Explore the medication rules of Chinese medicine of Professor Huang Wenzheng for the treatment of chronic kidney disease based on data mining
2016-09-14ShaoNingDongYaoGuangWangBingXuLiangJinCuiHanWang
Shao-Ning Dong,Yao-Guang Wang ,Bing Xu,Liang Jin,Cui-Han Wang
1Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine Affiliated Hospital,Tianjin,300120,China.2First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,300193,China.3Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Tianjin,300193,China.
1.Background
Chronic kidney disease(CKD)is a kind of kidney damage where the glomerular filtration rate(GFR)has been below the RSV 60ml(min 1.73 m2)for at least 3 months.The renal damage is diagnosed by either pathological abnormalities, or kidney damage experimental indexes (such as blood,urine,or abdominal images)[1].CKD refers to multiple diseases including chronic glomerulonephritis,IgA nephropathy and diabetic nephropathy.A recent national survey has demonstrated that the prevalence of CKD reached 10.8%in China[2].CKD has received increased attention due to its high prevalence,adverse effects,and tremendous medical cost[3].Current treatment options for chronic kidney disease are limited.Many patients seek alternative therapies such as traditional Chinese medicine(TCM).TCM has widely been used in the treatment of various diseases in China for thousands of years.TCM in the treatment of CKD can improve the clinical symptoms,reduce hematuria and proteinuria, alleviate western pharmaceuticals' adverse reactions,increase renal protection,and improve life quality of the patients,so as to improve the clinical curative effect of CKD.Research has revealed TCM could improve renal function through influencing glomerular filtration rate[4,5].

Figure1 Huang Wenzheng
Huang Wenzheng(August 5,1941-),male.The professor Huang Wensheng is the chief physician and doctoral tutor in the Department of Internal Medicine at the first Hospital Affiliated to Tianjin Traditional Chinese Medicine University.He also is the second and forth old Chinese Medical experts as well as an experienced inheritance guidance teacher.Prof.Huang has abundant experience to diagnose and treat CKD and achieved a good effect in treating CKD.The author collected the medial records of Professor Huang Wenzheng's traditional Chinese medicines for the treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis(CG),IgA nephropathy,diabetic nephropathy,and chronic renal failure to establish a structured medical record database.This study summarized professor Huang Wen Zheng's experience in the treatment of chronic kidney disease of herbal prescription law through retrospective analysis of clinical data and the data mining method.
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 Data Source
Collecting and collating medical records for CKD came from Professor.Huang Wenzheng in the TCM Nephropathy Clinic of First Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of TCM during Oct 20,2003 to Jan 13,2015.These records involved 131 cases and 1909 clinic visits,including CG without kidney biopsy;IgA nephropathy and diabetic nephropathy with kidney biopsy,as well as chronic renal failure progressed from the disease above with non-dialysis-requiring renal failure.
2.2 Diagnostic criteria
2.2.1 Western medicine diagnostic criteria
①In accordance with the diagnostic criteria for CKD in Kidney Disease Outcome Quality Initiative(K/DOQl)issued by National Kidney Foundation(NKF)in 2002.CKD refers to the disease of kidney damage or GFR less than 60ml/(min•1.73m2)lasting for at lease 3 months.Kidney damage refers to the renal pathological abnormalities,or renal damage experimental indexes(such as blood,urine or imaging abnormalities)[1,2].
②In accordance with the diagnostic criteria for Chronic nephritis in the standard developed by Kidney Disease Group of Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine editorial committee in Taiping,Anhui conference in Jun 1922[6].
③In accordance with the diagnostic criteria for IgA nephropathy in Guide on Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment:Clinical Practice Guidelines•Nephrology Volume[7]and Nephrology[8]issued by Kidney Disease Group of Chinese Medicine Association in 2012.
④In accordance with the diagnostic criteria for diabetic nephropathy in Guide on Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment: Clinical Practice Guidelines •Nephrology Volume[7]issued by Kidney Disease Group of Chinese Medicine Association in 2012 and clinical diagnostic criteria for diabetic nephropathy in WHO[9].
⑤In accordance with the diagnostic criteria for chronic renal failure in the standard developed by Kidney Disease Group of Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine editorial committee in Taiping,Anhui conference in June 1992[8].
2.2.2 TCM Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria
Should the original medical records contain Professor Huang Wenzheng’s notes,the original medical records shall prevail.
2.3 Medical Record Screening
2.3.1 Inclusion Criteria
The disease meets the diagnostic criteria of the 4 diseases stated above.The clinical data are complete and reliable.The patients have been treated with TCM decoction only,not taking other Chinese medicine.The patient hasn’t been taken dialysis.
2.3.2 Exclusion Criteria
Patients with severe infection;Myocardial infarction or heart failure; Hepatic insufficiency; Malignant hypertension and severe cerebrovascular disease;Diabetic ketoacidosis;Patients with malignancy and other emergent or severe illness;Patients who have received renal replacement;Lack of clinical data.
2.4.Research Methods
Establish a structured electronic medical record database with the help of“Information Sharing System of Medical Treatment and Clinical Research in TCM”(The sharing system for short).Log on to the database by using the PL/SQL Development software,use SQL statements to query the database,and save the query results.Use the Liquorice software to conduct homogeneous and heterogeneous network analyses by applying the complex network method,and extract 3 levels of prescription networks from the database.
3.Result
3.1 Analysis of prescription
3.1.1 Prescription for CG
The level 1 sub-network of the prescription for CG represented the initial part of Professor Huang’s prescription in clinical practice(Figure 1A),in which Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari)and Mai Dong(Radix Ophiopogonis)can nourish yin and benefit qi,Shan Yao(Rhizoma Dioscoreae),Fu Ling(Poria),and Sha Ren(Fructus Amomi Villosi)can invigorate spleen for eliminating dampness,Bai Mao Gen(Rhizoma Imperatae)can cool blood to stop bleeding.In the level 2 sub-network of the prescription,Bian Dou Yi(Semen Dolichoris Album),He Ye(Folium Nelumbinis),Si Gua Luo(Retinervus Luffae Fructus)and Liu Yi San consisted a commonly administrated herbal medicine prescription for summer-heat cold.The group of Dan Dou Chi(Semen Sojae Preparatum),Sang Ye(Folium Mori),She Gan(Rhizoma Belamcandae)and Ku Xing Ren(Semen Armeniacae Amarum)as well consisted a widely used herbal medicine prescription for wind-heat cough(Figure 1B).Moreover,the sub-network in the third level illustrated the paired herbs that Professor Huang used frequently for CG(Figure 1C).Combined with Wu Wei Zi(Fructus Schisandrae Chinensis),Wu Mei(Fructus Mume)can encourage production of body fluid to quench thirst and nourish yin to stimulate heart.The combination of Di Long(Lumbricus)and Hong Hua(Flos Carthami)can activate blood and dredge collaterals.Dong Kui Zi(Fructus Malvae)with Wang Bu Liu Xing(Semen Vaccariae)can relieve stranguria by diuresis. Additionly,Bai Wei(Radix Cynanchi Atrati),Yu Zhu(Rhizoma Polygonati Odorati)and Cong Bai(Bulbus Allii Fistulosi)can treat wind-heat cold associated with yin deficiency.Jiao Bin Lang(Semen Arecae),Ji Nei Jin(Endothelium Corneum Gigeriae Galli),Yu Jin(Radix Curcumae),Fo Shou(Fructus Citri Sarcodactylis),and Mai Ya(Fructus Hordei Germinatus)can treat gastrectasia and anorexia attributed by food accumulation and qi stagnation.Gua Lou (Fructus Trichosanthis),Xie Bai(Bulbus Allii Macrostemonis),Jiang Xiang(Lignum Dalbergiae Odoriferae),Yan Hu Suo(Rhizoma Corydalis),San Qi(Radix Notoginseng),Hu Bo(Succinum)and Gui Ban(Carapax Testudinis)can treat chest distress,angina and palpatataion.
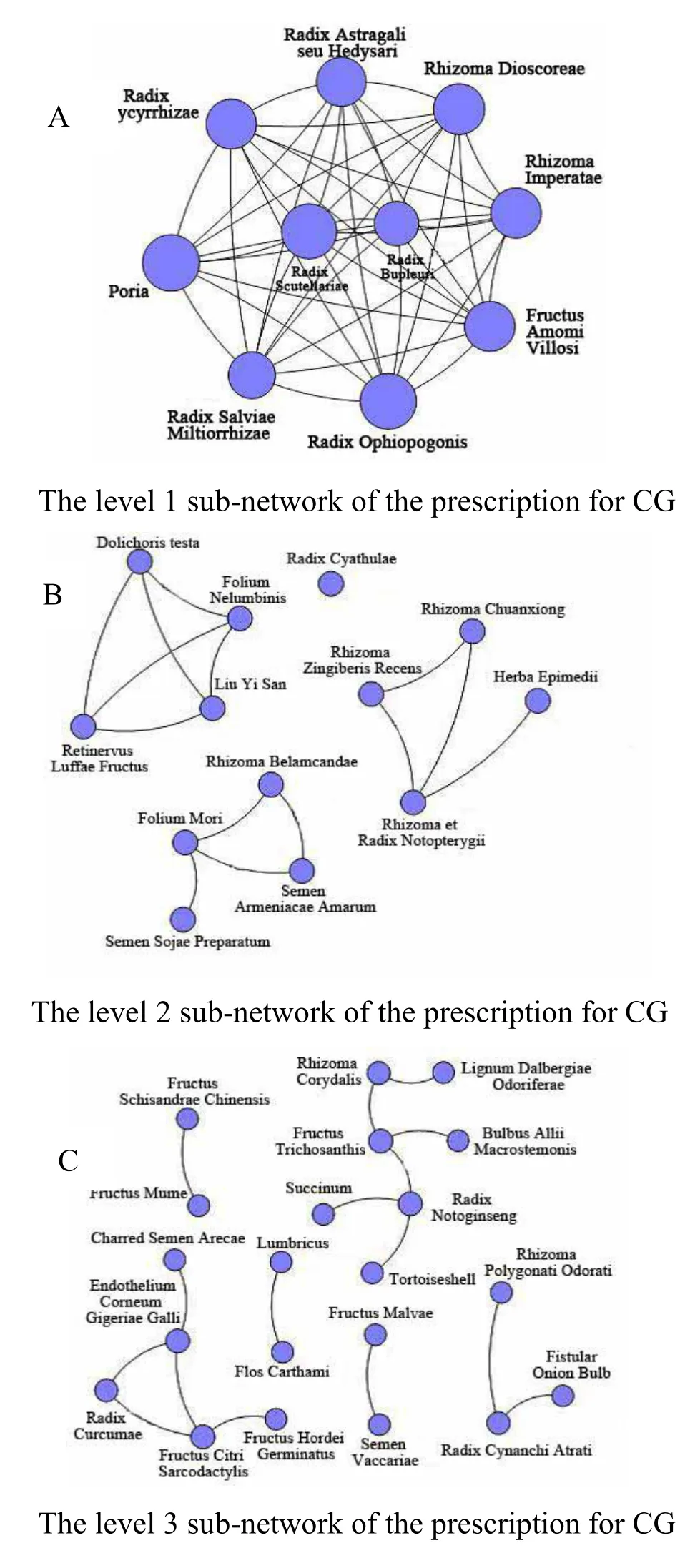
Figure 2Analysisof prescription for CG
3.1.2 Prescription analysis of IgA nephropathy
The core network analysis showed that Professor Huang used method of nourishing yin to benefit qi[Sheng Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Tai Zi Shen(Radix Pseudostellariae),Mai Dong(Radix Ophiopogonis)]combined with method of invigorating spleen for eliminating dampness[Sha Ren(Fructus Amomi Villosi),Bai Zhu (Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae),Fu Ling(Poria),Shi Wei(Folium Pyrrosiae), Bi Xie (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae)],and method of dredging sanjiao[Chai Hu(Radix Bupleuri),Huang Qin(Radix Scutellariae)]to treat IgA nephropathy(Figure 3).
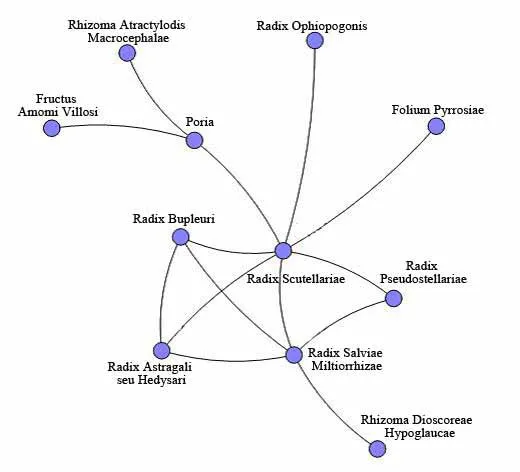
Figure 3 Prescription analysis of IgA nephropathy
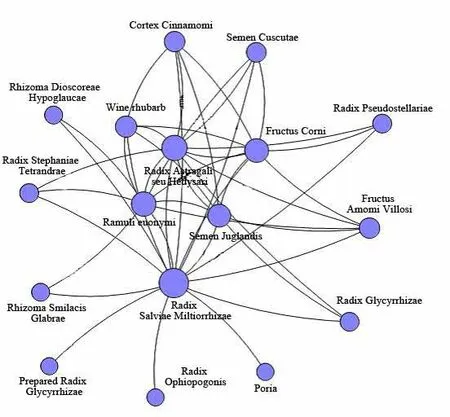
Figure 4 The Core Herbs Analysis for Diabetic Nephropathy
3.1.3 The Core Herbs Analysis for Diabetic Nephropathy
We found the core prescription for Diabetic Nephropathy(DN)according to backbone link analysis(Figure 4),in which Sheng Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Tai Zi Shen(Radix Pseudostellariae),Mai Dong(Radix Ophiopogonis)were used for tonifying qi and nourishing yin and Shan Zhu Yu(Fructus Corni),Rou Gui(Cortex Cinnamomi),Tu Si Zi(Semen Cuscutae)aimed to invigorate spleen and kidney.Fu Ling(Poria),Fang Ji(Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae), Bi Xie (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae),Tu Fu Ling(Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae)played the role of dampness remover and Gui Jian Yu(Ramulus Euonymi),Tao Ren(Semen Persicae),Jiu Da Huang (Radix et Rhizoma Rhei) acted as blood-invigorating workers.The prescription from Professor Huang was concocted for tonifying qi,nourishing yin and invigorating spleen and kidney to strengthen the foundation and invigorating blood and removing dampness to eliminate the symptoms.
3.1.4 The Core Herbs Analysis for Chronic Renal Failure

Figure 5 The Core Herbs Analysisfor CRF
In prescription for treating CRF,Sheng Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Mai Dong(Radix Ophiopogonis),Tai Zi Shen(Radix Pseudostellariae),Zhi Gan Cao(Radix Glycyrrhizae)were mainly for tonifying qi and nourishing yin,Dan Shen(Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae),Dang Gui(Radix Angelicae Sinensis),Yi Mu Cao(Herba Leonuri),Gui Jian Yu(Ramulus Euonymi),Jiu Da Huang(Radix et Rhizoma Rhei)were aimed to promote blood circulation and tonify blood.Fu Ling(Poria)and Sha Ren(Radix Adenophorae)were used for reinforcing the spleen,He Shou Wu(Radix Polygoni Multiflori)and Tu Si Zi(Semen Cuscutae)had the function of tonifying kidney.Tu Fu Ling(Poria)and Bi Xie(Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglauca)intended to remove dampness(Figure 5).Regulating qi xue yin yang is the main principle for treating CRF guided by Professor Huang,and we should pay close attention to invigorating spleen and replenishing qi and reinforcing kidney and activating blood circulation.
3.2 The study in drug usages

Table 1 Frequency statisticsof common herbs

3.2.1 Frequency statistics of common herbs
After calculating frequency of occurrences of 100 flavor herbs,herbs which showed more than 50 times(Table 1).The top 25 are Dan Shen(Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae),Fu Ling(Poria),Huang Qin(Radix Scutellariae),Sheng Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Sha Ren(Fructus Amomi Villosi),Mai Dong (Radix Ophiopogonis),Gan Cao (Radix Glycyrrhizae),Shan Yu Rou(Fructus Corni),Bi Xie(Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae),Chai Hu(Radix Bupleuri),Tai Zi Shen(Radix Pseudostellariae),Bai Mao Gen(Rhizoma Imperatae),Dang Gui(Radix Angelicae Sinensis),Shan Yao(Rhizoma Dioscoreae),Sheng Di Huang(Radix Rehmanniae Recens),Shi Wei(Folium Pyrrosiae),Lu Han Cao(Pyrola Calliantha),Di Jin Cao(Herba Euphorbiae Humifusae),Gui Jian Yu (Ramulus Euonymi), Bai Zhu (Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae),Ze Xie(Rhizoma Alismatis),Tu Fu Ling(Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae),Xiao Ji(Herba Cirsii),Yi Mu Cao(Herba Leonuri),Mu Dan Pi(Cortex Moutan Radicis).
3.2.2 The backbone network analysis for the commonly used medicine
The total commonly used medicines for the backbone network analysis consists of 19 herbs(Figure 6).They are classified into four groups according to their coordination efficiency.The first group are Di Jin Cao(Herba Euphorbiae Humifusae)and Ji Cai Hua(Capsella Bursapastoris Medic),which are the bases of bloody urine treatment;the second group are Jie Geng(Radix Platycodonis)and Gan Cao(Radix Glycyrrhizae)without explicitly clinical guiding significance;the third group are Fu Ling(Poria),Bai Zhu(Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae),Ze Xie (Rhizoma Alismatis),Mu Dan Pi(Cortex Moutan Radicis),Zhi Gan Cao(Radix Glycyrrhizae)and Sha Ren(Fructus Amomi Villosi),which are used for invigorating spleen for diuresis;the fourth group consist of several of herbs such as Tai Zi Shen(Radix Pseudostellariae)and Mai Dong(Radix Ophiopogonis)which are used for supplementing Qi and nourishing Yin;Chai Hu(Radix Bupleuri)and Huang Qin(Radix Scutellariae)which are used for reconciling Shaoyang;Bai Hua She She Cao (Herba Hedyotis) and Bi Xie (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglauca)which are used for clearing heat and promoting diuresis;Dan Shen(Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae)and Gui Jian Yu(Ramulus Euonymi)which are used for promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis and Bai Mao Gen(Rhizoma Imperatae)used for cooling blood and hemostasis.

Figure 6 The backbone network analysis for the commonly used medicine
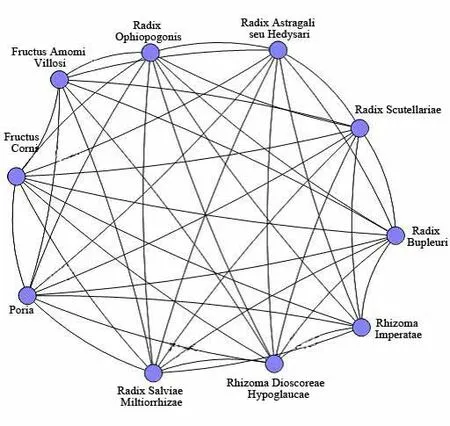
Figure 7 The level 1 sub-network for the commonly used medicine
3.2.3.Level 3 network analysis for the commonly used medicine
Level 1 sub-network represents 10 herbs for treating chronic kidney diseases,such as raw Huang Qi(Radix astragalis),Chai Hu(Radix Bupleuri),Huang Qin(Radix Scutellariae),Bai Mao Gen(Rhizoma Imperatae), Bi Xie (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae),Dan Shen(Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae),Fu Ling(Poria),Shan Zhu Yu(Fructus Corni),Sha Ren(Fructus Amomi Villosi)and Mai Dong(Radix Ophiopogonis)Shui Zhi(Hirudo)(Figure 7)
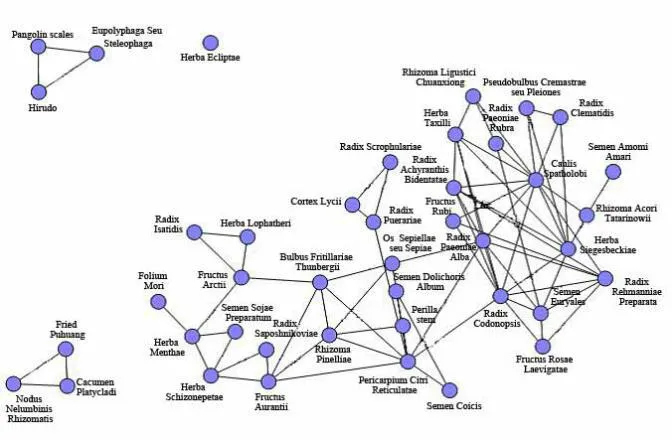
Figure8 Thelevel 2 sub-network for the commonly used medicine
Level 2 sub-network represents 42 herbs used for treating types of syndrome or principal syndrome and accompanying symptoms,which are divided into four groups(Figure 8).The first group is Mo Han Lian(Herba Ecliptae)used for deficiency of the liver and kidney;the second group are worm medicine such as Chuan Shan Jia(Squama Manis),Tu Bie Chong(Eupolyphaga Seu Steleophaga),which are used for treating collateral stasis and obstruction;the third group are herbs all used in cooling blood and hemostasis,such as Chao Pu Huang(Pollen Typhae),Ou Jie(Nodus Nelumbinis Rhizomatis)and Ce Bai Ye(Cacumen Platycladi),which are common drugs combination for treating in blood in the urine bleeding;the fourth group,there are 10 herbs on the left,such as Ban Lan Gen(Radix Isatidis),Zhu Ye(Herba Lophatheri),Niu Bang Zi(Fructus Arctii),Sang Ye(Folium Mori),Bo He(Herba Menthae),Dan Dou Chi(Semen Sojae Preparatum),Zhe Bei Mu(Bulbus Fritillariae Thunbergii), Jing Jie (Herba Schizonepetae),Fang Feng(Radix Saposhnikoviae)and Zhi Ke(Fructus Aurantii),which are used for expelling wind to resolve the exterior and clearing away heat and toxic materials,and specially treated in Wei phase syndrome,Qi phase syndrome and syndromes in upper-jiao.There are 9 herbs in the middle,such as Yuan Shen(Radix Scrophularia e),Di Gu Pi(Cortex Lycii),Ge Gen(Radix Puerariae),Hai Piao Shao(Os Sepiellae seu Sepiae),Bai Bian Dou(Semen Dolichoris Album),Zi Su Geng(Perilla Stem),Qing Ban Xia(Rhizoma Pinelliae Preparata),Chen Pi(Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae),and Chao Yi Yi Ren(Semen Coicis),which are used for nourishing Yin to adjust stomach,and especially treated in syndromes in the middle-jiao.There are 16 herbs on the right,and some herbs are inclined to treat diseases in lower-jiao,such as Sang Ji Sheng(Herba Taxilli),Niu Xi(Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae),Fu Pen Zi(Fructus Rubi),Jin Ying Zi(Fructus Rosae Laevigatae),Qian Shi(Semen Euryales),Yi Zhi Ren(Alpinia oxyphylla Miq),Shi Chang Pu(Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii),and Xi Xian Cao(Herba Siegesbeckiae),and some are used for treating blood phase syndromes,such as Chuan Qiong(Rhizoma Ligustici Chuanxiong),Chi Shao(Radix Paeoniae Rubra),Ji Xue Teng(Caulis Spatholobi),Bai Shao(Radix Paeoniae Alba)and Shu Di(Radix Rehmanniae Preparata).
Level 3 sub-network stands for the medication adjustment based on the symptoms, including commonly used paired drugs:Chao Gu Ya(Fructus Setariae Germinatus)-Chao Dao Ya(Fructus Oryzae Germinatus),Tian Ma(Rhizoma Gastrodiae)-Gou Teng(Ramulus Uncariae Cum Uncis),She Gan(Rhizoma Belamcandae)-Mu Hu Die(Semen Oroxyli),Chong Wei Zi(Fructus Leonuri)-Sheng Pu Huang(Pollen Typhae),Liu Ji Nu (Herba Artemisiae Anomalae)-Ma Bian Cao(Herba Verbenae),Yin Chen(Herba Artemisiae Scopariae)-Ji Gu Cao(Herba Abri),Shi Hu(Herba Dendrobii)-Jin Yin Hua(Flos Lonicerae)(Figure 9).

Figure 9 The level 3 sub-network for the commonly used medicine
Discussion
In the terms of treating CDK clinical practice by traditional Chinese medicine, Professor Huang Wenzheng advocated to treat these diseases on the basis of TCM syndrome differentiation and treatment and take western pathological diagnosis of diseases into consideration at the same time,which also called the combination of disease and syndrome differentiation.We can conclude the core prescription and triple drug laws of Professor Huang Wenzheng in treating CG,IgA nephropathy,diabetic nephropathy and renal failure by complex network analysis methods.The clinical features of therapeutic methods and herbs are as follows:1)tonifying qi and yin:Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Bai Zhu(Rhizoma Atractylodis Macrocephalae),Fang Feng (Radix Saposhnikoviae);2)strengthen spleen and nourish kidney:Sheng Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Shan Zhu Yu(Fructus Corni),Chai Hu(Radix Bupleuri), Dan Shen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae), Bi Xie (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae),Tu Fu Ling (Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae),Gui Jian Yu(Ramulus Euonymi),Tu Si Zi(Semen Cuscutae), Tai Zi Shen (Radix Pseudostellariae),Sha Ren(Fructus Amomi Villosi),Huang Qin(Radix Scutellariae),Gan Cao(Radix Glycyrrhizae),Shan Yao(Rhizoma Dioscoreae),Fu Ling(Poria),Dang Gui(Radix Angelicae Sinensis),Yi Mu Cao(Herba Leonuri);3)dispersing blood stasis and dredging collaterals:Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Tai Zi Shen(Radix Pseudostellariae),Dan Shen(Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae),Yi Mu Cao(Herba Leonuri),Gui Jian Yu(Ramulus Euonymi),Tao Ren(Semen Juglandis),Dang Gui(Radix Angelicae Sinensis),Tu Si Zi(Semen Cuscutae),Sha Ren(Fructus Amomi Villosi),Shan Zhu Yu(Fructus Corni),Fu Ling (Poria),Bi Xie (Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae),Huang Qin(Radix Scutellariae),Tu Fu Ling(Rhizoma Smilacis Glabrae),Tu Bie Chong(Eupolyphaga Seu Steleophaga);4)Shu-li triple energizer:Sheng Huang Qi(Radix Astragali seu Hedysari),Chai Hu(Radix Bupleuri),Huang Qin(Radix Scutellariae),Dan Shen (Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae),Tai Zi Shen(Radix Pseudostellariae),Mai Dong(Radix Ophiopogonis),Bi Xie(Rhizoma Dioscoreae Hypoglaucae),Shi Wei(Folium Pyrrosiae),Bai Mao Gen(Rhizoma Imperatae),Xiao Ji(Herba Cirsii),Bai Hua She She Cao(Herba Hedyotis),Zhu Ma Gen(Radix Boehmeriae),Di Jin Cao(Herba Euphorbiae Humifusae),Lu Han Cao (Pyrola Calliantha),Shan Zhu Yu(Fructus Corni).
Reference
1.National Kidney Foundation.K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease:evaluation,classification,and stratification.Am J Kidney Dis 2002,39(1):1-266.
2.Zhang L,Wang F,Wang L,et al.Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China:a cross-sectional survey.Lancet,2012,379(9818):815-22.
3.Gao B,Zhang L,Wang H,et al.Chinese cohort study of chronic kidney disease:design and methods. Chinese Medical Journal, 2014,127(11):2180-2185.
4.Lin M Y,Chiu Y W,Chang JS,et al.Association of prescribed Chinese herbal medicine use with risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2015,88(6):1365-1373.
5.Wen J,Xie X S,Zhang M H,et al.Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Guided by the Theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine:an Experimental Study.JSichuan Univ 2014,45(1):34-38.
6.Wang HY,Zheng FL,Liu WC,et al.Summary of the Symposium on the classification and diagnosis of primary glomerular diseases.Chin J Int med 1993,32(2):131-134.
7.Chen MX,Clinical Practice Guidelines •Nephrology Volume,Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House,2012.
8.Wang HY,Nephrology.Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House,2nd Edition,2001:708.
9.Ye RG,Lu ZY.Internal medicine,Fifth Edition.Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House,2003:810.
杂志排行
Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Feiji Recipe Reverses Lung Cancer Immune Escapeby Inhibiting the Expression of IDO
- Uncertainty profile for NIR analysis of tanshinone Icontent in tanshinone extract powders
- Computational study of the molecular mechanism of Lonicera japonica organic acidsagainst influenza
- Molecular docking study on the molecular mechanism of rhaponticin for treatment of chronic myelocytic leukemia
- The present treatment and mechanism progress of arsenic trioxide in hematological malignancies
- Traditional Chinese medicine should not beignored during the development of precision medicine with Chinese characteristics