解甲基橙的实验结果表明,3%RGO/ZnO样品在紫外-可见光照射下光催化活性最佳,其在120min内降解甲基橙的效率是纯ZnO的2.5倍;在波长大于400nm的可见光照射下,该样品在180min内降解甲基橙的效率达到26.2%,表明RGO/ZnO纳米复合材料具有一定的可见光活性。
(3)5次循环光降解甲基橙实验结果表明,3%RGO/ZnO复合材料具有较好的光稳定性。
[1] SAFA S,SARRAF-MAMOORY R,AZIMIRAD R.Investigation of reduced graphene oxide effects on ultra-violet detection of ZnO thin film[J].Physica E:Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostruc-tures,2014,57:155-160.
[2] KUMAR K,CHITKARA M,SANDHU S I,et al.Photocatalytic,optical and magnetic properties of Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by chemical route[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2014,588:681-689.
[3] LI D,HUANG J F,CAO L Y,et al.Microwave hydrothermal synthesis of Sr2+doped ZnO crystallites with enhanced photocatalytic properties[J].Ceramics International,2014,40(2):2647-2653.
[4] PANT H R,PANT B,KIM H J,et al.A green and facile one-pot synthesis of Ag-ZnO/RGO nanocomposite with effective photocatalytic activity for removal of organic pollutants[J].Ceramics International,2013,39(3):5083-5091.
[5] HUANG K,LI Y H,LIN S,et al.A facile route to reduced graphene oxide-zinc oxide nanorod composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J].Powder Technology,2014,257(5):113-119.
[6] LIU Y,HU Y,ZHOU M,et al.Microwave-assisted non-aqueous route to deposit well-dispersed ZnO nanocrystals on reduced graphene oxide sheets with improved photoactivity for the decolorization of dyes under visible light[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2012,125(33):425-431.
[7] LAI Y,MENG M,YU Y,et al.One-step synthesis,characterizations and mechanistic study of nanosheets-constructed fluffy ZnO and Ag/ZnO spheres used for Rhodamine B photodegradation[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2010,100(3-4):491-501.
[8] LI P,WEI Z,WU T,et al.Au-ZnO hybrid nanopyramids and their photocatalytic properties[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2011,133(15):5660-5663.
[9] KUNDU P,DESHPANDE P A,MADRAS G,et al.Nanoscale ZnO/CdS heterostructures with engineered interfaces for high photocatalytic activity under solar radiation[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry,2011,21(12):4209-4216.
[10] SHI L,LIANG L,MA J,et al.Improved photocatalytic performance over AgBr/ZnO under visible light[J].Superlattices and Microstructures,2013,62:128-139.
[11] ZHOU Q,ZHONG Y H,CHEN X,et al.Mesoporous anatase TiO2/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites:a simple template-free synthesis and their high photocatalytic performance[J].Materials Research Bulletin,2014,51(2):244-250.
[12] WANG X W,ZHOU L,LI F.ZnO disks loaded with reduced graphene oxide for the photodegradation of methylene blue[J].New Carbon Materials,2013,28(6):408-413.
[13] HUANG Q,TIAN S,ZENG D,et al.Enhanced photocatalytic activity of chemically bonded TiO2/graphene composites based on the effective interfacial charge transfer through the C-Ti bond[J].ACS Catalysis,2013,3(7):1477-1485.
[14] ZENG B,CHEN X,LUO Y,et al.Graphene spheres loaded urchin-like CuxO (x=1 or 2) for use as a high performance photocatalyst [J].Ceramics International,2014,40(3):5055-5059.
[15] KAVERI S,THIRUGNANAM L,DUTTAB M,et al.Thiourea assisted one-pot easy synthesis of CdS/rGO composite by the wet chemical method:structural,optical,and photocatalytic properties[J].Ceramics International,2013,39(8):9207-9214.
[16] LI X,XU X,XIA F,et al.Electrochemically active MnO2/RGO nanocomposites using Mn powder as the reducing agent of GO and the MnO2precursor[J].Electrochimica Acta,2014,130(4):305-313.
[17] NAGARAJU G,EBELING G,GONCALVES R V,et al.Controlled growth of TiO2and TiO2-RGO composite nanoparticles inionic liquids for enhanced photocatalytic H2generation[J].Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical,2013,378(11):213-220.
[18] LIU X,PAN L,ZHAO Q,et al.UV-assisted photocatalytic synthesis of ZnO-reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity in reduction of Cr(VI)[J].Biochemical Engineering Journal,2012,183(4):238-243.
[19] ZHANG L,DU L,CAI X,et al.Role of graphene in great enhancement of photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticle-graphene hybrids[J].Physica E:Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures,2013,47(5):279-284.
[20] DONG S,LI Y,SUN J,et al.Facile synthesis of novel ZnO/RGO hybrid nanocomposites with enhanced catalytic performance for visible-light-driven photodegradation of metronidazole [J].Materials Chemistry and Physics,2014,145(3):357-365.
[21] 薄小庆,刘唱白,何越,等.多孔纳米棒氧化锌的制备及其气敏特性[J].材料工程,2014,(8):86-89.
BO X Q,LIU C B,HE Y,et al.Fabrication and gas sensing properties of porous ZnO nanorods[J].Journal of Materials Engineering,2014,(8):86-89.
[22] HUMMERS W S Jr,OFFEMAN R E.Preparation of graphitic oxide[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,1958,80(6):1339-1339.
[23] RUAN C,ZHANG L,QIN Y,et al.Synthesis of porphyrin sensitized TiO2/graphene and its photocatalytic property under visible light[J].Materials Letters,2015,141:362-365.
[24] HU J,LI H,WU Q,et al.Synthesis of TiO2nanowire/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites and their photocatalytic performances[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,263:144-150.
[25] SUN H,LIU S,LIU S,et al.A comparative study of reduced graphene oxide modified TiO2,ZnO and Ta2O5in visible light photocatalytic/photochemical oxidation of methylene blue[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2014,146(3):162-168.
[26] LIU I T,HON M H,TEOH L G,et al.The preparation,characterization and photocatalytic activity of radical-shaped CeO2/ZnO microstructures[J].Ceramics International,2014,40(3):4019-4024.
[27] 龙梅,丛野,李轩科,等.部分还原氧化石墨烯/二氧化钛复合材料的水热合成及其光催化活性[J].物理化学学报,2013,29(6):1344-1350.
LONG M,CONG Y,LI X K,et al.Hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic activity of partially reduced graphene oxide/TiO2composite[J].Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2013,29(6):1344-1350.
[28] FENG Y,FENG N N,WEI Y Z,et al.An in situ gelatin-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO-reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic performance under ultraviolet and visible light[J].RSC Advances,2014,4(16):7933-7943.
[29] LIU X,DU H,SUN X W,et al.High-performance photoresponse of carbon-doped ZnO/reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanocomposites under UV and visible illumination[J].RSC Advances,2014,4(10):5136-5140.
[30] LI Y,ZHANG B P,ZHAO J X.Enhanced photocatalytic performance of Au-Ag alloy modified ZnO nanocomposite films[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2014,586:663-668.
[31] WANG P,WANG J,WANG X,et al.One-step synthesis of easy-recycling TiO2-rGO nanocomposite photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J].Applied Catalysis B:Environmental,2013,132-133(12):452-459.
[32] YANG N L,ZHAI J,WANG D,et al.Two-dimensional graphene bridges enhanced photoinduced charge transport in dye-sensitized solar cells[J].ACS Nano,2010,4(2):887-894.
[33] ZHANG Y,ZHANG N,TANG Z R,et al.Graphene transforms wide band gap ZnS to a visible light photocatalyst:the new role of graphene as a macromolecular photosensitizer[J].ACS Nano,2012,6(11):9777-9789.
Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of RGO/ZnO Nanorod Composites
LU Jia1,WANG Hui-hu1,2,DONG Yi-fan1,CHANG Ying3,MA Xin-guo4,DONG Shi-jie1,2
(1 School of Mechanical Engineering,Hubei University of Technology,Wuhan 430068,China;2 Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Green Materials for Light Industry,Hubei University of Technology,Wuhan 430068,China;3 School of Materials Science and Technology,Hubei University of Technology,Wuhan 430068,China;4 School of Science,Hubei University of Technology,Wuhan 430068,China)
ZnO nanorods and RGO/ZnO nanorods composites were prepared by hydrothermal method. The influence of RGO content on the photocatalytic activity of RGO/ZnO nanorods composites was studied. ZnO nanorods and RGO/ZnO nanocomposites were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission electron microscopy (FESEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and diffuse reflectance UV-visible absorption spectroscopy techniques. The results show that RGO/ZnO samples are synthesized successfully. With different additions of GO, the RGO/ZnO samples obtained exhibit different absorption characteristics in visible light region. The photocatalytic results of using methyl orange (MO) as the simulated pollutant show that RGO/ZnO nanorods composites exhibit high degradation efficiency under UV-Vis light illumination. The highest photocatalytic performance is obtained for RGO/ZnO composites when the mass ratio of RGO to ZnO is 3%. MO is almost completely degraded in 120min. RGO/ZnO also shows the visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity under visible light illumination (λ>400nm), and the maximum MO degradation efficiency in 180min can reach 26.2%, meanwhile, RGO/ZnO samples exhibit good photostability.
reduced graphene oxide;ZnO;photocatalysis;methyl orange
10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.12.008
O643
A
1001-4381(2016)12-0048-06
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51202064,51472081);湖北省自然科学基金资助项目(2013CFA085);武汉市青年晨光科技计划资助项目(2013070104010016)
2015-01-09;
2016-04-27
王辉虎(1978-),男,副教授,博士,研究方向为纳米材料制备与性能,联系地址:湖北省武汉市洪山区南湖李纸路一村1号湖北工业大学机械工程学院(430068),E-mail:wanghuihu@126.com
