CTA斑点征对急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的预测价值分析
2016-06-28陈文鑫吴学良陈汉杰邹社昌张丹霓刘国江黄妙珊
陈文鑫,吴学良,陈汉杰,邹社昌,张丹霓,刘国江,黄妙珊
·诊治分析·
CTA斑点征对急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的预测价值分析
陈文鑫,吴学良,陈汉杰,邹社昌,张丹霓,刘国江,黄妙珊
515300广东省普宁市人民医院神经内科
【摘要】目的分析CTA斑点征对急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的预测价值。方法选取2013—2015年在普宁市人民医院神经内科急诊就诊的急性高血压脑出血患者72例,均在发病6 h内进行颅脑CT及CTA检查,发病24 h后复查CT。比较CTA斑点征阳性患者和CTA斑点征阴性患者一般资料,记录血肿扩大情况,并分析CTA斑点征对急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的预测价值。结果颅脑CTA原始图像斑点征阳性20例(27.8%),斑点征阴性52例(72.2%)。CTA斑点征阳性患者和CTA斑点征阴性患者性别、血肿部位、血肿形态、出血是否破入脑室、年龄及首次CT检查时血肿体积比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。72例患者血肿扩大率为29.1%,其中14例血肿扩大发生在6 h内、7例血肿扩大发生在6~24 h;21例血肿扩大患者中18例出现病情加重,其中2例在24 h内死亡。CTA斑点征预测血肿扩大的灵敏度为80.9%,特异度为94.1%,诊断准确率为90.3%。结论急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大发生率较高、预后较差,而CTA斑点征可有效预测急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大。
【关键词】颅内出血,高血压性;斑点征;血肿扩大
陈文鑫,吴学良,陈汉杰,等.CTA斑点征对急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的预测价值分析[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2016,24(5):78-80.[www.syxnf.net]
Chen WX,Wu XL,Chen HJ,et al.Predictive value of spot sign of CTA on hematoma expansion in patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage[J].Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease,2016,24(5):78-80.
急性脑出血是神经科常见的急危重症,占脑卒中总发病人数的9%~27%[1],其病死率较高。临床研究显示,75%的高血压脑出血患者会遗留残疾甚至死亡[2],其中13%~32%的患者在脑出血后24 h内发生血肿扩大[3],且血肿扩大能加重患者病情,甚至增加患者病死率[3-4]。因此,如何早期预测血肿扩大、识别血肿扩大高危人群是目前临床关注的热点之一。本研究选择72例急性高血压脑出血患者作为研究对象,拟通过CTA斑点征预测其血肿扩大情况,旨在为急性高血压脑出血的临床诊治提供参考依据。
1资料与方法
1.1纳入与排除标准纳入标准:(1)符合急性高血压脑出血的诊断标准,且经颅脑CT检查证实;(2)幕上出血;(3)发病至首次颅脑CT检查时间在6 h内;(4)首次颅脑CT检查后采用内科保守治疗,患者病情恶化或发病24 h后能完成颅脑CT复查。排除标准:(1)颅脑CTA检查证实为动脉瘤、烟雾病、脑动静脉畸形及脑瘤性卒中者;(2)合并严重肾功能不全、甲状腺疾病及造影剂过敏者;(3)既往有脑血管意外、颅脑创伤史者;(4)入院时深度昏迷者。
1.2一般资料选取2013—2015年在普宁市人民医院神经内科急诊就诊的急性高血压脑出血患者72例,其中男46例,女26例;年龄33~73岁,平均年龄(57.1±8.1)岁;高血压病程3~20年;首发症状:偏侧肢体无力、言语不利者38例,头痛、呕吐者24例,意识障碍者10例;出血部位:基底核区49例,脑叶23例;血肿形态:规则、类圆形57例,不规则15例;出血破入脑室者18例。
1.3检查方法
1.3.1CT检查所有患者入院后行颅脑CT检查,采用多田公式计算血肿体积,因破入脑室的血液难以计算且无法明确是否存在血肿扩大,故出血破入脑室者出血量只计算脑实质血肿体积。患者病情恶化或发病24 h后复查颅脑CT,比较两次血肿体积。血肿扩大是指血肿绝对增长超过6 ml或血肿相对增长超过33%[5]。
1.3.2CTA检查所有患者选用90 ml碘帕醇(上海博莱科信谊药业有限责任公司生产)作为CT造影剂,以4 ml/s的速度注射30 ml,然后以3 ml/s的速度注射60 ml,延迟17 s后进行螺旋CT扫描。由两位资深的影像科医师在互相不了解对方判断结果的情况下在CTA原始图像上寻找斑点征。CTA斑点征判定标准[6-7]:(1)在颅内血肿的造影剂外渗处,出现≥1个增强斑点样病灶;(2)周围血肿与其密度相比,对比衰减≥120 HU;(3)在颅内血肿周围存在相邻的不连续的正常或异常血管走形;(4)斑点征存在于颅内血肿范围内。
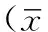
2结果
2.1CTA斑点征阳性和CTA斑点征阴性患者一般资料比较颅脑CTA原始图像斑点征阳性20例(27.8%),斑点征阴性52例(72.2%)。CTA斑点征阳性患者和CTA斑点征阴性患者性别、血肿部位、血肿形态、出血是否破入脑室、年龄及首次CT检查时血肿体积比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表1)。
2.2血肿扩大情况72例患者中共21例发生血肿扩大,血肿扩大率为29.1%;其中14例血肿扩大发生在6 h内,7例血肿扩大发生在6~24 h。21例患者中18例出现病情加重,其中2例在24 h内死亡。典型急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的CT及CTA图像见图1。

注:①为颅脑CT平扫显示左侧基底核区出血;②为CTA原始图像,黑箭头所示的地方为斑点征;③为复查颅脑CT显示血肿扩大
图1急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的CT及CTA图像
Figure 1CT and CTA images of hematoma expansion in patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage
2.3CTA斑点征对血肿扩大的预测价值21例血肿扩大患者中CTA斑点征阳性17例,其中11例为1个斑点征、3例为2个斑点征、2例为3个斑点征、1例为4个斑点征。CTA斑点征预测血肿扩大的灵敏度为80.9%,特异度为94.1%,诊断准确率为90.3%,见表2。

表2 CTA斑点征对血肿扩大的预测价值(例)
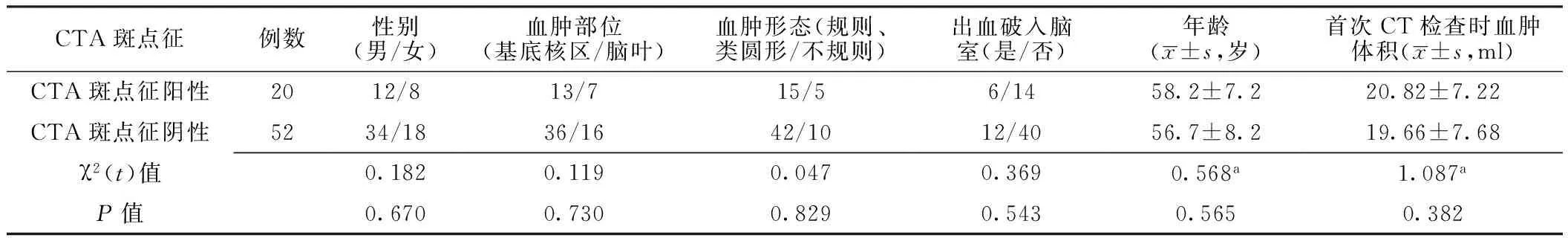
表1 CTA斑点征阳性患者和CTA斑点征阴性患者一般资料比较
注:a为t值
3讨论
高血压脑出血发病凶险,病情变化快,致死率高,致残率高,且脑出血可导致局部脑组织占位性病变而释放凝血酶和炎性递质等活性物质,进而引发血肿周围脑组织继发性损伤。临床研究显示,继发性损伤(尤其是脑水肿)是导致神经功能障碍的主要原因,且早期血肿扩大可导致临床症状加重和神经功能进行性恶化,甚至导致死亡。Dowlatshahi等[3]研究显示,早期血肿扩大能明显加重脑水肿、增加继发性脑梗死发生率,是神经功能恶化的主要原因,对预测神经功能恢复及评估病死率具有重要意义。Delcourt等[4]学者指出,血肿扩大提示患者神经功能预后不良及病死率增加,血肿体积每增加1 ml患者死亡风险增加5%。本研究结果显示,急性高血压脑出血患者24 h内血肿扩大发生率为29.1%,与Dowlatshahi等[3]报道的13%~32%一致,提示急性高血压脑出血患者早期血肿扩大发生率较高。
血肿扩大是一个血液不断从血管渗漏到组织间隙的动态出血过程,目前脑出血早期血肿扩大的发生机制尚未明确,推测其主要原因包括原发破裂血管持续性出血或再出血及血肿周围血管破裂出现持续性出血[5-6]。但目前预测脑出血患者早期血肿扩大的手段非常有限,以往临床常通过观察血肿形态、是否使用抗凝药物、凝血机制异常、血压骤升及头痛、呕吐等临床症状推断可能存在血肿扩大,但准确性较低。近年来,随着影像学技术的迅速发展及临床医生对血肿扩大认识的提高,临床上对急性脑出血血肿扩大的诊断取得一定成果。多项研究指出,CTA斑点征与血肿扩大具有相关性[7-9],且CTA斑点征可预测血肿扩大、评估神经功能改善情况及临床预后[10-11]。CTA斑点征是指行CTA检查时由于造影剂从通透性增大的血管渗漏到血管外组织间隙,导致脑血肿范围内非血管走形区出现单发或多发的点或线样高密度影,其出现原因可能为活动性出血[12]。Demchuk等[7]研究证实,CTA斑点征为血肿扩大的独立预测指标,可提示患者预后不良,且与脑出血患者3 个月神经功能损伤和病死率相关。本研究结果显示,CTA原始图像斑点征阳性率为27.8%,与既往报道的24%~27%[7-8]基本一致。本研究进一步分析了CTA斑点征对血肿扩大的预测价值,结果显示,CTA斑点征诊断血肿扩大的灵敏度为80.9%、特异度为94.1%、诊断准确率为90.3%,提示CTA斑点征对急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大具有一定的预测价值。
有研究指出,可以利用CTA斑点征指导脑出血患者血压管理及抗高血压治疗[13]。Delgado Almandoz等[14]研究指出,CTA斑点征可以筛选需要止血治疗的高危患者,特别是使采用重组人凝血因子Ⅶa治疗的原发性脑出血患者获益。最近正在进行一项关于CTA斑点征和氨甲环酸用于控制血肿扩大的临床随机多中心双盲试验[15],期待会有令人兴奋的结论。本研究侧重分析了CTA斑点征对急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大的预测价值,而未对血肿扩大的影响因素进行分析,有待于今后进一步研究证实。
综上所述,急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大发生率较高、预后较差,而CTA斑点征可有效预测急性高血压脑出血患者血肿扩大,有助于指导临床医生进行及时治疗。
参考文献
[1]Steiner T,Al-Shahi Salman R,Beer R,et al.European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage[J].Int J Stroke,2014,9(7):840-855.
[2]Van Asch CJ,Luitse MJ,Rinkel GJ,et al.Incidence,case fatality,and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time,according to age,sex,and ethnic origin:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Lancet Neurol,2010,9(2):167-176.
[3]Dowlatshahi D,Demchuk AM,Flaherty ML,et al.Defining hematoma expansion in intracerebral hemorrhage: relationship with patient outcomes[J].Neurology,2011,76(14):1238-1244.
[4]Delcourt C,Huang Y,Arima H,et al.Hematoma growth and outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage: the INTERACT1 study[J].Neurology,2012,79(4):314-319.
[5]Boulouis G,Dumas A,Betensky RA,et al.Anatomic pattern of intracerebral hemorrhage expansion:relation to CT angiography spot sign and hematoma center[J].Stroke,2014,45(4):1154-1156.
[6]Ovesen C,Christensen AF,Krieger DW,et al.Time course of early postadmission hematoma expansion in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage[J].Stroke,2014,45(4):994-999.
[7]Demchuk AM,Dowlatshahi D,Rodriguez-Luna D,et al.Prediction of haematoma growth and outcome in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage using the CT-angiography spot sign(PREDICT):a prospective observational study[J].Lancet Neurol,2012,11(3):307-314.
[8]Rizos T,Dorner N,Jenetzky E,et al.Spot signs in intracerebral hemorrhage: useful for identifying patients at risk for hematoma enlargement?[J].Cerebrovasc Dis,2013,35(6):582-589.
[9]Radmanesh F,Falcone GJ,Anderson CD,et al.Risk factors for computed tomography angiography spot sign in deep and lobar intracerebral hemorrhage are shared[J].Stroke,2014,45(6):1833-1835.
[10]Dowlatshahi D,Wasserman JK,Momoli F,et al.Evolution of computed tomography angiography spot sign is consistent with a site of active hemorrhage in acute intracerebral hemorrhage[J].Stroke,2014,45(1):277-280.
[11]Del Giudice A, D′Amico D, Sobesky J,et al.Accuracy of the spot sign on computed tomography angiography as a predictor of haematoma enlargement after acute spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage:a systematic review[J].Cerebrovasc Dis,2014,37(4):268-276.
[12]Romero JM,Brouwers HB,Lu J,et al.Prospective validation of the computed tomographic angiography spot sign score for intracerebral hemorrhage[J].Stroke,2013,44(11):3097-3102.
[13]Delcourt C,Huang Y,Wang J,et al.The second (main) phase of an open,randomised,multicentre study to investigate the effectiveness of an intensive blood pressure reduction in acute cerebral haemorrhage trial (INTERACT2)[J].International Journal of Stroke,2010,5(2):110-116.
[14]Delgado Almandoz JE,Yoo AJ,Stone MJ,et al.Systematic characterization of the computed tomography angiography spot sign in primary intracerebral hemorrhage identifies patients at highest risk for hematoma expansion:the spot sign score[J].Stroke,2009,40(9):2994-3000.
[15]Meretoja A,Churilov L,Campbell BC,et al.The spot sign and tranexamic acid on preventing ICH growth-AUStralasia Trial(STOP-AUST):Protocol of a phase II randomized,placebo-controlled,double-blind,multicenter trial[J].Int J Stroke,2014,9(4):519-524.
(本文编辑:谢武英)
Predictive Value of Spot Sign of CTA on Hematoma Expansion in Patients With Acute Hypertensive Cerebral Hemorrhage
CHENWen-xin,WUXue-liang,CHENHan-jie,etal.
DepartmentofNeurology,thePeople′sHospitalofPuning,Puning515300,China
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo explore the predictive value of spot sign of CTA on hematoma expansion in patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage.MethodsFrom 2013 to 2015 in the Department of Neurology,the People′s Hospital of Puning,a total of 72 patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage were selected,all of them received craniocerebral CT examination and CTA examination within 6 hours after attack,they received reexamination of CT scan after 24 hurs of attacle.General information and incidence of hematoma expansion were compared in patient with or without spot sign of CTA,and the predictive value of spot sign of CTA on hematoma expansion in patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage was analyzed.ResultsOf the 72 patients,20 cases found spot sign of CTA(accounting for 27.8%),52 cases did not found(accounting for 72.2%).No statistically significant differences of gender,hematoma locations,hematoma shapes,incidence of hematoma breaking into ventricles,age or hematoma volume at the first CT scan was found in patients with or without spot sign of CTA(P>0.05).The incidence of hematoma expansion was 29.1%(21/72),thereinto 14 cases occurred hematoma expansion within 6 hours after attack,7 cases occurred hematoma expansion within 6 to 24 hours after attack;18 cases occurred diseases aggravation and 2 cases of them died within 24 hours.The sensitivity of spot sign of CTA in predicting hematoma expansion in patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage was 80.9%,the specificity was 94.1%,and the diagnosis accuracy was 90.3%.ConclusionThe incidence of hematoma expansion is relatively high in patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage,and the prognosis is relatively poor,spot sign of CTA has certain predictive value on hematoma expansion in patients with acute hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage.
【Key words】Intracranial hemorrhage,hypertensive;Spot sign;Hematoma expansion
通信作者:陈文鑫,515300广东省普宁市人民医院神经内科;E-mail:285792509@qq.com
【中图分类号】R 743.34
【文献标识码】B
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2016.05.020
(收稿日期:2016-01-26;修回日期:2016-05-10)
