豚鼠膀胱Cajal样间质细胞钙震荡特性*
2016-08-24朱国栋王勤章
朱国栋 王勤章
豚鼠膀胱Cajal样间质细胞钙震荡特性*
朱国栋①王勤章②
目的:探讨正常成年豚鼠膀胱Cajal样间质细胞(Cajal-like interstitial cells)是否有自发周期性钙震荡(calcium oscillation),以期为膀胱兴奋性起搏细胞为Cajal样间质细胞这一学说提供实验依据。方法:运用胶原酶V消化法,获得原代豚鼠膀胱Cajal样间质细胞进行培养,采用激光共聚焦显微镜成像技术,Fluo-4AM负载后的Cajal样间质细胞内钙离子荧光强度的变化采用激光共聚焦显微镜成像技术进行记录,荧光强度的改变代表细胞内钙离子浓度的变化。结果:培养后的Cajal样间质细胞保持其固有特征,可见胞体为梭形且胞体两极有两个细长突起;培养的Cajal样间质细胞有两类不同的钙震荡:一类震幅小而频率不规则,另一类震幅大而频率慢。第二类钙震荡与膀胱逼尿肌细胞的钙震荡显著不同。结论:与消化道起搏细胞Cajal间质细胞(interstitial cells of Cajal,ICCs)自发性钙震荡类似,成年豚鼠膀胱Cajal样间质细胞亦存在自发钙震荡,提示膀胱收缩活动的起搏细胞可能为其中一种类型的膀胱Cajal样间质细胞。
钙震荡;Cajal样间质细胞;膀胱;起搏细胞;激光共聚焦显微镜
First-author’s address:Yankuang Group General Hospital,Zoucheng 273500,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2016.18.001
文献[1-2]研究证明消化道慢波活动的传导者和起搏细胞为ICCs,并参与调节神经肌肉信号传递。膀胱兴奋性的理论研究主要有两大学说:肌源性和神经源性。Smet等[3]首先描述了在人膀胱和豚鼠膀胱中存在形态结构及免疫荧光特性与ICCs类似的间质细胞,被称为膀胱Cajal样间质细胞(interstitial cells of Cajal,ICCs)。由于膀胱Cajal间质细胞的发现使肌源性学说受到更加重视[4-5]。越来越多的研究表明,逼尿肌以及神经与Cajal样间质细胞关系密切,其在电化学信号扩散、神经信号传递中挥重要作用。膀胱兴奋异常很大程度与膀胱Cajal样间质细胞兴奋性有关[6-8]。临床上常见的膀胱功能障碍,如膀胱过度活动症(overactive bladder,OAB)、糖尿病性膀胱、神经源性膀胱等的共同发病机制之一是膀胱逼尿肌兴奋性异常[9-11]。由此推测膀胱Cajal样间质细胞是膀胱收缩活动的起搏细胞,可能就是控制膀胱兴奋性的中心环节。膀胱Cajal样间质细胞的功能学研究尚处于探索阶段,未见其为起搏细胞的报到。本研究运用激光共聚焦显微镜连续成像技术记录膀胱Cajal样间质细胞和膀胱逼尿肌细胞钙离子浓度变化,探讨膀胱Cajal样间质细胞的钙震荡特性及相关生理功能,现报道如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1实验动物豚鼠10只,1~2 个月龄,雌雄不限。
1.2主要试剂DMEM培养基、重组干细胞因子、pluronic F-127、V型胶原酶购自Sigma公司,FBS (Gibco公司),fluo-4AM(Molecular Probes,美国),二甲基亚砜(DMSO,上海生工)。
1.3主要仪器与设备SW-CJ-2FD超净工作台,S/N27709-1462 CO2培养箱,激光共聚焦显微镜META.510 Zeiss(德国蔡司公司)。
1.4方法
1.4.1原代细胞培养颈部脱臼法处死豚鼠,75%酒精浸泡10 min,无菌条件下离断膀胱颈取出膀胱。自膀胱颈部向底部纵行剖开并去除膀胱黏膜,解剖显微镜下去除浆膜层,在磷酸盐缓冲溶液中加双抗(链霉素100 mg/L和青霉素100 U/L)浸泡膀胱肌层10 min。将膀胱肌层剪成大小约1 mm×1 mm×1 mm的组织小块,以磷酸盐缓冲溶液漂洗2次,加入胶原酶Ⅴ溶液(10 g/L),37 ℃培养箱中消化,30 min后见组织块成絮状,离心管中离心。新鲜配制的DMEM 培养基溶液(含体积分数为0.2的胎牛血清)加入沉淀的细胞中,吹打均匀后以1×105/mL的密度接种于激光共聚焦显微镜专用培养皿中,按照50 ng/mL加入重组SCF,5%CO2、37 ℃培养箱内静置培养。24 h后观察接种细胞,可见膀胱逼尿肌细胞尚未贴壁,有两个突起的胞体为梭形的细胞贴壁。细胞换液将未贴壁的逼尿肌细胞移至另一培养皿,继续培养箱内静置3 d后见逼尿肌细胞贴壁。
1.4.2荧光标记将用DMSO溶解fluo-4AM,配制成浓度为1 mmol/L的母液,-20 ℃保存。在实验当天以培养基溶液稀释母液至终浓度为4 μmol/L,配制成工作液。取出原代细胞培养皿并移除培养基,PBS液冲洗2次,加入荧光染料Fluo-4 AM(4 μmol/L)1.5 mL,同时加入20%(w/v)的pluronic F-127促进fluo-4AM进入细胞内,5%CO2、37 ℃培养箱内孵育40 min,为使细胞温度与室温同,恢复细胞稳定性,孵育后室温下静放10 min。
1.4.3膀胱Cajal样间质细胞及膀胱逼尿肌细胞钙震荡测定在激光共聚焦显微镜下每个培养皿随机选10个细胞作为测定对象,以荧光强度变化代表钙离子浓度变化,以200 ms/张图片速度进行扫描,获得连续钙离子浓度的动态变化。
1.4.4实验结束后期分析处理选定细胞图像,使用META自带分析软件进行处理,展示每个时间点的静态图片并得到每一时间点的钙离子荧光强度值,并转为相应数据。对每一时间点的荧光强度值进行统计学的分析处理进行定量分析。细胞内钙离子荧光强度的连续变化以动画形式加以显示。
1.4.5钙离子震荡曲线由SPSS 16.0软件绘制并分析,荧光强度数据用(±s)表示。
2 结果
2.1体外培养的豚鼠膀胱Cajal样间质细胞形态学观察细胞接种于培养皿第2天,倒置显微镜下可见胞体为梭形两极有两个突起的贴壁细胞。根据其免疫荧光特性和形态证实该类细胞为Cajal样间质细胞。2 d逼尿肌细胞未能贴壁,贴壁能力差,将其转移至另一培养皿,3 d后贴壁,倒置显微镜下细胞突起不明显,呈不规则形。相同放大倍数下Cajal样间质细胞明细小于逼尿肌细胞。
2.2运用激光共聚焦显微镜连续扫描成像技术观察膀胱逼尿肌细胞及Cajal样间质细胞钙震荡根据荧光强度的变化见体外膀胱逼尿肌细胞钙震荡不规则,震幅小(30.61±0.20),显著低于Cajal样间质细胞第二类钙震荡震幅(P<0.05)(图1)。培养的原代膀胱Cajal样间质细胞钙震荡有2种类型:一类频率快,震幅小(49.69±0.28)且不规则(图2),第二类频率慢(约为3次/min),震幅大(67.56±0.72)而规则的钙震荡(图3)。钙离子是胞浆重要成分,是细胞内信号传递重要成分Fluo-4 AM染色动态观察显示,钙震荡起源于胞体,向突足扩布(图4)。
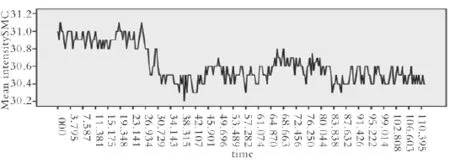
图1 膀胱逼尿肌细胞
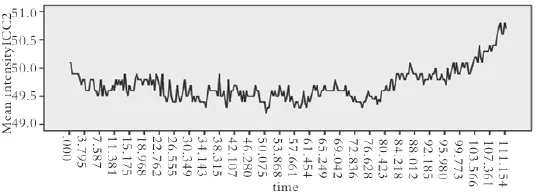
图2 膀胱Cajal样间质细胞震幅小而不规则钙震荡
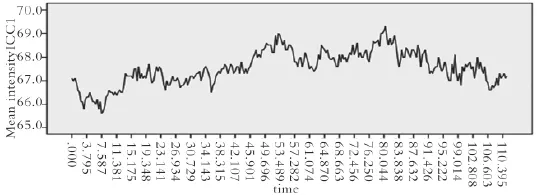
图3 膀胱Cajal样间质细胞震幅大而规则钙震荡

图4 膀胱Cajal样间质细胞钙震荡动态观察视觉图
3 讨论
ICCs是一类特殊的细胞,分布在消化道平滑肌细胞和自主神经末梢之间,与肠运动平滑肌细胞和神经末梢组成一个基本功能单位。ICCs在消化道内有四类不同的分布位置,近年的研究表明,引起胃肠平滑肌自动节律性运动的起搏细胞是位于纵行肌和环行肌之间的ICCs[12-13],肌间ICCs可以参与神经一肌肉信息传递过程并把信息传给相邻的肌细胞[14]。膀胱Cajal样间质细胞形态及免疫组化特性与消化道的ICCs相同,在膀胱的分布与ICCs在消化道中分布相似[15]。膀胱逼尿肌在充盈张力牵拉下才会出现自发的兴奋、收缩,这和胃肠道平滑肌主动自发兴奋不同,膀胱充盈时黏膜上皮在张力牵拉刺激下释放ATP等物质,诱发膀胱逼尿肌自发的兴奋、收缩,因而认为膀胱黏膜下Cajal样间质细胞同时具有起搏和感受器的作用[16-17]。这些提示Cajal样间质细胞可具有膀胱收缩起搏细胞的功能。钙离子是机体中最普遍、最重要的第二信使之一,参与包括细胞分裂、代谢、凝血和受精以及突触传递、激素分泌、肌肉收缩、基因转录等多种生理过程[18];钙离子内流使慢反应细胞具有四相舒张期自动除极的特征[19]。
研究证实,钙离子震荡是ICCs慢波功能为基础[20],因而研究膀胱Cajal样间质细胞是否具有钙震荡及震荡特征对于了解其生理功能有极其重要的意义。钙离子荧光剂是Fluo-4AM,通过培养,能够轻易进入细胞内。本研究在激光共聚焦显微镜下动态观察记录膀胱Cajal样间质细胞钙离子浓度的变化,发现膀胱Cajal样间质细胞存在两种钙震荡类型,提示钙震荡不规则而震幅小的细胞可能是起到传导、耦合信息的作用。膀胱Cajal样间质细胞钙震荡规则而荡幅度大的可能是膀胱逼尿肌收缩活动的起搏细胞。与ICCs在胃肠道的作用相符合,不同分布位置的细胞具有不同的功能,这可能与膀胱Cajal样间质细胞在膀胱的分布有关[7-8]。本实验结果将充实膀胱运动调控的机制,为以Cajal样间质细胞作为潜在靶点治疗膀胱相关疾病的深入研究提供理论依据。
[1] Sanders K M,Koh S D,Ward S M.Interstitial cells of cajal as pacemakers in the gastrointestinal tract[J].Annu Rev Physiol,2006(68):307-343.
[2] Gfroerer S,Rolle U.Interstitial cells of Cajal in the normal human gut and in hirschsprung disease[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2013,29 (9):889-897.
[3] Smet P J,Jonavicius J,Marshall V R.Distribution of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactive nerves and identification of the cellular targets of nitric oxide in guinea-pig and human urinary bladder by cGMP immunohistochemistry[J].Neuroscience,1996,71(2):337-348.
[4] Brading A F,Brain K L.Ion channel modulators and urinary tract function[J].Handb Exp Pharmacol,2011(202):375-393.
[5] Torres Y P,Granados S T,Latorre R.Pharmacological consequences of the coexpression of BK channel alpha and auxiliary beta subunits[J].Front Physiol,2014,5:383.
[6] Wang Y,Fang Q,Lu Y,et al.Effects of mechanical stretch on interstitial cells of Cajal in guinea pig bladder[J].J Surg Res,2010,164(1):e213-219.
[7] Schwentner C,Oswald J,Lunacek A,et al.Loss of interatitial cells of Cajal and gap junction protein connexin 43 at the vesicoureteral junction in children with vesicoureteral reflux[J].J Urol,2005,174(5):1981-1986.
[8] Rothberg B S.The BK channel:a vital link between cellular calcium and electrical signaling[J].Protein Cell,2012,3(12):883-892.
[9] Bragg R,Hebel D,Vouri S M,et al.Mirabegron:a Beta-3 agonist for overactive bladder[J].Consult Pharm,2014,29(12):823-837.
[10] Arrellano-Valdez F,Urrutia-Osorio M,Arroyo C,et al.A comprehensive review of urologic complications in patients with diabetes [J].Springerplus,2014,3(1):549.
[11] Petkov G V.Central role of the BK channel in urinary bladder smooth muscle physiology and pathophysiology[J].Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol,2014,307(6):R571-R584.
[12] Edwards F R,Hirst G D.An electrical description of the generation of slow waves in the antrum of the guinea-pig[J].J Physiol,2005,564(Pt1):213-232.
[13] Kito Y,Ward S M,Sanders K M.Pacemaker potentials generated by interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine intestine[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol,2005,288(3):C710-20.
[14] Iino S,Horiguchi K.Interstitial cells of cajal are involved in neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract[J].Acta Histochem Cytochem,2006,39(6):145-153.
[15] Davidson R A,McCloskey K D.Morphology and localization interstitial cells in the guinea pig bladder:Structural relationships with smooth mnscle and neurous[J].J Urol,2005,173(4):1385-1390.
[16] Biers S M,Reynard J M,Doore T,et al.The functional effects of a c-kit tyrosine inhibitor on guinea-pig and human detrusor[J]. BJU Int,2005,97(3):612-616.
[17] Kubota Y,Kojima Y,Shibata Y,et al.Role of KIT- positive interstitial cells of Cajal in the urinary bladder and possible therapeutic target for overactive bladder[J].Adv Urol,2011,2011(1687-6369):816 342.
[18] Ganong W F.Review of medical physiology[M].New York:McGraw-Hill,2001:369-382.
[19]唐尚杰,郭涛,杜云惠.食管内心脏电生理检查[M].昆明:云南科技出版社,2005:3-4.
[20] Nakayama S,Ohya S,Liu H N,et al.Sulphonylurea receptors differently modulate ICC pacemaker Ca2+activity and smooth muscle contractility[J].J Cell Sci,2005,118(Pt 18):4163-4173.
Calcium Oscillation Characteristics of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in Guinea Pig Bladder
ZHU Guodong,WANG Qin-zhang.//Medical Innovation of China,2016,13(18):001-004
Objective:To ascertain the spontaneous and cyclical calcium oscillation in Cajal-like interstitial cells of Cajal in the bladder of adult guinea-pig.Method:The V-type enzyme collagenase was used to separate primary cells from myoblast of the preparation muscle tissue,primary cells were cultured.Using fluo-4 AM dye the Cells.The change of calcium fluorescence intensity was recorded with laser scanning microscope imaging. The changes of the intracellular calcium concentration was on behalf with the Fluorescence intensity.Result:The Cajal-like interstitial cells maintained its inherent characteristics by primary cultivation.We could see that the cell had a spindle cell body with two slender bipolars.In the Cajal-like interstitial cells of bladder:there were 2 different types of spontaneous calcium,small irregular calcium oscillation and large oscillation slow calcium oscillation.The second type of calcium oscillation was completely different from those of smooth muscle cells.Conclusion:We have confirmed the existence of the spontaneous calcium oscillation in the Cajal-like interstitial cells in the bladder of adult guinea-pig,that like the pacemaker cells of interstitial cells of Cajal in the digestive tract.Implying that part of the Cajal-like interstitial cells may be the pacemaker cells of contraction or activity of bladder.
Calcium oscillation;Cajal-like cells;Bladder;Pacemaker cell;Laser scanning confocal microscopy
国家自然科学基金(30860281)
①兖矿集团有限公司总医院山东邹城273500
②石河子大学医学院第一附属医院
朱国栋
(2016-03-11)(本文编辑:程旭然)
