一类存在参数摄动的线性随机系统的鲁棒间歇故障诊断方法
2016-08-11鄢镕易何潇周东华
鄢镕易 何潇 周东华,2
一类存在参数摄动的线性随机系统的鲁棒间歇故障诊断方法
鄢镕易1何潇1周东华1,2
间歇故障(Intermittent faults,IFs)具有随机性,其检测要求在本次间歇故障消失之前检测出间歇故障的发生,在下一次间歇故障发生之前检测出间歇故障的消失.本文针对一类存在未知时变参数摄动的离散线性随机动态系统,研究了其鲁棒间歇故障检测与分离问题.基于降维未知输入观测器,通过引入滑动时间窗口,本文设计了一组与未知时变摄动解耦的结构化截断残差,并提出其存在的一个充分条件.与传统残差相比,截断残差信号更为显著地反映了间歇故障的发生和消失.为满足间歇故障的检测要求,本文提出两个假设检验分别用于检测间歇故障的发生时刻和消失时刻,并给出了一个详细算法.最后,在沿参考轨道运行的卫星模型上对所述方法进行了仿真实验,结果表明该方法能够有效检测出间歇故障的所有发生时刻和消失时刻,并准确实现故障分离.
间歇故障,鲁棒故障诊断,时变参数摄动,降维未知输入观测器,假设检验
引用格式鄢镕易,何潇,周东华.一类存在参数摄动的线性随机系统的鲁棒间歇故障诊断方法.自动化学报,2016,42(7): 1004-1013
间歇故障(Intermittent faults,IFs)是实际工业系统中一种普遍存在的故障类型[1[5],约90%的数字电路系统崩溃由间歇故障引起;混合电路中,间歇故障发生频率是持续故障的10~30倍[6].在航空航天系统中,元器件老化、高负荷振动、装配不良等因素都有可能导致间歇故障NFF(No-fault-found)发生[7].在机械传动系统中,器件磨损、载荷过重以及阀门、气缸密闭性不良都会引起间歇故障[8-10].电力电气系统发生间歇故障的原因包括外部环境污染、电气接触点腐蚀和松动等[11-13].间歇故障的发生会降低系统可靠性和安全性,增加维护维修成本[14].据统计,在军工系统中,间歇故障导致的不必要维护维修、元部件过早更换等问题会直接引起巨额经济损失,降低战备完好率[6,15].随着计算机、电子、通信等技术飞速发展,在数字化装置广泛普及的工业背景下,间歇故障诊断对有效避免灾难性事故发生,提高系统可靠性、可维修性和保障性,降低生产成本具有十分重要的现实意义[6,15].
与持续故障不同,间歇故障具有一定随机性,持续时间有限,故障幅值未知,无需外部补偿措施失,且通常即可自行消会重复发生[16].在故障初期,间歇故障往往以类似小噪声扰动形式出现;随着系统运行时间增加,其持续时间和幅值逐渐增加,呈现出明显的间歇性;在很多情况下,间歇故障能够进一步演化为永久性故障,造成系统失效[12].考虑到间歇故障的特点,间歇故障诊断要求在每次故障消失(发生)之前检测出间歇故障的发生(消失)[2],并能准确定位间歇故障.因此,尽管众多研究学者对持续故障提出了很多行之有效的方法[12,16-18],却很难满足上述间歇故障诊断要求.
现阶段,间歇故障诊断研究主要采用定性分析方法[1-2,4,12,15-16,19].文献[12]通过构建实验平台模拟间歇故障对嵌入式系统的影响,结果表明间歇故障在整个使用周期中都可能出现.文献[16]验证了Petri网模型用于描述计算机系统接口间歇故障的有效性.现有文献中,基于定量分析方法的间歇故障诊断理论研究成果十分有限[1-2].文献[17]基于双线性奉献观测器研究了感应电机传感器间歇故障检测问题,结果表明上述残差需要充分时间衰减才能进行下一次间歇故障检测.文献[20]针对一类满足Bernouli分布且均值、方差已知的执行器间歇故障,在均方稳定框架下研究了其容错控制问题.但上述方法都只考虑间歇故障发生时刻的检测,却没有检测消失时刻,不满足其检测要求.文献[2]针对一类线性连续随机动态系统,在不考虑测量噪声条件下,研究了间歇故障发生时刻和消失时刻的检测问题.然而,在实际工业环境中,不仅难以获得精确的系统解析模型,而且存在大量测量噪声,因此,考虑存在测量噪声条件下,研究带有时变参数摄动的线性随机系统的间歇故障诊断问题是十分必要的.
针对一类带有时变参数摄动的线性离散随机动态系统,本文研究了其鲁棒间歇故障检测与分离问题,其主要创新点包括:1)基于降维未知输入观测器,通过引入滑动时间窗口,设计了一组结构化截断残差,使其与未知时变摄动解耦且对特定方向的间歇故障敏感,以实现故障定位;2)考虑测量噪声的影响,分析了新残差信号的统计特性,并提出两个假设检验分别用于检测间歇故障的发生时刻和消失时刻;3)针对结构化残差的存在性问题,本文给出了该问题可解的一个充分条件.
1 问题描述
考虑一类存在时变参数摄动的线性随机系统

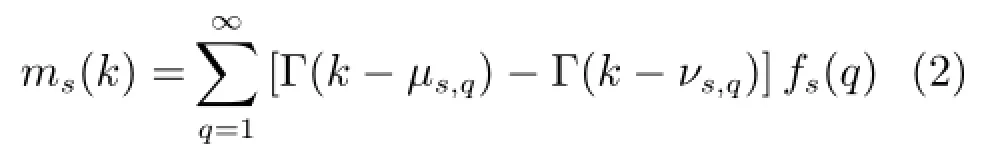
对上述系统和间歇故障,给出如下假设.
假设2.1)同一时刻仅有一个故障方向发生间歇故障;2)每一间歇故障都有已知幅值下界即每个间歇故障的持续时间/间隔时间具有最小值令假设 ττe¯先验τe已知. τe
2 鲁棒间歇故障诊断方法
本节针对系统(1)所示一类存在未知时变参数摄动的线性离散随机动态系统的间歇故障检测与分离问题,提出了一种鲁棒故障诊断方法.
2.1鲁棒残差设计
对系统(1)进行如下改写

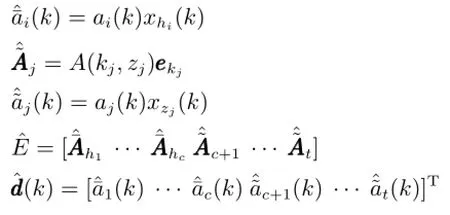

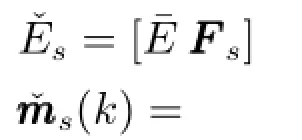

系统(4)改写为如下l组系统模型,其中第s(s∈ lll)组系统为

定理1.对系统(3)所示一类存在未知时变参数摄动的线性离散随机动态系统,设计l组残差生成器(6),使其满足条件1所示要求的一个充分条件是系统(3)满足:具有稳定不变零点.
证明.通过线性变换,显然,系统(4)等价于系统(3).对系统(4),为实现间歇故障分离,设计满足式(7)所示要求的l组残差,当满足时,对第组系统(6),根据文献[16],可以采用如下算式计算式(6)中参数
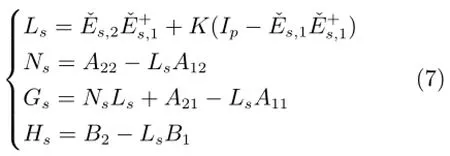
使得rs(k)对未知时变参数摄动和间歇故障ms(k)解耦.显然,由于p=n-1,dim[rs(k)]=1.为简化表示,令根据文献[16],条件2)满足时,残差生成器(6)稳定,其极点能够在单位圆内任意配置.下文中,仅以情况为例进行分析.由式(6)和式(7),可得降维估计误差为


引入滑动时间窗口∆ks,构造新的标量截断残差


综上所述,若条件1)~3)满足,基于残差生成器(6),能够对系统(3)设计l组满足条件1要求的结构化鲁棒残差.

图1 间歇故障与滑动时间窗口的相对位置关系Fig.1 Relative positions between the intermittent fault and the sliding-time window
2.2鲁棒残差统计特性分析



为简化表示,记

2.3鲁棒间歇故障诊断方法
间歇故障诊断要求在本次间歇故障消失之前确定间歇故障的发生时刻,在下一次间歇故障发生之前确定本次间歇故障的消失时刻,并准确定位故障.因此,针对间歇故障的发生和消失,本节提出两个假设检验分别检测,并给出鲁棒间歇故障诊断算法.
2.3.1间歇故障发生时刻的检测

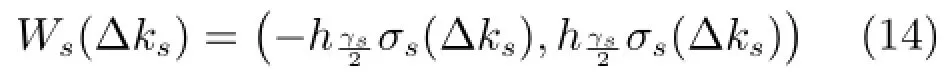

2.3.2间歇故障消失时刻的检测


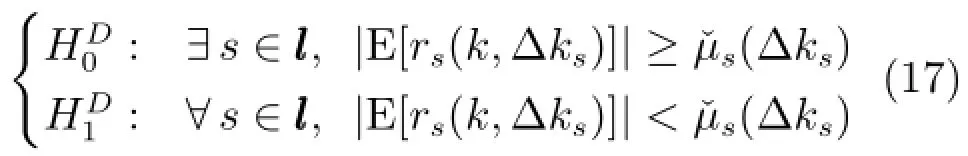

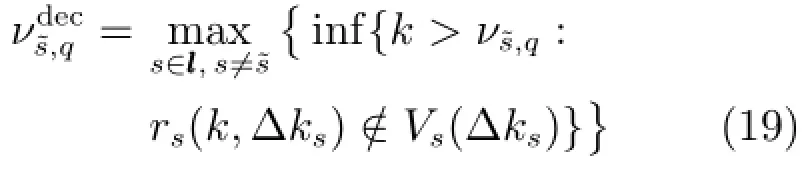
2.3.3鲁棒间歇故障分离策略

2.3.4鲁棒间歇故障诊断算法
根据上述分析并参考文献[22]给出的算法,本节给出如下鲁棒间歇故障诊断算法.
步骤1.对系统(1)进行线性变换得系统(4).
步骤3.由式(4)整理得到式(5)所示l组系统;验证每组系统是否满足若满足则继续;若不满足,对式(4)进行线性变换使式(5)满足上述条件.
步骤7.根据式(7)计算Gs和Hs.
步骤12.根据式(13)和式(17)检测间歇故障的发生和消失,并根据分离策略定位故障方向.
3 仿真验证
为验证上述方法有效性,考虑在椭圆参考轨道运行的某卫星的间歇故障诊断问题[23],其受到未知参数摄动和间歇故障影响的动力学模型为


仿真中,ai(k)服从[-1,1]的均匀分布为独立零均值高斯白噪声,其协方差分别为Rw=采用状态反馈跟踪控制律Kx=[60,7,0,8,0,0;0,-8,2,3,0,0;0,0,0,0,-14,3]使卫星沿参考轨道运行.
易知,系统(20)满足定理1所示条件,因此,基于降维未知输入观测器,能够设计3组残差生成器,使得对未知摄动间歇故障ms(k)解耦,而对间歇故障mj(k)(j 6=s)敏感.根据上述算法,3组标量残差生成器参数为


设计第三组残差生成器时,可得


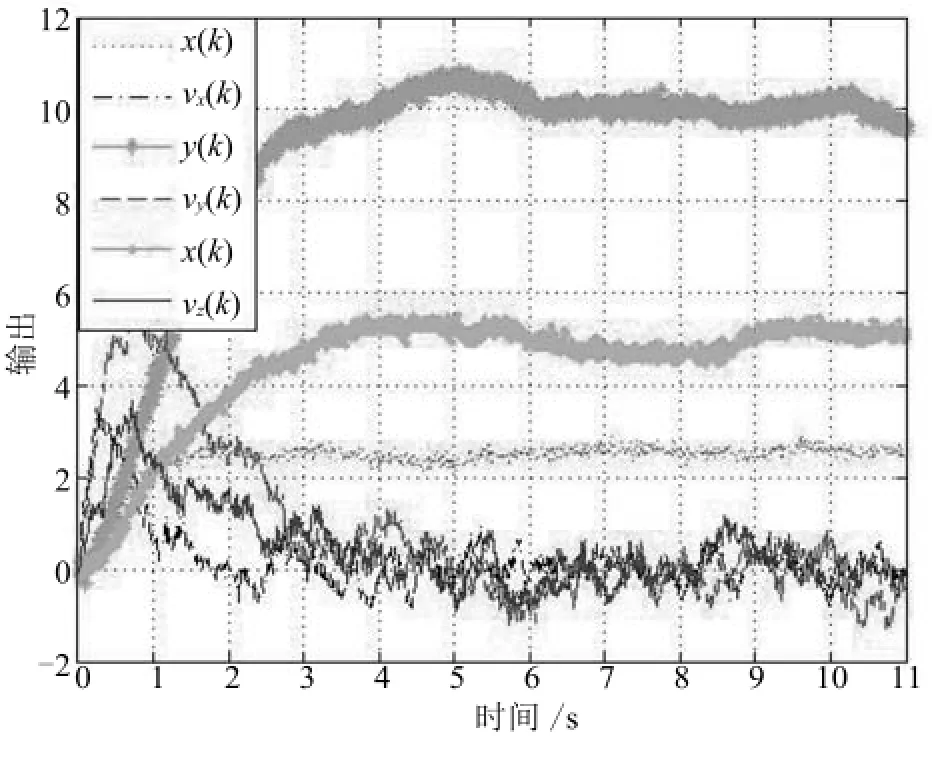
图2 正常运行时的系统输出Fig.2 Normal output of the satellite system(20)

图3 在k=500时发生间歇m3(k)的系统输出Fig.3 Output of system(20)subject to the IF m3(k)
当没有故障发生时,卫星系统运动状态如图2所示.可以看出,由于系统动力参数存在未知时变摄动以及受到随机噪声影响,卫星的位移和速度出现波动.以 FF3方向发生间歇故障为例,本文给出了该卫星在间歇故障m3(k)影响下的运动状态.如图3所示,在k=500(即第5秒)时, FF3方向发生最小幅值ρ=0.6、最小持续/间隔时间为0.4s的间歇故障m3(k).间歇故障m3(k)的发生使系统不能按原定轨迹运行,根据图3,无法确定m3(k)的发生时刻和消失时刻,更不能确定发生故障的执行器通道.
对上述发生间歇故障的系统(20),设计3组残差生成器(6),利用式(13)和式(17)进行间歇故障诊断.设定滑动时间窗口选择为显然,满足仿真结果如图4~6所示.由条件1可知m3(k)敏感,与m1(k)解耦m3(k)敏感,与m2(k)解耦m2(k)敏感,与m3(k)解耦.从图4~6可以看出,当m3(k)发生时,残差能够快速超过间歇故障发生时刻的检测阈值,从而迅速确定本次间歇故障的发生时刻;间歇故障消失之后,残差能够在下一次间歇故障发生之前衰减到消失时刻的检测阈值之下,从而确定本次间歇故障的消失时刻.由于与间歇故障m3(k)解耦,因此,其一直位于阈值范围内.根据分离策略,我们可以判断 FF3方向发生间歇故障,其发生时刻、消失时刻及实际检测值如表1所示,检测结果如图7所示.可以看出,本文方法能够迅速检测出间歇故障的发生时刻和消失时刻并准确定位故障.

图4 初始残差信号r1(k)和新残差信号r1(k,∆k1)Fig.4 Comparing r1(k,∆k1)with r1(k)

图5 初始残差信号r2(k)和新残差信号r2(k,∆k2)Fig.5 Comparing r2(k,∆k2)with r2(k)
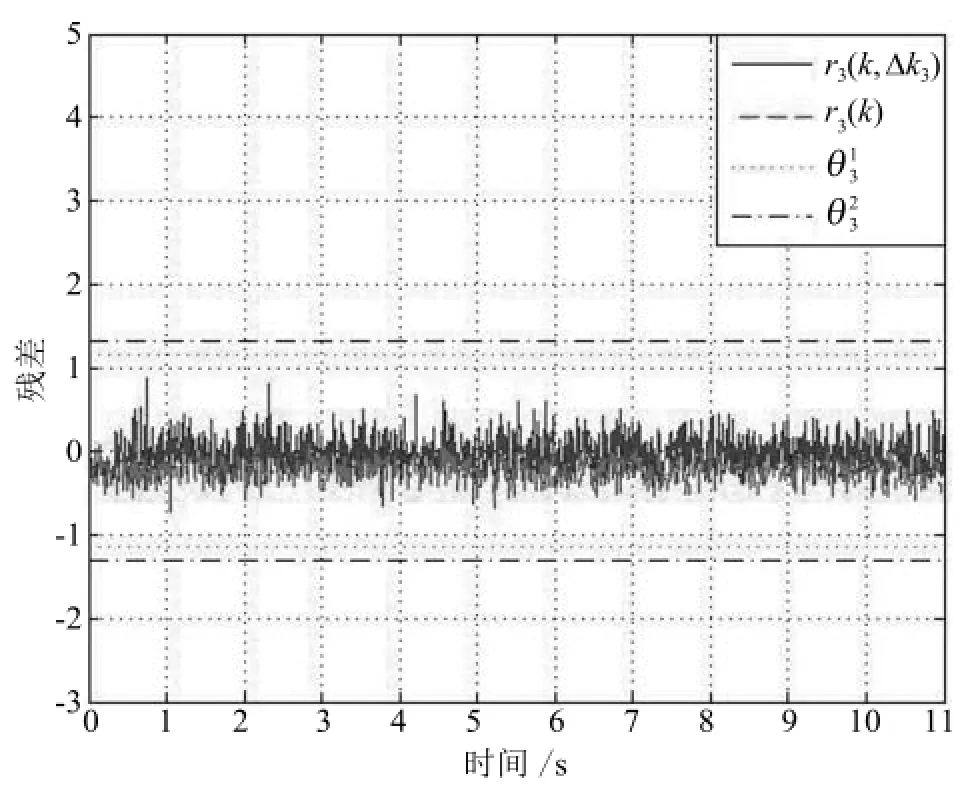
图6 初始残差信号r3(k)和新残差信号r3(k,∆k3)Fig.6 Comparing r3(k,∆k3)with r3(k)
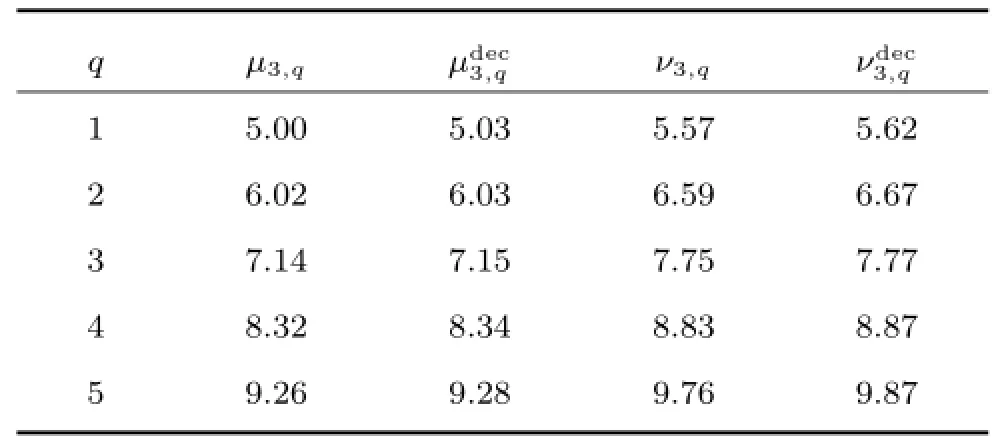
表1 间歇故障发生(消失)时刻及其实际检测值Table 1 The detection result of m3(k)by using the proposed method
为了进一步说明上述方法的有效性,对于发生相同间歇故障m3(k)的系统(20),基于Kalman滤波器得到系统状态估计值设计残差信号为选择构造如下的残差评价函数其仿真结果如图8所示,可以看出,根据此残差值无法检测出间歇故障m3(k)的发生时刻和消失时刻.
4 结论
本文针对一类存在未知时变参数摄动的线性离散随机动态系统的间歇故障诊断问题,提出一种鲁棒诊断方法.基于降维未知输入观测器,通过引入滑动时间窗口,本文设计了一组对系统未知参数摄动解耦的新的结构化标量残差,该组残差对间歇故障发生和消失更为敏感.基于对其统计特性的分析,根据间歇故障与滑动时间窗口相对位置关系,本文提出两个假设检验用于检测间歇故障的发生时刻和消失时刻.并利用结构化残差集,准确实现故障定位.通过沿参考轨道运行的某卫星系统的仿真实验,验证了本文方法的有效性.

图7 间歇故障检测结果Fig.7 The detection result of m3(k)by using the proposed method

图8 基于Kalman滤波方法的残差信号Fig.8 The Kalman filter based residual
References
1 Zhou Dong-Hua,Shi Jian-Tao,He Xiao.Review of intermittent fault diagnosis techniques for dynamic systems.Acta Automatica Sinica,2014,40(2):161-171(周东华,史建涛,何潇.动态系统间歇故障诊断技术综述.自动化学报,2014,40(2):161-171)
2 Chen M Y,Xu G B,Yan R Y,Ding S X,Zhou D H.Detecting scalar intermittent faults in linear stochastic dynamic systems.International Journal of Systems Science,2015,46(8):1337-1348
3 Correcher A,Garc´ıa E,Morant F,Quiles E,Blasco-Gimenez R.Intermittent failure diagnosis in industrial processes.In:Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics.Rio de Janeiro,Brazil:IEEE,2003. 723-728
4 Rashid L,Pattabiraman K,Gopalakrishnan S.Characterizing the impact of intermittent hardware faults on programs. IEEE Transactions on Reliability,2015,64(1):297-310
5 Shivakumar P,Kistler M,Keckler S W,Burger D,Alvisi L.Modeling the impact of device and pipeline scaling on the soft error rate of processor elements.Computer Science Department,University of Texas at Austin,2002.
6 Zhou Dong-Hua,Wei Mu-Heng,Si Xiao-Sheng.A survey on anomaly detection,life prediction and maintenance decision for industrial processes.Acta Automatica Sinica,2013,39(6):711-722(周东华,魏慕恒,司小胜.工业过程异常检测、寿命预测与维修决策的研究进展.自动化学报,2013,39(6):711-722)
7 Sorensen B A,Kelly G,Sajecki A,Sorensen P W.An analyzer for detecting intermittent faults in electronic devices. In:Proceedings of AUTOTESTCON′94 IEEE Conference on Systems Readiness Technology— “Cost Effective Support into the Next Century”.Anaheim,USA:IEEE,1994. 417-421
8 Yesilyurt I,Gu F S,Ball A D.Gear tooth stiffness reduction measurement using modal analysis and its use in wear fault severity assessment of spur gears.NDT and E International,2003,36(5):357-372
9 Zanardelli W G,Strangas E G,Aviyente S.Identification of intermittent electrical and mechanical faults in permanent-magnet AC drives based on time-frequency analysis.IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,2007,43(4):971-980
10 Ma Jie,Li Gang,Chen Mo.Nonlinear fault reconstruction based fault prognosis for rotating machinery.Acta Automatica Sinica,2014,40(9):2045-2049(马洁,李刚,陈默.基于非线性故障重构的旋转机械故障预测方法.自动化学报,2014,40(9):2045-2049)
11 Hamel A,Gaudreau A,Cote M.Intermittent arcing fault on underground low-voltage cables.IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery,2004,19(4):1862-1868
12 Correcher A,Garc´ıa E,Morant F,Quiles E,Rodriguez L. Intermittent failure dynamics characterization.IEEE Transactions on Reliability,2012,61(3):649-658
13 Kim C J.Electromagnetic radiation behavior of low-voltage arcing fault.IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery,2009,24(1):416-423
14 Zhou Dong-Hua,Chen Mao-Yin,Xu Zheng-Guo.The Reliabibility Prediction and Optimal Maintenance Technology. Hefei:Press of University of Science and Technology of China,2013.(周东华,陈茂银,徐正国.可靠性预测与最优维护技术.合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社,2013.)
15 Xu Gui-Bin.Researches on Fault Diagnosis and Prediction in Dynamic Systems[Master dissertation],Tsinghua University,China,2011.(徐贵斌.动态系统故障诊断及预测研究[硕士学位论文],清华大学,中国,2011.)
16 Krasnobaev V A,Krasnobaev L A.Application of Petri nets for the modeling of detection and location of intermittent faults in computers.Automation and Remote Control,1989,49(9):1198-1204
17 Bennett S M,Patton R J,Daley S,Newton D A.Torque and flux estimation for a rail traction system in the presence of intermittent sensor faults.In:Proceedings of United Kingdom Automatic Control Council International Conference on Control′96.Exeter University,UK:IET,1996.72-77
18 Wang Y,Xu G H,Zhang Q,Liu D,Jiang K S.Rotating speed isolation and its application to rolling element bearing fault diagnosis under large speed variation conditions. Journal of Sound and Vibration,2015,348:381-396
19 Zhou C J,Huang X F,Xiong N X,Qin Y Q,Huang S. A class of general transient faults propagation analysis for networked control systems.IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics:Systems,2015,45(4):647-661
20 Gu Zhou,Zhang Jian-Hua,Du Li-Long.Fault tolerant control for a class of time-delay systems with intermittent actuators failure.Control and Decision,2011,26(12):1829-1834(顾洲,张建华,杜黎龙.一类具有间歇性执行器故障的时滞系统的容错控制.控制与决策,2011,26(12):1829-1834)
21 Edelmayer A,Bokor J,Szigeti F,Keviczky L.Robust detection filter design in the presence of time-varying system perturbations.Automatica,1997,33(3):471-475
22 Kudva P,Viswanadham N,Ramakrishna A.Observers for linear systems with unknown inputs.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,1980,25(1):113-115
23 Meskin N,Khorasani K.Fault detection and isolation of discrete-time Markovian jump linear systems with application to a network of multi-agent systems having imperfect communication channels.Automatica,2009,45(9):2032-2040

鄢镕易清华大学自动化系博士研究生.主要研究方向为间歇故障诊断与容错控制,高速列车故障诊断与容错控制.
E-mail:yry10@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn
(YAN Rong-YiPh.D.candidate in the Department of Automation,Tsinghua University.His research interest covers fault diagnosis and tolerance control of intermittent faults,fault diagnosis for the information control system of high-speed trains.)

何潇清华大学自动化系副教授.主要研究方向为网络化系统的鲁棒滤波、故障诊断与容错控制,无人机(群)智能自主控制中的安全性问题,高速列车信息控制系统的故障诊断.
E-mail:hexiao@tsinghua.edu.cn
(HE XiaoAssociate professor in the Department of Automation,Tsinghua University.His research interest covers robust estimation,fault diagnosis and tolerant control of networked systems,safety problems in intelligent autonomous control of unmanned aerial vehicles,fault diagnosis for the information control system of high-speed trains.)

周东华山东科技大学电气与自动化工程学院教授,清华大学自动化系教授.主要研究方向为动态系统的故障诊断与容错控制,故障预测与智能维护技术.本文通信作者.
E-mail:zdh@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
(ZHOUDong-HuaProfessor at the College of Electrical Engineering and Automation,Shandong University of Science and Technology,and the Department of Automation,Tsinghua University.His research interest covers fault diagnosis and tolerant control,fault prediction and intelligent maintenance. Corresponding author of this paper.)
Robust Diagnosis of Intermittent Faults for Linear Stochastic Systems Subject to Time-varying Perturbations
YAN Rong-Yi1HE Xiao1ZHOU Dong-Hua1,2
Since intermittent faults(IFs)have an intermittency property,the detection of IFs requires:the current appearing time of an IF must be detected before its disappearing time;the current disappearing time of an IF must be detected before the subsequent appearing time.In this paper,the robust detection problem of IFs for a class of linear discrete-time stochastic systems subject to unknown time-varying perturbations is investigated.Based on reducedorder unknown input observers(UIOs),a novel set of structured truncated residuals is designed to detect and isolate IFs by introducing sliding-time windows,and a sufficient condition is proposed for the existence of the residual generators. Compared to traditional residuals,the novel truncated residuals,which get decoupled from time-varying perturbations,are more sensitive to the IFs.Based on the analysis of these novel residuals,two hypothesis tests are proposed to detect all the appearing times and the disappearing times of an IF.In addition,a detailed algorithm is provided to perform the given scheme.Finally,simulation results on a model of a satellite moving in a circular reference orbit are presented to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Intermittent faults(IFs),robust fault diagnosis,unknown time-varying perturbations,reduced-order unknown input observer,hypothesis tests
10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150756
Yan Rong-Yi,He Xiao,Zhou Dong-Hua.Robust diagnosis of intermittent faults for linear stochastic systems subject to time-varying perturbations.Acta Automatica Sinica,2016,42(7):1004-1013
2015-11-11录用日期2016-03-20
Manuscript received November 11,2015;accepted March 20,2016
国家自然科学基金(61490701,61290324,61473163,61522309),山东省泰山学者优势特色学科人才团队支持计划(鲁政办字[2015]73),清华大学自主科研项目(025-陈茂银-Z09)资助
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61490701,61290324,61473163,61522309),Research Fund for the Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province([2015]73),and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program (025-CMY-Z09)
本文责任编委钟麦英
Recommended by Associate Editor ZHONG Mai-Ying
1.清华大学自动化系北京1000842.山东科技大学电气与自动化学院青岛266590
1.Department of Automation,Tsinghua University,Beijing 1000842.College of Electrical Engineering and Automation,Shandong University of Science and Technology,Qingdao 266590
