The present treatment and mechanism progress of arsenic trioxide in hematological malignancies
2016-09-14LinLiuZhiGangZhao
Lin Liu,Zhi-Gang Zhao*
1Department of Hematology and Oncology,Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital,National Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China.
Introduction
Arsenic trioxide(ATO)is an important component of arsenic.The Chinese scholars first proved ATO could effectively treat acute promyelocytic leukemia(APL).The main mechanisms were inducing tumor cells apoptosis.With the in-depth study of ATO,it has been widely used in the treatment of various hematological malignancies,such as leukemia,multiple myeloma,myelodysplastic syndrome,lymphoma,and has been recognized around the world.This paper summarized the historical development of the ATO,and explained its roles and related mechanisms in hematologic malignancies.
1 The development history of ATO
Arsenic is characteristics as acrid and poisonous,subordinated to large intestine,stomach and lung meridian,which is used to relieve asthma,treat malaria and carbuncle.In ancient prescriptions,arsenic always was taken orally or externally.Considering the minimal available dosage of arsenic,it cannot be used alone but as compound.From old ages,arsenic has been seen as extremely poisonous medicine as it can attribute to serious adverse reactions included canner,gastrointestinal trauma and fetal damage.All of these factors limit the using of arsenic.Xiucheng Rong,a pharmacist in Heilongjiang province,who collected a prescription that could treat tumors from popular legend:the combination of arsenolite and calomel.In 1971,Taiyun Han,a pharmacist in Harbin Medical University,who extract ATO and Hg2CI2and product“Ailing No.1 injection” according to Rong’s prescription,which has been used widely to treat leukemia.However,the effectiveness of this injection is not obvious.Professor Tingdong Zhang et al combined it with TCM theory and chemotherapy to treat different kinds of leukemia.They concluded that the active ingredient of“Ailing No.1 injection” was ATO, which has the best effectiveness to promyelocytic leukemia.In 1990,China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences professor Hongde Sun et al reported the ATO for APL based on long follow-up to leukemia patients.After that,ATO has been widely used to manage hematological malignancies.
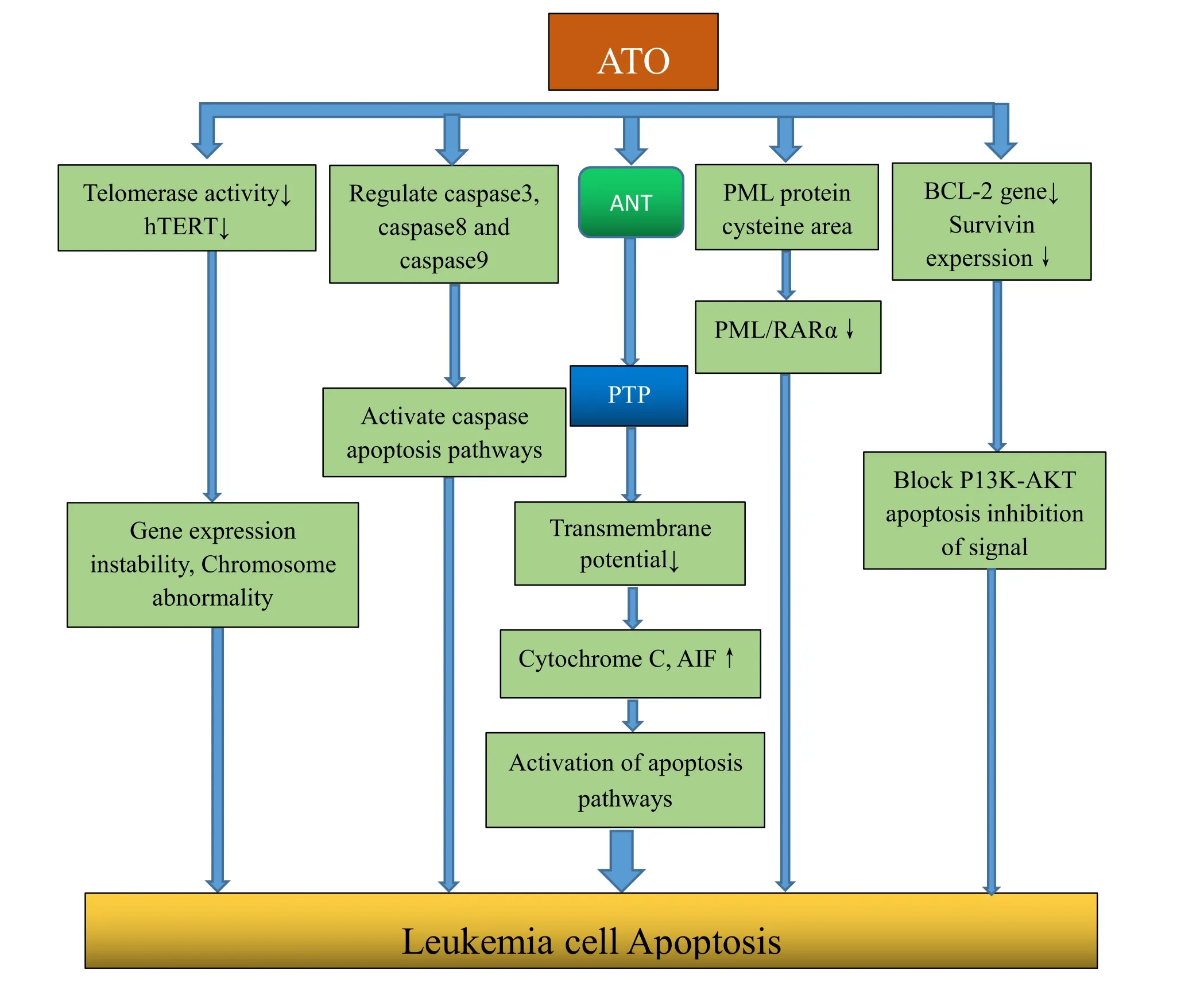
Figure 1 Anti-tumor mechanisms of ATO.
2 The anti-tumor mechanisms of ATO
2.1 ATO induces tumor cell apoptosis
ATO induced apoptosis is a multi-channel,multi-target process and is one of the main mechanisms of anti-tumor(Figure 1).①ATO induces apoptosis by degenerating PML/RARαprotein.ATO combines with cysteine-rich region in the PML protein,and thus resulting in PML/RARα protein degeneration,to achieve induction of APL cell apoptosis.②ATO combines to adenine nucleotide translocation(ANT),a protein located in the inner mitochondrial membrane,and promote mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore(PTP)open.PTP opening lead to mitochondrial transmembrane potential decreased or disappeared,then a series of biochemical reactions appear,and many kinds of protease activator release,such as cytochrome C,apoptosis-inducing factor(AIF),etc.The above factors could activate the apoptotic pathways and induce apoptosis.③ATO activates the apoptotic cascade pathway by regulating caspase 3,caspase 8 and caspase 9.Previous studies have found that caspase 8 and caspase 9 were exceptions in induced cells by ATO,and caspase inhibitor could prevent the effects induced by ATO.④
ATO reduces telomerase reverse transcriptase(hTERT)expression and inhibit the activity of telomerase to promote gene expressional instability and chromosomal abnormalities,which will lead to apoptosis.⑤ ATO regulates the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins.Previous studies found ATO significantly reduces expression of bcl-2 and survivin in the resistance cell lines(K562/ADM),blocking downstream signaling pathways to promote apoptosis.
2.2 ATO induces tumor cell differentiation
ATO have a certain effect of inducing differentiation on many types of blood cancer cells.Previous studies have found that the function of ATO on tumor cells played a dual role and was dose-related.High concentrations induce apoptosis,low concentrations cause incomplete differentiation.In vitro,low-dose(0.1-0.5μmol/L)ATOmain induced cell differentiation.Jing et al found 0.1-1.0μmol/L ATO major induced primary APL cells differentiation(20-30%of the cells differentiated only 10%apoptosis).ATO-induced cells showed nuclear cytoplasm ratio decreases,chromatin condensation and cytoplasmic neutral granules,CD11b expression increased and CD33 expression decreased.This kind of differentiation is partially,which was different from terminal differentiation induced by ATRA.Most differentiated cells induced by ATO were blocked in interphase cells phase tablets,and sustained ATOaction would lead cells to apoptosis ultimately.
2.3 Other mechanisms
In addition to the above mechanisms,ATO also exert anti-tumor effects by the following mechanisms:①ATO inhibits the expression of multidrug resistance protein,for example,the substrate(P-glycoprotein)of multidrug resistance protein 1(MDR1),to reverse multidrug resistance.In addition,the study found that ATO is not the substrate of P-glycoprotein and cannot be pumped out of the cell;P-glycoprotein is not involved in the transport and metabolism of ATO.This means that the probability of drug resistance of ATO is much lower than conventional chemotherapy drugs.②The sensitivity of tumor cells to ATO are inversely proportional with intracellular glutathione (GSH)levels.ATO combines with GSH,leading to intracellular redox imbalance,increasing the content of active oxygen species and inducing cells apoptosis.③ATO has an effect on cell cycle.Studies found out that ATO reduced the CDC2 kinase activity,increases p21 protein effect.This causes cell cycle arrest(in G1 phase or G2/M phase),thereby inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis.④ATO induces vascular endothelial cells and leukemia cells apoptosis,as well as reduce VEGF production so that the interaction between the two loops is broken,thereby inhibiting angiogenesis, ultimately inhibit cell proliferation leukemia.
Early researches mainly focused on that ATO could induce tumor cells apoptosis and differentiation,inhibit proliferation of tumor cell and tumor angiogenesis etc.With the rapid development of molecular biology in recent years,scholars have proposed ATO could enhance the immune response,inhibit of tumor stem cells.Low doses arsenic could induce glycolysis of normal tissues to protect normal tissue from chemotherapy etc.①ATO promotes the production of peroxynitrite(ONOO-)to consume regulatory T cells(Treg),thereby improving the anti-tumor activity of effector T cells,enhances tumor immune response.This provides a new strategy for tumor adoptive immunotherapy.②ATO bands to SHH-of GLI protein,inhibiting cancer stem cells’(CSCs)activity.ATO down regulates some stemness genes(ADAR,DTX2,WNT1,FGF1),inhibiting CSCs self-renewal and tumorigenicity.③ Low dose ATO selectively promotes normal tissue glycolysis and play a protective role.ZM Yuan et al found that low doses of ATO(100nM)could inhibit p53 gene expression of normal tissues,activate NF-κB,upregulate GLUF3,HIF1a and turnover normal tissue metabolism to glycolysis,thus normal tissues could resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs toxicity.
3 The application of ATO in treating hematological malignancy
3.1 Acute myeloid leukemia(APL)
As the most serious type of acute leukemia,acute myeloid leukemia(APL)often leads the patients to die due to severe hemorrhage and other reasons before treatment or during early treatment.Chinese scholars first used ATO to treat APL and have achieved remarkable efficacy.At present,APL has become the kind of acute leukemia which can receive the best curative effect.Early and rational use of ATO is of great significance for improving the cure rate and the prognosis of APL patients.The t(15;17)translocation of APL cells leads to the fusion of PML gene and RARα (retinoic acid receptorα)gene,producing the PML-RARα fusion gene and expressing related proteins,which finally result in leukemia.Earlier studies found that ATO could induce apoptosis of APL cells by degrading the PML-RARαfusion protein.Subsequent studies discovered that in PML-/-mice,ATO could inhibit cell proliferation and induce cell apoptosis,implying that ATO plays an important role in treating APL through a variety of mechanisms.
ATO is suitable for:① newly diagnosed APL patients, especially those who have positive PML-RARαgene with t(15;17)translocation;②refractory or recurrent APL patients with retinoic acid resistance or ineffective combined chemotherapy;③APL patients who are intolerant of or not suitable for retinoic acid or combined chemotherapy.Ghavamzadeh et al.used ATO in the first-line treatment for 197 APL patients and had the following findings:the CR rate was 85.5%after monotherapy;the 5-year median DFS was 66.7±4.0%;the recurrence in patients with complete remission was rare;the 5-year overall survival rate was 64.4±4.0%.Among the 197 cases,19 pediatric APL patients received ATO treatment,17 of whom achieved CR.The 5-year overall survival rate and DFS was 83.9%and 72.7% respectively,without chronic arsenic poisoning or secondary tumor.After summarizing the clinical research data of 14 cases in which ATO is used to treat recurrent APL in 15 years,Lengfelder et al.conclude that by using ATO solely to induce APL recurrence,the CR2 of the patients could reach 86%,and the 2-year survival rate could achieve 50%-81%.In recent years,arsenic trioxide has been widely used to treat APL together with ATRA combined chemotherapy.As an effective medicine,arsenic trioxide can shorten the time to reach CR without long-term toxic side effects.
3.2 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia(CML)
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia(CML)is a type of clonal cancer of hematological system derived from hemopoietic stem cells.CML is associated with a characteristic Philadelphia chromosome(ph),t(9;22),a gene marker of malignant clone,which means that ABL,a proto oncogene on chromosome 9,is fused with BCR,a gene from chromosome 22 to form BCR/ABL chimeric gene.The fused BCR/ABl protein has abnormal tyrosine kinase activity,can activate multiple intercellular signal pathways to increase cell proliferation,which causes the white blood cells to grow rapidly without control,and then result in the malignant transformation of cells.Previous studies indicated that ATO could partially reduce BCR/ABL and STAT1 protein of the mononuclear cells,and inhibit BCR/ABL and STAT1 protein activity,which indicated its potential in the treatment of CML.Zhao Pu applied ATO to treat 30 CML patients,which included 16 new cases and 14 relapsed refractory cases.The effective rate of ATO reached 83.3%(25/30),with 19 cases of complete remission(CR)(63.3%),6 cases of partial remission(PR)(20%),5 invalided cases(16.7%).This study indicates that ATO is an effective medicine for the treatment of CML[24].Zhang Ying et al combined ATO and thalidomide to treat 11 patients with CML accelerated phase,and found the total effective rate was 63.6%(7/11)with 2 cases of complete remission(CR)(18.2%),2 cases of partial remission(PR)(18.2%),3 cases of improvement(27.3%),4 invalided cases(36.4%).These results were satisfied with slight adverse reaction and good tolerance[25].
3.3 Multiple myeloma(MM)
Multiple myeloma(MM)is a clonal malignant plasma cell disease.It is characterized by the abnormal proliferation of bone marrow plasma cells and the overproduction of monoclonal immunoglobulin or light chain.Currently,MM is still an incurable disease.ATO inhibits the adhesion of bone marrow stromal cells by inhibiting the secretion of VEGF,which can inhibit the proliferation of myeloma cells.Li et al applied ATO,ATRA,ifosfamide and prednisone regimen to treat 30 relapsed and refractory MM patients (including patients with relapse of lenalidomide and bortezomib treatment).The total effective rate after 2,4 and 6 cycles of treatment were 66.7% (20/30),50% (10/20) and 40% (2/5)respectively.Overall survival and disease-free survival are 48 (29-120)months and 6 (2-8)months respectively[26].Fu Kun treated 51 MM patients applying ATO and thalidomide combination therapy,with the total effective rate of 90.19%(46/51),where PR was 60.8%(31/51),without significant adverse reactions[27].Wang Yan et al used ATO and low dose thalidomide combined treatment to treat 26 elderly MM patients with the total effective rate of 76.9%(20/26).The total effective rate of 14 new cases was 78.57%,with 42.85%(6/14)of PR,35.71%(5/14)of improvement and 21.42%(3/14)of invalid cases.While the total effective rate of 12 relapsed refractory cases was 75%,with 33.3%(4/12)of PR,41%(5/12)of improvement and 25%(3/12)of invalid cases.And toxic and side effects reduced obviously during the treatment[28].These studies suggest that even in the era of high efficacy of targeted drugs,the treatment regimen containing ATO can still be a part of the effective and safe treatment of recurrent refractory MM.
3.4 Myelodysplastic Syndrome(MDS)
Myelodysplastic Syndrome(MDS)is heterogeneous and myeloid clonal myeloproliferative disease of the hematopoietic stem cell.The characteristics are the differentiation and development anomaly of myeloid cells.The manifestations of MDS are ineffective hematopoiesis,hematopoietic failure and high risk to acute myeloid leukemia.The prognosis of MDS in high risk group was poor.The high risk group easily converts to AML, and need high intensity treatment including chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.The high intensity treatment has a high treatment related morbidity and mortality,so it’s not suitable for all patients.Studies have found that ATO could inhibit the methyltransferase DNMT3A and DNMT3B,and played the role of De methylation[29].This effect is similar in mechanisms to that of De methyl drug Decitabine which is the drug of Clinical first choice in the MDS treatment,and the studies prompt the therapeutic potential of ATO in MDS treatment.Xu et al.have found that ATO blocked the NF-κB pathway by inhibiting the activity of HTERT,and improved apoptosis of MDS cell line in vitro[6].ATO combined with thalidomide has been recommended for the treatment of MDS[21].Weiwei et al reported that ATO and thalidomide regimens treatment of 20 cases of MDS patients was less side effect with the total effective rate 75%(15/20)[30].Yaxi Chang et al reported that the total effective rate was 90%with the same regimens treatment and cases[31].Tianjing Guo reported that the treatment of 38 cases of patients with MDS by Combination of ATO and cytosine arabinoside could be well tolerated with mild advent reactions,and the total effective rate was 89.47%(34/38)[32].
3.5 Malignant Lymphoma(ML)
Malignant lymphoma(ML)is a lymphoid cell malignant monoclonal proliferative disease occurred in the lymph node,bone marrow,spleen or digestive tract.Up to now,about 30-40%patients are still relapsed and refractory,and with short survival time.Early in vitro studies,ATO has inhibition effect on proliferation in tumor cell lines and primary tumor cells.These studies point out that ATO has the clinical potential in the treatment of CLL and malignant lymphoma[33].Domestic scholars reported that 21 cases of relapsed and refractory ML were treated with ATO with the total effective rate 61.9%(13/21)among which CR 14.3%(3/21),PR 47.6%(10/21).These results indicate that ATO can be used as a clinical treatment of relapsed and refractory ML[34].
4 Brief Summary
ATO can induce tumor cell apoptosis,tumor cell differentiation and regulate the key signaling pathways to play a role in the treatment of various hematological malignancies.At present,Domestic and foreign researchers used ATO or ATO combined with traditional induction agent in the consolidation of the program,which can effectively improve the cure rate and reduce the mortality rate and recurrence rate,prolong patients’disease-free survival and reduce the use of chemotherapy drugs.Future researches focusing on the precise mechanism of ATO in the treatment of hematological malignancies will provide theoretical basis and treatment strategy for the precise treatment of ATO.With the progress of basic research and the continuous testing of clinical practice,ATO will have a more broad application prospects and significant therapeutic effect.
Reference
1.Zhang TD,Li YS.Clinical findings and experimental study on treatment of acute myelocytic leukemia with Ailing NO.1.Chin J Integr Tradit West Med 1984,4(1):19-20.
2.Sun HD,Ma L,Hu XC,et al.Combined Ailing NO.1 with TCM theory and chemotherapy to treat 32 cases of acute promyelocytic leukemia.Chin J Integr Tradit West Med 1992,12:170-171.
3.Cai X,Shen YL,Zhu Q,et al.Arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis and differentiation are associated respectively with mitochondrial transmembrane potential collapse and retinoic acid signaling pathways in acute promyelocytic leukemia.Leukemia 2000,14(2):262-270.
4.Ma XD,Qiao DF,Tian XM,et al.Mechanism of opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pore induced by arsenic trioxide.Chin J Cancer 2006,25(1):17-21.
5.Kitamura K,Minami Y,Yamamoto K,et al.Involvement of CD95-independent caspase 8 activation in arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis.Leukemia 2000,14(10):1743-50.
6.Xu W,Wang Y,Tong H,et al.Downregulation of hTERT:an important As2O3 induced mechanism of apoptosis in myelodysplastic syndrome.PLoS One 2014,9(11):e113199.
7.Zhang YL,Wei HL,Sun LJ.Impact of As2O3 on Bcl-2,Survivin and Reactive Oxygen Species(ROS)Expressions during the Process of Induced Apoptosis in Multidrug-Resistant Human Leukemia K562/ADM Cells.Chin Cancer 2008,17(6):495-498.
8.Jing YK,Wang L,Xia LJ,et al.Combined effect of all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo.Blood 2001,97(1):264-269.
9.Wei HL,Yao XJ,Li YN,et al.Arsenic trioxide inhibits P-glycoprotein expression in multidrug-resistant human leukemia K562/ADM cell line that overexpresses mdr-1 gene and enhances their chemotherapeutic sensitivity.Chin JHematol 2003,24(1):28-31.
10.Seo T,Urasaki Y,Takemura H,et al.Arsenic trioxide circumvents multidrug resistance based on different mechanisms in human leukemia cell lines.Anticancer Res 2005,25(2A):991-998.
11.Zhang W,Ohnishi K,Shigeno K,et al.The induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by arsenic trioxide in lymphoid neoplasms.Leukemia 1998,12(9):1383-1391.
12.Roboz GJ,Dias S,Lam G,et al.Arsenic trioxide induces dose-and time-dependent apoptosis of endothelium and may exert an antileukemic effect via inhibition of angiogenesis.Blood 2000,96(4):1525-1530.
13.Thomas-Schoemann A,Batteux F,Alexandre J,et al.A new strategy to target regulatory T cells in solid tumors. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2(3):e23338
14.Baj G,Arnulfo A,Deaglio S,et al.Arsenic trioxide and breast cancer:analysis of the apoptotic,differentiative and immunomodulatory effects.Breast Cancer Res Treat 2002,73(1):61-73.
15.Han JB,Sang F,Chang JJ,et al.Arsenic trioxide inhibits viability of pancreatic cancer stem cells in culture and in axenograft model via binding to SHH-Gli. Onco Targets Ther 2013, 6(8):1129-1138.
16.Yuan ZM,Ganapathy S,Xiao S,et al.Low-dose arsenic induces chemotherapy protection via p53/NF-κB-mediated metabolic regulation.Oncogene 2013,33(11):1359-1366.
17.Rao Y,Li RH,Zhang DQ.A drug from poison:how the therapeutic effect of arsenic trioxide on acute promyelocytic leukemia was discovered.Sci China Life Sci 2013,56(6):495-502.
18.Chen SJ,Zhou GB,Zhang XW.From an old remedy to a magic bullet:molecular mechanisms underlying the therapeutic effects of arsenic in fighting leukemia. Blood 2011, 117(24):6425-6435.
19.Keyhani M.Use of arsenic trioxide as a first-line single agent in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia.JClin Oncol 2012,30(2):217-222.
20.Ghavamzadeh A,Alimoghaddam K,Rostami S,et al.PhaseⅡstudy of single-agent arsenic trioxide for the front-line therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia.JClin Oncol 2011,29(20):2753-2757.
21.Lengfelder E,Hofmann WK,Nowak D.Impact of arsenic trioxide in the treatment of acute promyelocytic.Leukemia 2012,26(3):433-442.
22.Lo-Coco F,Avvisati G,Vignetti M,et al.Retinoic Acid and Arsenic Trioxide for Acute promyelocytic Leukemia.N Engl J Med,2013,369(2):111-121.
23.Liu Z,Wu X,Duan Y,et al.AID expression is correlated with Bcr-Abl expression in CML-LBC and can be down-regulated by As2O3 and/or imatinib.Leuk Res 2011,35(10):1355-1359.
24.Zhao P.Study of arsenic trioxide in terating chronic myelogenous leukemia.J Med Res 2008,37(12):54-56.
25.Zhang Y,Fan H.Combined arsenic trioxide and thalidomide to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia accelerated phase clinical observation.Chin Mod Med,2011,18(6):59-60.
26.Li X,Sun WJ.The clinical activity of arsenic trioxide,ascorbic acid,ifosfamide and prednisone combination therapy in patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma.Onco Targets Ther 2015,8:775-781.
27.Fu K.Analysis of clinical effect on arsenic trioxide and thalidomide combination therapy in multiple myeloma.Guide Chin Med 2014,12(15):199.
28.Wang Y,Yang XY.Clinical study of arsenic trioxide combined with low dose thalidomide in elderly patients with multiple myeloma.Chin J Mod Med 2014,24(6):86-88.
29.Khaleghian A,Ghaffari SH,Ahmadian S,et al.Metabolism of arsenic trioxide in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.Cell Biochem 2014,115(10):1729-1739.
30.Wei W,Hou J,Zhou F.Combintion of arsenic trioxide and thalidomide therapy in Myelodysplastic Syndromes.JClin Hematol 2011,24(3):142-144.
31.Zhang YX,Liang YN.Clinical Study of Arsenic Trioxide Combined with Thalidomide for Refractory Multiple.Prict J Cancer.2013,28(4):436-438.
32.Guo TJ,Gong JM,Wu BJ,et al.Clinical observation on Arsenic Trioxide combined with Cytarabine in the treatment of 38 patients with myelodysplastic syndrome.Chin Med Guide 2012,9(9):80-81,84.
33.Li CL,Wei HL,Chen J,et al.Arsenic trioxide induces autophagy and antitumor effects in Burkitt's lymphoma Raji cells.Oncol Rep 2014,32(4):1557-1563.
34.Huang Y,Qin SK,Wang L.Clinical study of arsenic trioxide for patients with malignant lymphoma.Chin Clin Oncol 2007,12(8):598-600.
杂志排行
Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- Explore the medication rules of Chinese medicine of Professor Huang Wenzheng for the treatment of chronic kidney disease based on data mining
- Feiji Recipe Reverses Lung Cancer Immune Escapeby Inhibiting the Expression of IDO
- Uncertainty profile for NIR analysis of tanshinone Icontent in tanshinone extract powders
- Computational study of the molecular mechanism of Lonicera japonica organic acidsagainst influenza
- Molecular docking study on the molecular mechanism of rhaponticin for treatment of chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Traditional Chinese medicine should not beignored during the development of precision medicine with Chinese characteristics