Com putational in telligence in tropicalm edicine
2016-09-07SomsriWiwanitkitVirojWiwanitkitWiwanitkitHouseBangkhaeBangkokThailandHainanMedicalUniversityHaikouChinaFacultyofMedicineUniversityofNisNisSerbiaJosephAyobabalolaUniversityIlesaNigeriaDrDYPatilMedicalUniversityPuneIndia
SomsriW iwanitkit,VirojW iwanitkitWiwanitkit House,Bangkhae,Bangkok,ThailandHainan Medical University,Haikou,ChinaFaculty ofMedicine,University of Nis,Nis,SerbiaJoseph Ayobabalola University,Ilesa,NigeriaDr DYPatil Medical University,Pune,India
Com putational in telligence in tropicalm edicine
SomsriW iwanitkit1*,VirojW iwanitkit2,3,4,51Wiwanitkit House,Bangkhae,Bangkok,Thailand
2Hainan Medical University,Haikou,China
3Faculty ofMedicine,University of Nis,Nis,Serbia
4Joseph Ayobabalola University,Ilesa,Nigeria
5Dr DYPatil Medical University,Pune,India
M ini review http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.11.009
ARTICLE INFO
Article history:
Received in revised form 10Oct2015 Accepted 25Oct2015
Availableonline 12 Jan 2016
Computer
Tropicalmedicine
Computational intelligence Application
ABSTRACT
The application of computational technology formedical purpose is a very interesting topic.Know ledge content development and new technology search using computational technology becomes the newest approach in medicine.W ith advanced computational technology,several om ics sciences are available for clari fi cation and prediction in medicine.The computational intelligence is an important application that should be mentioned.Here,the author details and discusses on computational intelligence in tropicalmedicine.
1.Introduction
Computer is w idely used at present and the advent of computation science is accepted.Computational technology can be applied in several fi elds.The application of computational technology for medical purpose is a very interesting topic. Know ledge content development and new technology search using computational technology becomes the newest approach in medicine.W ith advanced computational technology,several om ics sciences are available for clari fi cation and prediction in medicine[1].The computational intelligence is an important application that should be mentioned.In tropical medicine, which is a speci fi c branch of medicine dealing w ith tropical diseases(especially for infections)and public health,the computational technology can be very useful[2].The new drug fi ndings,vaccine search as well as biomarker discovery can be based on advanced computational technology.The application can be used for answering the question on gene, protein,expression and interaction of host,pathogen and environment[2].Here,the author details and discusses on computational intelligence in tropicalmedicine.
2.How can com putational intelligence be usefu l in tropicalmedicine?
As already mentioned,the computational technology can be useful formedicalwork.Theapplication of thenew computation intelligence or arti fi cial intelligence is a new thing inmedicine. In fact,the arti fi cial intelligence is proved to be useful and cost effective in several research studies[3].Formany decades,until present 2015,the arti fi cial intelligence has been developed, introduced and applied in medicine[4].Peek et al.concluded that“there has been a major shift from know ledge-based to data-drivenmethodswhile the interest for other research themes such as uncertainty management,image and signal processing, and natural language processing has been stable since the early 1990s”[4].Patel etal.noted that thearti fi cial intelligence can be applied in severalworks including to“clinical decision-making, reasoning under uncertainty and know ledge representation to systems integration”[5].
In tropicalmedicine,computational technology can be used for research and development[2].Dif fi cult questions can besimply answered w ith help of advanced computational technology.Simple,bioinformatics tools can be used for basic genom ics and proteom ics studies.W ith arti fi cial intelligence,“translational bioinformatics”can be supported[5].Several online tools are available for medical purpose and most of those tools are developed based on arti fi cial intelligence principles[1].Mainly,the tools can be classi fi ed as a)database for searching purpose and b)manipulation tool for prediction or simulation purpose[1].
2.1.Computational intelligence:interactive database in tropicalmedicine
In bioinformatics,themanagement of data is the basic principle.The fi rst step is to gathering data to form database[1,6]. The database is the basic source of information.To make use of a database,searching is needed.With help of advance computational technology,there are many new developed medical databases at present.Borok noted that“work w ith data m ining tools in health care is in a developmental stage that holds great prom ise,given the combination of demographic and diagnostic information”[7].It is no doubt that the computational intelligence technique is used for supporting the online medical database.Berger and Berger noted that the computational intelligence can help“analyze massive amounts of data and provide useful and interesting information about patterns and relationships that exist w ithin the data thatm ight otherw ise be m issed”[8].The interactive database can be helpful and help shorten the time for database searching.
At present,there are several interactive medical databases. One of the most w idely used interactive medical database is PubMed(www.pubmed.com).It is a freely accessible open medical database.The PubMed contains several information in medicine including to medical journals,publications,books, proteins,genes,sequences,structures,etc.It is also the referencing website inmedical society.Nevertheless,there are also other new interesting interactive medical databases.Here,the author w ill show some interesting interactive databases in tropicalmedicine in Table 1.
2.2.Computational intelligence:simulation tool in tropicalmedicine
The application of computational intelligence to perform an in silico experiment is an exact usefulness of computational technology in medicine.Many phenomena in medicine are dif fi cult to study in vivo or in vitro,hence,using computation technology to help predict the result can help solve the complex queries[1].The simulation can beused for predicting the change due to time and place.In addition,interaction can also be predicted.At present,many new neural networks are developed for using as computational intelligence in medicine. Traeger et al.noted that computation neural network can be very useful to model and forecast“complex,non-linear,and time depending relationships”[13].
The application of the new simulation tools inmedicine can be in either diagnostic or therapeutic purposed.In diagnosis, Cleophas and Cleophas noted that the new tools could“predict clinical diagnoses w ith accuracies sim ilar to those of other methods”[14].In tropicalmedicine,there are alsomany reports on using arti fi cial intelligence for help diagnose the disease. For example,Shamshirband et al.reported using arti fi cial immune recognition system for diagnosing tuberculosis[15]. According to their study,the“classi fi cation accuracy was 99.14%,sensitivity 87.00%,and speci fi city 86.12%”[15]. Saybani et al.reported a sim ilar study reported using arti fi cial immune recognition system for diagnosing tuberculosis[16].In this reported,classi fi cation accuracy was 100%,sensitivity 100%,and speci fi city 100%[16].Rao and Kumar proposed for“a new computational intelligence-based methodology that predicts the diagnosis in real time,m inim izing the number of false positives and false negatives”[17]. Rao and Kumar concluded that their develop computational intelligence was“more accurate than the state-of-the-art methodologies used in the diagnosis of the dengue fever”[17].Andrade et al.used the neural network for help diagnose malaria[18].Andrade et al.concluded that“an expert computational system based on arti fi cial neural networks was worse that the lightm icroscopy(56%of correct diagnoses)”[18].

Table1 Some interesting interactive databases in tropicalmedicine.
In therapy,the intelligence can also be applied.For example,a“component-based approach to automation of protocol-directed therapy”was recently reported by Musen et al.[19].Musen et al.reported that the new tool could help“offer advice regarding themanagement of patients who are follow ing clinical trial protocols for AIDS or HIV”[19]. Luan et al.reported the use of neural netw ork for predicting effect of the antimalarial activity of 1,4-naphthoquinonyl derivatives as potential antimalarial agents[20].In this work, Luan et al.used forward stepw ise multilinear regression and radial basis function neural networks asmain techniques [20].
In addition to diagnosis and treatment,the application of neural network can also be used in preventive purpose inmedicine.This can be seen inmodeling of vaccination effectiveness. The good example is a recent report by Trtica-M ajnaric et al. [21].Trtica-Majnaric et al.reported the prediction of in fl uenza vaccination outcome by neural networks and logistic regression [21].
Sim ilar to the previous mentioned available databases in tropicalmedicine,therearealsomany new online computational intelligence tools formedical use in tropicalmedicine.Here,the author showed some interesting simulation tools in tropical medicine in Table 2.
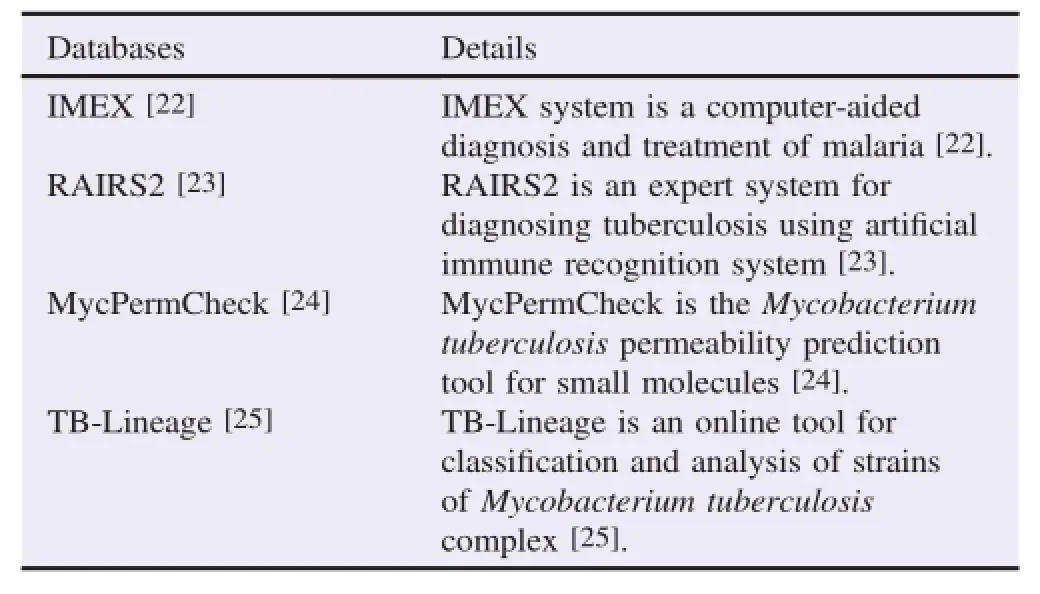
Table2 Somes interesting simulation tools in tropicalmedicine.
3.Conclusions
The application of computational intelligence in tropical medicine can be seen in both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.There are many new interactive databases and online simulation tools for help clari fi cation and prediction in tropical medicine.Many reportsmentioned advantage of the new system.Nevertheless,some problems on accuracy can still be seen. Computational intelligence in tropicalmedicine is an interesting topic for further research and development.
Con fl ict of interest statement
We declare thatwe have no con fl ictof interest.
References
[1]W iwanitkit V.Medical biochemoinformatics.New York:Nova Science Publishers;2008.
[2]W iwanitkit V.Utilization ofmultiple“omics”studies inmicrobial pathogeny for microbiology insights.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2013;3(4):330-3.
[3]Parkes DC,Wellman MP.Economic reasoning and arti fi cial intelligence.Science 2015;349(6245):267-72.
[4]Peek N,Combi C,Marin R,Bellazzi R.Thirty years of arti fi cial intelligence inmedicine(AIME)conferences:a review of research themes.Artif Intell Med 2015;65(1):61-73.
[5]Patel VL,Shortliffe EH,Stefanelli M,Szolovits P,Berthold MR, Bellazzi R,et al.The coming of age of arti fi cial intelligence in medicine.Artif IntellMed 2009;46(1):5-17.
[6]W iwanitkit V.Database and tools for nutrigenomics:a brief summary.JMed Nutr Nutraceut2012;1:87-91.
[7]Borok LS.Data mining:sophisticated forms of managed care modeling through arti fi cial intelligence.J Health Care Finance 1997;23(3):20-36.
[8]Berger AM,Berger CR.Data mining as a tool for research and know ledge development in nursing.Comput Inf Nurs 2004;22(3): 123-31.
[9]Fjell CD,Hancock RE,Cherkasov A.AMPer:a database and an automated discovery tool for antimicrobial peptides.Bioinformatics 2007;23(9):1148-55.
[10]Chizzali-Bonfadin C,Adlassnig KP,Koller W.MONI:an intelligent database and monitoring system for surveillance of nosocomial infections.Medinfo 1995;8:1684.
[11]Br´eh´elin L,Dufayard JF,Gascuel O.PlasmoDraft:a database of Plasmodium falciparum gene function predictions based on postgenomic data.BMC Bioinforma 2008;9:440.
[12]HariKL,Goates AT,Jain R,Towers A,Harpin VS,Robertson JM, etal.The M icrobial Rosetta Stone:a database system for tracking infectiousmicroorganisms.Int JLeg Med 2009;123(1):65-9.
[13]Traeger M,Eberhart A,GeldnerG,Morin AM,Putzke C,Wulf H, et al.[Arti fi cial neural networks.Theory and applications in anesthesia,intensive care and emergency medicine].Anaesthesist 2003;52(11):1055-61.German.
[14]Cleophas TJ,Cleophas TF.A rti fi cial intelligence for diagnostic purposes:principles,procedures and lim itations.Clin Chem Lab Med 2010;48(2):159-65.
[15]Shamshirband S,Hessam S,Javidnia H,AmiribesheliM,VahdatS, Petkovic D,et al.Tuberculosis disease diagnosis using arti fi cial immune recognition system.Int JMed Sci2014;11(5):508-14.
[16]Saybani MR,Shamshirband S,Golzari Hormozi S,Wah TY, Aghabozorgi S,Pourhoseingholi MA,et al.Diagnosing tuberculosisw ith a novel support vectormachine-based arti fi cial immune recognition system.Iran Red CrescentMed J 2015;17(4):e24557.
[17]Rao VS,Kumar MN.A new intelligence-based approach for com puter-aided diagnosisof dengue fever.IEEETrans Inf Technol Biomed 2012;16(1):112-8.
[18]Andrade BB,Reis-Filho A,Barros AM,Souza-Neto SM, Nogueira LL,FukutaniKF,etal.Towards a precise test formalaria diagnosis in the Brazilian Amazon:comparison among fi eld microscopy,a rapid diagnostic test,nested PCR,and a computational expertsystem based on arti fi cialneuralnetworks.Malar J 2010;9: 117.
[19]Musen MA,Tu SW,Das AK,Shahar Y.EON:a component-based approach to automation of protocol-directed therapy.JAm Med Inf Assoc 1996;3(6):367-88.
[20]Luan F,Xu X,Cordeiro MN,Liu H,Zhang X.QSARmodeling for the antimalarial activity of 1,4-naphthoquinonyl derivatives as potential antimalarial agents.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 2013; 9(1):95-107.
[21]Trtica-Majnaric L,Zekic-Susac M,Sarlija N,Vitale B.Prediction of in fl uenza vaccination outcome by neural networks and logistic regression.JBiomed Inf 2010;43(5):774-81.
[22]Suan OL.Computer-aided diagnosis and treatment ofmalaria:the IMEX system.Comput BiolMed 1990;20(5):361-72.
[23]SaybaniMR,Shamshirband S,Golzari S,W ah TY,Saeed A,Mat Kiah ML,et al.RAIRS2 a new expert system for diagnosing tuberculosis w ith real-world tournament selection mechanism inside arti fi cial immune recognition system.Med Biol Eng Comput 2015;http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1323-6.
[24]Merget B,Zilian D,M¨uller T,Sotriffer CA.MycPermCheck:the Mycobacterium tuberculosis permeability prediction tool for small molecules.Bioinformatics 2013;29(1):62-8.
[25]Shabbeer A,Cowan LS,Ozcaglar C,Rastogi N,Vandenberg SL, Yener B,et al.TB-Lineage:an online tool for classi fi cation and analysis of strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex.Infect Genet Evol 2012;12(4):789-97.
9 Oct 2015
*Corresponding author:Somsri W iw anitkit,W iwanitkit House,Bangkhae, Bangkok10160,Thailand
E-mail:wviro j@yahoo.com
Peer review under responsibility of Hainan M edical University.The journal implements double-blind peer review practiced by specially invited international editorial boardmembers.
2221-1691/Copyright©2016 Hainan Medical University.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.This is an open accessarticle under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
杂志排行
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Sudden death in a captive mee rkat(Suricata surica tta)w ith arterial m edial and m yocardial calcification
- Salivary leptin concentrations in Bruneian secondary school children
- Characteristics o f obese or overweight dogs visiting private Japanese vete rinary c linics
- Risk factors from HBV infection among blood donors:A system atic review
- The African Moringa is to change the lives ofm illions in Ethiopia and far beyond
- Pediculosis capitis among p rimary and m idd le school children in Asadabad,Iran:An epidem iological study
