A Study of the Factors that Affect Safe Full Heading of Machine-transplanted Rice Seedlings in the Temperate and Cool Rice-growing Areas
2016-01-12,,,,,
, , , , ,
1.Luliang County Agricultural Technology Extension Center, Luliang 655699, China; 2. Qujing Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Qujing 65500, China
1 Introduction
Luliang County of Yunnan Province is located in the center of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, with average elevation of l840 m and average annual temperature of 15.3℃. The total accumulated temperature is insufficient, and there is often cold rainy weather from the end of July to mid-August. It is the temperate and cool rice-growing area, and safe full heading is the main problem to be solved in rice production. In production practice, the heading period of machine-transplanted rice seedlings is 3-7 d later than that of manually transplanted rice seedlings due to delayed sowing period. If there is cold rain, there will be a great risk of reduction in production, becoming one of the important factors that limit the expanded application of machine-transplanted rice seedling technology. In this paper, we make an experiment from varieties, seedling age, application rate of nitrogen fertilizer and planning and management to study the factors that affect the safe full heading of machine-transplanted rice seedlings in temperate and cool rice-growing areas.
2 Materials and methods
2.1MaterialsThe machine-transplanted rice seedling varieties include Chujing 28, Yunjing 26, Yunjing 29 and Lu 08-139.
2.2Methods
2.2.1Variety screening. Chujing 28, Yunjing 26, Yunjing 29 and Lu 08-139 are chosen as machine-transplanted rice varieties, and the traditional manually transplanted rice seedlings are selected as control (Yunjing 29), a total of five treatments. The randomized block design is adopted, with three replications, and the plot area is 13.3 m2. The film is wetted to raise rice seedlings. The machine-transplanted rice seedlings are sown on April 5, and the seedling age is 35 d. The manually transplanted rice seedlings are sown on March 21, and the seedling age is 50 d. The seedlings are transplanted on May 10, and the density is 270000 per ha. 1200 kg/ha 8∶ 10∶ 8 special rice fertilizer is applied at the bottom. Within 7 d after transplanting, in the 11.5-leaf period and 13.5-leaf period, 146.25, 140.85 and 93.9 kg/ha topdressing with urea is completed, respectively, equivalent to pure N 270 kg/ha. The diseases and pests are controlled twice in the field.
2.2.2Seedling age test. The test variety is Yunjing 26. The age of machine-transplanted rice seedlings is set to 20, 25, 30, 35 d, with the manually transplanted rice seedlings with age of 50 d as control, a total of five treatments. The randomized block design is adopted, with three replications, and the plot area is 13.3 m2. The film is wetted to raise rice seedlings. The seedlings are sown at different stages (from April 7), and transplanted on May 12. The transplanting density, fertilization and related management are the same as that under the screening test of machine-transplanted rice varieties.
2.2.3Application rate of nitrogen fertilizer and planning and management. The test variety is Yunjing 29. The pure nitrogen application rate (A) includes A1(225 kg/ha), A2(300 kg/ha) and A3(375 kg/ha); nitrogen fertilizer planning and management (B) includes B1(basal tillering fertilizer∶ panicle fertilizer=7∶ 3, spikelet-promoting fertilizer∶ spikelet-developing fertilizer=6∶ 4), B2(basal tillering fertilizer∶ panicle fertilizer=6∶ 4, spikelet-promoting fertilizer∶ spikelet-developing fertilizer=5∶ 5). With conventional fertilization as control (artificial transplanting, 345 kg/ha pure nitrogen, applied as basal fertilizer and tillering fertilizer), there are a total of seven treatments (A1B1, A2B1, A3B1, A1B2, A2B2, A382, CK). The randomized block design is adopted, with three replications, and the plot area is 13.3 m2. Calcium superphosphate and potassium sulfate are applied for once at the bottom, and the urea is applied in batches. The machine-transplanted rice seedlings are sown on April 8, and the seedling age is 35 d; the manually transplanted rice seedlings are sown on March 24, and the seedling age is 50 d. The seedlings are transplanted on May 13. The transplanting density is 270000 per ha, and as for the holes with no seedlings transplanted by machine, the seedlings are sown manually in these holes. The diseases and pests are controlled twice in the field.
3 Results and analysis
3.1Effectofvarietiesonthesafefullheadingofmachine-transplantedriceseedlingsFrom Table 1, it is found that the heading stage of machine-transplanted rice varieties with different growth period is 1-7 d later than that of manually transplanted rice seedlings (CK) with age of 50 d. If the growth period is prolonged, the heading will be postponed and the blighted grain rate will increase. Lu 08-139 has the longest growth period and the latest heading, and the blighted grain rate reaches 28.73%. The yield significantly decreases compared with the control. Yunjing 26 and Yunjing 29 are mid-early maturity varieties, with the heading period 1-3 d later than the control but 4-6 d earlier than Lu 08-139. Compared with the control, the blighted grain rate only increases by 0.16% and 1.93%, and the yield is significantly increased. It indicates that selecting the varieties with growth period of not more than 180 d for machine-transplanting helps to reduce the days of delayed heading, avoid chilling damage and achieve safe full heading. The cold tolerance of rice varieties also has a significant effect on the safe full heading of machine-transplanted rice seedlings. Chujing 28 and Yunjing 29 have the same heading period, but the cold tolerance of Chujing 28 is weak, and the blighted grain rate is 14.26% and 16.19% higher than that of Yunjing 29 and control, respectively. Therefore, the varieties with strong cold tolerance should be selected for machine-transplanting in the production.
3.2Effectofseedlingageonthesafefullheadingofmachine-transplantedriceseedlingsFrom Table 2, it is found that the age of machine-transplanted rice seedlings is shortened, the heading period is delayed and the blighted grain rate is increased. The sowing date under A20and A25is 30, 25 d later than under CK, and the heading period is delayed to July 31 and July 29. The blighted grain rate reaches 33.64% and 26.11%, respectively, and the yield is significantly reduced compared with the control, especially for A20. The sowing date under A30and A35is 5-15 d earlier than under A20and A25, and the heading period is 3-6 d brought forward. The blighted grain rate decreases by 6.24%-14.68%, and the yield is significantly higher than under CK, A25and A20, indicating that the seedling age is controlled to 30-35 d, which can ensure safe heading[1-2].
Table1Effectofdifferentvarietiesonthesafefullheadingofmachine-transplantedriceseedlings
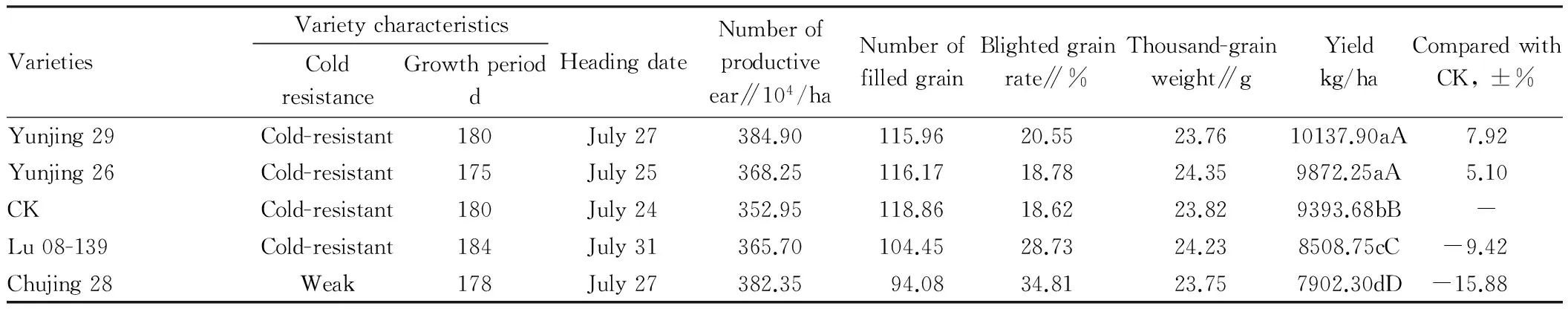
VarietiesVarietycharacteristicsColdresistanceGrowthperioddHeadingdateNumberofproductiveear∥104/haNumberoffilledgrainBlightedgrainrate∥%Thousand-grainweight∥gYieldkg/haComparedwithCK,±%Yunjing29Cold-resistant180July27384.90115.9620.5523.7610137.90aA7.92Yunjing26Cold-resistant175July25368.25116.1718.7824.359872.25aA5.10CKCold-resistant180July24352.95118.8618.6223.829393.68bB-Lu08-139Cold-resistant184July31365.70104.4528.7324.238508.75cC-9.42Chujing28Weak178July27382.3594.0834.8123.757902.30dD-15.88
Note: Different lower case letters in the same column indicate significant differences between varieties (P<0.05); different capital letters indicate highly significant differences between varieties (P<0.01).
Table2Effectofseedlingageonthesafefullheadingofmachine-transplantedriceseedlings

TreatmentHeadingdateNumberofproductiveear∥104/haNumberoffilledgrainBlightedgrainrate∥%Thousand-grainweight∥gYield∥kg/haComparedwithCK,±%A35July25378.90116.9318.9624.5210323.30aA5.75A30July26381.75115.3519.8724.4710177.95aA4.26A50(CK)July23362.25117.6218.6424.589762.0bAB-A25July29390.15105.4826.1124.439418.65bB-3.52A20July31393.4594.5733.6424.358035.2cC-17.69
Note: Different lower case letters in the same column indicate significant differences between varieties (P<0.05); different capital letters indicate highly significant differences between varieties (P<0.01).
3.3Effectofapplicationrateofnitrogenfertilizerandplanningandmanagementonthesafefullheadingofmachine-transplantedriceseedlingsTable 3 shows that the heading stage is delayed and the blighted grain rate is increased with the increase of application rate of nitrogen fertilizer. The analysis of variance shows that the application rate of nitrogen fertilizer has a highly significant impact on yield (F=108.045﹥F0.01=7.56). The heading is latest under the application rate of 375 kg/ha, and the blighted grain rate reaches 26.17%-32.63%. The yield decreases compared with the control, and the yield decreases significantly under A3B2. The heading under 300 kg/ha treatment is 2-3 d later than under the control, but 2-5 d earlier than under 375 kg/ha treatment, the blighted grain rate increases slightly, and the yield increases significantly compared with the control. Under 225 kg/ha treatment, the heading is early and the blighted grain rate is low, but it lacks effective panicles, and the yield does not increase obviously. It indicates that applying 300 kg/ha pure nitrogen can ensure safe full heading and rice yield[3]. In the case of controlling total amount of pure nitrogen, the nitrogen fertilizer planning and management have a certain impact on the heading period[4]. In the treatment components, there are no significant differences in nitrogen fertilizer planning and management (F=4.25
Table3Effectofapplicationrateofnitrogenfertilizerandplanningandmanagementonthesafefullheadingofmachine-transplantedriceseedlings

TreatmentHeadingdateNumberofproductiveear∥104/haNumberoffilledgrainBlightedgrainrate∥%Thousand-grainweight∥gYield∥kg/haComparedwithCK,±%A2B2July26376.95117.1619.6423.8210147.95aA6.92A2B1July25372.75118.5318.8523.7610002.6aAB5.39A1B2July24355.05118.8618.4523.889581.55bBC0.95CKJuly23361.05117.9318.8023.799491.25bCD-A1B1July23356.85117.4818.5423.829260.7bcCD2.43A3B1July28387.30106.4526.1723.739037.65cD-4.78A3B2July30388.2097.0432.6323.778042.7dE-15.26
Note: Different lower case letters in the same column indicate significant differences between varieties (P<0.05); different capital letters indicate highly significant differences between varieties (P<0.01).
4 Conclusions
The growth period of machine-transplanted rice varieties is related to cold tolerance and seedling age. The application rate of nitrogen fertilizer and planning and management affect the heading period and blighted grain rate of machine-transplanted rice seedlings. Long growth period, young seedlings, excess nitrogen fertilizer and large postponing amount for machine-transplanted rice varieties will delay the heading stage and increase the risk of chilling damage. At the same time, the weak cold tolerance of machine-transplanted rice varieties can also lead to an increase of blighted grain rate. On the contrary, it will help to reduce the heading delay period and avoid cold damage to achieve safe full heading. In the mechanized rice production in temperate and cool rice-growing areas, we should select the mid-early maturity cold-resistant varieties with growth period of not exceeding 180 d, control the seedling age to be 30-35 d and total amount of pure nitrogen to be not more than 300 kg/ha, and moderately reduce the nitrogen fertilizer postponing ratio, so as to achieve safe full heading of machine-transplanted rice seedlings and ensure the yield.
[1] LIAO WW, YU ZL. Test of seedling age delaying for mechanized transplanting rice[J]. Modern Agricultural Sciences and Technology,2011(9):51. (in Chinese).
[2] WANG XZ, WU M, LIAO DB,etal. Effect of transplanting seedling age of machine-transplanted seedlings on its yield and component factors[J]. Barley and Cereal Sciences,2013(1):18-20. (in Chinese).
[3] MOU BA. Effect of seedling age, fertilization and cultivation density on the yield of machine-transplanted rice seedlings[J]. Southwest Horticulture,2013(5);35-36. (in Chinese).
[4] HU JF. Effects of application of nitrogen fertilizer on population growth, yield and quality of machincal-transplanting rice with long-aged seedlings[D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University,2009. (in Chinese).
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Innovation on Distant Hybridization of Saline-tolerant Mud Flat Spartina and Rice Germplasm
- Advances in Studies of Genetic Improvement of Sugarcane
- Necessities and Practical Approaches for Beautiful Countryside Construction
- A Study of the Issues concerning Development of China’s Agricultural Product Logistics
- Review of Agricultural Insurance Development in the New Period in China
- Development of Neural Network for BLSOM Clustering of HA Genes of Avian Influenza Viruses Isolated in Guangdong Province
