视网膜静脉阻塞继发黄斑水肿的OCT特点分析
2016-05-14田洁张波徐莅华
田洁 张波 徐莅华

【摘要】 目的:分析视网膜静脉阻塞(RVO)继发黄斑水肿(ME)患者的Cirrus HD-OCT特点。方法:选择2014年3月-2015年8月在本院经眼底荧光血管造影(FFA)或眼底照相确诊为RVO继发ME的患者20例20只眼作为RVO组,选择年龄匹配的健康人20例20只眼作为对照组,回顾性分析其Cirrus HD-OCT黄斑容积512×128扫描结果。结果:Cirrus HD-OCT结果显示RVO组ME部位视网膜增厚且层间反射降低。1例(5%)外核层(ONL)/外丛状层(OPL)局限性囊泡改变;5例(25%)黄斑区神经上皮增厚,ONL/OPL有液性暗腔;其余14例(70%)均有不同程度混合性水肿,即位于内核层(INL)的囊样水肿,位于ONL/OPL的弥漫性水肿。12例(60%)神经上皮脱离。6例(30%)视网膜内外光感受器的连接部(IS/OS)及外界膜(ELM)完整,余患者均不完整。RVO组9个分区视网膜平均厚度、总容积及总平均厚度均高于对照组,比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:Cirrus HD-OCT能断层显示RVO患者继发ME的形态及微细病变所在的视网膜层次;能非侵入性地分9个区域测量黄斑区视网膜平均厚度,是诊断与治疗RVO继发ME的必备工具之一。
【关键词】 视网膜静脉阻塞; 黄斑水肿; OCT
【Abstract】 Objective:To study the characters of the optical coherence tomography of macular edema in patients with retinal vein occlusion.Method:20 eyes of 20 patients who were diagnosed with macular edema secondary to RVO by FFA or fundus photography in our hospital from March 2014 to August 2015 were selected as the RVO group.20 eyes of 20 age-matched healthy persons were selected as the control group.The characters of Cirrus HD-OCT 512×128 scans in both groups were analyzed.Result:The results of Cirrus HD-OCT showed that the edema areas of the retina thickened and the reflectivity reduced in the RVO group.Limitations of vesicle changes was found in ONL/OPL in 1 case(5%).The thickened neurosensory of macular region and liquidity dark chamber in ONL/OPL were found in 5 cases(25%).The mixed edema of different extent was found in the left 14 cases(70%),including cystoid edema in the INL and diffuse edema in the ONL/OPL.The detachment of the neurosensory exited in 12 cases(60%).IS/OS and ELM were integritied in 6 cases(30%),while the left were not.The average thickness of the retina of the nine partitions,the total volume and total average thickness in the RVO group were higher than those in the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion:Cirrus HD-OCT can show cross sections of macular edema secondary to RVO and retinal layers in which minor changes existed.It can measure the average thicknesses of the retina in nine subfield of macular invasively.It is one of the necessary tools for diagnosing and remedying macular edema secondary to RVO.
【Key words】 Retinal vein occlusion; Macular edema; Optical coherence tomography
First-authors address:Dalian Municipal Friendship Hospital,Dalian 116001,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2016.05.012
黄斑水肿(macular edema,ME)是视网膜静脉阻塞(retinal vein occlusion,RVO)患者视力下降的主要原因之一[1]。光学相干断层扫描仪(optical coherence tomography,OCT)可以准确地测量视网膜厚度,明确诊断ME,而且新一代频域OCT可更清晰地显示视网膜各层结构的微细改变[2]。本文应用Cirrus HD-OCT对20例RVO继发ME患者和20例健康人进行检查,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选择2014年3月-2015年8月在本院住院的经眼底荧光血管造影(fundus fluorescein angiography,FFA)或眼底照相确诊为RVO继发ME的患者20例20只眼为RVO组,其中视网膜分支静脉阻塞(branch retinal vein occlusion,BRVO)10例,视网膜中央静脉阻塞(central retinal vein occlusion,CRVO)8例,半侧性视网膜阻塞(hemiretinal vein occlusion,HRVO)2例;非缺血型3例,缺血型17例;右眼11例,左眼9例;男10例,女10例;年龄49~84岁,平均(61±7)岁;矫正视力为指数/眼前~1.0。非缺血型患者给予血栓通等药物治疗,缺血型患者分次给予视网膜激光光凝治疗。选择年龄匹配的健康人20人20只眼作为对照组,平均年龄(59±6)岁,两组年龄比较差异无统计学意义(t=1.308,P=0.199)。
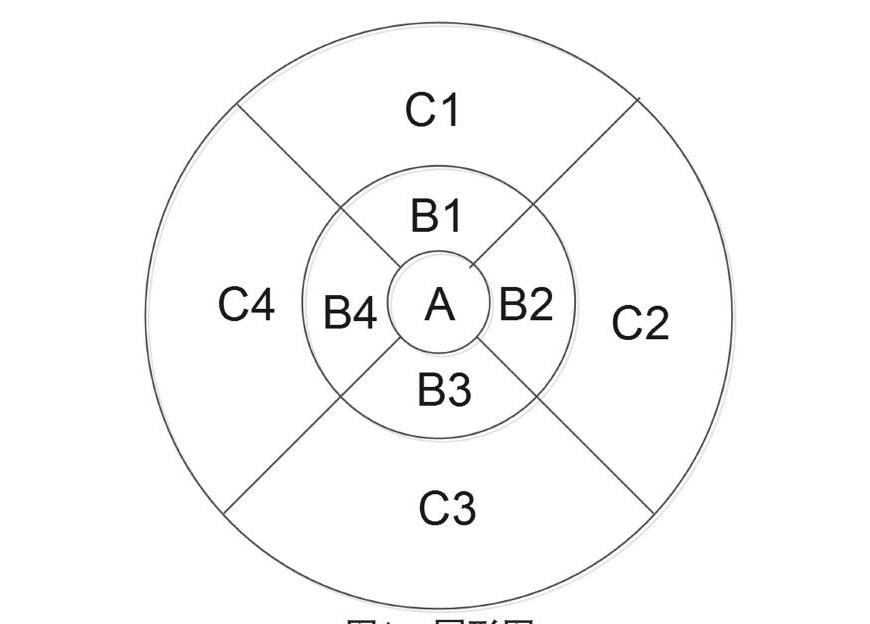
1.2 方法 主要检查仪器为Zeiss-Cirrus HD-OCT 4000,采用黄斑容积512×128扫描,生成圆形图的中心子区厚度、整个6 mm×6 mm的正方形扫描区内界膜-视网膜色素上皮细胞(retinal pigment epithelium,RPE)的总容积和总平均厚度等数据。此圆形图由直径为1(中心子区)、3(中间区)和6 mm(外层区)的三个同心圆组成,并且分为上象限、鼻象限、下象限和颞象限(图1)。每个分区每个象限均测出视网膜厚度平均值。
1.3 统计学处理 所有数据均采用SPSS 19.0统计学软件进行处理,计量资料以(x±s)表示,比较采用t检验或t检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 形态学结果 Cirrus HD-OCT结果显示RVO组ME部位视网膜增厚且层间反射降低。1例(5%)外核层(outer nuclear layer,ONL)/外丛状层(outer plexiform layer,OPL)有局限性囊泡改变;5例(25%)黄斑区神经上皮增厚,ONL/OPL有液性暗腔,中心凹结构尚可辨认;其余14例(70%)均有不同程度混合性水肿,即位于内核层(inner nuclear layer,INL)的囊样水肿,表现为低反射囊泡,其间有组织柱分隔;位于ONL/OPL的弥漫性水肿表现为视网膜组织增厚,反射降低(图2A)。12例(60%)神经上皮脱离,表现为神经上皮与RPE分离,其间有低反射液性空腔(图2B)。6例(30%)视网膜内外光感受器的连接部(inner and outer segments of the photoreceptors,IS/OS)及外界膜(external limiting membrane,ELM)完整,其余患者IS/OS及ELM均不完整。
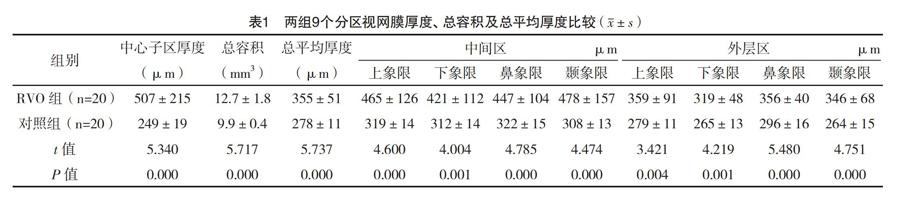
2.2 两组视网膜厚度比较 RVO组中心子区厚度、总容积、总平均厚度均高于对照组,中间区及外层区上象限、下象限、鼻象限、颞象限视网膜平均厚度均高于对照组,比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表2。
3 讨论
RVO的特点是视网膜受累静脉扩张迂曲,沿静脉分布区域的视网膜有出血、水肿和渗出。ME是RVO最常见的并发症。ME多数情况下为细胞外水肿,也存在细胞内水肿[3]。FFA可见中心凹旁毛细血管渗漏形成典型的花瓣样外观。如果渗漏源很小,渗漏慢,且很快播散到细胞内液体腔,则FFA未能显示ME,而3D-OCT可以较敏感地探测到[4]。Jittpoonkuson等[5]发现18.52%的RVO患者的ME被FFA漏诊。此外,OCT可以非侵入性地快速的提供黄斑中心凹形态和厚度的客观记录,从而取代FFA在视网膜厚度变化随访中起重要作用[6]。本研究主要检查仪器为Zeiss-Cirrus HD-OCT 4000,采用频域光学相干断层扫描成像技术获取和分析眼的三维X线断层照片,每秒A扫描次数为27 000次,轴向分辨率为5 μm;有更清晰的视网膜分层,可以明确微细病变所在的视网膜层次。
本研究Cirrus HD-OCT结果显示RVO组ME部位视网膜增厚且层间反射降低,表现为ONL/OPL局限性囊泡改变;黄斑区神经上皮增厚,ONL/OPL有液性暗腔;混合性水肿;神经上皮脱离等形式。薛康等[7]检查了92只眼,其中弥漫性水肿占13.0%,囊样水肿占22.8%,混合性水肿占64.1%;水肿位于OPL/ONL占100%,位于INL占74.2%,位于神经节细胞层占25.0%,浆液性视网膜脱离占40.2%,与本研究结果有差异。Brar等[8]发现RVO继发ME患者OCT上有囊腔形成,但与视力无关。FFA所示的弥漫性水肿在OCT上也有微囊腔形成,且与OCT上视网膜增厚或扭曲有关。本研究显示,RVO组中心子区厚度(507±215)μm,而梁婧等[9]测量23例RVO继发ME患者的黄斑中心凹平均厚度为(595.32±172.56)μm,金昱等[10]测量结果为(447.00±116.67)μm,与本研究结果有差异。Hatef等[11]用Cirrus SD-OCT测量30例RVO继发ME患者9个分区视网膜厚度与本研究结果有差异。相关研究与本研究有差异,推测与所收集患者的ME程度变化较大或者所用OCT的类型不同有关。尽管如此,各研究RVO继发ME患者中心子区厚度均明显增加,这与CRVO患者视力预后差相关,与BRVO患者不相关[12]。Adelman等[13]研究证实RVO继发ME患者的治疗方法中,某些患者玻璃体切除联合ILM剥除术可以提高视力,而玻璃体内注射抗血管内皮生长因子是最有效的非手术疗法,玻璃体内注射地塞米松植入物或曲安奈德只能有限地提高视力。本研究发现,6例(30%)患者IS/OS及ELM完整,余患者均不完整,有因视网膜出血遮挡而致IS/OS及ELM中断的现象存在。IS/OS或ELM不完整是RVO患者治疗前后视力差的征象[14-15]。
综上所述,Cirrus HD-OCT能断层显示RVO继发ME的形态及微细病变所在的视网膜层次;能非侵入性地分9个区域测量黄斑区视网膜平均厚度,是诊断与治疗RVO继发ME的必备工具之一。
参考文献
[1] Johnson M W.Etiology and treatment of macular edema[J].Am J Ophthalmol,2009,147(1):11-21.
[2] Badaró E,Novais E,Prodocimo L M,et al.Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography for macular edema[J].Scientific World Journal,2014,2014(1):191 847.
[3] Augustin A,Loewenstein A,Kuppermann B D.Macular edema.General pathophysiology[J].Dev Ophthalmol,2010,47(1):10-26.
[4] Ouyang Y,Keane P A,Sadda S R,et al.Detection of cystoid macular edema with three-dimensional optical coherence tomography versus fluorescein angiography[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2010,51(10):5213-5218.
[5] Jittpoonkuson T,Garcia P M,Rosen R B.Correlation between fluorescein angiography and spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in the diagnosis of cystoid macular edema[J].Br J Ophthalmol,2010,94(9):1197-1200.
[6] Kozak I,Morrison V L,Clark T M,et al.Discrepancy between fluorescein angiography and optical coherence tomography in detection of macular disease[J].Retina,2008,28(4):538-544.
[7]薛康,姜春晖,徐格致,等.视网膜静脉阻塞黄斑水肿的光相干断层扫描观察[J].中华眼底病杂志,2011,27(2):127-131.
[8] Brar M,Yuson R,Kozak I,et al.Correlation between morphological features on spectral domain optical coherence tomography and angiographic leakage patterns in macular edema[J].Retina,2010,30(3):383-389.
[9]梁婧,李芙蓉,袁容娣.玻璃体腔内注射曲安奈德治疗视网膜静脉阻塞继发黄斑水肿的临床观察[J].临床眼科杂志,2015,23(2):138-140.
[10]金昱,石安娜,刘淼.玻璃体内注射雷珠单抗(Ranibizumab)治疗视网膜静脉阻塞继发黄斑水肿[J].眼科新进展,2014,34(9):855-857.
[11] Hatef E,Khwaja A,Rentiya Z,et al.Comparison of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in measurement of macular thickness in macular edema secondary to diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion[J].J Ophthalmol,2012,2012(8476):354 783.
[12] Hoeh A E,Ruppenstein M,Ach T,et al.OCT patterns of macular edema and response to bevacizumab therapy in retinal vein occlusion[J].Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol,2010,248(11):1567-1572.
[13] Adelman R A,Parnes A J,Bopp S,et al.Strategy for the management of macular edema in retinal vein occlusion:the European VitreoRetinal Society macular edema study[J].Biomed Res Int,2015,2015(1):870 987.
[14]冯超,肖璇,杨安怀.视网膜中央静脉阻塞黄斑水肿患者中心凹光感受器状态与视力的相关性[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2010,31(4):520-523.
[15] Kang H M,Chung E J,Kim Y M,et al.Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) patterns and response to intravitreal bevacizumab therapy in macular edema associated with branch retinal vein occlusion[J].Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol,2013,251(2):501-508.
(收稿日期:2015-10-26) (本文编辑:王利)
