基于尺度不变特征转换算法的棉花双目视觉定位技术
2016-05-17朱镕杰朱颖汇张志川
朱镕杰,朱颖汇,王 玲,卢 伟,罗 慧,张志川
(南京农业大学工学院,南京 210031)
基于尺度不变特征转换算法的棉花双目视觉定位技术
朱镕杰,朱颖汇,王 玲※,卢 伟,罗 慧,张志川
(南京农业大学工学院,南京 210031)
为了给采棉机器人提供运动参数,设计了一套双目视觉测距装置以定位棉株。对获取的左右棉株图像进行经背景分割等预处理。求取其在8个尺度下的高斯图,通过尺度不变特征转换SIFT(scale-invariant feature transform)算法在相邻高斯差分图中提取出SIFT关键点;计算每个高斯图中关键点邻域内4×4个种子点的梯度模值,得到128维特征向量。分割右图关键点构成的128维空间,得到二叉树;利用最优节点优先BBF(best bin first)算法在二叉树中寻找到172个与左图对应的粗匹配点。由随机采样一致性RANSAC(random sample consensus)算法求出基础矩阵F,恢复极线约束,剔除误匹配,得到分布在11朵棉花上的151对精匹配。结合通过标定和F得到的相机内外参数,最终重建出棉花点云的三维坐标。结果表明,Z轴重建结果比较接近人工测量,平均误差为0.039 3 m,能够反映棉花间的相对位置。
机器人;图像处理;视觉;棉花;SIFT特征;双目视觉;二叉树;RANSAC算法
朱镕杰,朱颖汇,王 玲,卢 伟,罗 慧,张志川.基于尺度不变特征转换算法的棉花双目视觉定位技术[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(6):182-188.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.025 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhu Rongjie,Zhu Yinghui,Wang Ling,Lu Wei,Luo Hui,Zhang Zhichuan.Cotton positioning technique based on binocular vision with implementation of scale-invariant feature transform algorithm[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE),2016,32(6):182-188.(in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.025 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引言
棉花是中国的主要经济作物之一。美国、俄罗斯、埃及等产棉大国通常采用大规模机械化采收方式[1]。中国棉花常用的人工采摘方式劳动强度大、成本高,严重制约着棉花生产规模的进一步扩大[2]。为此,采用棉花采摘机器人代替人工劳作有望大幅度降低采摘成本并提高生产效率[3-5],而双目立体视觉系统正是采棉机器人的核心技术之一。
国内外对农业中的双目视觉应用均有不同程度的研究。国外方面,Kassay[6]等利用双目立体视觉系统采集到水果图像后,采用霍夫变换进行图像处理获取水果的中心位置。Kondo[7]等基于番茄的颜色特征寻找和识别成熟的果实,采用立体视觉技术获取番茄的位置信息。Takahashi[8-10]等根据苹果在立体图像对中的视差将给定范围的三维空间分割成若干个等距离的区间,将2幅图像合成一幅中心图像,然后获取苹果的深度信息。国内方面,王玲[11]等利用激光传感器采用了非接触式的方法测量棉株表面的深度信息,但处理速度较慢且稳定性不高。彭辉[12]等结合加速鲁棒特征SURF(speed-up robust features)算子和极线约束对柑橘立体图像对进行匹配,在果实光线强弱不同时仍然能较好的进行匹配,但是SURF算子对匹配对象视角差异的容忍度仍有不足。
本文在分析了国内外对采摘机器人视觉系统的研究的基础上,利用尺度不变特征转换SIFT(scale-invariant feature transform)[13-14]算法对棉花的平移、旋转、尺度缩放良好的抑制性提取棉花表面特征,采用基于最优节点优先BBF(best bin first)[15]算法的二叉树搜索算法提高特征匹配的精度与效率,利用随机采样一致性RANSAC(random sample consensus)[16]算法估计基础矩阵并去除误匹配,并结合标定结果得到相机内部参数和外部运动参数进行匹配点的三维重建完成棉花定位,以此为采摘机器人运动轨迹的规划提供参数。
1 棉花图像采集与预处理
将镜头焦距为16mm的双目相机、投影仪、1.8m×0.7m× 1.8 m角钢架和PC机组建测距试验装置,相机固定在投影仪两侧,可随意调整其俯仰角和偏转角,以保证棉株处在相机的视野范围内(图1-a)。
在投影仪打光和不打光二种条件下连续拍摄二张棉株图像(图1-b,c)。利用打光图像棉花与背景对比度强的特点对图像进行二值化处理,以去除背景;结合不打光图像获取边界清晰、纹理丰富的黑背景棉花图像,进一步进行灰度拉伸、锐化等预处理,以增强棉花的灰度细节(图1-d)。
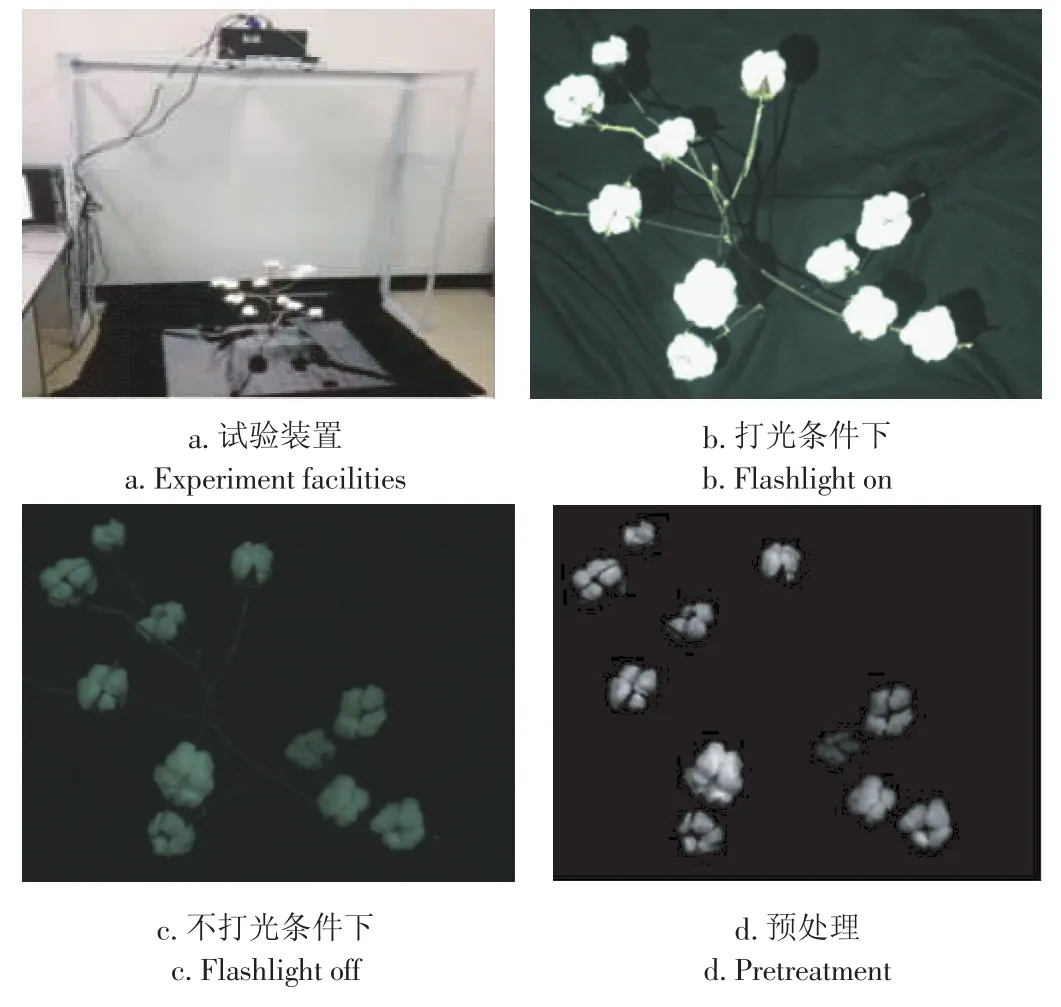
图1 图像采集与预处理Fig.1 Image acquisition and pretreatment
2 基于SIFT算法的粗匹配
2.1 SIFT关键点检测与特征提取
尺度不变特征转换SIFT特征仅依赖于图像的局部信息,具有平移、旋转、缩放不变性,同时,对光照、投影、仿射的变化也具有一定的鲁棒性。
首先,用不同尺度的二维高斯核函数(式1)与二维图像卷积,实现棉花图像的模糊滤波处理,获取尺度k(k= 0~8)的高斯图(式2);进一步计算相邻尺度高斯图之间的差分图(式3),获得尺度k(k=1~8)的高斯差分图。
其次,将尺度1~8的高斯差分图堆积成一个三维尺度空间,检测该空间中的数据点是否为其3×3×3立体邻域内的局部极值点,局部极值点即为关键点(图2-a),进一步基于曲面拟合来精确定位关键点的坐标,并用二阶求导法消除边缘处的噪声响应。
最后,以关键点为中心,在其4×4邻域窗口内采样16个种子点,针对每一个种子点,在尺度1~8的高斯图上分别计算其梯度模值和方向(式4-5),基于种子点的8个模值获取关键点的16×8=128维SIFT特征(图2-b)。
试验结果表明,左、右图分别检测出1 529、1 493个关键点。
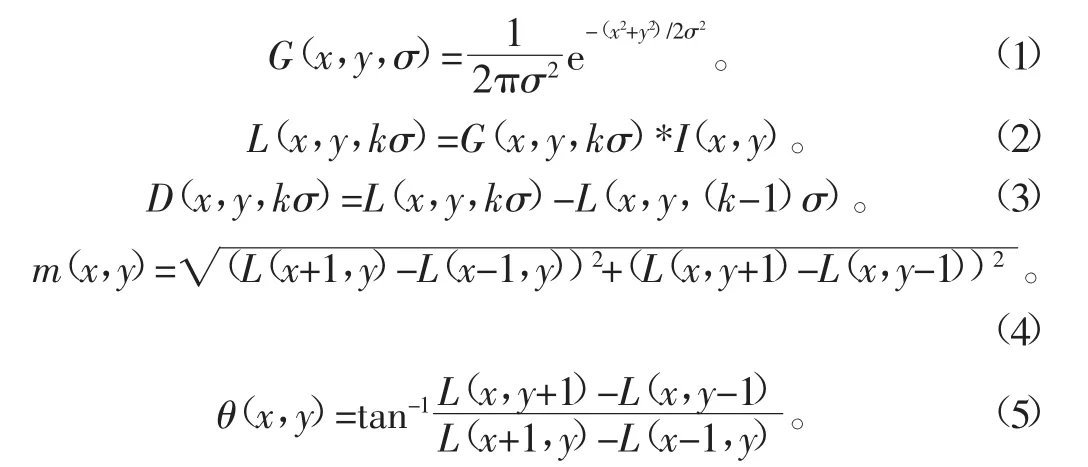
式中(x,y)表示图像I上像素点的位置;σ为尺度空间因子。
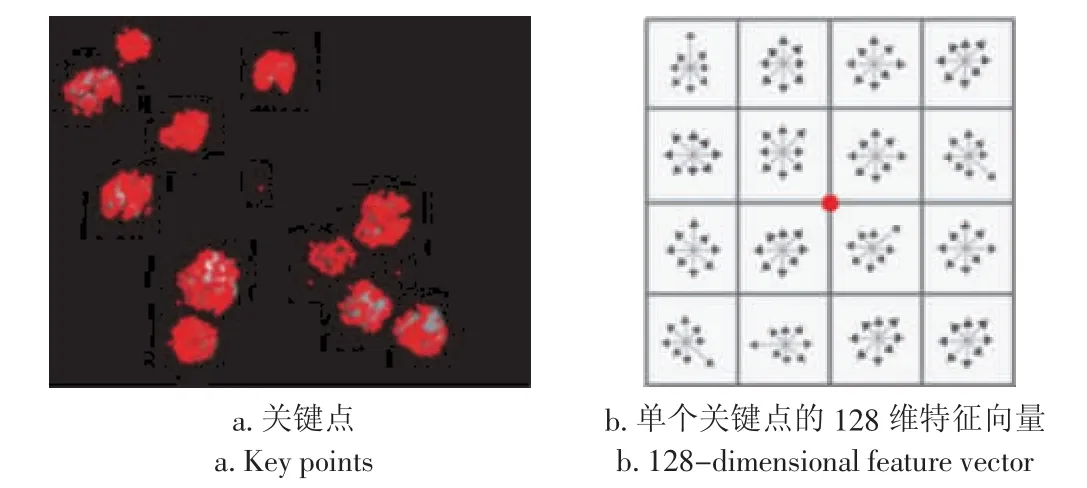
图2 SIFT特征向量Fig.2 SIFT feature vectors
2.2 二叉树搜索
关键点匹配可以归结为一个通过距离函数在高维空间上的相似性检索问题,穷尽搜索虽能搜索到正确的匹配点,但耗时大;基于二叉树搜索算法并结合最优节点优先BBF的嵌套搜索算法可有效解决该问题。以左图的第14个关键点为例,在右图中搜索其匹配点的方法如图3所示。
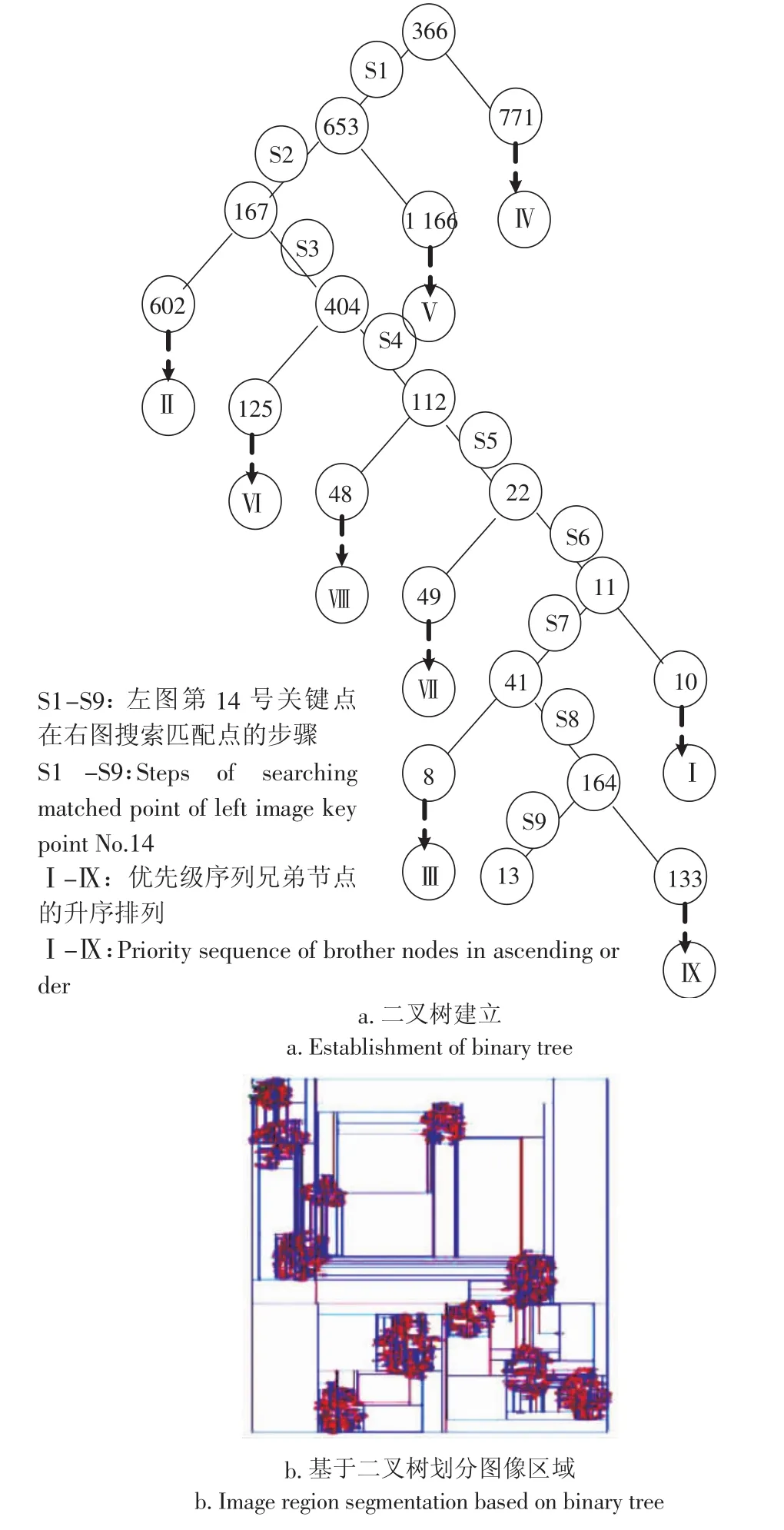
图3 二叉树搜索Fig.3 Search of binary tree
首先,创建二叉树。在128维上分别计算右图1 493个关键点的特征值方差,最大方差所在维为第105维,该维特征排序后的中值56.270 6对应关键点366,以此为根节点,将小于或等于中值的关键点集合归入根节点的左枝,否则归入右枝;依此类推,分别划分根节点的左枝和右枝,直至叶节点,从而创建了一个二叉树(图3-a)。同时按照寻找到的各节点划分右图棉花的二维图像区域,这样搜索匹配点时只需在由对应节点划分的区域内寻找,而不必遍历所有关键点,有效地缩小了匹配点的搜索范围(图3-b)。
其次,二叉树搜索。从二叉树根节点366开始,在第105维上,由于左图关键点14的特征值25.707 8小于等于右图根节点的特征值56.2706,即表1中L-R≤0,则搜索路径指向根节点的左子节点,即关键点653,反之亦然。重复以上步骤,直至搜索路径指向叶节点,即366、653、167、404、112、22、11、41、164、13(图3-a),搜索过程中同时依次记录途经节点的兄弟节点771、1 166、602、125、48、49、10、8、133。
再次,二叉树嵌套搜索。获取上述兄弟节点在二叉树创建过程中产生的最大方差所在维及其特征值,并与左图关键点14在对应维上的特征值进行比较,并将比较结果| L′-R′|进行升序排序(表1),生成BBF优先级序列兄弟节点10、602、8、771、1 166、125、49、48、133。依次从优先级序列中的兄弟节点出发,嵌套搜索二叉树至叶节点(图3-a),直至优先级序列为空或到达200次搜索限制,返回若干个叶节点。
最后,确定匹配点。在128维特征空间下用欧氏距离比较左图关键点14与右图二叉树搜索到的所有叶节点的相似度,返回欧氏距离最小的相似点13和次相似点121,对应的相似度和次相似度分别为47.875 8和297.975 9(表2),定义相似度小于0.49×次相似度的相似点为匹配点,则相似点13为左图关键点14的匹配点。
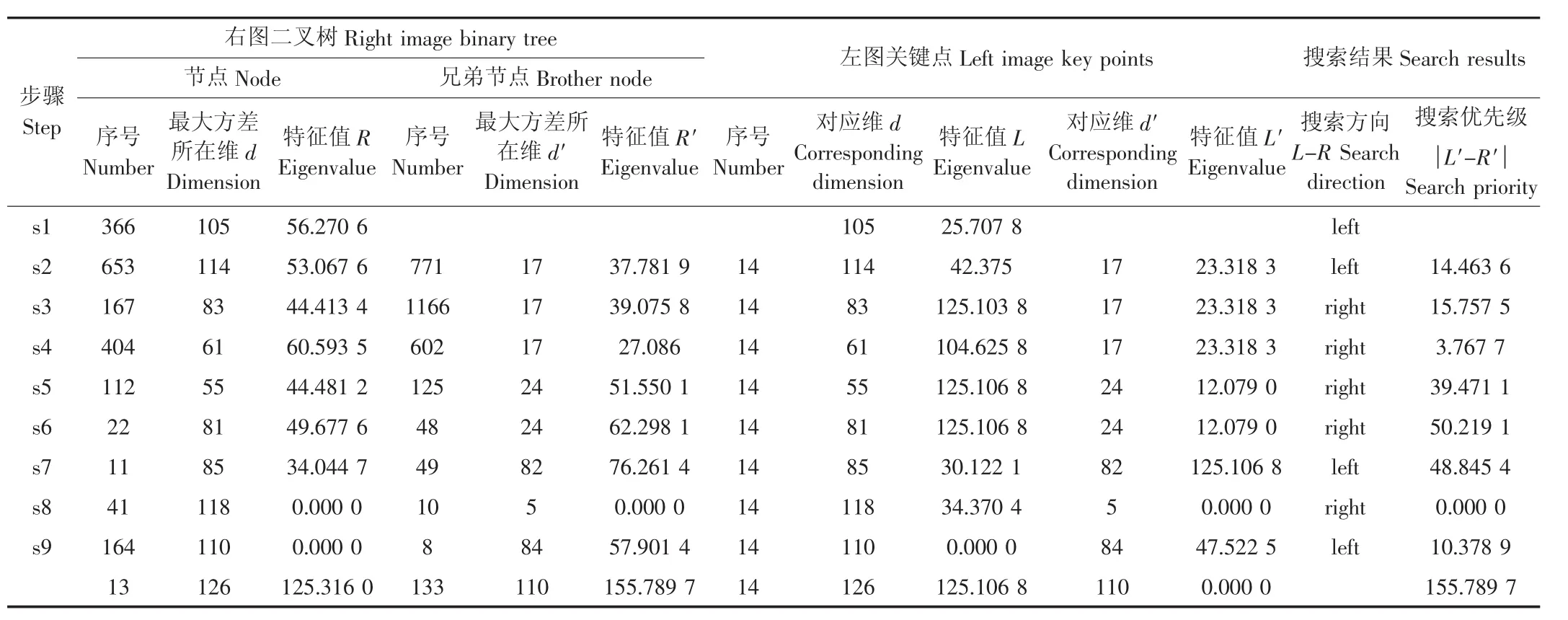
表1 二叉树搜索过程Table 1 Search procedure of binary tree
试验结果表明,针对左图的1 529个关键点,在右图二叉树上总计搜索出172对粗匹配点(表2),将匹配点在原图中用线连起来(图4),对应于空间中的同一点。棉花在左右图像中的对应位姿不尽相同,有些差异甚至很大,由于SIFT特征对旋转、平移和仿射的高抑制性,关键点的匹配效果良好,SIFT算法适应棉花的形貌。

图4 左右图中棉花粗匹配点连线Fig.4 Connected lines of rough matches in left and right cotton images
3 基于极线几何约束的精匹配
3.1 基础矩阵估计原理
从不同角度对同一场景拍摄的影像I与I′的极线几何关系如图5所示,空间任一点X在平面I与I′上的投影点分别为m与m′,2相机的光心C与C′的连线与平面I与I′相交于极点e与e′,平面XCC′与图像平面I与I′的交线lm与lm′分别为点X在平面I和I′上的极线。
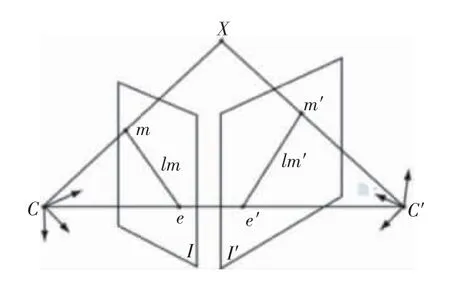
图5 极线几何约束Fig.5 Epipolar geometry constraint
假设匹配点对m与m′的齐次坐标为u=(x,y,1)与u′=(x′,y′,1),平面I上的极线lm用基础矩阵F或矢量f(式6-7)描述,由匹配点对与极线共面可给出平面I的极线方程(式8),u′TF为极线的直线坐标,极线方程展开后可表示为一个矢量内积(式9),则基础矩阵F可由在平面I与I′上的对应点u与u′求出。由n组匹配点对的集合可得到一个线性齐次方程组(式10),A的子空间的解即为矢量f。由于基础矩阵具有7个自由度,故至少需要7个匹配点对,通常采用7点或8点算法来估计基础矩阵[17]。
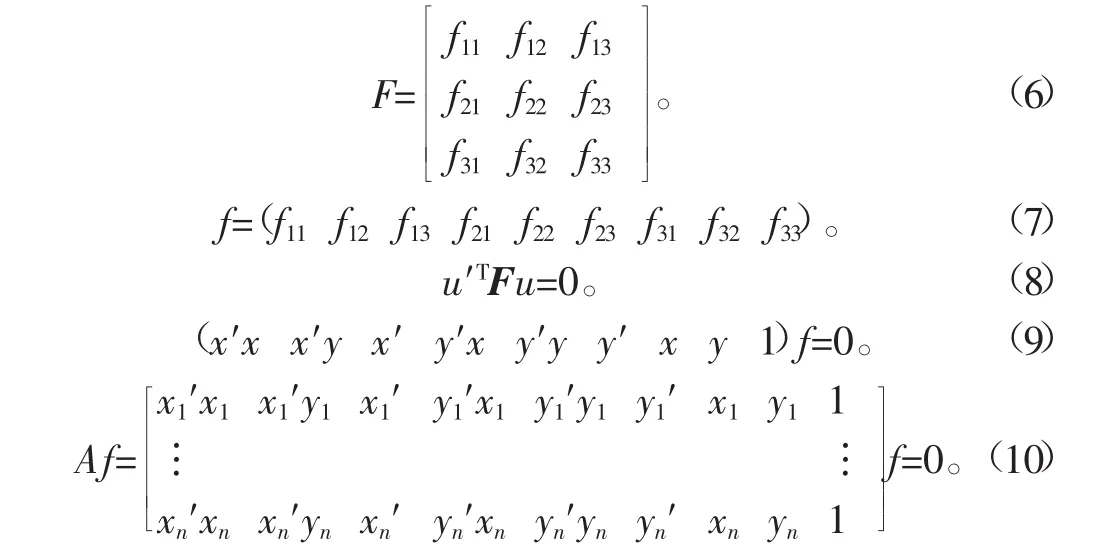
3.2 基于RANSAC算法的基础矩阵优化
实际应用中,由于噪声的影响,粗匹配点对可能存在误匹配,其中的误匹配点对姑且称作外点对,因而有外点对参与的8点法对基础矩阵的估计会产生误差,从而使基础矩阵的估计值恶化。为了解决这一问题,采用随机采样一致性RANSAC方法,通过重复地对特征集采样,基于欧式距离来获得内点对并剔除外点对,基于内点对的基础矩阵估算可提高8点算法的鲁棒性。具体步骤分二步:
首先,基于8点法求解基础矩阵并估计参数。从172个粗匹配点对中任取8个匹配点对,对这些匹配点对坐标进行归一化处理[18],以提高结果的稳定性。将归一化的8组匹配点坐标代入线性齐次方程组(式10),求解基础矩阵F(表3)。将左图的关键点坐标u=(x,y,1)和基础矩阵F代入平面I的极线方程(式8),以恢复右图的极线,计算右图的粗匹配点到该极线的距离distL,反之可获取左图的关键点到极线的距离distR,距离均小于1.5的粗匹配点对为内点对(表4),并估计所有内点对的误差(式11)。
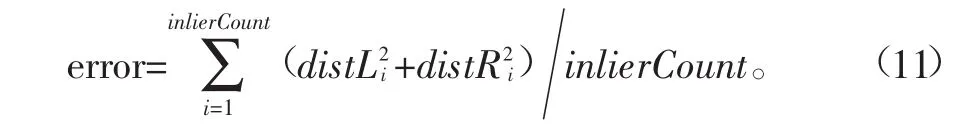
式中inlierCount表示内点对数。
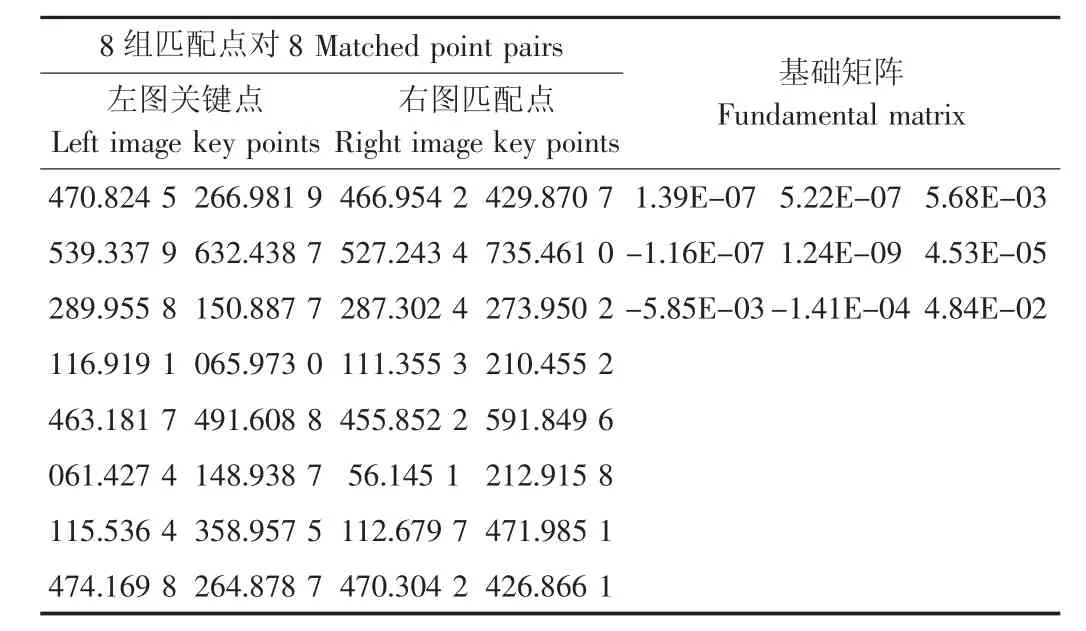
表3 8点法的输入与输出Table 3 Inputs and outputs of 8 point algorithm
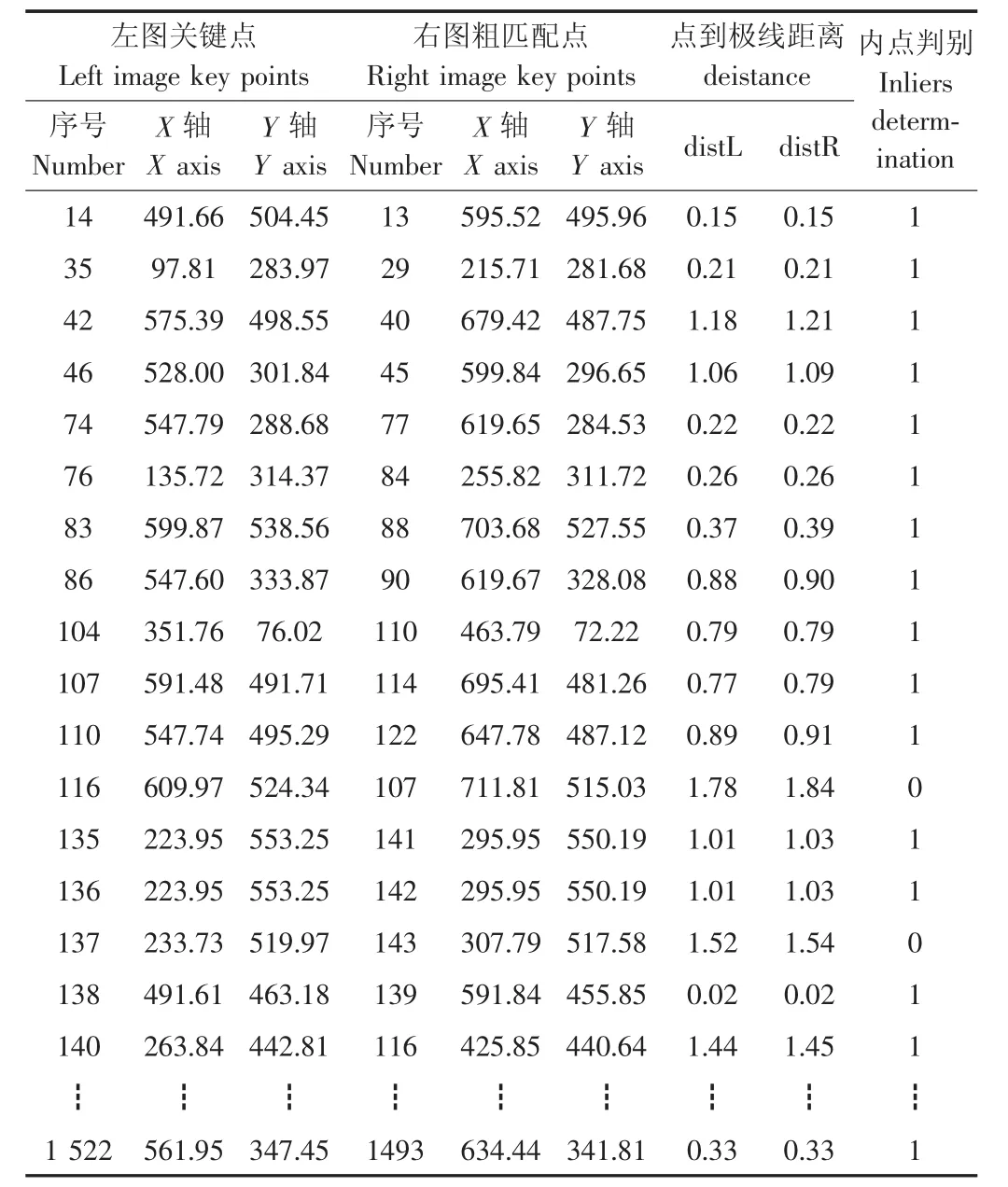
表4 判别内点对Table 4 Determination of inliers
然后,基于RANSAC法优化基础矩阵。在采样次数N足够大的情况下,假设n=8组匹配点对组成的随机样本中,至少有一次没有外点对的概率为P,默认值为0.99;在粗匹配点对中,出现外点对的概率为e,默认值为0.6;则初始N=7 024.6(式12)。在每一次重复采样过程中,都要基于8点法求解基础矩阵,估计内点对数及其误差,以内点对数最多或误差较小来优化F(表5);同时,还要根据上一次的e自适应地决定新的N,这样,随着内点对数的不断增加,e和N越来越小,从而使得重复采样过程快速收敛,提高算法的运算速度。试验结果表明,在第16次采样过程中(表4,表5),内点对数增加到151时,由N<16终止重复采样过程,从172组粗匹配点对中剔除了误匹配。
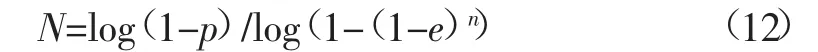
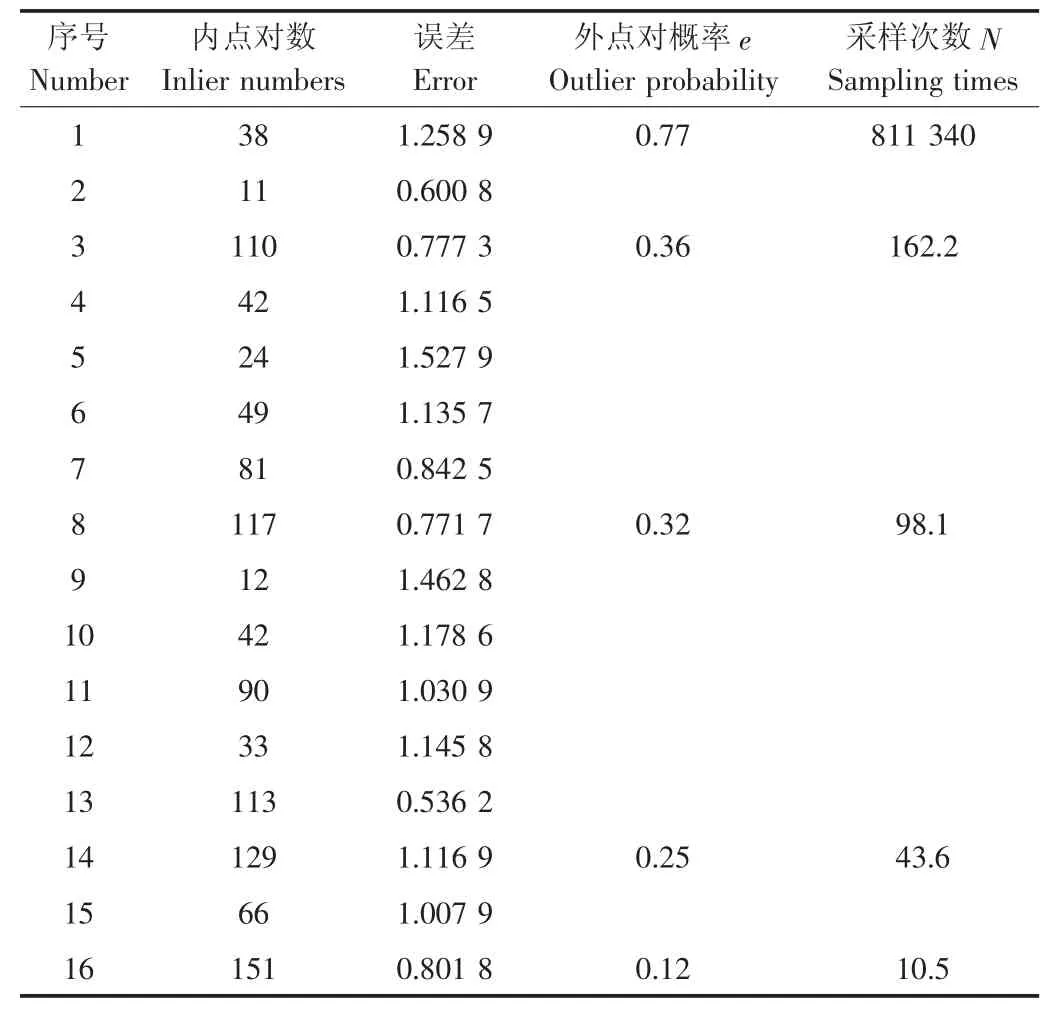
表5 基于RANSAC法优化基础矩阵Table 5 Refined fundamental matrix based on RANSAC
4 棉花的三维重建
4.1 相机内外参数的获取
假设世界坐标系下的一个点(X,Y,Z)在图像坐标系下的坐标为(u,v),根据针孔成像模型和图像坐标系与世界坐标系之间的转换关系[19-20](式13)可知,必须标定相机的内参矩K和外参矩阵M,才能根据图像坐标点转换成世界坐标点。
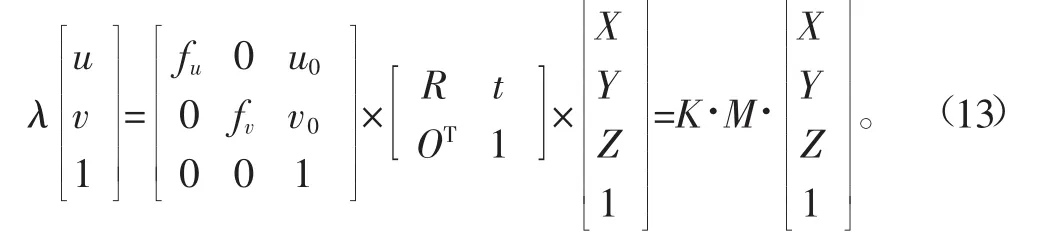
式中λ为比例系数,相机的内参K包括u、v轴的归一化焦距fu、fv,相机光心坐标(u0,v0);相机的外参M包括相机之间的旋转矩阵R和平移矩阵t。
首先,相机内参标定。张正友[21]和Tsai[22]的方法假设平面网格在世界坐标系中,通过线性模型计算摄像机内部参数的优化解,并基于最大似然法进行非线性求解,标定出考虑镜头畸变的目标函数,从而求出左右相机的内参矩阵(表6)。由于标定试验中采用了DH-HV3151UC-ML型CMOS工业数字相机,其分辨率为2 048×1 536,单位像素尺寸为3.2 μm×3.2 μm,镜头焦距为16 mm。因而,理想情况下,相机的归一化焦距fu=fv=16 000 μm/3.2 μm=5 000,相机的光心坐标u0=1 024、v0=768。由此可见,相机内参的实际标定结果与理论值有些许偏差,这可能是由相机制造工艺引起的。
然后,相机外参标定。在已知相机内参K的情况下,基础矩阵F可由本质矩阵E求取(式14),使用归一化坐标系时,基础矩阵F的一种特殊形式就是本质矩阵[23]。本质矩阵最早由Longuet-Higgins在1981年由从运动到结构的求解中导出[24],该矩阵是一个自由度为5、秩为2的3× 3矩阵,它的一个重要性质就是与内参无关,仅由相机的外参确定(式14),实际计算时用四元数表示法[25](式15)通过本质矩阵E恢复出相机的旋转矩阵R和平移矩阵t(表6)。
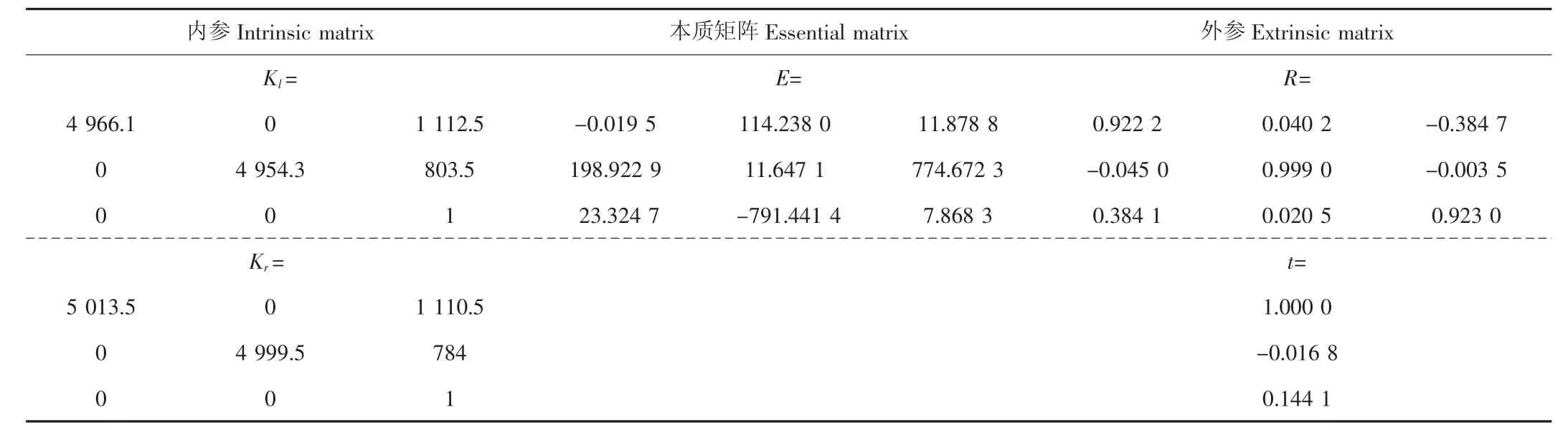
表6 相机内外参数标定Table 6 Calibration of camera intrinsic and extrinsic parameters
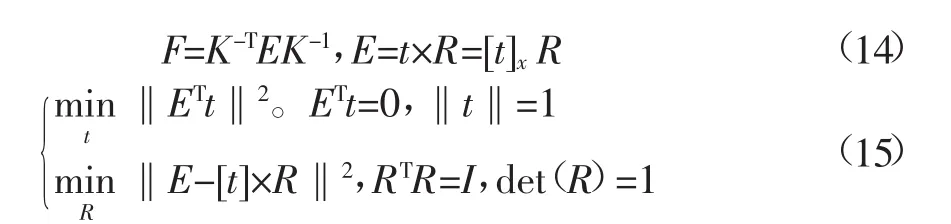
4.2 棉花的三维重建
采摘机器人工作时,随着机器人在田间行走,固定在机械臂上空横杆上的两相机角度可调,需要不断估计2个相机之间的外参。因而可将左相机光心作为世界坐标系的原点,调整左相机的俯仰角和偏转角,使世界坐标系的Z轴垂直于地面,这样左相机相对自身的旋转、平移矩阵为单位阵I、零向量,右相机相对左相机的旋转、平移矩阵为R、t,将151组精匹配点对的图像坐标以及左右相机的内外参数代入方程组(式13)进行最小二乘法求解,得到151个空间点的三维坐标(图6),由图可知,11簇点云团代表了棉花的空间位置。
将预处理后的棉花灰度图(图1-d)二值化,并以其为模板获取单朵棉花表面的点云,进而求取单朵棉花的三维质心坐标,将其Z轴坐标转化为棉花到地面的距离(表7)。试验结果表明,双目视觉的Z轴测距结果比较接近人工测量,平均误差为0.039 3 m,能够反映棉花间的相对位置。
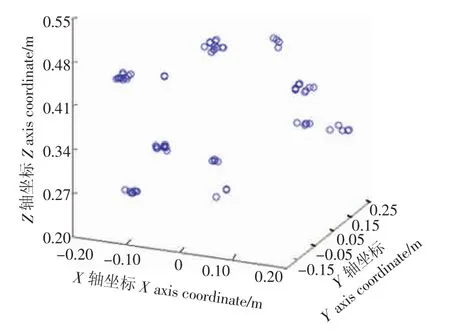
图6 棉花点云三维坐标Fig.6 Scatter diagram of cotton point cloud

表7 棉花三维重建结果Table 7 Result of cotton 3D reconstruction
5 结论
1)设计试验装置时,采用投影仪打光和不打光结合的方式采集图像,在保留了棉花表面丰富纹理的同时兼顾了边界的清晰;相机角度的可调性要求不断估计新的相机外参,能够适应机器人田间行走的多样性。
2)SIFT特征的旋转,平移,缩放和仿射不变性能够适应田间棉花的形貌。
3)结合BBF优先级序列的二叉树搜索算法提高了粗匹配的运行效率,并且避免了高维特征搜索问题;基于RANSAC的基础矩阵优化算法极大地降低了精匹配的计算开销。
[1]王玲,姬长英.农业机器人采摘棉花的前景展望与技术分析[J].棉花学报,2006,18(2):124-128.Wang Ling,Ji Changying.Technical analysis and expectation for cotton harvesting based on agricultural robot[J].Cotton Science, 2006,18(2):124-128.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[2]王玲,姬长英,陈兵林,等.基于机器视觉技术的田间籽棉品级抽样分级模型研究[J].中国农业科学,2007,40(4):704-711.Wang Ling,Ji Changying,Chen Binglin,et al.Researches of grading model of field sampling cotton based on machine vision technology[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2007,40(4):704-711.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[3]韦皆顶,费树岷,汪木兰,等.采棉机器人的研究现状及关键技术[J].农机化研究,2007(7):14-18.Wei Jieding,Fei Shumin,Wang Mulan,et al.Key techniques and research statue for cotton picking robot[J].Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research,2007(7):14-18.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4]Edan Y,Miles G E.Design of an agricultural robot for harvesting melons[J].Transactions of the ASAE,1993,36(2):593-603.
[5]Arima S,Kondo N.Cucumber harvesting robot and plant training system[J].Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics,1999,11(3): 208-212.
[6]Kassay L,Slaughter D.Robotic apple harvest[Z].St.Joseph. Mich:ASAE,1992,ASAE Paper No.922047.
[7]Kondo N,Nishitsuji Y,Ling P.Visual feedback guided robotic cherry tomato harvesting[J].Transactions of the ASAE,1996,39 (6):2331-2338.
[8]Takahashi T,Zhang S,Sun M,et al.New method of image processing for distance measurement by a passive stereo vision [Z].St.Joseph,Mich:ASAE,1998,ASAE Paper No.983031.
[9]Takahashi T,Zhang S,Fukuchi H,et al.Binocular stereo vision system for measuring distance of apples in orchard(Part 1)-Method due to composition of left and right images[J].Journal of the Japanese Society of Agricultural Machinery,2000,62(1): 89-99.
[10]Takahashi T,Zhang S,Fukuchi H,et al.Binocular stereo vision system for measuring distance of apples in orchard(Part 2)-Analysis of and solution to the correspondence problem[J]. Journal of the Japanese Society of Agricultural Machinery,2000, 62(3):94-102.
[11]王玲,刘思瑶,卢伟,等.面向采摘机器人的棉花激光定位算[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(14):42-48.Wang Ling,Liu Siyao,Lu Wei,et al.Laser detection method for cotton orientation in robotic cotton picking[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE),2014,30(14):42-48.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[12]彭辉,文友先,翟瑞芳,等.结合SURF算子和极线约束的柑橘立体图像对匹配[J].计算机工程与应用,2011,47(8):157-160.Peng Hui,Wen Youxian,Zhai Ruifang,et al.Stereo matching for binocular citrus images using SURF operator and epipolar constraint[J].Computer Engineering and Applications,2011,47 (8):157-160.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[13]Lowe D G.Distinctive image features from scale-invariant key points[C].International Journal of Computer Vision,2004,60(2): pp91-110.
[14]Lowe D G.Object recognition from local scale invariant features [C].Proceeding of the Seventh International Conference on Computer.Vision.Washington,DC:IEEE Computer Society, 1999:1150.
[15]张开玉,梁凤梅.基于改进SURF的图像配准关键算法研究[J].科学技术与工程,2013,13(10):2875-2879.Zhang Kaiyu,Liang Fengmei.Research on the key algorithm for image matching based on improved SURF[J].Science Technology and Engineering,2013,13(10):2875-2879.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[16]Fischler M,Bolles R.Random sample consensus:A paradigm formodel fitting with application to image analysis and automated cartography[J].Communications of the ACM,1981(24):381-395.
[17]Richard I.Hartley.In defense of the 8-point algorithm[C],In Proceeding of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV),1995:1064-1070.
[18]Hartley,Richard.计算机视觉中的多视图几何[M].安徽:安徽大学出版社,2002:193.
[19]马颂德,张正友.计算机视觉-计算理论与算法基础[M].北京:科学出版社,1998:53~58.
[20]David A,Forsyth,Jean Ponce.计算机视觉-一种现代方法[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2004,54~55.
[21]Zhang Zhengyou.Flexible camera calibration by viewing a plane from unknown orientations[C],IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision,1999,1:666-673.
[22]Tsai R Y.An efficient and accurate camera calibration technique for 3D machine vision[C],CVPR,1986,364-374.
[23]Quanquan Gu,Jie Zhou.Belief propagation on Riemannian manifold for stereo matching[C].IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,2008,15:1788-1791.
[24]HughC.Longuet-Higgins.Acomputeralgorithm forreconstructing a scene from two projections[J].Nature,1981,293(5):133-135.
[25]Zhang Zhengyou.A new multistage approach to motion and structure estimation by gradually enforcing geometric constraints [C].Proceedings of the ACCV’98,Hong Kong,l998:567-574.
Cotton positioning technique based on binocular vision with implementation of scale-invariant feature transform algorithm
Zhu Rongjie,Zhu Yinghui,Wang Ling※,Lu Wei,Luo Hui,Zhang Zhichuan
(College of Engineering,Nanjing Agricultural University,Nanjing 210031,China)
Rapid development of mechanization in agriculture has made it possible to lower the manual labor hour and increase efficiency at the same time.In order to provide the mechanical arm of the cotton picking robot with the needed movement locus parameters,a cotton distance measuring device based on binocular vision with a full implementation of SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform)algorithm was introduced,which realized the positioning of all 11 pieces of cotton planted. Under indoor environment,the cotton images were captured with the control of projector flashlight and the unneeded backgrounds were segmented.Turn the RGB images into gray scale and enhance the gray value to make the cotton more obvious,and after sharpening the edges,the pretreatments of cotton images were finished.Blur the images through Gaussian filter with 8 different scales,calculate the DoG(difference of Gaussian)of Gaussian images and acquire the extrema of 26 neighboring pixels within neighboring scales,and thus SIFT key points were detected,all these key points were invariant to rotation,translation,zoom and affine,which was suitable for the match of cotton images.Calculate the gray gradient modulus value of the 4×4 seed points in 8 directions within the key point neighborhood,and the 128-dimensional SIFT descriptor of each key point was acquired.As to all the SIFT key points in the right image,select the dimension with the maximum variance,and calculate the median value of this dimension,find its corresponding key point and split the other key points according to the median value,repeat this step and the binary tree was built.As to every SIFT key point in the left image, search its potential matches(probably more than one)in the binary tree of the right image until its leaf node was found;save the brother nodes found along the path,establish priority sequence with BBF(best bin first)and expand from the brother nodes to their leaves,find the nearest and second nearest neighbors according to the similarity degree of the 128-dimensional key points between the potential matches until the sequence was empty or the algorithm exceeded its 200 times constraint. Thus 172 pairs of rough cotton matches of key points in 2 images were acquired,but there was still a possibility that there might be wrong matches among rough matches.In order to eliminate the wrong matches,estimate fundamental matrix with RANSAC(random sample consensus)algorithm and recover epipolar geometry constraint;during each sampling,use 8-point algorithm to compute an initial fundamental matrix,calculate the distance from every point to its corresponding epipolar line and count the ones within the threshold as inliers.Repeat this step and choose the fundamental matrix with the most inliers or the least error(in case there were more than one fundamental matrix with the same inlier number)as the final output fundamental matrix,and the corresponding inliers were called refined cotton matches.Using the RANSAC algorithm we got 151 pairs of refined cotton matches,and there were no wrong matches in the refined matches,which helped make the results of cotton three-dimensional(3D)reconstruction more accurate.Calibrate the camera to get its intrinsic matrix,and then get essential matrix according to fundamental matrix and intrinsic matrix through transformation.Split essential matrix and the camera′s external rotation matrix and translation vector were acquired.To this point,inputs needed for cotton 3D reconstruction were all ready,and they were 151 pairs of refined matches of cotton,intrinsic matrix,external rotation matrix and translation vector.Put these inputs into the equations and 2D cotton image coordinates could be transformed into 3D coordinates,and the 3D reconstruction of cotton point cloud on the plant was realized.At last the 3D coordinate values of every cotton were obtained and their centroid coordinate values were calculated.Result showed that all 11 pieces of cotton were all successfully 3D positioned,with an average error of 0.039 3m compared with manual measurement,which proves the calculated data are valid and this binocular vision system is reliable enough for practical application.
robots;image processing;vision;cotton;SIFT features;binocular vision;binary tree;RANSAC algorithm
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.06.025
S24;TP242.6
A
1002-6819(2016)-06-0182-07
2015-12-01
2016-01-28
朱镕杰(1991-),男,江苏南通人,主要从事双目视觉技术研究。南京 南京农业大学工学院 210031。Email:zrj564366@126.com
※通信作者:王 玲(1966-),女,江西南昌人,副教授,博士,硕士生导师,主要从事图像处理与模式识别技术研究。南京 南京农业大学工学院 210031。Email:Lingw@njau.edu.cn
