牛羊鲜乳冷藏过程中蛋白质沉淀率比较及粒度分析
2016-09-12田万强田苏辉朱莉莉李林强梅楚刚昝林森
田万强,王 亮,田苏辉,朱莉莉,李林强,梅楚刚,昝林森
(1.杨凌职业技术学院 动物工程分院,陕西杨凌 712100;2.陕西师范大学 食品工程与营养科学学院,西安710119; 3.西安宏兴乳业公司,陕西临潼 710600;4.西北农林科技大学 动物科技学院,陕西杨凌 712100)
牛羊鲜乳冷藏过程中蛋白质沉淀率比较及粒度分析
田万强1,王亮2,田苏辉3,朱莉莉2,李林强2,梅楚刚4,昝林森4
(1.杨凌职业技术学院 动物工程分院,陕西杨凌712100;2.陕西师范大学 食品工程与营养科学学院,西安710119; 3.西安宏兴乳业公司,陕西临潼710600;4.西北农林科技大学 动物科技学院,陕西杨凌712100)
旨在分析牛羊鲜乳冷藏过程中蛋白质沉淀率变化及粒度大小。通过离心沉淀、原子力显微镜、激光粒度分析仪、SDS-PAGE 电泳分析牛羊鲜乳冷藏过程中蛋白质沉淀率变化、鲜乳蛋白质粒子形貌、粒径分布范围、酪蛋白组成。结果表明:羊乳蛋白质沉淀率显著高于牛乳;牛乳蛋白质粒子数目(45 μL-1)、密度(1.8 μm-2)低于羊乳蛋白粒子数目(437 μL-1)、密度(17.48 μm-2);牛乳蛋白粒度大小主要集中在1 nm以下,羊乳蛋白粒度只有19.3%在1 nm以下,主要分布在1~1 000 nm,其中100 nm左右最多;牛羊乳酪蛋白主要有β酪蛋白和αs1酪蛋白2种,分子质量分别为34 ku和26 ku左右。牛乳蛋白质冷藏稳定性显著高于羊乳,羊乳蛋白质颗粒直径大于牛乳,牛羊乳蛋白质粒子数目和大小是影响冷藏稳定性差异的主要因素;原子力显微镜结合激光粒度仪是分析乳蛋白粒度大小的有效手段。
牛乳;羊乳;蛋白质;沉淀率;粒度
牛乳在冷藏和加工过程中会产生一定量的蛋白沉淀,即使经过均质,热处理后随着货架期延长沉淀现象也较为明显[1-4],羊乳则更为严重。影响乳稳定性的因素有酸度[5-6]、酪蛋白组成[7-8]、乳清蛋白和酪蛋白的比例[9-10]、处理温度[11-15]等,这些因素导致蛋白质粒子凝聚,直径增大,胶体结构遭到破坏,布朗运动消失,产生沉淀。刘红霞等[16]发现搅拌和均质条件不同,牛羊乳粒度大小和稳定性不同;李子超等[17]和Anema等[18-19]研究发现热处理使牛乳的酪蛋白粒子直径发生变化,产生沉淀,可见蛋白质粒度大小是影响乳稳定性的直接物理因素。牛羊乳蛋白质沉淀率差异是由二者本身粒度大小差异所致,还是仅由外因所致,相关研究相对较少。有研究[20]报道牛乳酪蛋白平均粒径大于羊乳,但难于解释羊乳无论是冷藏还是热处理后沉淀率高于牛乳的事实。因此,牛羊鲜乳蛋白质粒度大小的差异及其对蛋白质沉淀率的影响尚需进一步研究。
1985年Binning 和 Quate发明原子力显微镜(AFM)[21],AFM 能在纳米尺度水平测到物体的微观结构[22],并且可以呈现样品表面的三维形貌[23],甚至可以在离子缓冲溶液中进行成像[24],基于原子力显微镜的这些优点,本研究使用原子力显微镜表征牛羊乳蛋白质粒子微观形貌,并结合使用激光粒度分析仪测定牛羊鲜乳蛋白质粒度大小,试图更加全面反映牛羊乳蛋白粒子大小差异,以期揭示牛羊乳粒度对蛋白沉淀率的影响,为改善乳蛋白稳定性提供理论基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1材 料
牛羊乳采自西北农林科技大学畜牧站荷斯坦牛和萨能奶山羊。
1.2主要试剂
蛋白Mark(SM 0671,Fermentas公司),干酪素(01-010,北京奥博星生物技术有限责任公司),三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)、硝酸银、丙烯酰胺、N,N-甲叉双丙烯酰胺、十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)、N,N,N,N-四甲基乙二胺(TEMED)、甘氨酸、甘油、β-巯基乙醇、溴酚蓝、盐酸、氯化钠、三氯乙酸、戊二醛、碳酸钠、甲醛、柠檬酸、醋酸钠、氢氧化钠、醋酸、φ=95%乙醇、乙醚等均为分析纯。
1.3主要仪器
台式离心机(800 B,上海安亭科学仪器厂),原子力显微镜(Veeco Bruker,J探头),激光粒度分析仪(MS 2000,英国马尔文仪器公司),电泳系统(PowerPacTM Universal,美国Bio-rad伯乐),凝胶成像系统(Universal Hood II,XRS,美国Bio-rad)。
1.4方 法
1.4.1蛋白质沉淀率的测定常温牛羊乳样2~4 ℃ 冷却保存,每12 h取乳样1次,采用400 g相对离心力离心15 min,倾出上液,称量沉淀蛋白,每次平行测定3个样,共测定5次,按下式计算蛋白沉淀百分率。
W=(m1/m)×100
式中W为100 g乳中蛋白沉淀百分率;m1为沉淀蛋白质量,单位为g;m为样液质量,单位为g。
1.4.2蛋白质粒子形貌观察取10 mL乳样400 g相对离心力离心15 min,除去上层脂肪,加入等体积乙醚,通过分液漏斗进一步脱脂。取脱脂乳样1 mL,稀释25倍,超声处理10 min,取1 μL样液滴于云母片上,自然风干,用Veeco Bruker原子力显微镜J探头进行形貌观察。
1.4.3粒度测定各取50 mL牛羊乳,加入等体积乙醚,静置10 min,1 200 g离心力离心15 min,倾去上层脂肪,用激光粒度分析仪测定粒度大小及其相应体积分数。
1.4.4酪蛋白组成的SDS-PAGE电泳分析取牛羊乳各30 mL,200 g相对离心力离心5 min,弃去上层脂肪;下层液体加入等体积0.2 mol·mL-1醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲液(pH 4.6),摇匀后加热至40 ℃,冷却至室温,放置5 min,200 g相对离心力离心5 min后倾出上层液体,沉淀物用蒸馏水洗涤,200 g相对离心力离心5 min,洗涤重复3次。所得沉淀物即为粗酪蛋白。将粗酪蛋白置于30 mLφ=95%乙醇中洗涤,200 g相对离心力离心5 min,洗涤重复2次,再用乙醚洗涤2次,抽滤,将所得沉淀物摊开在表面皿上,使乙醚完全挥发,所得即为酪蛋白。
取酪蛋白1 mg溶于1 mL样品缓冲液中,沸水加热5 min。配制12%分离胶加入凝胶板中,凝固40 min,加入3%浓缩胶,凝固40 min,在加样孔中加入样品10 μL,80 V恒压 40 min,然后100 V恒压2.5 h后停止电泳;φ=20%三氯乙酸浸泡凝胶板8 h,150 mL去离子水充分洗涤凝胶板20 min,重复洗涤3次;φ=1% 戊二醛溶液150 mL避光浸泡凝胶板6 h,去离子水洗涤10 min,重复洗涤3次;氨银染液100 mL避光染色20 min;去离子水150 mL洗涤凝胶表面2次,每次1 min。加入显色液至显色清晰后弃去显色液,去离子水洗涤2次,每次1 min,加入终止显色液终止显色。
1.5数据处理
运用 SPSS19.0 软件进行数据处理,方差显著性分析采用LSD法,结果以“平均数±标准差”表示。
2 结果与分析
2.1牛羊乳蛋白质沉淀率
图1表明,牛乳在2~4 ℃冷藏过程中蛋白质发生沉淀,但在60 h内无显著增加(P>0.05 );羊乳则在24 h后沉淀率显著增加(P<0.05),且冷藏过程中蛋白质沉淀率显著高于牛乳(P<0.05)。张小苗[25]认为羊乳胶体稳定性低于牛乳,另有研究[4,26-27]表明羊乳的热稳定性低于牛乳。结果提示羊乳稳定性远低于牛乳。

图1 牛羊乳冷藏过程中沉淀率动态变化
2.2牛羊乳蛋白质粒子形貌的原子力显微镜观察
从图2、3蛋白质粒子形貌分析可知,牛乳蛋白粒子数目(45 μL-1)、密度(1.8 μm-2)明显低于羊乳蛋白粒子数目(437 μL-1)、密度(17.48 μm-2);牛乳蛋白质颗粒平均直径(100.106 nm)大于羊乳(80.407 nm),羊乳中虽然存在一定数量直径较大的蛋白颗粒(图3),但是,牛乳的蛋白质粒子数目远远少于羊乳蛋白质粒子数目,所以这可能影响2种乳蛋白质颗粒的平均直径大小,总体表现为牛乳大于羊乳,这也与Fava等[28]、Jenness[29]和李子超等[20]报道羊乳蛋白质粒子平均直径比牛乳小的结果一致。但是羊乳冷藏稳定性为什么低于牛乳的事实,看来难于用乳蛋白质颗粒平均直径大小解释,原因可能还需进一步探究。由图2、3剖面分析结果可见:羊乳蛋白质粒子表面起伏程度较大(-5 nm~+5 nm),牛乳蛋白质粒子表面起伏程度则相对较小(-4 nm~+4 nm),表明羊乳蛋白质颗粒大小分布范围较大,存在较大直径蛋白颗粒,结果提示牛羊乳蛋白粒子直径平均值不能真实反映牛羊乳蛋白质粒子大小差异,蛋白质颗粒数目和其大小应该是共同影响牛羊乳稳定性差异的主要因素。

图2 牛乳蛋白质粒子形貌(左)及其剖面图(右)
2.3牛羊乳蛋白质粒度
由图4可知,牛乳蛋白粒度大小主要集中在1 nm以下。由图5可知,羊乳蛋白粒度只有19.3%在1 nm以下,主要分布在1~1 000 nm,其中100 nm左右最多,结果表明,羊乳蛋白颗粒直径差异较大,存在较大数量大颗粒蛋白质粒子,这与原子力显微镜分析结果一致。表明牛羊乳蛋白粒径大小是影响其冷藏稳定性差异的主要因素之一。
2.4牛羊乳酪蛋白SDS-PAGE
由图6可知,牛羊乳酪蛋白主要有β-酪蛋白和αs1酪蛋白,这与Bramanti等[30]、Crudden等[31]和Veloso等[32]的研究结果一致,依据标准蛋白Marker,β酪蛋白和αs1酪蛋白分子质量分别为34 ku和26 ku左右,这与郭军等[33]、赵丽丽[34]报道羊乳的β酪蛋白分子质量大于αs1酪蛋白结果类似。表明酪蛋白分子质量不是影响牛羊乳冷藏稳定性差异的主要原因,牛羊乳酪蛋白结构差异可能是影响两者稳定性差异的基础性因素。
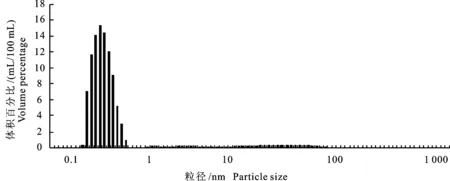
图4 牛乳蛋白粒度大小

图5 羊乳蛋白粒度大小分布
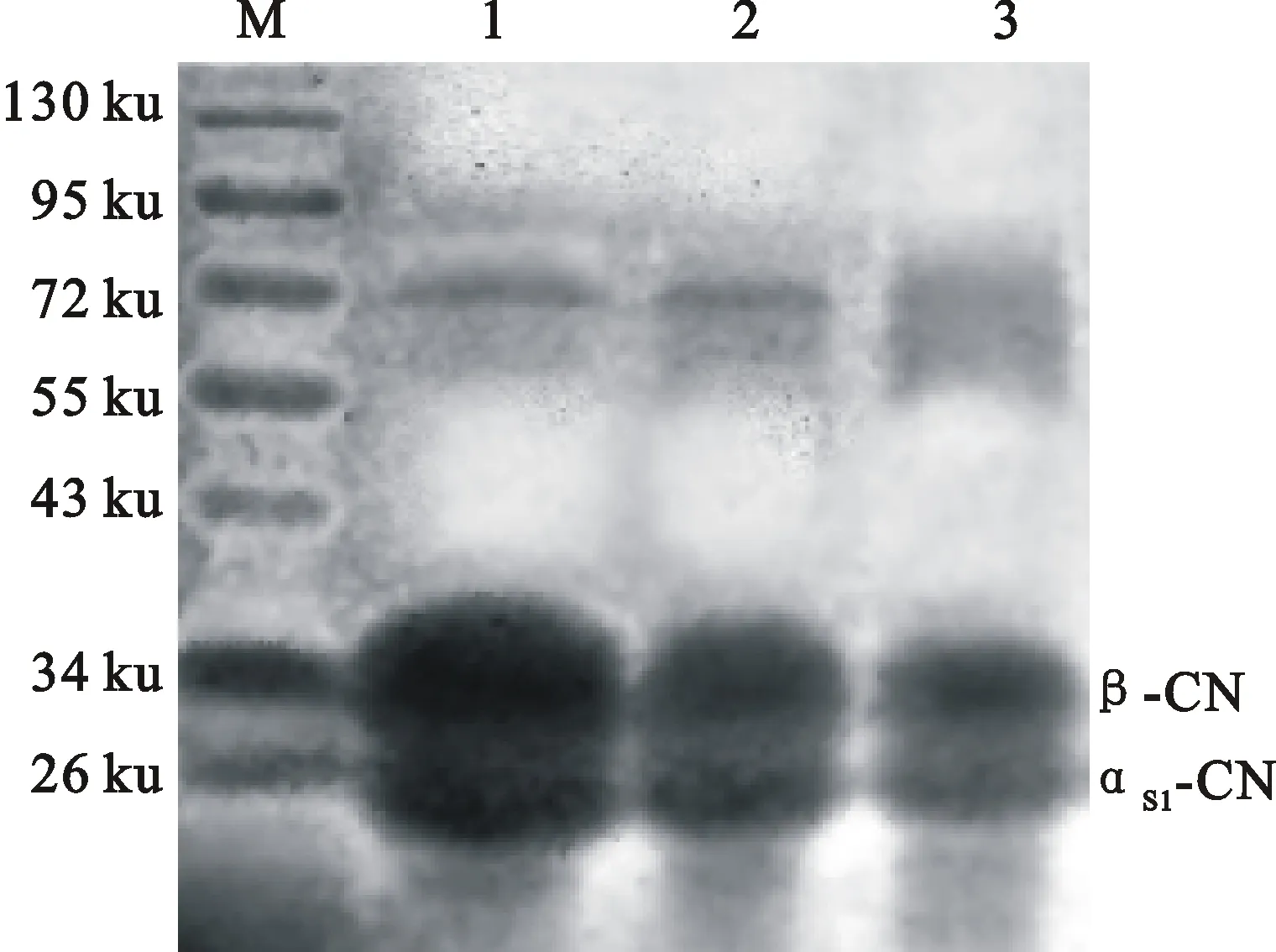
图中条带1~2分别为鲜牛羊乳酪蛋白,条带3为干酪素标品Band 1 and 2 are caseins from cow milk and goat milk respectively,and band 3 is the standard casein
图6牛羊乳酪蛋白SDS-PAGE
Fig.6SDS-PAGE of caseins in cow and goat milk
3 结 论
牛乳的冷藏稳定性显著高于羊乳;牛乳蛋白质粒子数目和密度均低于羊乳;牛乳蛋白粒度大小主要集中在1 nm以下,羊乳蛋白粒度主要分布在1~1 000 nm。羊乳蛋白质颗粒直径大于牛乳,蛋白质粒子数目和大小是影响牛羊乳冷藏稳定性差异的主要因素;原子力显微镜结合激光粒度仪是分析乳蛋白质粒度大小的有效手段。
Reference:
[1]ANEMA S G,LI Y M.Reassociation of dissociated caseins upon acidification of heated pH-adjusted skim milk [J].FoodChemistry,2015,174:339-347.
[2]CROWLEY S V,MEGEMONT M,GAZI N,etal.Heat stability of reconstituted milk protein concentrate powders[J].InternationalDairyJournal,2014,37(2):104-110.
[3]MORGAN F,JACQUET F,MICAULT S,etal.Study on the compositional factors involved in the variable sensitivity of caprine milk to high-temperature processing[J].InternationalDairyJournal,2000,10(1/2):113-117.
[4]RAYNAL-LJUTOVAC K,PARK Y W,GAUCHERON F,etal.Heat stability and enzymatic modifications of goat and sheep milk [J].SmallRuminantResearch,2007,68(1):207-220.
[5]赵正涛,李全阳,赵红玲,等.酪蛋白在不同pH值下特性的研究[J].乳业科学与技术,2009,134(1):26-29.
ZHAO ZH T,LI Q Y,ZHAO H L,etal.Research on the characteristic of caseins at different pH[J].JournalofDairyScienceandTechnology,2009,134(1):26-29(in Chinese with English abstract).
[6]乔 星,张富新,乌 素,等.羊奶热稳定因素的研究[J].农产品加工(学刊),2012,268(1):46-48.
QIAO X,ZHANG F X,WU S,etal.Heat stability factors of goat’s milk[J].AcademicPeriodicalofFarmProductsProcessing,2012,268(1):46-48(in Chinese with English abstract).
[7]TZIBOULA A.Casein diversity in caprine milk and its relation to technological properties:heat stability [J].InternationalJournalofDairyTechnology,1997,50(4):134-138.
[8]HORNE D S,MUIR D D.Alcohol and heat stability of milk protein[J].JournalofDairyScience,1990,73(12):3613-3626.
[9]MORGAN F,MICAULT S,FAUQUANT J.Combined effect of whey protein and αS1-casein genotype on the heat stability of goat milk [J].InternationalJournalofDairyTechnology,2001,54(2):64-68.
[10]LAURENCE D,FANNY G.Formation and properties of the whey protein/κ-casein complexes in heated skim milk-a review[J].DairyScienceTechnology,2009,89(1):3-29.
[11]HARJINDER S.Heat stability of milk[J].InternationalJournalofDairyTechnology,2004,57(2/3):111-119.
[12]周洁瑾,张列兵,梁建芬.加热及贮藏对牛乳脂肪及蛋白聚集影响的研究[J].食品科技,2010,35(5):72-76.
ZHOU J J,ZHANG L B,LIANG J F.Effect of heating and storage on aggregation of fat globule and protein in milk[J].FoodScienceandTechnology,2010,35(5):72-76(in Chinese with English abstract).
[13]HEILIG A,CELIK A ,HINRICHS J.Suitability of Dahlem Cashmere goat milk towards pasteurisation,ultrapasteurisation and UHT-heating with regard to sensory properties and storage stability[J].SmallRuminantResearch,2008,78(1/3):152-161.
[14]ELFAGM A A,WHEELOCK J V.Heat interactions between α-lactalbumin,β-lactoglobulin and casein in bovine milk[J].JournalofDairyScience,1978,61(2):159-163.
[15]HAQUE Z K,JOHN E.Interaction between heated κ-casein and β-lactoglobulin:Predominance of hydrophobic interactions in the initial stages of complex formation [J].JournalofDairyResearch,1988,55(1):67-80.
[16]刘红霞,贾少婷,桂仕林,等.搅拌和均质对牛乳稳定性的影响[J].中国乳品工业,2009,37(9):58-61.
LIU H X,JIA SH T,GUI SH L,etal.Studies on the stability influence of agitating and homogenization of milk[J].DairyIndustry,2009,37(9):58-61(in Chinese with English abstract).
[17]李子超,徐明芳,向明霞,等.巴氏杀菌与超高温灭菌牛乳酪蛋白结构差异性的研究[J].华南农业大学学报,2013,34(2):192-196.
LI Z CH,XU M F,XIANG M X,etal.Research on the structural differences of the casein from milk by pasteurization and ultrahigh temperature sterilization[J].JournalofSouthChinaAgricuituralUniversity,2013,34(2):192-196(in Chinese with English abstract).
[18]ANEMA S G,LI Y.Effect of pH on the association of denatured whey proteins with casein micelles in heated reconstituted skim milk[J].JournalofAgriculturalandFoodChemistry,2003,51(6):1640-1646.
[19]ANEMA S G,LOWE E K,LEE S K.Effect of pH at heating on the acid induced aggregation of casein micelles in reconstituted skim milk [J].LebensmittelWissenschaftundTechnologie,2004,37(7):779-787.
[20]李子超,王丽娜,李昀锴,等.3种乳源酪蛋白粒径及胶束结构的差异性[J].食品科学,2012,33(5):58-61.
LI Z CH,WANG L N,LI Y K,etal.Differences in particle size and structure of casein micelle from different milk sources[J].FoodScience,2012,33(5):58-61(in Chinese with English abstract).
[21]陈天星.利用原子力显微镜对近壁面受限液体性质的研究[D].北京:清华大学,2011.
CHEN T X.Study on properties of the confined liquids at solid surface with AFM[D].Beijing:Qinghua University,2011(in Chinese with English abstract).
[22]桑青.新型多扫描器原子力显微镜技术及系统[D].杭州:浙江大学,2013.
SANG Q.A new multi-scanner Atomic Force Microscope(AFM) technology and system[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2013(in Chinese with English abstract).
[23]徐井华,李 强.原子力显微镜的工作原理及其应用[J].通化师范学院学报(自然科学),2013,34(1):22-24.
XU J H,LI Q.Working principle of atomic force microscopy and its application[J].JournalofTonghuaNormalUniversity(NaturalScience),2013,34(1):22-24(in Chinese).
[24]王芳芳,黄 峰.高速及高分辨率原子力显微镜用于研究Trichoderma reesei纤维素酶在结晶纤维素上的行为[J].林产化学与工业,2014,34(3):130-134.
WANG F F,HUANG F.The action of Trichoderma reesei cellulases on crystalline cellulose with high speed and high resolution Atomic Force Microscopy[J].ChemistryandIndustryofForestProducts,2014,34(3):130-134(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25]张小苗.牛乳和羊乳理化特性比较和掺假检测研究[D].西安:陕西科技大学,2012.
ZHANG X M.Physichemical properities of goat and cow milk and adulteration detection of cow milk in goat milk[D].Xi’an:Shaanxi University of Science and Technology,2012(in Chinese with English abstract).
[26]BOUHALLAB S,LECONTE N,GRAET Y L,etal.Heat-induced coagulation of goat milk:modification of the environment of the casein micelles by membrane processes[J].DairyScienceandTechnology,2002,82(6):673-681.
[27]周强.羊乳理化特性及其胶体稳定性研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2007.
ZHOU Q.Study physicochemical properities and colloid stability of goat milk[D].Xi’an:Shaanxi Normal University,2007(in Chinese with English abstract).
[28]FAVA L W,SERPA P B S,KÜLKAMP-GUERREIRO I C,etal.Evaluation of viscosity and particle size distribution of fresh,chilled and frozen milk of Lacaune ewes[J].SmallRuminantResearch,2013,113(1):247-250.
[29]JENNESS R.Composition and characteristics of goat milk:review 1968-1979 [J].JournalofDairyScience,1980,63(10):1605-1630.
[30]BRAMANTI E,SORTINO C,ONOR M,etal.Separation and determination of denatured αs1-,αs2-,β- andκ- caseins by hydrophobic interaction chromatography in cows’,ewes’ and goats’ milk,milk mixtures and cheeses[J].JournalofChromatography,2003,994(1/2):59-74.
[31]CRUDDEN A,AFOUFA-BASTIEN D,FOX P F,etal.Effect of hydrolysis of casein by plasmin on the heat stability of milk[J].InternationalDairyJournal,2005,15(10):1017-1025.
[32]VELOSO A C A,TEIXEIRA N,FERREIRA I M P L V O.Separation and quantification of the major casein fractions by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis:Detection of milk adulterations[J].JournalofChromatographyA,2002,967(2):209-218.
[33]郭军,张和平,杨月欣.免疫乳的研究与开发利用[J].食品科学,2003,24(9):152-156.
GUO J,ZHANG H P,YANG Y X.Research and development of immune milk[J].FoodScience,2003,24(9):152-156(in Chinese with English abstract).
[34]赵丽丽.羊乳热稳定性及凝胶特性的研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2014.
ZHAO L L.Study on thermal stability and gel properties of goat milk[D].Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,2014(in Chinese with English abstract).
Corresponding authorLI Linqiang,male,Ph.D,associate professor.Research area: animal products and functional food.E-mail:lilinq@snnu.edu.cn
(责任编辑:顾玉兰Responsible editor:GU Yulan)
Comparison of Protein Sedimentation Rate and Particles Size of Milk from Cow and Goat during Cold Storage
TIAN Wanqiang1,WANG Liang2,TIAN Suhui3,ZHU Lili2,LI Linqiang2,MEI Chugang4and ZAN Linsen4
(1.Animal Engineering Department,Yangling Vocational and Technical College,Yangling Shaanxi712100,China;2.College of Food Engineering and Nutritional Science,Shaanxi Normal University,Xi’an710119,China;3.Xi’an Hongxing Dairy Company,Lintong Shaanxi710600,China; 4.College of Animal Science and Technology,Northwest A&F University,Yangling Shaanxi712100,China )
In this paper,protein sedimentation rate changes of milk from cow and goat during cold storage and their particles size were explored.Particle morphology,particle size distribution,casein composition of protein from fresh milk of cow and goat were analyzed by centrifugal sedimentation,atomic force microscope,laser particle size analyzer,and SDS-PAGE electrophoresis,respectively.The results showed that the sedimentation rate of goat milk protein was significantly higher than that of cow milk.The count of cow milk protein particles (45 μL-1),and density (1.8 μm-2) were lower than those (437 μL-1and 17.48 μm-2respectively) of goat milk.Goat milk protein particle size was mainly in less than 1 nm range,however,the same size was only 19.3% in cow milk,and mainly distributed in 1-1 000 nm range,and focused on 100 nm.Beta casein and alpha s1- casein were two main kinds of casein in cow and goat milk,with molecular weight of 34 ku and 26 ku respectively.Storage stability of cow milk protein was significantly higher than that of goat.Cow milk protein particles diameter was larger than that of goat milk,and the milk protein particles count and their sizes were the main factors on milk protein cold storage stability.Atomic force microscopy combined with laser particle size analyzer is an effective method to analyze the particle size of milk protein.
Cow milk; Goat milk; Protein; Sedimentation rate; Particles size
2015-09-11Returned2015-10-13
Shaanxi Science and Technology Development Project (No.2014K13-20,2011K01-09); National Science and Technology Support Program (No.2012BAD12B07); Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No.2007C127).
TIAN Wanqiang,male,Ph.D,associate professor.Research area: livestock breeding and production process and quality control of livestock products.E-mail:twqiang2003@163.com
2015-09-11
2015-10-13
陕西省科学技术发展计划(2014K13-20,2011K01-09);国家科技支撑计划(2012BAD12B07);陕西省自然科学基金(2007C127)。
田万强,男,博士,副教授,研究方向为家畜遗传育种及畜产品生产加工与质量控制。E-mail:twqiang2003@163.com
李林强,男,博士,副教授,研究方向为畜产品及功能食品。E-mail: lilinq@snnu.edu.cn
TS252.2
A
1004-1389(2016)08-1144-06
网络出版日期:2016-07-14
网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/61.1220.S.20160714.1103.010.html
