Resource Dependence Relationship between Grass-roots Government and Farmers’ Specialized Cooperatives
2016-01-11,
,
College of Economics and Management, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
ResourceDependenceRelationshipbetweenGrass-rootsGovernmentandFarmers’SpecializedCooperatives
XuebinSHEN,YiCAI*
College of Economics and Management, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
Based on theories of resource dependence and government functions, this paper analyzed benefit interaction between grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives in Hubei Province. It was intended to make clear the path dependence relationship between grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives and find out problems in between. Besides, from the perspective of grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives, it came up with corresponding recommendations, to promote constant improvement of farmers’ specialized cooperatives, and help them to become key forces of leading farmers to get rich, pull agricultural economic development, and promote new socialist countryside construction.
Grass-roots government, Farmers’ specialized cooperatives, Resource dependence, Government functions
1 Introduction
Since the formal promulgation of theLawofthePeople’sRepublicofChinaonFarmers’SpecializedCooperativeson July 1st, 2007, legally registered farmers’ specialized cooperatives have reached 1289000. The growth in recent 8 years is up to 9 times the total number of various cooperative economic organizations in the past 28 years. However, with sharp increase in number, the quality of cooperatives seriously declines and deviates from the development principle. Besides, policy support of government for farmers’ specialized cooperatives enters new normal development stage from guiding stage and the relationship in between becomes a hot spot of scholars.
Hou Baojiang (2007) classified and summarized the relationship according to development stages and relationship with government. Ren Mei (2013) believed that as representative of public benefit, grass-roots government should perform functions of support and guidance, to provide favorable external environment for growth of cooperatives. Jiang Yufu (2011) held that grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives have their own scarce resources necessary for each other, and resource exchange and complementation will realize win-win. At present, scholars have made extensive researches on the relationship between cooperatives and grass-roots government, but few scholars have made researches through combining government function and resource dependence theories.
On this basis, we combined government functions and resource dependence theories to study the relationship between grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives taking questionnaire and interview records of 43 township party secretaries, 240 copies of survey data, and 15 interview records of leaders of cooperatives. In this study, township cadres and farmers’ specialized cooperatives are defined as interest agent of grass-roots government and cooperative members. In the development process of cooperatives, grass-roots government takes economic growth as objective, grass-roots cadres take political performance as motive force, and cooperatives take constant growth of income of cooperative members as principle of sustainable development, to build close benefit link relationship on the basis of mutual reciprocal and complementation of resources.
2 Theoretical foundation: government function based resource dependence theory
2.1TheoryofgovernmentfunctionGovernment function is function of government brought into play according to actual needs of the national and social development in certain period. At early stage, the representative of classical economics, Adam Smith, believed that the government should manage less. Later, Keynesianism stressed government intervention. Subsequent scholars advocated combination of liberalism and intervention doctrine. In the cooperation of grass-roots government and cooperatives, Chinese scholar Huang Zuhui (2010) stated that farmers’ specialized cooperatives are set up and developed under the framework of local government. Yao Weichuan and He Pinetal(2010) held that government should provide great support in legislation, policy support, organization and management, and service improvement. In our opinion, grass-roots government should manifest management functions of regulation and supervision in the development of cooperatives, bring into full play service functions of guidance and support, to seek the optimum balance between grass-roots government and cooperatives.
2.2TheoryofresourcedependenceAccording to theory of resource dependence, an organization needs absorbing resources from the surrounding environment for survival, and reduces dependence on key resource suppliers through controlling key resources, so as to form interdependent and complementary relationship. In this study, we define resource as material elements different from general material, financial power and manpower. It mainly consists of two levels of meanings: first, grass-roots government has management resources such as policy, information, and power, so it can make up for drawbacks of weak original accumulation and profitability and low competitiveness through reasonable allocation of resources; second, cooperatives organize decentralized farmers to realize unified allocation of fragmentary land, rural surplus labor, and idle funds, which is favorable for agricultural modernization, increasing farmers’ income and developing township economy, and promoting grass-roots government to properly make social management of towns, as shown in Fig. 1.
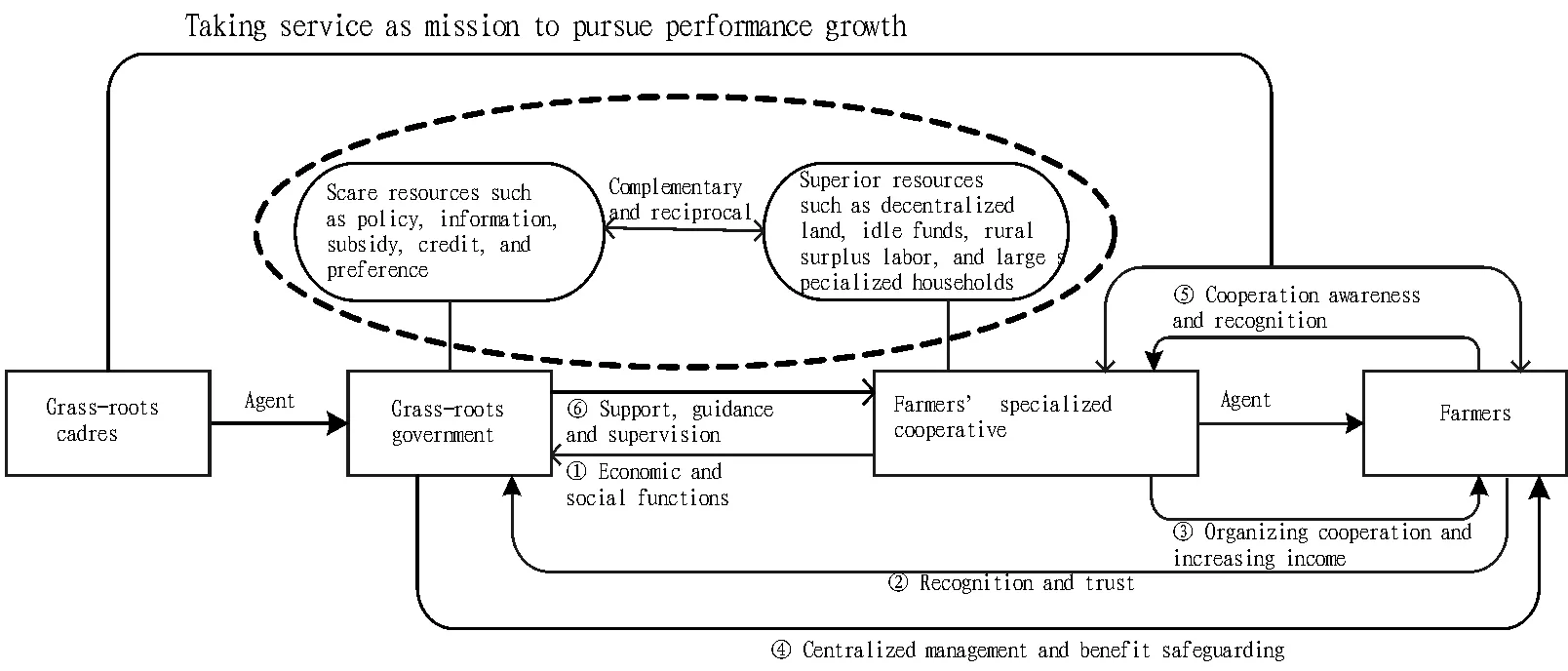
Fig.1 Path for relationship between farmers’ specialized cooperative and grass-roots government
3 Analysis on path dependence relationship between grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperative based on two theories
According to nature and basic principle of farmers’ specialized cooperatives, most participants of farmers’ specialized cooperatives are rural residents living in rural areas for a time and engaged in farm labor, while these labors set up a basic administrative area due to geographical, blood, and relative relation, and grass-roots government undertakes centralized management just in this area. Farmers’ specialized cooperatives are organizations founded by farmers voluntarily. Therefore, there is close relationship between grass-roots government and cooperatives in resource complementation and environment exchange. As shown in Fig. 1, grass-roots government supports, guides, and supervises healthy development of cooperatives, while development of cooperatives has function of economic promotion and assisting social management for grass-roots government. Complementary and reciprocal relation between both parties is interdependence foundation.
3.1Cooperativeshavedoublefunctionofeconomicpromotionandsocialmanagementfromtheperspectiveofgrass-rootsgovernmentCooperatives have outstanding superiority in cooperation of decentralized farmers. Standard rules, excellent rural construction talents, and powerful market competitiveness are indispensible resource foundation for grass-roots government developing township economy and promoting social management.
3.1.1Cooperatives boost growth of local economy and drive increase of farmers’ income. As major force promoting development of farmers’ specialized cooperatives, grass-roots government pays high cost and price. Farmers’ specialized cooperatives, as new agricultural operating entities, gather idle funds, fragmentary land and surplus labor, skillful farmers, and large specialized households, and directly or indirectly control scarce resources for rural economic development, thus constitute core forces of China’s agricultural modernization, large-scale operation, and mechanization. Grass-roots government, taking advantage of management resources, cultivates and supports many farmers’ specialized cooperatives with local characteristics and tremendous strength, to help them become new engine for township economic development.
The statistical data of 2013 indicated that near 30000 cooperatives in Hubei Province directly pulled township investment up to 40 billion yuan, operating farmland up to 20 million mu, covering 30% farmland area of the whole province. In brand construction, 3500 cooperatives in Hubei Province have obtained certification of pollution-free agricultural products, green products, and organic foods, created a good many famous, excellent, and special brands of agricultural products such as Wudao Tea, Medaka, Yantianhe Castanea mollissima (chestnut). At the same time of raising competitiveness of local agricultural product market, they have made great contribution to promoting agricultural industrialization, increasing farmers’ employment opportunity, and transferring rural surplus labor. This directly influences economic management function of grass-roots government and improves ability of grass-roots government in promoting economic development.
3.1.2Cooperatives provide unified social services for cooperative members, which raises recognition and trust of farmers. Grass-roots government has social management function of adjusting social distribution and organizing social security, promoting social service system, and protecting ecological environment and natural resources. Democracy and harmony, civilized village culture, clean village environment are tasks of grass-roots government in building beautiful countryside. Cooperatives stress equal status of members, democratic management, fair income distribution, and seeking common benefit of whole members. These principles are consistent with concept of grass-roots government in building new socialist countryside. Both parties can realize mutual complementation in management, which is favorable for cultivating cooperation spirit of farmers, strengthening sense of recognition and democratic awareness.
We found that the work evaluation of cooperative members for performance of grass-roots government is 2.74, higher than 2.20 from non cooperative members, reflecting cooperatives can improve recognition of farmers for grass-roots government to a certain extent, as listed in Table 1. Firstly, cooperatives play an irreplaceable role in pulling employment of farmers, and strengthening democratic cooperation awareness of farmers, which significantly improves overall construction level of towns. Under the support and guidance of grass-roots government, 157 cooperatives in Hubei Province have won the title of national demonstration farmers’ specialized cooperatives. Secondly, grass-roots government guides leading enterprises to explore cooperative based poverty-relief mode. Changyang County of Hubei Province develops 120000 mu tuber crops through "industrial park + cooperatives + farmer households" mode, covering near 200 households of poor families; Yunxian County supports agricultural enterprises and specialized households to jointly set up specialized vegetable cooperatives, and develop 7900 mu vegetable base in 6 towns, directly including more than poor families into cooperative members. Thirdly, cooperatives actively participate in public activities of rural communities. A cooperative in Macheng City not only solves employment problem of returning migrant workers, but also inputs 80000 yuan annually, helping near 500 elderly people without family, disabled children, and laid-off women workers.
Table1Comparisonbetweencooperativemembersandnon-cooperativemembers
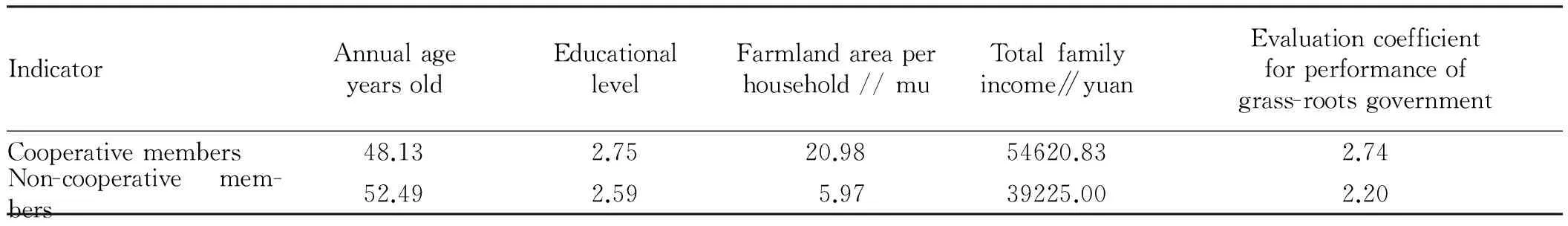
IndicatorAnnualageyearsoldEducationallevelFarmlandareaperhousehold//muTotalfamilyincome∥yuanEvaluationcoefficientforperformanceofgrass-rootsgovernmentCooperativemembers48.132.7520.9854620.832.74Non-cooperativemem-bers52.492.595.9739225.002.20
Note: data came from our survey and total samples of the survey were 240 (educational level and performance evaluation of grass-roots government were expressed by number 1-5, the larger the number, the higher the educational level and the higher performance evaluation of grass-roots government).
3.2Grass-rootsgovernmentguidesandsupportsdevelopmentofcooperatives,tomakeupforshortageofscarceresourcesFarmers’ specialized cooperatives organize weak farmers to carry out cooperative operation, but low quality of farmers, backward rural infrastructure, and deficient resources seriously hinder sustainable development of cooperatives. Through reasonable allocation of fund, information, and policy, grass-roots government guides talents, funds, and materials to flow to cooperatives, support farmers to carry out cooperation, so as to increase farmers’ income and production benefits of cooperatives.
3.2.1Farmers need improving competitiveness through well organized cooperation. Due to inborn weakness, farmers stay weak position in market competition and unavoidably suffer market exploitation. Through unified purchase of production means and unified sales of agricultural products, it is able to effectively reduce transaction costs. Secondary profit return of cooperatives also can increase farmers’ income. From Table 1, we can see that total family income of cooperative members is 15395.83 yuan more than non-cooperative members, and farmers’ income increased 30% after joining the cooperatives. According to interview records, increase of income mainly gives the credit to reduce of transaction costs and increase of sales price due to large-scale, standardized and unified operation of cooperatives. Some cooperatives increase added value of agricultural products through extending the industrial chain and conducting deep processing. This added value narrows the scissors difference between industrial and agricultural products and realizes internalization of external benefit.
Grass-roots government creates favorable development environment for cooperatives taking advantage of superior resources such as policy and power. Promoting agriculture through industries and financial support for agriculture are compensation for externality of agriculture. In addition, grass-roots government provides policy subsidies for agricultural production, promotes internalization of externality of agricultural production. Through effective regulation means, grass-roots government can undertake regulation of means of agricultural production, agricultural product trading market, strike at behavior of fake and forged commodities and acts of disrupting market order, and rectify market failure.
3.2.2As agent of farmers, cooperatives can not develop without resource inclination of grass-roots government. Grass-roots government has function of providing public goods and services. Through formulating cooperative support policy, agriculture industrial planning, and infrastructure construction, grass-roots government can introduce talents, capitals, technologies, and information to cooperatives. Yantianhe township government in Macheng City relies on local high quality chestnut resources, provides great support in policy, and holds chestnut festival, sets up chestnut cooperative, and introduce fine germplasm resources, advanced production line, and external capitals, realizing increase of planting farmers’ income for near 5000 yuan.
The survey of willingness of farmers for joining cooperative indicated that cooperative members are highly dependent on policy resources of grass-roots government. From Table 2, we can obtain following four results. (i) About 40% information of agricultural production means and agricultural product market comes from introduction of village cadres, agro-technical and supply and marketing cooperatives. (ii) About 45.25% farmers hoped that grass-roots government officials are leaders of cooperatives, while 58% farmers hoped that government officials participate in cooperatives, because special status of government officials can bring more resources to cooperatives. (iii) 16.25% cooperative members thought that existing problems of cooperatives are resulted from insufficient support of government. (iv) About 50% farmers hoped to obtain support of special funds or subsidies of government. In sum, current development situations of cooperatives in Hubei Province reflect that cooperatives need policy encouragement and support of government and makeup of functional resources of grass-roots government.
Table2Desireoffarmersforguidanceandsupportofgrass-rootsgovernmentforcooperatives
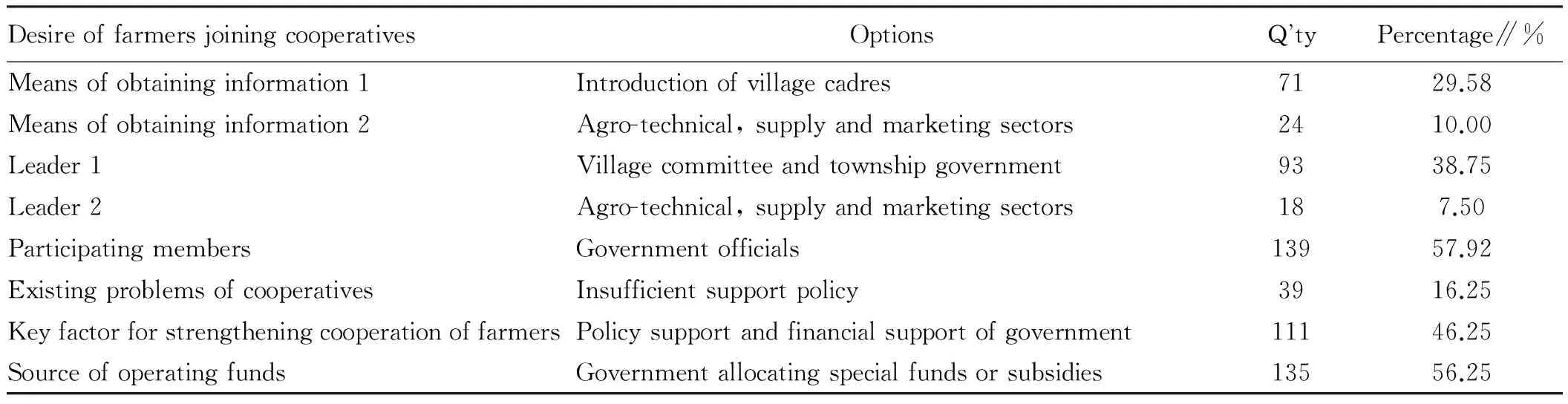
DesireoffarmersjoiningcooperativesOptionsQtyPercentage∥%Meansofobtaininginformation1Introductionofvillagecadres7129.58Meansofobtaininginformation2Agro-technical,supplyandmarketingsectors2410.00Leader1Villagecommitteeandtownshipgovernment9338.75Leader2Agro-technical,supplyandmarketingsectors187.50ParticipatingmembersGovernmentofficials13957.92ExistingproblemsofcooperativesInsufficientsupportpolicy3916.25KeyfactorforstrengtheningcooperationoffarmersPolicysupportandfinancialsupportofgovernment11146.25SourceofoperatingfundsGovernmentallocatingspecialfundsorsubsidies13556.25
Data source: arranged by our study team with total 240 samples.
4 Problems of the relationship between grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives in Hubei Province and causes
In recent years, cooperatives in Hubei Province increased in a large number, but the standardization degree and development situations are worrying. There are few specialized cooperatives having ability of independent operating, assuming sole responsibility for their profits or losses, and sustainable development. In this study, on the basis of questionnaire survey and interview of party secretaries of 43 towns and 15 leaders of cooperatives, we analyzed the relationship between cooperatives and grass-roots government, to find out causes resulting in existing problems.
4.1Inaccuratepositioningofgrass-rootsgovernment,suchasabsenceandoffsideIn accordance with principle of the Cooperative Law and government functions, grass-roots government should provide support for cooperatives in policies, funds, technologies, and information, and play a good role of servants. In fact, grass-roots government has lost its direction in the process of providing services and public goods for farmers’ specialized cooperatives.
On the one hand, grass-roots government becomes invisible man, especially in examination and registration, institutional regulation, and operation supervision of cooperatives. In Table 3, less than 30% towns have made periodical examination of cooperatives, and average score of comment of township cadres to support action of grass-roots government was only 2.98. On the other hand, grass-roots government is superman. It goes beyond its responsibility scope of support and guidance, and directly participates in operation and management of cooperatives, leading to chaos of structure of cooperatives and lack of institution. 25 grass-roots cadres believed that grass-roots government shows general concern for cooperatives, accounting for 58.14%; their evaluation for effort of grass-roots government was 2.09 on average, which remains between no enough effort and no good effect of effort. Therefore, grass-roots government fails to bring into play advantages of policy resources in the process of support and guidance of farmers’ specialized cooperatives. In other words, there is the problem of "government failure".
Table3Regulationofgrass-rootsgovernmentoverdevelopmentofspecializedcooperatives
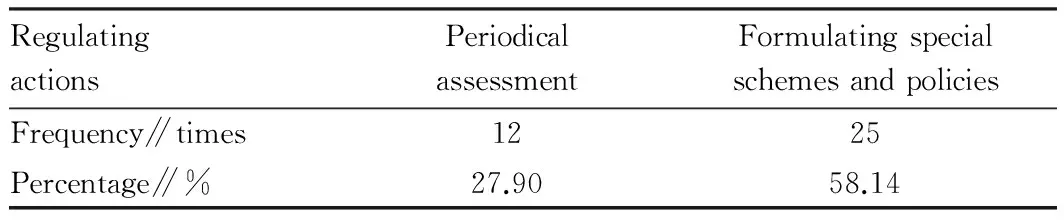
RegulatingactionsPeriodicalassessmentFormulatingspecialschemesandpoliciesFrequency∥times1225Percentage∥%27.9058.14
Note: data came from our survey of grass-roots cadres with total samples of 43.
4.2Economicbenefitofspecializedcooperativeislowandgrass-rootsgovernmentprovidesfewpreferentialpoliciesSuppose grass-roots government is rational economic man, it will incline to low-input and high output non-agricultural construction with limited land, funds, and human resources, while farmers’ specialized cooperatives are just agricultural organizations having high resource consumption but low return rate. In accordance with the principle of seeking maximum benefit, grass-roots government lacks preference for resource input of farmers’ specialized cooperatives. In demands of cooperatives for policy resources, about 80% need financial subsidies of grass-roots government, and 72% need credit coordination, as listed in Table 4. These indicate that cooperatives depend largely on financial subsidies, while their blood-making ability is very limited. After receiving support of preferential policies, there is no hope for them. According to introduction of a township cadre, although the number of registered cooperatives increased year by year, many cooperatives just exist in name due to lack of effective capital accumulation. Besides, farmers’ specialized cooperatives bring limited taxes to grass-roots government, and their contribution to political performance of grass-roots government is little, thus benefit drive of grass-roots government to development of farmers’ specialized cooperatives is considerably weak.
Table4Demandsofleadersandmembersofcooperativesforpolicyresources

PolicyresourcesbadlyneededFinancialsubsidiesCreditcoordinationPreferentialtaxesFrequency∥times90.0081.0066.00Percentage∥%79.6571.6858.41
Note: data came from our survey of cooperative leaders and members with total samples of 113 (98 cooperative members and 15 cooperative leaders).
4.3Policyresourcedependenceofcooperativesongrass-rootsgovernmentformspathdependencetrapIn Table 4, the support badly needed by cooperatives includes financial subsidies, credit coordination, and preferential taxes, and cooperatives have strong desire for policy inclination of grass-roots government. Nevertheless, such desire leads to dependence and consequently results in a general idea widespread in cooperatives: grass-roots government opens door to fund raising, tax reduction, and land circulation for cooperatives; if cooperatives fail to obtain policy inclination, they will think grass-roots government is inactive, about 16.25% cooperative members impute the existing problems of cooperatives to grass-roots government, as listed in Table 2. For a long time, such path dependence trap disrupts reciprocal and complementary relationship between grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives, which lays hidden trouble for healthy development.
4.4Smallscaleandweakprofitabilityarerootcausefordependenceonpolicyresourcesofgrass-rootsgovernmentCurrently, major problems of specialized cooperatives in Hubei Province are small operating scale, low service level, low standardization level, and weak driving ability. Due to limitation in funds, talents, technologies, and brands, cooperatives are weak in resisting risks. Once there are natural disasters or large fluctuation of market price, cooperatives will face huge losses or even disintegrate. As a result, cooperatives remain weak position in market competition and have to depend on support of grass-roots government.
According to introduction of a township party secretary, there are 42 registered farmers’ specialized cooperatives in the town, 15 cooperatives have high recognition of grass-roots government, while only 6 cooperatives meet specifications in strict sense. Cooperatives are organizations of farmers, production and operation are not stable, and there are many conflicts. They separate from each other and integrate together from time to time; some cooperatives survive just for two years; some cooperatives just exist in name and like corpse, once there are favorable policies, they revive again. In sum, such dependence of cooperatives on grass-roots government lies fundamentally on their weak ability.
5 Recommendations for rebuilding the relationship between grass-roots government and farmers’ specialized cooperatives
5.1Exploringthecombinationpointbetweengrass-rootsgovernmentandfarmers’specializedcooperativesfollowingthemarketrulesFarmers’ specialized cooperatives should follow basic principles and market economic laws of international cooperatives, to really help farmers to get rich. Grass-roots government should incorporate policy resources into development of cooperatives, explore development mode suitable for local cooperatives, and find optimal combination point. Firstly, it is recommended to properly deal with the relationship between regulations and development and between benefit and fairness. Grass-roots government should increase number of cooperatives, and also stress institutional construction of cooperatives, take advantage of limited resources to promote rural economic development to an utmost degree, cultivate demonstration cooperatives, and give consideration to characteristic small cooperatives. Secondly, it is recommended to promote complement of superior resources on the basis of resource dependence relationship. On the one hand, grass-roots government should provide excellent services and bring into full play policy resource advantages in supply of public goods and policy formulation, to provide favorable external environment for development of cooperatives. On the other hand, cooperatives should improve internal system, improve competitiveness, cultivate cooperation awareness of cooperative members, and improve their sense of belongingness and recognition.
5.2Grass-rootsgovernmentshouldbringintoplayresourceadvantagesinthescopeoffunctionsFirstly, Grass-roots government should do what is appropriate and discard what is inappropriate and follow the principle of moderate degree. They should foster a correct view on evaluating their performances, take serving cooperatives as their responsibilities, formulate scientific evaluation indicator system, and comprehensively recognize social, economic, and ecological benefits of cooperative development. Also, it is recommended to regulate specific guidance and organization actions of grass-roots government over specialized cooperatives, and pertinently bring into play functions by stages. At the early stage of foundation of cooperatives, grass-roots government should mainly provide guidance and support, strengthen financial, credit support and training and education of cooperatives; at the growth stage, grass-roots government should help cooperatives to improve organization systems and administration mechanism; at the development stage, grass-roots government should mainly provide services together with supervision and provide excellent services and public goods for expansion and competitiveness improvement of cooperatives.
Secondly, it is recommended to bring into full play functions of grass-roots forces. Village Party branch and village committee are frontier of grass-roots bringing into play and also essential forces leading development of cooperatives. It is recommended to bring into play exemplary role of party branch and village committee, adapt to demands of cooperative development, and encourage more village cadres and rural talents to set up cooperatives and help cooperative members to get rich.
5.3Farmers’specializedcooperativesshouldrelyontheirowneffortsTo survive independently, farmers’ specialized co-operatives should be good at using policy resources, get rid of the resource dependence trap, and make self blood making through blood transfusion of resources. Firstly, under the guidance of grass-roots government, it is recommended to set up perfect benefit allocation and financial and accounting mechanism, property system and democratic management structure. In benefit mechanism, it is recommended to formulate clear property relation; in allocation mechanism, it is recommended to draw common reserve funds and public welfare funds for long-term development and risk resistance of cooperatives, coordinate bonus and dividend allocation between investors and ordinary cooperative members; in benefit security system, it is recommended to set up perfect financial management system and auditing supervision system, to ensure safety of financial operation. Secondly, it is recommended to comprehensively raise profitability of cooperatives. An organization with profitability is unable to survive in cut-throat market competition. Thus, cooperatives should comprehensively raise profitability to get rid of dependence on resources of grass-roots government. Farmers’ specialized cooperatives should take full advantage of scarce resources of grass-roots government in credit, tax preference, training and education, technical extension, and agricultural machinery subsidies, and combine their own superior resources, to turn the blood transfusion to blood making function.
[1] JIANG YF. Study on the relationship between rural primary party organization and farmers’ professional cooperative——From the angle of resource dependence theory[J]. Socialism Studies, 2011(5):58-61.(in Chinese).
[2] ZHAO GJ, GUO CL. Life cycle analysis of farmers’ cooperatives and discussion of government’s role transferring[J]. Issues in Agricultural Economy,2009,30(1):76-80, 112. (in Chinese).
[3] DU FG. Development of farmers professional cooperative and government role[J]. Reform,2012(9):77-83. (in Chinese).
[4] HAN B, LIU XW. Transforming the the role of government and promoting the development of cooperation ——Based on the investigation on the development status of farmers’ professional cooperative in Beijing City[J]. Problems of Agricultural Economy, 2007(S1): 153-157. (in Chinese).
[5] HOU BJ. The function of local government in farmers’ professional cooperative organization development[J]. Socialism Studies, 2007(6):144-146. (in Chinese).
[6] ZHANG GQ. Discussion on the role definition of basic-level government in the development of farmer’s specialized cooperative organization[J]. Economic Tribune, 2011(2):38-41.(in Chinese).
[7] FAN HM. The involution of new farmer cooperative organization and its systematic logic——Based on the investigation on A County and B City of Henan Province[J]. China Rural Survey,2011(6):12-21,45,94. (in Chinese).
[8] LIANG H, REN DP. Analysis on the interests binding mechanism of farmers’ specialized cooperative[J]. Rural Economy, 2011(10): 118-120. (in Chinese).
September 20, 2015 Accepted: November 17, 2015
Supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2012RW009); Study on Development Models and Performance of Farmers’ specialized cooperatives in Hubei Province.
*Corresponding author. E-mail:caiyi@webmail.hzau.edu.cn
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Application and Residue Pollution of Mulching Films in Xinjiang
- Urban Residents’ Consumption Risk Perception about the Dairy Products
- Study on the Aromatic Components of Green Plum Wine by HS-SPME-GC-MS
- Effect of Vacuum Packaging on Storage Quality of Peanut
- Innovative Development of Fishery and Ecological Protection of Poyang Lake
- Effect of Silicon Application on Rice Growth and Production Structure
