汞胁迫对两种暖季型草坪草生理生化特征的影响
2016-02-22过昱辰刘莹莹王赛王瑞莹陆
过昱辰++刘莹莹++王赛++王瑞莹++陆小平++王波
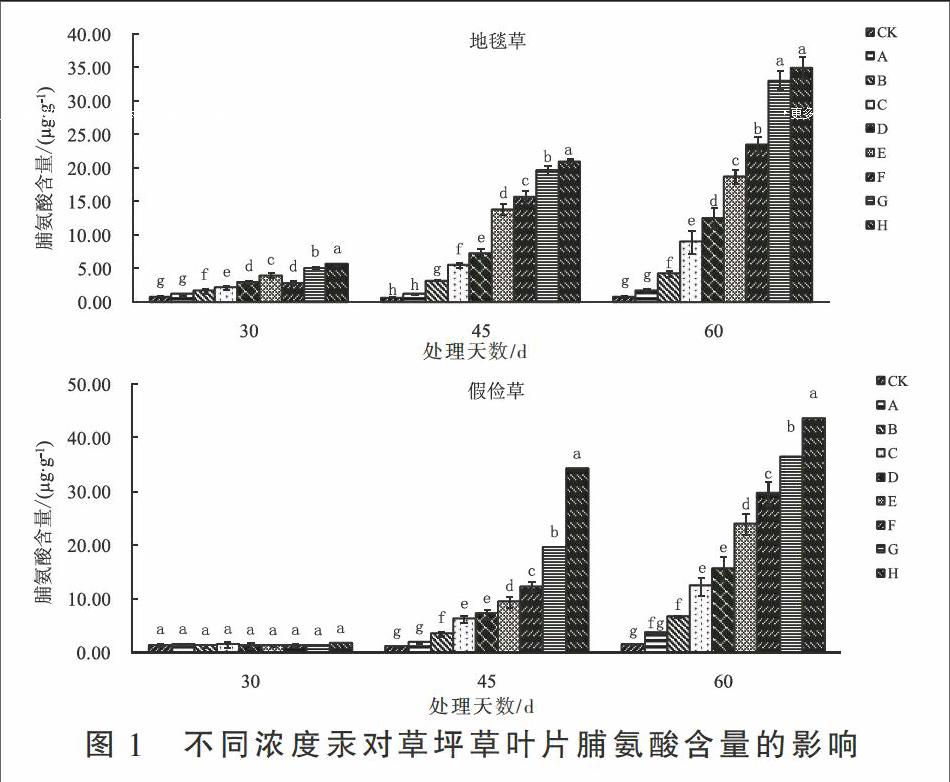
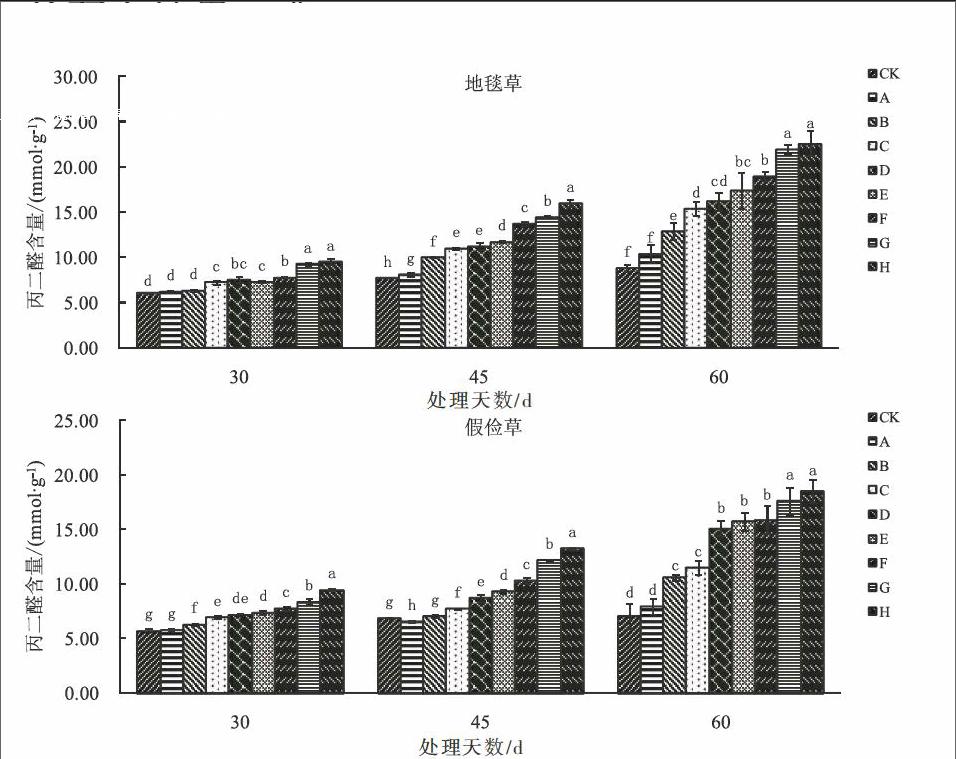
摘 要:当前我国土壤汞污染情况日益严重,寻找对汞胁迫具有一定抗性的园林植物已刻不容缓。本研究采用盆栽模拟的试验方法,研究不同土壤汞浓度水平对两种暖季型草坪草地毯草和假俭草生理生化特征的影响。结果表明,随着汞胁迫强度的增加和时间的延长,两个草种叶片内脯氨酸和丙二醛含量持续上升,可溶性蛋白含量和超氧化物歧化酶活性均呈现出先升高后下降的趋势,其中地毯草和假俭草超氧化物歧化酶活性最大值分别达到482.98 U·g-1和557.18 U·g-1,地毯草叶片过氧化物酶活性表现为先持续升高后趋于稳定的趋势,其最大值为1 254.60 U·g-1·min-1,而假俭草过氧化物酶活性则持续升高,其最大值达到1 510.16 U·g-1·min-1。本研究结果可为探索草坪草对汞胁迫的适应机制提供一定的理论依据。
关键词:汞胁迫;草坪草;生理生化特征
中图分类号:S688.4 文献标识码:A DOI 编码:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2016.02.004
Effects of Hg2+ on Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Two Warm-season Turf Grasses
GUO Yuchen, LIU Yingying, WANG Sai, WANG Ruiying, LU Xiaoping, WANG Bo
(Department of Horticulcture, Soochow University, Suzhou,Jiangsu 215123, China)
Abstract: Currently, the pollution of mercury in soil in China is getting worse. It's extremely urgent to search for the landscape plants with some resistance to mercury stress. This research took the two warm-season turf grasses Carpet grass and Centipede grass as materials, studied the effects of Hg2+ on physiological and biochemical characteristics of them by using the method of pot simulation. The results showed that with the increase of the concentrations of Hg2+ and the processing time of stress, the content of MDA and Pro were increased. At the same time the content of soluble protein and the activities of SOD showed a trend of first rising and then decreasing. The maximum of SOD activities of Carpet grass and Centipede grass were 482.98 U·g-1 and 557.18 U·g-1 respectively. The POD activities of Carpet grass showed the trend of stable after the first sustained increasing, the maximum of POD activities of it was 1 254.60 U·g-1·min-1. While, the POD activities of Centipede grass showed the trend of sustained rising, the maximum of POD activities of it was 1 510.16 U·g-1·min-1. Through comprehensive evaluation of some physiological and biochemical characteristics of two warm-season turf grasses at seedling stage under mercury stress, the conclusion was drawn that Centipede grass has better resistance to mercury stress than Carpet grass. The results of this research could provide a theoretical basis for exploring the adaptation mechanism of turf grasses under mercury stress.
Key words: mercury stress; turf grasses; physiological and biochemical characteristics
随着科技的进步和社会生产力的极大提高,人口剧增、资源过度消耗、环境污染、生态破坏等问题日益突出,我国土壤资源的数量逐渐减少,质量不断退化,重金属污染情况日益严重,尤其是土壤汞污染问题愈发严峻,其间发生了一系列具有重大影响的汞污染事件,这对我国农作物食品安全带来严重威胁。
土壤中的汞主要来自于工业“三废”的排放,含汞农药的使用和污水灌溉,以及城市垃圾的焚烧。此外,大气中的汞可以通过干湿沉降进入土壤中,在粘土矿物和有机物的吸附作用下,被土壤迅速吸附或固定,富集于表层土壤,造成土壤汞浓度的进一步升高。土壤汞通过植物的富集和食物链进入人体,进而危害人类健康。但也有研究表明,生活在重金属含量较高环境中的植物在长期的生物适应进化过程中,逐渐形成了对重金属的抗逆性,其中一些植物能大量吸收环境中的重金属元素并蓄积在体内,同时植物仍能正常生长。有关汞对植物生长发育的影响,国内外都有研究,但大多集中在对粮食作物和经济作物产量和品质的影响上,对园林植物生长发育影响的研究并不多。
