覆冰导线非线性舞动系统的奇异性和混沌分析
2016-01-28刘习军张素侠
霍 冰, 刘习军, 张素侠, 刘 鹏
(1.天津大学 机械工程学院力学系,天津 300072; 2. 天津市非线性动力学与混沌控制重点实验室,天津 300072)
覆冰导线非线性舞动系统的奇异性和混沌分析
霍冰1,2, 刘习军1,2, 张素侠1,2, 刘鹏1,2
(1.天津大学 机械工程学院力学系,天津300072; 2. 天津市非线性动力学与混沌控制重点实验室,天津300072)
覆冰导线舞动是输电线路覆冰后形成非圆截面,导致气动力发生改变,引起的一种低频大幅自激振动现象。导线舞动严重时会造成杆塔倾倒,供电系统瘫痪,给人民群众的生命财产造成重大威胁。导线舞动的影响因素繁多又相互关联耦合,且导线对于参数的改变十分敏感。因此,长期以来舞动问题得到了国际上的广泛关注[1]。
覆冰导线舞动机理的发展主要经历了Den Hartog垂直舞动机理[2],Nigol扭转激发舞动机理[3-4],以及Yu等[5]提出的偏心惯性耦合失稳机理。随着非线性动力学的日益发展,20世纪90年代以来,越来越多的学者通过非线性理论研究舞动问题。Luongo和Benedettini,Lee,Perkins以及Nayfeh[6-9]就悬索的稳定性和多模态间内共振引起的丰富动力学现象进行了大量的研究。李黎,赵丽等[10-11]采用有限元方法研究覆冰导线中存在的非线性问题。近年来有学者发现在舞动系统中还存在多解、滞后和跳跃等不稳定现象[12-14]。覆冰导线的分岔与混沌等复杂的动力学现象也备受关注[15-16],然而对于覆冰导线系统中的奇异性现象还鲜有涉及。
奇异性理论作为一种研究微小扰动对系统稳定性影响的手段越来越广泛的应用于工程实际当中[17-18]。然而以往的奇异性分析中,分岔参数与开折参数通常相互耦合,很难还原为原始的工程参数,因而对于所求得转迁集不同区间的拓扑结构,难以实现数值模拟的验证,所得到的转迁集与分岔曲线难与工程实际参数相结合,具有一定的局限性。
本文针对三自由度覆冰导线舞动的非线性控制方程,利用奇异性理论研究其局部分岔行为。首先借助平均法得到系统的分岔方程,建立分岔参数、开折参数与工程参数的对应关系,将分岔参数与开折参数解耦,得到以工程参数界定的转迁集和以面内阻尼系数代表分岔参数的拓扑曲线,并辅助以数值验证,所得结果更加直观实用,为实际工程提供理论支撑。
1理论模型
将导线等效为长为l的柔性杆,只能承受拉力,而不能承受压力和弯矩,导线表面附着薄冰且沿输电导线均匀分布,其空间模型如图1(a)所示,Г0代表覆冰输电导线在自重作用下的初始构型,Г为t>0时输电导线在气动载荷作用下的构型。取图中微元dx进行研究,其运动示意图如图1(b)所示,AB和A″B″分别表示变形前后的微元部分。v、w和θ分别表示t时刻时输电导线面内、面外和扭转方向的位移。

图1 输电导线模型Fig.1 The model of transmission line
由图1(b)可知系统的原弧长与变形后弧长的表达式分别为
(1)
(2)
其中:y0是t=0时的悬链线方程,记为[19]
(3)
式中:T0和l分别为输电导线的初始拉力和档距,m为其单位长度的质量,g为重力加速度。
系统的势能可表示为
(4)
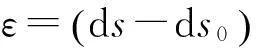
覆冰导线动能表达式为
(5)
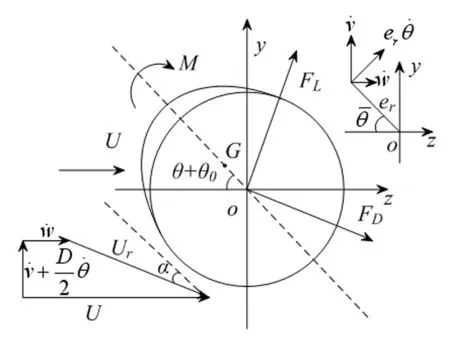
图2 覆冰导线气动受力分析图Fig. 2 Aerodynamic forces acting on the non-circular section
外力做功为
(6)
其中:Fy,Fz和M分别为作用在覆冰导线上面内和面外的气动力以及扭矩,表示为如下形式[5]
(7)
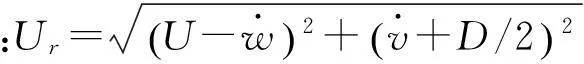
(8)
其中:ryi,rzi和rMi(i=1,2,3)为拟合系数,由实验测得[20],α为风攻角[21]:
(9)
利用Hamilton原理
(10)
将式(4)~(6)及其变量代入式(10)可得覆冰导线系统的偏微分运动方程
(11a)
(11b)
(11c)
2Galerkin法和平均法求解
(12a)
(12c)

(13a)

(13b)
(13c)

(13d)
式中:Gv和Gw为由位移引起的几何非线性项,Av和Aw表示由速度引起的气动载荷非线性项。
根据平均法设式(13)的近似解析解为如下形式

(14)

b1,4A1+b1,5A2+b1,6
(15a)
b2,4A1+b2,5A2+b2,6
(15b)
b3,5A22+b3,6A1+b3,7A2+b3,8
(15c)
b4,5A22+b4,6A1+b4,7A2+b4,8
(15d)
其中:bi,j(i=1,…,4;j=1,…,8)为计算系数,详见附录。
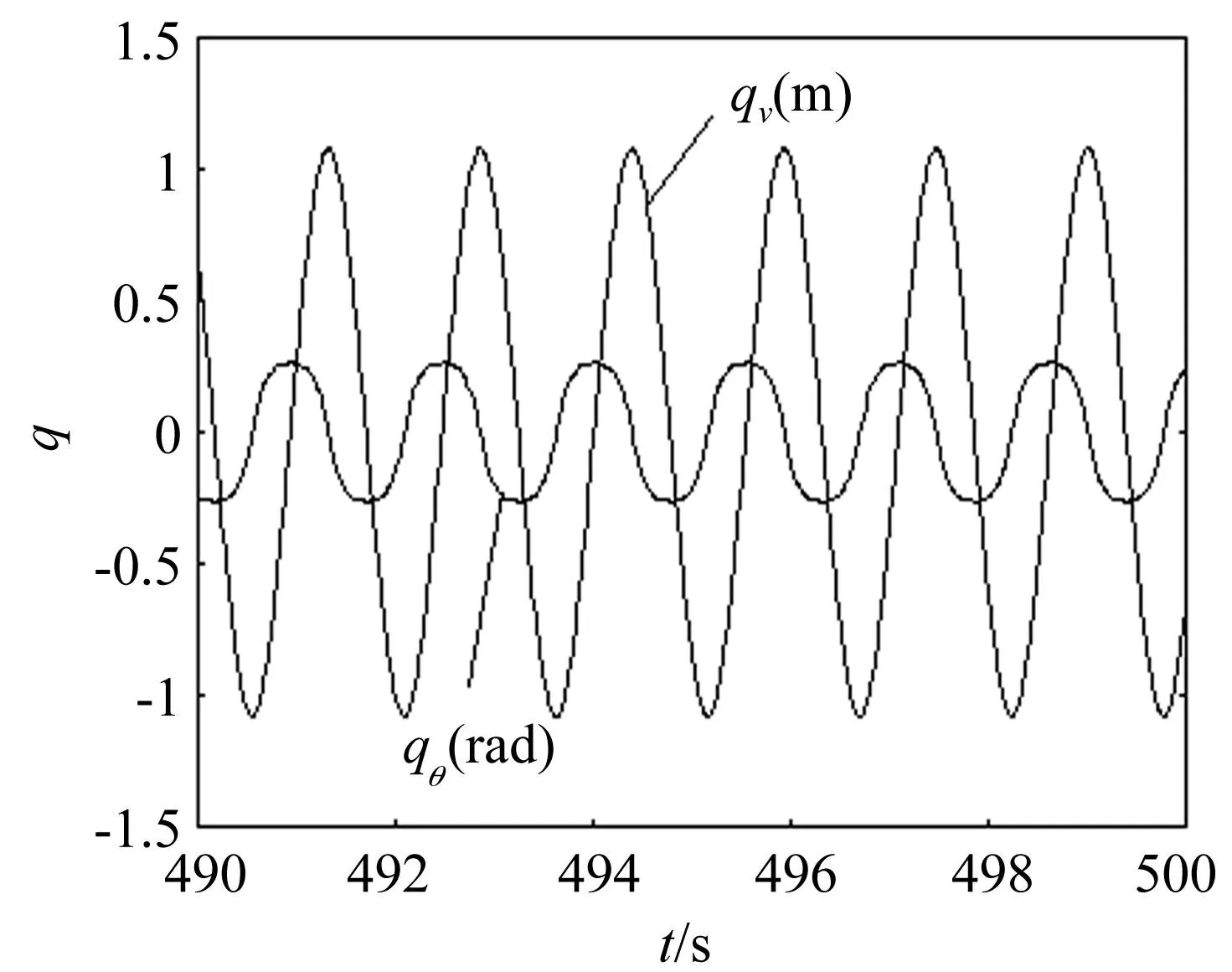
图3 覆冰导线舞动时程曲线图Fig.3 Time history of galloping for iced transmission line
3分岔理论分析
A14+A1λ+α1+α2A1+α3A12+α4A13=0
(16)
式中:λ=δζv为分岔参数,与面内阻尼系数成正比,αi(i=1,…,4)为开折参数,包含了除ζv之外的其他参数。αi和计算系数δ的具体表达式见附录。
借助奇异性理论[24],系统的转迁集为
(17)
由于αi为系统工程参数的函数,根据上式可直接在工程参数坐标中绘制转迁集曲线或曲面,绘制过程中可预留关心的参数作为工程开折参数,本文中选取风速U、空气密度ρ和面外阻尼系数ζw作为工程开折参数,其余参数选取为[20]:T0=30 000 N,l=110.5 m,m=2.378 9 kg/m,D=0.028 6 m,A=423.24 mm2,E=4.78×1010N/m2。如图4所示,系统的转迁集将空间U-ρ-ζw分成了四个子空间,逆时针方向依次将曲面和子空间定义为SF-Ⅰ、SP-Ⅰ、SF-Ⅱ、SP-Ⅱ、SF-Ⅲ、SP-Ⅲ、SF-Ⅳ和SP-Ⅳ八个不同的区域,其中SF-Ⅰ和SF-Ⅳ为分岔点集,SF-Ⅱ和SF-Ⅲ为滞后点集。
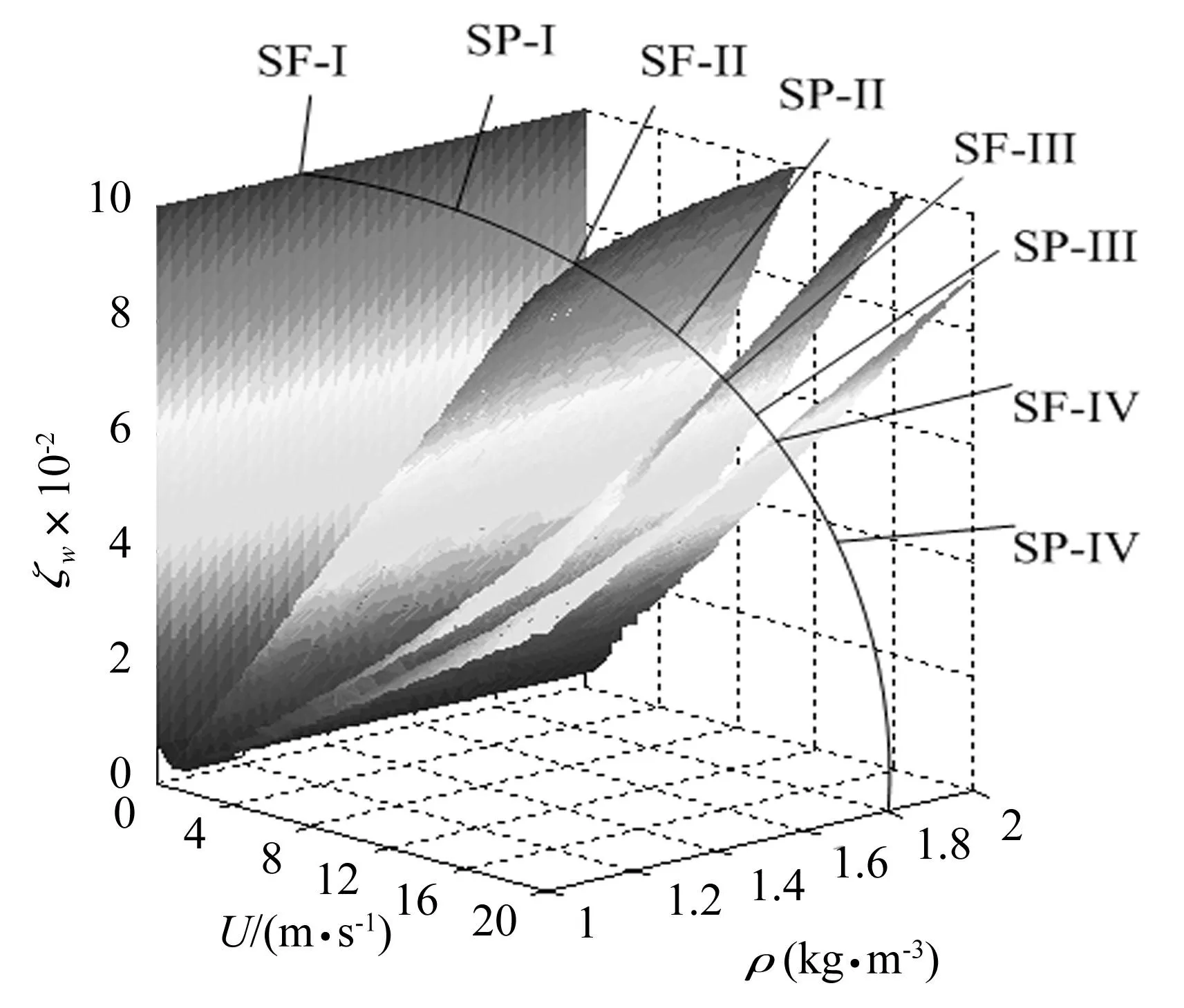
图4 系统在空间U-ρ-ζw中的转迁集Fig.4 Transition sets in coordinates U-ρ-ζw
每个曲面和子空间所对应的分岔曲线如图5所示。考虑到工程应用,只考查第一象限中的曲线分布。取ζw=0.04[11]为例,所有区域中的分岔曲线皆随着面内阻尼的增大而减小,只有在SP-Ⅲ和SF-Ⅳ中,发现了多解的存在。图5(f)中出现了两个鞍结分岔点,图5(g)中出现了一个叉形分岔点和一个鞍结分岔点,以上两种情形都会引起系统的不稳定产生跳跃现象,是工程中需要尽量避免的。工程中通常以增大阻尼达到减振目的,而在此种情况下,增大阻尼再不能满足工程的需求,当阻尼减小到某一区域内,非但幅值没有减小,还会引起幅值在两个相差悬殊的吸引域中进行跳变,对系统造成危害。因此在参数优化时应尽量缩小SP-Ⅲ范围。结合图4得到,风速和空气密度的增加都会增大SP-Ⅲ区域,而面外阻尼系数的增大首先会扩大SP-Ⅲ区域,当面外阻尼系数增大到一定程度时,SP-Ⅲ逐渐消失,因其所在区域已经超出了工程参数范围。

图5 不同区域的分岔曲线(ζw=0.04)Fig.5 Bifurcated curves in their corresponding regions
4数值验证
为了验证理论分析的有效性,将对式(12)进行数值计算以辅助支撑理论分析的结论。针对系统在不同区域所表现出的稳定和跳跃现象,将分别在稳定区域SP-Ⅱ和跳变区域SP-Ⅲ中选取参数进行对比验证。图6即为系统在区域SP-Ⅱ中的动态响应,从分岔响应图6(a)可以看出,随着面内阻尼系数的增大,舞动幅值迅速减小并在阻尼增大至0.07时,基本抑制了系统的舞动现象。此时系统的时间历程曲线(图6(b))为稳定的周期运动,相图(图6(c))呈现出一个封闭的圆环,庞加莱截面图(图6(d))为一个单独的点,可得系统在区域SP-Ⅱ中的运动属于单周期运动,这与理论计算结果(图5(d))一致。图7为系统在跳跃区域SP-Ⅲ中的数值模拟结果,从分岔响应图7(a)可以看到,一开始系统基本呈单值状态,随着面内阻尼系数的增大,舞动非但没有得到控制,反而出现了两个明显的吸引域,使得幅值在其间来回跳跃。相图7(c)和庞加莱截面图7(d)为面内阻尼系数取0.15时对应的响应,此时系统呈混沌特性,有两个明显的吸引域,与理论分析结果(图5(f))中出现的跳跃现象基本吻合。

图6 区域SP-Ⅱ中的数值模拟 (U=14,ρ=1)Fig.6 Numerical simulation with parameter selected in SP-Ⅱ (U=14,ρ=1)
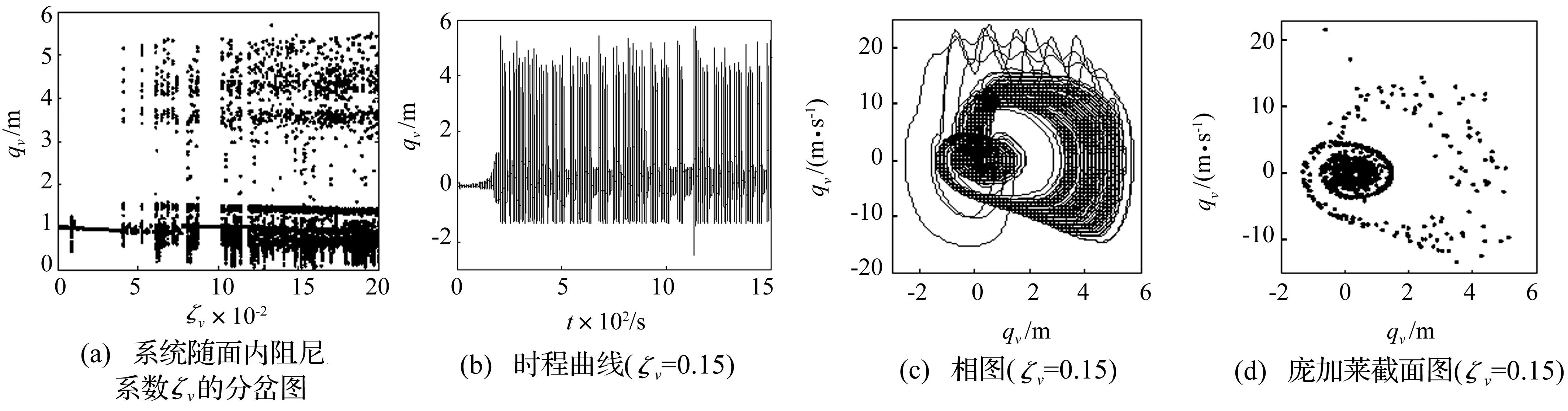
图7 区域SP-Ⅲ中的数值模拟 (U=10,ρ=1.5)Fig.7 Numerical simulation with parameter selected in SP-Ⅱ (U=10,ρ=1.5)
5结论
本文针对覆冰导线模型,考虑其几何非线性和气动载荷非线性因素,基于Hamilton原理建立了覆冰导线面内、面外及扭转三自由度耦合的动力学模型,并借助Galerkin法和平均法得到系统的分岔方程,进而考察了系统的奇异性并加以数值验证。
奇异性分析过程中,建立了分岔参数和开折参数与工程参数的对应关系,并且将分岔参数与开折参数所包含的工程参数解耦,使得转迁集和分岔曲线都可以直接反应工程参数对系统的影响并实现数值验证,更加直观实用。
研究结果表明,工程参数界定下的转迁集将系统分为了8个不同的区域,每个区域都存在着不同的拓扑结构,然而只有在区域SP-Ⅲ和SF-Ⅳ中发现了促使系统发生跳跃现象的鞍结分岔点,此种现象对实际工程存在着很大的危害,应尽量减小或消除SP-Ⅲ区域,而后的数值模拟也验证了理论分析的结果,并发现系统中存在混沌现象。
参 考 文 献
[1]王少华, 蒋兴良, 孙才新. 输电线路导线舞动的国内外研究现状[J]. 高电压技术, 2005, 31(10):14-17.
WANG Shao-hua, JIANG Xing-liang, SUN Cai-xin. Study status of conductor galloping on transmission line [J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2005, 31(10):14-17.
[2]Denhartog J P. Transmission line vibration due to sleet [J]. Electrical Engineering, 1932, 51(6): 413-413.
[3]Nigol O,Buchan P G. Conductor galloping part I: Den Hartog mechanism [J]. Power Apparatus and Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 1981, 100(2): 699-707.
[4]Nigol O,Buchan P G. Conductor galloping part I: Torsional mechanism [J]. Power Apparatus and Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 1981, 100(2): 708-720.
[5]Yu P, Shah A H, Popplewell N. Inertially coupled galloping of iced conductors [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1992, 59(1):140-145.
[6]Luongo A, Zulli D, Piccardo G.Analytical and numerical approaches to nonlinear galloping of internally resonant suspended cables [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 315 (2008): 375-393.
[7]Lee C L, Perkins N C.Nonlinear oscillations of suspended cables containing a two-to-one internal resonance [J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1992, 3:465-490.
[8]Benedettini F, Rega G, Alaggio R. Non-linear oscillations of a four-degree-of-freedom model of a suspended cable under multiple internal resonance conditions [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1995, 182(5): 775-798.
[9]Nayfeh A H, Arafat H N, Chin C M, et al. Multimode interactions in suspended cables [J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2002, 8(3): 337-387.
[10] 李黎, 陈元坤, 夏正春, 等. 覆冰导线舞动的非线性数值仿真研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2011, 30(8): 107-111.
LI Li, CHEN Yuan-kun, XIA Zheng-chun, et al. Nonlinear numerical simulation study of iced conductor galloping [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(8): 107-111.
[11] 赵莉, 严波, 蔡萌琦, 等. 输电塔线体系中覆冰导线舞动数值模拟研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(18):113-120.
ZHAO Li, YAN Bo, CAI Meng-qi, et al. Numerical simulation for galloping of iced conductors in a transmission tower-line system [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(18):113-120.
[12] Liu F H, Zhang Q C, Wang W. Analysis of hysteretic strongly nonlinearity for quad iced bundle conductors [J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2010, 27(3): 034703.
[13] Qin Z H, Chen Y S, Zhan X, et al. Research on the galloping and anti-galloping of the transmission line [J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2012,22(2):1250038.
[14] Liu X J, Huo B, Zhang S X. Nonlinear dynamic analysis on the rain-wind-induced vibration of cable considering the equilibrium position of rivulet [J]. Abstract and Applied Analysis, 2013, 2013: 927632(10).
[15] 李欣业, 张华彪, 高仕赵, 等. 三自由度模型覆冰输电导线舞动的数值仿真分析[J]. 河北工业大学学报, 2010, 39(3): 1-5.
LI Xin-ye, ZHANG Hua-biao, GAO Shi-zhao, et al. Numerical analysis of galloping of iced power transmission lines [J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 2010, 39(3): 1-5.
[16] 侯磊, 陈予恕. 输电线路导线舞动中的混沌运动研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2014, 27(1): 75-83
HOU Lei, CHEN Yu-shu. Study on chaos in galloping of the transmission line [J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2014, 27(1): 75-83.
[17] 熊蕊, 刘向东. 含PID控制器的迟滞非线性控制系统的主共振及奇异性[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(8): 72-77.
XIONG Rui, LIU Xiang-dong. Principal resonance and singularity of a hysteretic nonlinear control system with a PID controller [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014,33(8): 72-77.
[18] 王晓东, 陈予恕. 一类电力系统的分岔和奇异性分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(4): 1-6.
WANG Xiao-dong, CHEN Yu-shu. Bifurcation and singularity analysis for a class of power systems [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(4): 1-6.
[19] 孟遂民, 孔伟. 架空输电线路设计[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2007.
[20] Zhang Q,Popplewell N, Shah A H. Galloping of bundle conductor [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2000,234(1):115-134.
[21] McComber P, Paradis, A. A cable galloping model for thin ice accretions [J]. Atmospheric Research, 1998, 46(1): 13-25.
[22] 蔡君艳, 刘习军, 张素侠. 覆冰四分裂导线舞动近似解析解分析[J]. 工程力学, 2013, 30(5): 305-310.
CAI Jun-yan, LIU Xi-jun, ZHANG Su-xia. Analysis of approximate analytical solution on galloping of iced quad bundle conductors [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013,30(5): 305-310.
[23] 陈予恕. 非线性振动[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002.
[24] 陈予恕. 非线性振动系统的分岔和混沌理论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1993.
附录
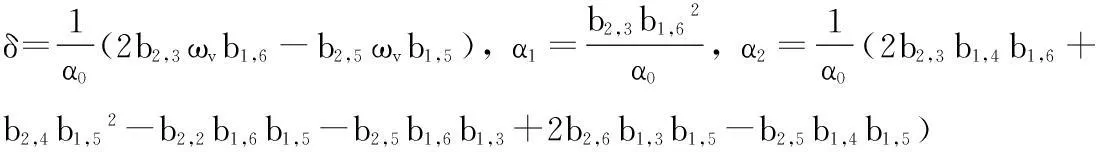



第一作者 霍冰 女,博士生,1987年12月生
摘要:考虑几何非线性和气动载荷非线性,基于Hamilton原理建立了面内、面外和扭转三自由度耦合的连续动力学模型。借助Galerkin法对连续体模型进行空间离散得到系统的常微分方程。利用平均法解析求得系统的平均方程和分岔方程,建立了分岔参数、开折参数与工程参数的对应关系,并对分岔参数和开折参数进行解耦。根据奇异性理论得到关于工程参数的转迁集空间和各区域的拓扑结构,发现系统存在鞍结分岔点和跳跃现象。就理论解所得不同区域内典型的拓扑结构进行数值模拟,发现周期解与混沌解的存在,验证了理论解的正确性,同时为工程参数优化提供一定的理论支撑。
关键词:非线性振动;覆冰导线;舞动;奇异性理论;混沌
Singularity and chaos of nonlinear galloping for an iced transmission line
HUOBing1,2,LIUXi-jun1,2,ZHANGSu-xia1,2,LIUPeng1,2(1. Dept. Of Mechanics, School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China; 2. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos Control, Tianjin 300072, China)
Abstract:A continuous dynamic model for an iced transmission line was proposed for describing the coupling of its in-plane, out-of-plane and torsional vibrations. It was built on the basis of Hamilton principle considering geometric and aerodynamic nonlinearities. Galerkin method was applied to spatially discrete the partial differential governing equations and acquire the oddinary differential equations of the line system. With the average method, the average equations and the bifurcation equation of the line system were deduced. The relationship between bifurcation parameters, unfolding parameters and physical ones was established, bifurcation parameters and unfolding ones were decoupled. Transition sets of the physical parameters and their topological structures in different regions were derived by employing the singularity theory. It was found that there exist saddle nodes and jumping phenomenon in the line system. Numerical simulations were implemented in stable and jumping regions, respectively. The bifurcation diagrams obtained with numerical simulations were consistent with those acquired with the theoretical analysis, the periodic and chaotic solutions were observed. The results provided a theoretical support for the optimization of the system’s physical parameters.
Key words:nonlinear vibration; iced conductor; galloping; singularity theory; chaos
中图分类号:TM726;O322
文献标志码:A
DOI:10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.13.007
通信作者刘习军 男,教授,1956年1月生
收稿日期:2014-10-17修改稿收到日期:2015-01-13
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51009107,51479136);天津市自然科学基金重点项目(13JCZDJC27100,09JCZDJC26800)
