CXCR4对大鼠背根神经节中交感芽生形成的干预作用
2016-12-20杨悦橙马冰洁
杨悦橙 马冰洁 马 柯 △
(1复旦大学附属肿瘤医院麻醉科 上海 200032; 2上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院疼痛科 上海 200092)
CXCR4对大鼠背根神经节中交感芽生形成的干预作用
杨悦橙1马冰洁2马 柯2 △
(1复旦大学附属肿瘤医院麻醉科 上海 200032;2上海交通大学医学院附属新华医院疼痛科 上海 200092)
目的 研究CXCR4在大鼠脊神经结扎(spinal nerve ligation,SNL)后对背根神经节(dorsal root ganglion,DRG)交感芽生形成的干预作用。方法 将大鼠随机分为AMD3100(CXCR4特异抑制剂)实验组(n=16)、AMD3100对照组(n=8)、对照组(n=16)和空白对照组(n=16),对AMD3100实验组和对照组的大鼠行SNL术,术后7天内对AMD3100实验组大鼠每天给予AMD3100,术后3、5、7、10、14天(d3、d5、d7、d14)检测机械痛阈(mechanical withdrawal threshold,MWT),分别用实时PCR和Western blot检测神经生长因子(nerve growth factor,NGF)的RNA和蛋白质水平,d7和d14行免疫荧光检测DRG中交感芽生。结果 与对照组相比, AMD3100实验组大鼠在d5、d7和d14的MWT均显著缓解,抑制CXCR4后,AMD3100实验组大鼠DRG中交感芽生在d7较对照组显著减少,但在d14减少不明显,且NGF的RNA和蛋白质水平均较对照组显著降低。结论 抑制CXCR4能改善大鼠SNL术后d5~d14的疼痛行为,并能减少d7的蓝状结构数量。
交感芽生; 趋化素; 背根神经节; 大鼠
针对交感神经的治疗能在复杂区域疼痛综合征中使部分患者获益[1-2],但在带状疱疹后遗神经痛中疗效一般[3]。基础研究已在神经损伤、关节炎症动物模型中发现交感芽生现象,即在背根神经节(dorsal root ganglion,DRG)中交感纤维绕着神经元生长形成蓝状结构。被交感神经包绕着的神经元更易产生自发电活动[4],这也可能是交感神经相关治疗的机制。
研究发现神经生长因子(nerve growth factor,NGF)在交感芽生中起着重要的作用,大鼠鞘内注射NGF可引起交感芽生[5],且抑制NGF受体P75会导致交感芽生的形态紊乱[6]。近年来,趋化因子在神经病理疼痛中的作用日益受到关注[7],在神经损伤模型中发现趋化因子CXCL12及其受体CXCR4的表达上调[8],大鼠鞘内注射CXCL12可诱发疼痛至少2 h,且疼痛可被CXCR4的特异性抑制剂AMD3100所逆转。在胚胎发育阶段,CXCR4的表达可决定神经嵴细胞向DRG或交感神经节的分化。关于CXCR4与交感芽生的研究尚不多见。本研究旨在探索CXCR4对神经损伤后交感芽生形成的作用及其与NGF的关系。
材 料 和 方 法
动物模型与分组 SD大鼠56只,体质量200~250 g,饲养于新华医院SPF动物房,室温23 ℃,湿度50%~60%,每日光照12 h,自由获取水和饲料,实验前大鼠适应性喂养3天,所有动物实验均符合动物疼痛研究伦理学的要求。大鼠随机分为4组:空白对照组(n=16)、AMD3100实验组(n=16)、AMD3100对照组(n=8)和对照组(n=16)。AMD3100实验组和对照组大鼠腹腔注射10%水合氯醛(0.3 mL/100 g)麻醉后,同时行鞘内置管术和脊神经结扎(spinal nerve ligation,SNL),术后即刻AMD3100实验组给予AMD3100(0.5 μg/μL,10 μL),对照组予以生理盐水10 μL,两组大鼠术后第2天行利多卡因试验,置管成功大鼠继续实验。AMD3100实验组、AMD3100对照组和对照组大鼠在术后第3、5、7、10、14天(d3、d5、d7、d14)检测机械痛阈(mechanical withdrawal threshold,MWT),并在d3对AMD3100实验组和对照组大鼠取材行RT-PCR检测NGF,d7取材行Western blot检测NGF,d7和d14取材行免疫荧光观察交感芽生。
MWT检测 MWT由一位不了解分组情况且不参与数据处理的研究人员来实施。在基础状态和d3、d5、d7、d14检测MWT,检测时间限于上午9点至下午4点。检测前大鼠置于独立、避光暗盒至少15 min,MWT通过Von-frey纤维刺激大鼠术侧足底,刺激5次中3次能引起大鼠明显抬腿的最低纤维即为大鼠MWT,检测最高值限定为26 g。
Western blot检测 大鼠麻醉后置干冰上,快速取同侧L5 DRG, -80 ℃冻存。取材完毕后,加裂解液提上清,加入上样缓冲液,100 ℃加热3 min变性。应用十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳转至PVDF膜,5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭1 h,一抗于4 ℃封闭过夜(NGF,1∶2 000,美国CST公司;GAPDH,1∶1 000,碧云天生物技术研究所),对应二抗室温孵育1 h。增强化学发光法显影,化学发光成像系统记录影像,目标蛋白质与GAPDH标准化灰度值表示该蛋白质相对表达量,重复3次。
免疫荧光大鼠腹腔麻醉,4%多聚甲醛PBS灌注后取同侧L5 DRG,固定后蔗糖脱水。OTC包埋后于恒冷切片机中切片,切片厚度为15 μm,切片时每隔2张取1张。检测时,样本复温后置于5%驴血清室温封闭1 h,TH抗体(1∶1 000,美国Pel-freeze公司)4 ℃孵育48 h,冲洗后荧光二抗37 ℃孵育1 h。采用莱卡DMI-3000B型倒置荧光显微镜观察样本,TH阳性纤维包绕神经元50%的周长定义为TH阳性细胞[9]。在20倍物镜下随机选择6个视野,分别记录每个视野下TH阳性细胞数量。
RT-PCR检测 大鼠腹腔麻醉,无菌下快速取同侧L5 DRG置于Trizol中,-80 ℃冻存。NGF引物序列:5′-CCTTCAACAGGACTCACA-GG-3′ (正向),5′-TCTCCAACCCACACACTGAC-3′ (反向)。GAPDH引物序列:5′-GACATGCCG-CCTGGAGAAAC-3′ (正向),5′-AGCCCAGGAT-GCCCTTTAGT-3′ (反向)。应用PrimeScript RT Master MIX试剂盒(日本TaKaRa公司)逆转录为cDNA,采用SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM试剂盒(日本TaKaRa公司)扩增DNA,NGF相较于GAPDH的表达采用2△△CT法,同时检测熔解曲线确定扩增的特异性。
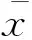
结 果
大鼠MWT改变AMD3100对照组和空白对照组大鼠在各个时间点的MWT均无显著差异。AMD3100实验组和对照组大鼠在d3的MWT均显著降低,两组之间差异无统计学意义。实验组大鼠MWT在d5较对照组显著缓解(t=2.8,P<0.01),并维持到d14(t=3.5,P<0.01)。然而,两组大鼠MWT之差约为3g(图1)。
交感芽生与蓝状结构 在空白对照组中无TH阳性纤维。SNL术后,大鼠DRG中交感芽生在d7显著增多,在d14有所减少但依然存在。在AMD3100实验组中,抑制CXCR4后大鼠DRG交感芽生在d7较对照组减少,且两组TH阳性细胞数的差异在d7有统计学意义(t=3.38,P<0.01),而在d14无统计学意义(P>0.05,图2)。
NGF的RNA和蛋白质水平 建立模型后d7,DRG中NGF的RNA和蛋白质水平均较空白对照组显著升高(P<0.01),且AMD3100实验组大鼠DRG中NGF表达均较对照组显著降低(P<0.01,图3、4)。
讨 论
本研究发现CXCR4在SNL大鼠的MWT和交感芽生中都起着重要的作用。虽然有研究发现鞘内抑制CXCR4可以缓解疼痛达2~4h,但AMD3100抑制CXCR4的效果无法持续24 h[10-11],但每日鞘内给予ADM3100仍然是一种长期抑制CXCR4的干预手段[12]。在本研究中,大鼠在脊神经结扎后出现疼痛行为和交感芽生,且CXCR4表达上调,提示模型建立成功且稳定。因疼痛模型的稳定与良好的对照,我们认为AMD3100实验组和对照组的差异是由鞘内注射AMD3100引起的。研究结果中行为学的显著性差异提示每日鞘内抑制CXCR4可以降低大鼠痛阈,且在停止给予AMD3100后,镇痛效果仍能维持7天。
There was no significant difference in mechanical withdrawal threshold between AMD3100 control group and naive group in all time points. There was no significant difference in mechanical withdrawal threshold between AMD3100 group and control group at the baseline and d3. The MWT in AMD3100 treatment group was significantly improved compared with those in control group at d5 (P<0.01), d7 (P<0.001), d10 (P<0.05) and d14 (P<0.01).
图1 SNL术后各组大鼠在不同时间点MWT的变化
Fig 1 MWT after SNL of rats in different groups at different time points
电生理研究认为蓝状结构是连接疼痛和交感系统的关键[4, 13],但其在疼痛行为中确切的功能至今仍是未知的。在许多研究中,干预措施包括注射曲安奈德和敲除IL-6都能减少蓝状结构,并能缓解疼痛[7, 14]。然而,至今尚无确切的研究证明其痛阈缓解是因为蓝状结构减少。在Kim等[15]的研究中,疼痛大鼠对酚妥拉明的敏感性与蓝状结构的密度无明显相关性,在Pertin等[9]的研究中,早期的交感神经毁损也不能缓解大鼠建立疼痛模型后的MWT,上述研究提示交感芽生在疼痛中并不起决定性的作用。在本研究中,术后14天蓝状结构的数量和交感芽生的密度显著少于术后7天,与文献[16]中术后28天蓝状结构少于术后7天的结果相符。研究发现早期的化学交感毁损不能改善保留坐骨神经结扎的大鼠术后28天的疼痛行为[9]。在本研究中,与术后7天相比,术后14天的疼痛行为并没有因为蓝状结构的减少而改善,这提示了交感芽生和蓝状结构在SNL大鼠术后14天的疼痛行为中并未起到决定性作用。
Immunofluorescence of TH in DRG in blank control group atd7 (A), AMD 3100 control group at d7 (B), control group at d7 (C), AMD3100 treatment group at d7 (d), control group at d14 (E), and AMD3100 group at d14 (F). G: The feature of the neuron wrapped by TH positive fibers at d14. The arrows in these figures indicated sympathetic sprouting, and the arrow heads indicated the basket-like structures. H: A significant difference in the numbers of neurons wrapped by TH positive fibers between two groups at d7 (t=3.38,P<0.01). A-G: Calibration bar=100 μm.
图2 SNL术后大鼠DRG中的蓝状结构与交感芽生
Fig 2 Sympathetic sprouting and basket-like structures in DRG of rats after SNL
The mRNA expression of NGF in the control group significantly increased compared to the blank control group (P<0.01). There was a significant difference in the mRNA expression of NGF between AMD3100 treatment group and control group (P<0.01).
图3 SNL术后d3大鼠DGR中NGF的mRNA水平
Fig 3 mRNA levels of NGF in DRG of rats at d3 after SNL
The grayscale of NGF band was defined as ratio of the grayscale of NGF and GAPDH, and the blot in the blank control group was regarded as a standardized control. The protein expression of NGF significantly increased atd7 after SNL (P<0.01). There was a significant difference in the protein expression of NGF between the AMD3100 treatment group and control group at d7 (P<0.01).
图4 SNL术后d7大鼠DGR中NGF的蛋白质水平
Fig 4 Protein levels of NGF in DRG of rats at d7 after SNL
免疫细胞在神经病理痛的发生和维持中起着重要的作用[7],巨噬细胞和T细胞均与交感芽生紧密相关,且缺乏IL-6的小鼠表达交感芽生减少,这提示可能是巨噬细胞释放的炎性因子参与交感芽生的发生和维持。研究提示全身或局部注射皮质醇药物能减少交感芽生,这可能是由于抑制了DRG中的炎性反应。在本研究中,我们发现持续抑制CXCR4在术后7天能显著减少蓝状结构数量,这提示CXCL12/CXCR4参与了交感芽生的过程。然而,此现象在术后14天并不明显,这可能是由于术后14天蓝状结构数量较少。因此我们认为蓝状结构的减少并不是改善疼痛行为最关键的原因,CXCL12/CXCR4可能通过独立于蓝状结构的其他机制改善大鼠疼痛。如在骨癌痛模型中,CXCL12/CXCR4可以通过兴奋神经元,激活星型胶质细胞和小胶质细胞参与疼痛的发生和维持[2]。
本研究中减少蓝状结构的机制可能包括神经细胞自发性放电和NGF的表达。研究显示,通过抑制神经元自发性放电可以减少蓝状结构[17],而趋化因子可以直接兴奋DRG神经元[18],抑制CXCR4可能通过抑制神经元电活动从而减少蓝状结构的形成,神经损伤后CXCL12的上调能激活钠离子通道NAV1.8[19],而蓝状结构的形成与NAV1.6相关[20],CXCL12/CXCR4是否通过钠离子通道参与蓝状结构的形成仍有待研究。另一方面,研究发现外源性NGF能显著增加蓝状结构的数量[5],本研究中抑制CXCR4后NGF的表达在RNA和蛋白质水平均下调,提示CXCR4使蓝状结构减少可能和NGF有关。已知DRG中卫星胶质细胞可以分泌NGF[21],且卫星胶质细胞和NGF的受体P75也有紧密的关系[6]。
本研究存在一定的局限性,尚不能确认大鼠疼痛行为改善是通过持续抑制CXCR4而减少蓝状结构的机制,也无法明确CXCR4调节NGF的机制,在疼痛模型中,NGF、蓝状结构、卫星胶质细胞的机制有待于进一步研究。综上所述,抑制CXCR4能改善大鼠SNL术后d5到d14的疼痛行为,并且能减少d7的蓝状结构数量,其机制可能与抑制NGF表达有关。
[1] ROCHA RDE O,TEIXEIRA MJ,YENA LT,etal. Thoracic sympathetic block for the treatment of complex regional pain syndrome type I: A double-blind randomized controlled study [J].Pain, 2014,155(11): 2274-2281.
[2] O′CONNELL NE,WAND BM,GIBSON W,etal. Local anaesthetic sympathetic blockade for complex regional pain syndrome [J].CochraneDatabaseSystRev, 2016,7:7CD004598.
[3] DWORKIN RH,O′CONNOR AB,KENT J,etal. Interventional management of neuropathic pain: NeuPSIG recommendations [J].Pain, 2013,154(11):2249-2261.
[4] XIE W,STRONG JA,MAO J,etal. Highly localized interactions between sensory neurons and sprouting sympathetic fibers observed in a transgenic tyrosine hydroxylase reporter mouse [J].MolPain, 2011,7: 53.
[5] JONES MG,MUNSON JB,THOMPON SW. A role for nerve growth factor in sympathetic sprouting in rat dorsal root ganglia [J].Pain, 1999,79(1):21-29.
[6] WALSH GS,KROL KM,KAWAJA MD. Absence of the p75 neurotrophin receptor alters the pattern of sympathosensory sprouting in the trigeminal ganglia of mice overexpressing nerve growth factor [J].JNeurosci, 1999,19(1):258-273.
[7] SCHOLZ J,WOOLF CJ. The neuropathic pain triad: neurons,immune cells and glia [J].NatNeurosci, 2007,10(11):1361-1368.
[8] DUBOVY P,KLUSAKOVA I,SVIZENSKA I,etal. Spatio-temporal changes of SDF1 and its CXCR4 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia following unilateral sciatic nerve injury as a model of neuropathic pain [J].HistochemCellBiol, 2010,133(3):323-337.
[9] PERTIN M,ALLCHORNE AJ,BEGGAH AT,etal. Delayed sympathetic dependence in the spared nerve injury (SNI) model of neuropathic pain [J].MolPain, 2007,3: 21.
[10] MENICHELLA DM,ABDELHAK B,REN D,etal. CXCR4 chemokine receptor signaling mediates pain in diabetic neuropathy [J].MolPain, 2014,10: 42.
[11] WILSON NM,JUNG H,RIPSCH MS,etal. CXCR4 signaling mediates morphine-induced tactile hyperalgesia [J].BrainBehavImmun, 2011,25(3):565-573.
[12] SHEN W,HU XM,LIU YN,etal. CXCL12 in astrocytes contributes to bone cancer pain through CXCR4-mediated neuronal sensitization and glial activation in rat spinal cord [J].JNeuroinflammation, 2014,11: 75.
[13] MCLACHLAN EM,JANIG W,DEVOR M,etal. Peripheral nerve injury triggers noradrenergic sprouting within dorsal root ganglia [J].Nature, 1993,363(6429):543-546.
[14] LI JY,XIE W,STRONG JA,etal. Mechanical hypersensitivity,sympathetic sprouting,and glial activation are attenuated by local injection of corticosteroid near the lumbar ganglion in a rat model of neuropathic pain [J].RegAnesthPainMed, 2011,36(1):56-62.
[15] KIM HJ,NA HS,SUNG B,etal. Is sympathetic sprouting in the dorsal root ganglia responsible for the production of neuropathic pain in a rat model? [J].NeurosciLett, 1999,269(2):103-106.
[16] LEE BH,YOON YW,CHUNG K,etal. Comparison of sympathetic sprouting in sensory ganglia in three animal models of neuropathic pain [J].ExpBrainRes, 1998,120(4):432-438.
[17] ZHANG JM,LI H,MUNIR MA. Decreasing sympathetic sprouting in pathologic sensory ganglia: a new mechanism for treating neuropathic pain using lidocaine [J].Pain, 2004,109(1-2):143-149.
[18] DAWES JM,MCMAHON SB.Chemokines as peripheral pain mediators [J].NeurosciLett, 2013,557 Pt A:1-8.
[19] YANG F,SUN W,YANNG Y,etal. SDF1-CXCR4 signaling contributes to persistent pain and hypersensitivity via regulating excitability of primary nociceptive neurons: involvement of ERK-dependent Nav1.8 up-regulation [J].JNeuroinflammation, 2015,12: 219.
[20] XIE W,STRONG JA,ZHANG JM. Local knockdown of the NaV1.6 sodium channel reduces pain behaviors,sensory neuron excitability,and sympathetic sprouting in rat models of neuropathic pain [J].Neuroscience, 2015,291: 317-330.
[21] CHENG CF,CHENG JK,CHEN CY,etal. Mirror-image pain is mediated by nerve growth factor produced from tumor necrosis factor alpha-activated satellite glia after peripheral nerve injury [J].Pain, 2014,155(5):906-920.
Effect of CXCR4 on sympathetic sprouting in dorsal root ganglion of rats
YANG Yue-cheng1, MA Bing-jie2, MA ke2 △
(1DepartmentofAnesthesiology,FudanUniversityShanghaiCancerCenter,Shanghai200032,China;2DepartmentofPainManagement,XinhuaHospital,SchoolofMedicine,ShanghaiJiaoTongUniversity,Shanghai200092,China)
Objective To explore the role of CXCR4 in sympathetic sprouting in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) after spinal nerve ligation (SNL) in rats. Methods Rats were randomly divided into AMD3100 treatment group (n=16), control group (n=16),AMD3100 control group (n=8) and naive group (n=16). SNL was performed in the rats in AMD3100 treatment group and control group. AMD3100, the inhibitor of CXCR4, was injected intrathecally into the rats of AMD3100 treatment group 1-7 days after SNL. Mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) was detected at d3, d5, d7, d10 and d14. Real-time PCR and Western blot were applied to detect the levels of RNA and protein of nerve growth factor (NGF), respectively. Sympathetic sprouting in DRG was detected by immunofluorescence at d7 and d14. Results The MWT of rats in AMD3100 treatment group was significantly improved compared with which in control group from d5 to d14. After the inhibition of CXCR4, sympathetic sprouting in DRG was dramatically decreased compared with which in control group at d7, but not at d14. In addition, The RNA and protein levels of rats in AMD3100 treatment group was significantly decreased compared with which of control group. Conclusions The inhibition of CXCR4 could not only improved pain behavior from d5 to d14, but also decreased basket-like structures at d7 after SNL.
sympathetic sprouting; chemokines; dorsal root ganglion; rat
国家自然科学基金面上项目(81371246)
R441.1
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2016.06.005
2016-03-07;编辑:段佳)
△Corresponding author E-mail:marke72@163.com
*This work was supported by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371246).
